java08面向对象
面向对象
一个类即使什么都不写也是有默认方法
显式定义的构造器
1.无参构造 1.1使用new关键字,本质是调用构造器1.2用来初始化值
public person(){
}
2.有参构造:一旦定义了有参构造,无参就必须显式定义
public person(String name){
}
alt+insert:生成构造器
构造器:与类名相同;没有返回值
定义有参构造后,如果想使用无参构造,显示的定义一个无参构造
crtl+h:打开继承树
crtl+左键:find
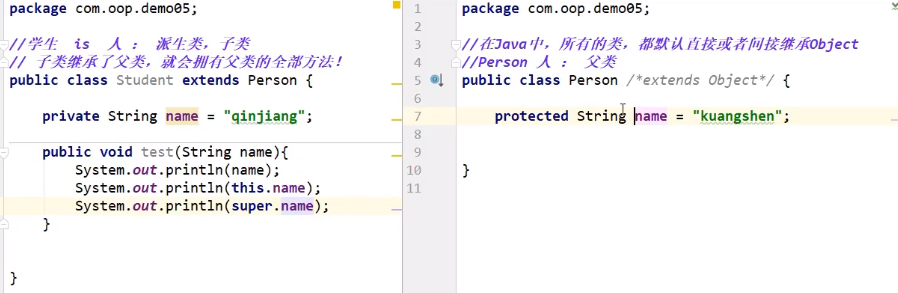
this.属性/方法:本类
super.属性/方法:父类
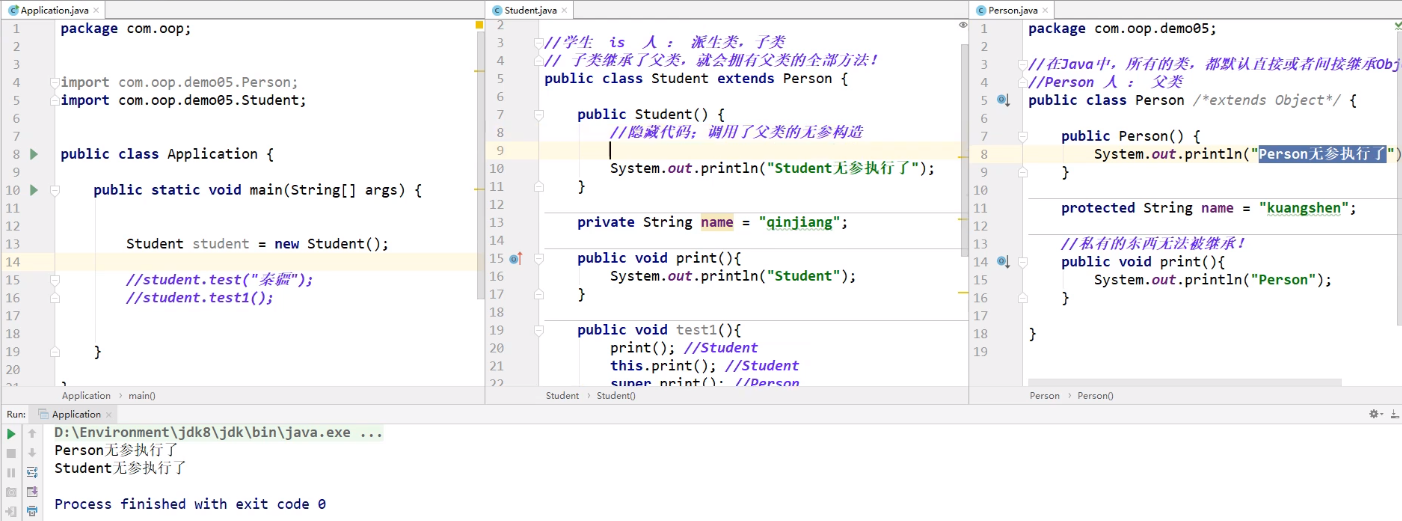
优先执行父类的无参构造
super注意点:
1.super调用父类的构造方法,必须在构造方法的第一个
2.super 必须只能出现在子类的方法或者构造方法中!
3.super和 this不能同时调用构造方法!
@Override:注解/重写,子类重写父类方法
alt+insert:Override
多态:方法有多态,属性没有
父类的引用指向子类
Student s1 = new Student();
Person s2 = new Student();
如果Student类中重写了Person的方法,那么s1,s2都会执行Student类的方法。
父类型可以指向子类,但是不能调用子类独有的方法:
如果Student类中存在Person类没有的方法,那么s2无法执行该方法(s2为person类,想执行需要强制转换((Student) s2).est()才可以)。
instanceof(类型转换) 判断对象类型
静态方法只能调用静态方法,非静态方法可以调用静态方法
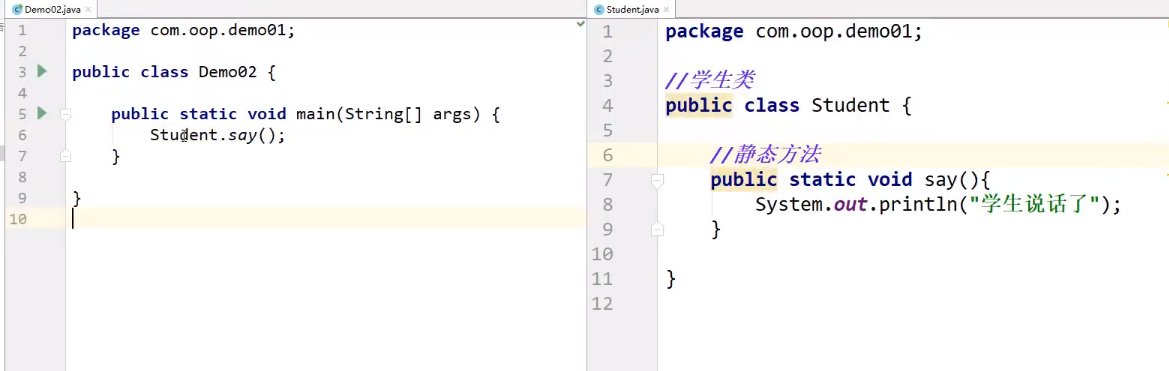
静态方法:引用别的类里的方法,需要别的类是static
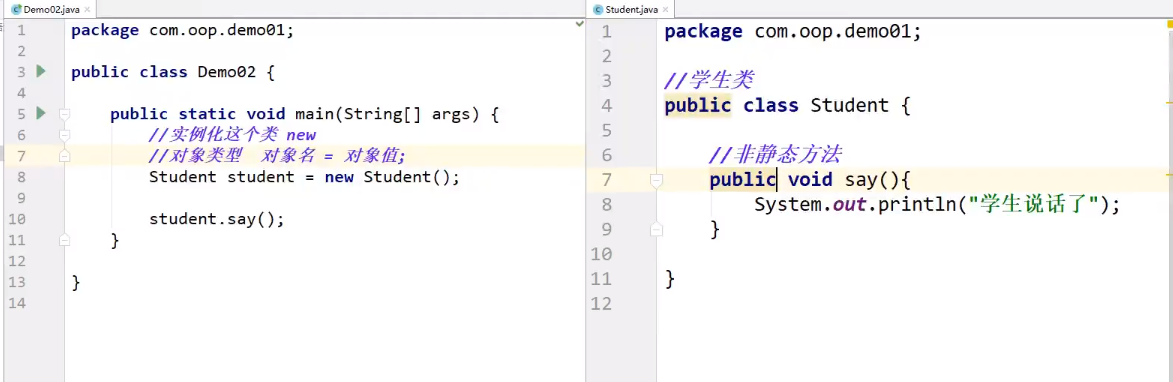
非静态方法:需要先实例化
instenceof

static
无法从 static 上下文引用非 static 字段
public class Student {
private static int age;
private double score;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(Student.age);//正常
System.out.println(Student.score);//error,无法从 static 上下文引用非 static 字段
System.out.println(s1.age);//正常
System.out.println(s1.score);//正常
}
}
static可以扩大使用范围
public class Student {
public void run(){
go();//非静态方法可以调用静态方法
}
public static void go(){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Student().run();//非static方法需要new对象
Student.go();//static方法不需要
}
}
匿名代码块
public class Student {
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
static{
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Student(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();//输出:静态代码块-匿名代码块-构造方法
//如果不new只输出静态代码块
}
}
抽象类
1.不能new抽象类,只能靠子类去实现它
2.抽象类中可以写普通的方法
3.抽象方法必须在抽象类中
interface接口
implements实现
内部类:可以获得私有属性
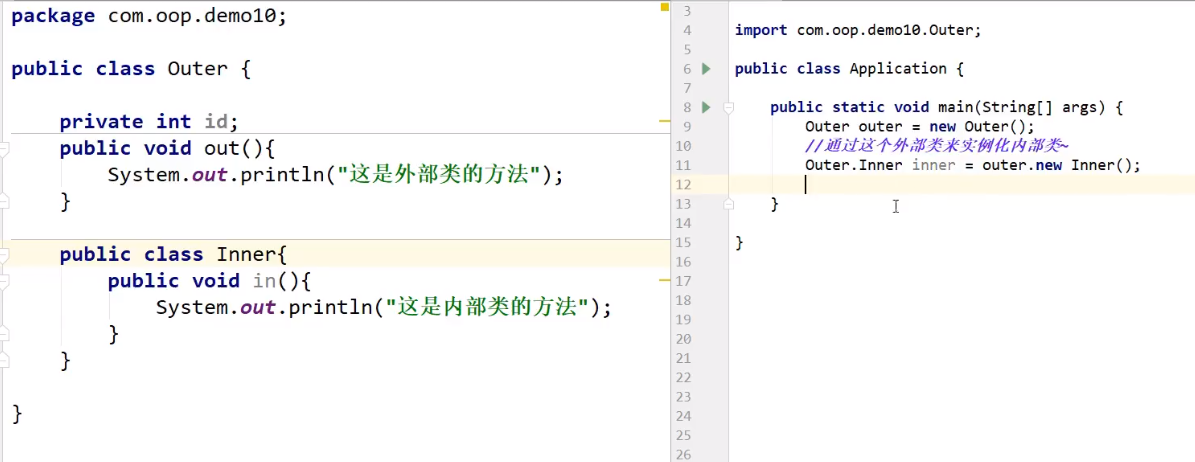
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Apple().eat();//没有名字初始化类,不用将实例保存到变量中
Userservice userservice = new Userservice() {
@Override
public void hello() {
}//引用接口
};
}
}
class Apple{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("1");
}
}
interface Userservice{
void hello();
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号