Java进阶 | 集合系列(一)PriorityQueue优先队列 | 综合运用 | 深入理解
参考资料:Java语言程序设计(进阶篇) ——梁勇先生 著 戴开宇先生 译
运行环境
- Windows10
- JDK8
- IDEA
前言
有一天

大雄惊讶地看着自己零分的考卷...

哆啦A梦说:"大雄,你怎么又考了个零分呀!

大雄:"什么嘛,哆啦A梦,因为考的题太难了!我不会呀"
然后......
哆啦A梦随着大雄来到学校进行了一场考试
结果是:
| 名字 | 成绩 |
|---|---|
| 大雄 | 0 |
| 哆啦A梦 | 100 |
| 静香 | 96 |
| 胖虎 | 60 |
| 小夫 | 90 |
哆啦A梦:哎,不愧是大雄,又是零分,咦? 怎么成绩没有排序啊?

哆啦A梦:接下来,就让我掏出一个宝贝来解决把!当当当当,\(Priority Queue优先队列\) !接下来,先创建一个实体类 \(Student.java\)来表示大雄他们吧~
class Student{
private String id;
private Character gender;
private Double score;
public Student(String id, Character gender, Double score) {
this.id = id;
this.gender = gender;
this.score = score;
}
public String getId() { return id; }
public Character getGender() { return gender;}
public Double getScore() {return score; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", gender=" + gender +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
}
1. 队列与优先队列概述
队列 \(queue\) 是一种 \(FIFO\) 即先进先出的数据结构,元素被追加到队列末尾,然后从队列头删除。
优先队列 \(Priority Queue\) 是 在 \(queue\) 的基础上给每个队列元素提供了一个优先级来进行比较
本篇文章,有许多关于比较器 \(Comparator\) 的知识,若需要了解,除了在网络上查询资料外,可以参考这篇博文:
【Java进阶】Comparable接口与Comparator接口的深入理解 | 有关排序的都会用到
2. 优先队列结构剖析
2.1 集合框架中的优先队列
PriorityQueue的UML图 制作工具: IDEA
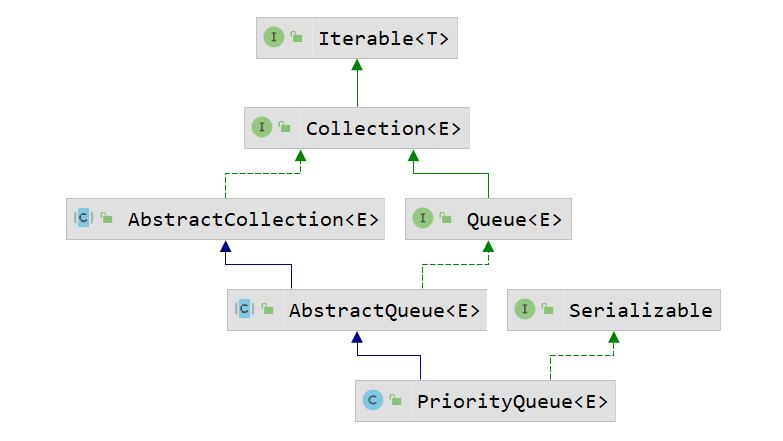
从图中可以看出
-
优先队列实现了 \(Serializable\) 接口,所以是可序列化的。
-
继承了\(AbstractQueue\) 类 ,这个类实现了 \(Iterable\) 接口的间接子接口\(Queue\),所以优先队列是可迭代的。故可通过 \(foreach\) 语句循环遍历(
注: 输出的结果无序的)
PriorityQueue<String> pq = new PriorityQueue<>();
for(String s : pq){
// System.out.println(s);
}
2.2 成员变量
成员变量除了自身的成员变量,其内部类中也有成员变量
可以通过下面的UML图进行了解:

2.2 常用方法
Java集合框架的方法有许多,而且有些方法是来自于接口,有的是本身独有的方法,非常繁杂,笔者认为没有必要记住所有的使用方法,最主要的是
-
记住所有的构造方法 ,方便创建对象
-
记住常用的方法,比如在队列中的peek() 、poll()、add()、offer()、remove() 等
2.2.1 构造器

优先队列构造器用到的主要对象有:
- \(Comparator\) 比较器,通过调用比较器的compare方法赋予元素优先级
- \(int\) ,整型变量表示优先队列的容量
- \(Collection\) 集合容器接口的实现类,这里并不表示接纳所有的集合类,具体得查看源码,之后会进行分析
- \(SortedSet\) 有序集合接口的实现类
最后一个可排序的集合有什么用呢?在成员变量中没有看到该类型,这说明肯定是在构造函数中调用了其他方法对该对象进行了类型变换,后经查询资料发现:
- PriorityQueue内部实现是采用
堆排序
接下来,先编写一个函数运用反射机制用于输出一个类的所有的成员变量,包括私有成员,这样方便查看不同构造器下的差异。
用到的包
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
printPriority() 方法
public static <T> void printPriority(PriorityQueue<T> q) {
// 反射机制获取类的内容
Field[] info = q.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : info) {
// 打开所有访问权限
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
//格式化输出
System.out.println(
String.format("Type:%-30s Name: %-25s Value:%-10s",
field.getType(),
field.getName(),
field.get(q)));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(1) 无参构造 new PriorityQueue<>()
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
printPriority(q);
}
}
运行结果
Type:long Name: serialVersionUID Value:-7720805057305804111
Type:int Name: DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY Value:11
Type:class [Ljava.lang.Object; Name: queue Value:[Ljava.lang.Object;@12a3a380
Type:int Name: size Value:0
Type:interface java.util.Comparator Name: comparator Value:null
Type:int Name: modCount Value:0
Type:int Name: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE Value:2147483639
(2) 传入容量参数 new PriorityQueue<>(int initialCapacity)
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>(100);
printPriority(q);
}
}
运行结果
Type:long Name: serialVersionUID Value:-7720805057305804111
Type:int Name: DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY Value:11
Type:class [Ljava.lang.Object; Name: queue Value:[Ljava.lang.Object;@12a3a380
Type:int Name: size Value:0
Type:interface java.util.Comparator Name: comparator Value:null
Type:int Name: modCount Value:0
Type:int Name: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE Value:2147483639
观察结果可以发现,优先队列本身size的值不会因此发生变化,因为它表示当前的元素个数
初始化时,实际变化的是其成员queue的容量,在源码中是这样实现的:
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
(3) 传入比较器, 使用匿名内部类实现
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getScore() - o2.getScore() > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
});
printPriority(q);
}
}
运行结果
Type:long Name: serialVersionUID Value:-7720805057305804111
Type:int Name: DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY Value:11
Type:class [Ljava.lang.Object; Name: queue Value:[Ljava.lang.Object;@12a3a380
Type:int Name: size Value:0
Type:interface java.util.Comparator Name: comparator Value:Demo$1@29453f44
Type:int Name: modCount Value:0
Type:int Name: MAX_ARRAY_SIZE Value:2147483639
可以观察到优先队列中的comparator 变量发生了变化,从而定义优先队列元素的优先级
对于其他的方法,部分是来自于父类 AbstracQueue 和父类实现的接口 Queue
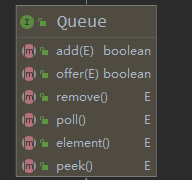
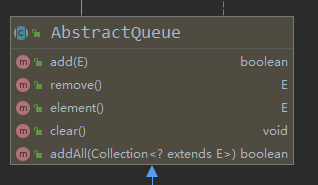
2.2.2 添加元素 | 入队 | add方法 | offer方法
public boolean add(E e){}
public boolean offer(E e) {}
优先队列 PriorityQueue 继承了 AbstractQueue 类,实现了Queue接口。
这两个方法都是在Queue接口中声明的,抽象类实现了其中的 add() 方法
在优先队列源码中,add()方法的原理就是调用自身实现的offer() 方法
它们的区别在于:
- offer() 方法 会抛出异常
在源码中,Queue接口的 offer() 方法 规定 若参数为null则抛出一个异常
2.2.3 删除元素 | 出队 | remove方法 | poll 方法
在队列中, remove(Object o) 方法执行时,若o==null,则会报错,但在优先队列里并没有这个规定
通过查看源码,队列的另一个java.util.LinkedList实现类中的remove方法才会在空值时抛出异常
public boolean remove(Object o) {}
public E poll() {}
3. 遍历优先队列的三种方式
遍历前,先插入测试的数据:
q.offer(new Student("大雄", 'M', 0.0));
q.offer(new Student("哆啦A梦", 'M', 100.0));
q.offer(new Student("静香", 'M', 96.0));
q.offer(new Student("胖虎", 'W', 60.0));
q.offer(new Student("小夫", 'M', 90.0));
3.1 直接For循环遍历 (无序)
for (Student student : q) {
System.out.println(student);
}
3.2 出队方式遍历 (有序)
PriorityQueue<Student> temp = new PriorityQueue<>(q);
while(!temp.isEmpty()){
System.out.println(temp.poll());
}
3.3 迭代器遍历 (无序)
Iterator<Student> iterator = temp.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
3.4 toArray方法遍历 (无序)
Object[] students = (Object[]) q.toArray();
for (Object student : students) {
System.out.println(student);
}
3.5 反射机制遍历(无序) (少用)
try {
Field field = q.getClass().getDeclaredField("queue");
field.setAccessible(true);
Object []obj = (Object[]) (field.get(q));
for (Object o : obj) {
System.out.println(o);
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
4. 优先队列的自动化排序机制
4.1 单一排序 升序
单一排序是指仅仅以一个参数作为标准来进行比较,当创建优先队列的对象没有指定比较器时,如果是可比较的类型(String、int等),那么队列会默认以升序进行排列,比如:
PriorityQueue<Integer> q2 = new PriorityQueue<>();
q2.add(1);
q2.add(3);
q2.add(2);
while(!q2.isEmpty())
System.out.println(q2.poll());
运行结果
1
2
3
自定义类的比较器实现
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getScore() - o2.getScore() > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
});
q.offer(new Student("大雄", 'M', 0.0));
q.offer(new Student("哆啦A梦", 'M', 100.0));
q.offer(new Student("静香", 'M', 96.0));
q.offer(new Student("胖虎", 'W', 60.0));
q.offer(new Student("小夫", 'M', 90.0));
while(!q.isEmpty())
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
运行结果
Student{id='大雄', gender=M, score=0.0}
Student{id='胖虎', gender=W, score=60.0}
Student{id='小夫', gender=M, score=90.0}
Student{id='静香', gender=M, score=96.0}
Student
4.2 单一排序 降序
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Integer> q2 = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder());
q2.add(1);
q2.add(3);
q2.add(2);
while(!q2.isEmpty())
System.out.println(q2.poll());
}
运行结果
3
2
1
自定义类 比较器
这里其实不用调用 Collections.reverseOrder() 方法,直接修改compare的返回值也是可以的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>(Collections.reverseOrder(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getScore() - o2.getScore() > 0 ? 1 : -1;
}
}));
q.offer(new Student("大雄", 'M', 0.0));
q.offer(new Student("哆啦A梦", 'M', 100.0));
q.offer(new Student("静香", 'M', 96.0));
q.offer(new Student("胖虎", 'W', 60.0));
q.offer(new Student("小夫", 'M', 90.0));
while (!q.isEmpty())
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
4.3 综合排序
假设 " 女士优先 " ,先把女孩子都排在前面,然后再根据成绩排序,实现如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> q = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
if(!o1.getGender().equals(o2.getGender()))
return o1.getGender().equals('W') ? -1 : 1;
else
return o1.getScore() - o2.getScore() > 0 ? -1 : 1;
}
});
q.offer(new Student("大雄", 'M', 0.0));
q.offer(new Student("哆啦A梦", 'M', 100.0));
q.offer(new Student("静香", 'M', 96.0));
q.offer(new Student("胖虎", 'W', 60.0));
q.offer(new Student("小夫", 'M', 90.0));
while (!q.isEmpty())
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
运行结果
Student{id='胖虎', gender=W, score=60.0}
Student{id='哆啦A梦', gender=M, score=100.0}
Student{id='静香', gender=M, score=96.0}
Student{id='小夫', gender=M, score=90.0}
Student
emmmm,笔者不小心把胖虎性别弄成女孩了,问题不大...
5. 总结
- 优先队列是基于队列 FIFO 先进先出的一种数据结构
- 优先队列 通过比较器
Comparator为元素设置优先级,队列内的元素会按优先级的高低排序 - 优先队列的底层是通过堆排序实现的
- 除了出队方式遍历以外,其他方式遍历的优先队列结果都将是无序的,只能通过出队的方式才是有序的
- 优先队列默认是升序,降序的话可以通过
Collections.reverseOrder()方法获得一个降序的比较器 - 继承于
AbstractQueue类 ,直接实现了java.io.Serializable接口 表示可序列化,间接实现Queue接口 remove()方法不会抛异常


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号