实验二
实验一:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define N 5
#define R1 586
#define R2 701
int main()
{
int number;
int i;
srand( time(0) );
for(i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
number = rand() % (R2 - R1 + 1) + R1;
printf("20228330%04d\n", number);
}
return 0;
}
运行: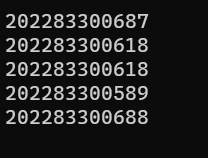
讨论:1.取586到701之间的随机数。2.随机选择后四位从568到701的五个随机学好;
实验二:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
float x, y;
char c1, c2, c3;
int a1, a2, a3;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a1, &a2, &a3);
printf("a1 = %d, a2 = %d, a3 = %d\n", a1,a2,a3);
getchar();
scanf("%c%c%c", &c1, &c2, &c3);
printf("c1 = %c, c2 = %c, c3 = %c\n", c1, c2, c3);
getchar();
scanf("%f%f", &x, &y);
printf("x = %f, y = %f\n",x, y);
return 0;
}
运行:
实验三:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main()
{
double x, temp;
while(scanf("%lf", &x) != EOF)
{
temp = 9*x/5 + 32;
printf("摄氏度:%.2f,华氏度:%.2f\n", x, temp);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行: 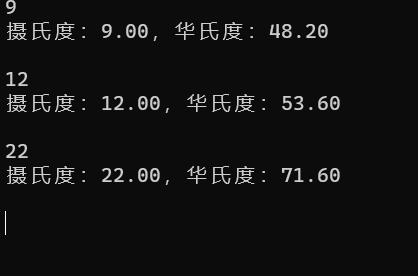
实验四:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
char ans;
printf("输入r表示red,输入g表示green, 输入y表示yellow\n");
while(scanf("%c", &ans) != EOF)
{
getchar();
switch( ans )
{
case 'r' :
case 'R' :printf("stop\n");
break;
case 'y' :
case 'Y' :printf("wait a minute\n");
break;
case 'g' :
case 'G' :printf("go go go\n");
break;
default :printf("something must be wrong...\n") ;
}
}
return 0;
}
运行: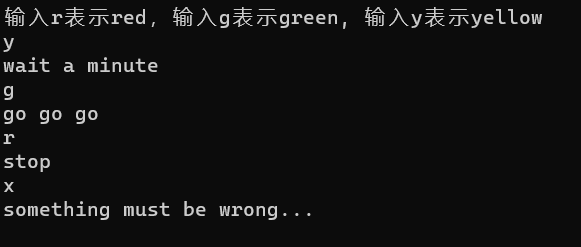
实验五:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
int main()
{
int ans, luckyday, i=2;
srand( time(0) );
luckyday = rand() % (30 - 1 + 1) + 1;
printf("猜猜2023年4月的哪一天是你的luckyday?\n");
while(scanf("%d", &ans) != luckyday && i != 0)
{
if(ans > luckyday)
printf("你猜的日期晚啦,已经过了\n");
else
printf("你猜的日期早啦,还没到呢\n");
printf("再猜吧(1-30):\n")
i--;
}
if(ans != luckyday)
printf("次数用完啦,偷偷告诉你,luckyday是%d\n", luckyday);
else
printf("恭喜你猜对啦\n");
return 0;
}

实验六:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int l, c;
for(l = 1; l <= 9; l++)
{
for(c = 1; c <= l; c++)
{
printf("%d * %d = %2d ", c, l, c * l);
}
printf("\n");
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}

实验7:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, i, j=0;
for(scanf("%d", &n); n>0; n--)
{
for( i=1; i<=j; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for( i=1; i<=(2*n - 1); i++)
{
printf(" o ");
}
printf("\n");
for( i=1; i<=j; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for( i=1; i<=(2*n - 1); i++)
{
printf("<H> ");
}
printf("\n");
for( i=1; i<=j; i++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for( i=1; i<=(2*n - 1); i++)
{
printf("I I ");
}
j++;
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
运行: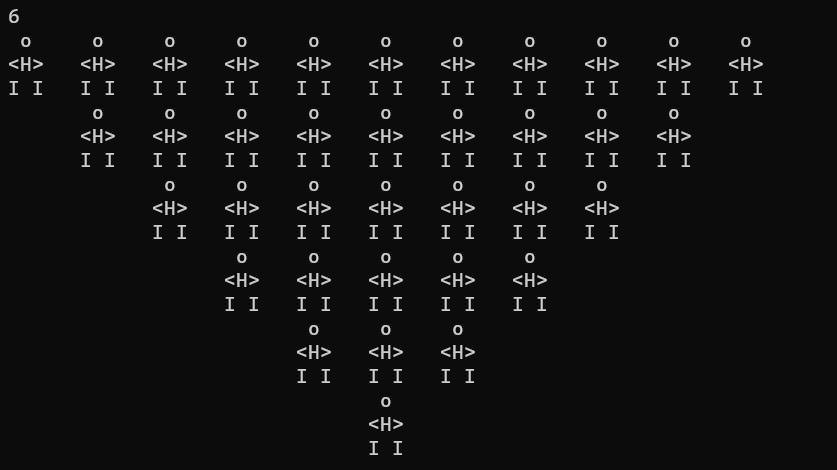
(同学教我的)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号