从实验现象详细分析BGP的路由策略与选路原则
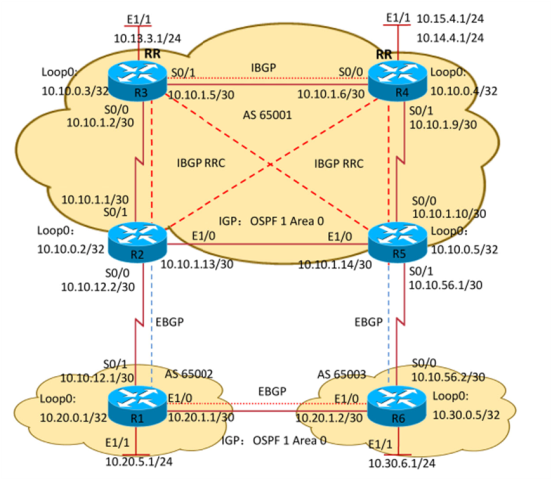
1.1 组网需求
1) AS65001边界网段发布:R2,R5重发布直连路由至ospf(metric 1000 type 1)
2) AS65002 边界网段发布:R1,R6network至ospf,并配置被动接口
3) R3,R4发布业务网段至ospf1 area0 (10.13.3.0/24、10.14.4.0/24、10.15.4.0/24)
4) BGP配置要求
No synchronization
No auto-summary
Neighbor<IBGP邻居>update-source loopback0
Neighbor<IBGP邻居>next-hop-self
5) R2,R3,R4,R5都运行BGP;R3,R4为同簇RR(簇ID为R3loopback0),R2,R5都分别为R3,R4 的客户端,且R3与R4之间建立普通的IBGP邻居
6) R3,R4发布AS65001的汇总路由至BGP:10.10.0.0/16、10.13.0.0/16、10.14.0.0/16、10.15.0.0/16
7) R1,R6发布AS65002的汇总路由至BGP:10.200.0.0/16、10.30.0.0/16
1.2 组网拓扑
1.3 选路需求
AS 65002(R1,R6)去往10.13.0.0/16的主路径走R1—R2
AS 65002 (R1,R6)去往10.14.0.0/16、10.15.0.0/16的主路径走R6—R5
AS 65001 (R2,R3,R4,R5)去往10.20.0.0/16的主路径走R2—R1
AS 65001 (R2,R3,R4,R5)去往10.30.0.0/16的主路径走R5—R6
1.4 基本连通性测试
1.5 BGP配置及调测
1) BGP配置
R3(config)#
router bgp 65001
bgp cluster-id 10.10.0.3
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.10.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.13.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.14.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.15.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor as65001-rr peer-group
neighbor as65001-rr remote-as 65001
neighbor as65001-rr update-source Loopback0
neighbor as65001-rr route-reflector-client
neighbor as65001-rr next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.2 peer-group as65001-rr
neighbor 10.10.0.4 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.0.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.10.0.4 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.5 peer-group as65001-rr
no auto-summary
!
ip http server
no ip http secure-server
ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.13.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.14.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.15.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R4(config)#
router ospf 1
router-id 10.10.0.4
log-adjacency-changes
passive-interface Ethernet1/1
passive-interface Ethernet1/2
network 10.10.0.4 0.0.0.0 area 0
network 10.10.1.4 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.10.1.8 0.0.0.3 area 0
network 10.14.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
network 10.15.4.0 0.0.0.255 area 0
!
router bgp 65001
no synchronization
bgp cluster-id 10.10.0.3
network 10.10.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.13.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.14.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.15.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor as65001-rr peer-group
neighbor as65001-rr remote-as 65001
neighbor as65001-rr update-source Loopback0
neighbor as65001-rr route-reflector-client
neighbor as65001-rr next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.2 peer-group as65001-rr
neighbor 10.10.0.3 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.0.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.10.0.3 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.5 peer-group as65001-rr
no auto-summary
!
no ip http secure-server
ip route 10.10.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.13.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.14.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.15.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R2(config)#
router bgp 65001
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
neighbor 10.10.0.3 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.0.3 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.10.0.3 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.0.4 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.0.4 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.10.0.4 next-hop-self
neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 65002
neighbor 10.10.12.1 route-map as65002-in in
no auto-summary
R5(config)#(略)
R1(config)#
router bgp 65002
no synchronization
bgp log-neighbor-changes
network 10.20.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
network 10.30.0.0 mask 255.255.0.0
neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65001-in in
neighbor 10.30.0.5 remote-as 65002
neighbor 10.30.0.5 update-source Loopback0
neighbor 10.30.0.5 next-hop-self
no auto-summary
no ip http secure-server
ip route 10.20.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
ip route 10.30.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0
R6(config)#(略)
2) 查看邻居状态
R1#show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.12.2, remote AS 65001, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.2
BGP state = Established, up for 01:58:07
BGP neighbor is 10.30.0.5, remote AS 65002, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.30.0.5
BGP state = Established, up for 01:31:05
R2#show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.3, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.3
BGP state = Established, up for 02:11:05
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.4, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.4
BGP state = Established, up for 02:06:34
BGP neighbor is 10.10.12.1, remote AS 65002, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.20.0.1
BGP state = Established, up for 01:59:57
R3#show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.2, remote AS 65001, internal link
Member of peer-group as65001-rr for session parameters
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.2
BGP state = Established, up for 02:12:26
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.4, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.4
BGP state = Established, up for 02:07:38
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.5, remote AS 65001, internal link
Member of peer-group as65001-rr for session parameters
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.5
BGP state = Established, up for 01:33:47
R4#show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.2, remote AS 65001, internal link
Member of peer-group as65001-rr for session parameters
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.2
BGP state = Established, up for 02:09:08
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.3, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.3
BGP state = Established, up for 02:09:30
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.5, remote AS 65001, internal link
Member of peer-group as65001-rr for session parameters
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.5
BGP state = Established, up for 01:35:45
R5# show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.3, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.3
BGP state = Established, up for 01:36:07
BGP neighbor is 10.10.0.4, remote AS 65001, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.4
BGP state = Established, up for 01:36:32
R6#show ip bgp neighbors
BGP neighbor is 10.10.56.1, remote AS 65001, external link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.10.0.5
BGP state = Established, up for 01:36:32
BGP neighbor is 10.20.0.1, remote AS 65002, internal link
BGP version 4, remote router ID 10.20.0.1
BGP state = Established, up for 01:37:12
3) BGP路由策略部署(方案一:Local_preference)
R1(config)#
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
!
route-map as65001-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3
set local-preference 300
!
route-map as65001-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set local-preference 200
!
route-map as65001-in permit 30
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65001-in in
R1#clear ip bgp *soft
R6(config)#
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
!
route-map as65001-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3
set local-preference 200
!
route-map as65001-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set local-preference 300
!
route-map as65001-in permit 30
!
neighbor 10.10.56.1 route-map as65001-in in
R6#clear ip bgp * soft
R2(config)#
ip prefix-list p1 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
!
route-map as65002-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p1
set local-preference 300
!
route-map as65002-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set local-preference 200
!
route-map as65002-in permit 30
neighbor 10.10.12.1 route-map as65002-in in
R2#clear ip bgp * soft
ip prefix-list p1 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
!
route-map as65002-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p1
set local-preference 200
!
route-map as65002-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set local-preference 300
neighbor 10.10.56.2 route-map as65002-in in
R5#clear ip bgp * soft
查看设备的BGP表
R1#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
*>i10.14.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 300 0 65001 i
* 10.10.12.2 200 0 65001 i
*>i10.15.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 300 0 65001 i
* 10.10.12.2 200 0 65001 i
//选择local preference 最大的路由
//BGP只把最优的路由通告给它的邻居:以及基于邻居的水平分割
R2#show ip bgp
*> 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.12.1 0 300 0 65002 i
* i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
* 10.10.12.1 0 200 0 65002 i
// 选择local preference 最大的路由
// 选择router id 最大的BGP邻居通告的路由
//BGP只把最优的路由通告给它的邻居:以及基于邻居的水平分割
//从IBGP学习到的路由不通告给其他的IBGP邻居
R3#show ip bgp
*>i10.20.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 300 0 65002 i
*>i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
R4# show ip bgp
*>i10.20.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 300 0 65002 i
*>i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
R5#show ip bgp
* i10.20.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 300 0 65002 i
* 10.10.56.2 0 200 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.2 0 300 0 65002 i
*> 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.56.2 0 300 0 65002 i
//来吧,我们解释一下这里为这么10.20.0.0/16有三条,而10.30.0.0/16有一条:
首先,在刚开始的时候,R2将10.20.0./16网段发给R3,R5也将该网段发给R3,R3经过比较之后将从R2发过来的路由反射给R5,此时R5不会再发回去了(IBGP的水平分割),假设R5还与其他设备是BGP邻居关系,它只会将从R3反射过来的路由传播出去(传播最优路由),此时关于10.20.0.0/16网段有两个RR反射的和一个EBGP邻居传来的优先级是200的
而10.30.0.0/16网段根据前面的分析,及时这个网段从R1传到R2,R2再传到R3,但因为优先级是200,而R3从R5收到的关于该网段的优先级则为300,R3经过再三考虑,决定不将从R2传来的路由反射给R5,因为它不是最优的,所以10.30.0.0/16网段只有一条
R6#show ip bgp
* 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 200 0 65001 i
*>i 10.20.0.1 0 300 0 65001 i
*> 10.14.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
*> 10.15.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
验证:
① 用10.20.5.1 traceroute 10.13.3.1
分析:
R1#show ip route
B 10.13.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 02:44:05
C 10.10.12.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
数据包从s0/1转出到R2
R2#show ip route
O 10.13.3.0/24 [110/110] via 10.10.1.2, 03:13:06, Serial0/1
C 10.10.1.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
从s0/1出,到R3
R3# show ip route
C 10.13.3.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/1
到达目的地
查看traceroute 结果
R1#traceroute 10.13.3.1 sour 10.20.5.1
1 10.10.12.2 [AS 65001] 28 msec 76 msec 28 msec
2 10.10.1.2 [AS 65001] 76 msec * 488 msec
用10.20.5.1 traceroute 10.14.4.1
B 10.14.0.0/16 [200/0] via 10.30.0.5, 02:43:54
O 10.30.0.5/32 [110/101] via 10.20.1.2, 03:08:44, Ethernet1/0
C 10.20.1.0/30 is directly connected, Ethernet1/0
从e1/0出,到R6
R6#show ip route
B 10.14.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.56.1, 02:50:26
C 10.10.56.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
从s0/0出,到R5
O 10.14.4.0/24 [110/110] via 10.10.1.9, 03:16:39, Serial0/0
C 10.10.1.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
从s0/0出,到R4
R4#show ip route
C 10.14.4.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/1
到达目的地
查看traceroute 结果
R1#traceroute 10.14.4.1 sour 10.20.5.1
1 10.20.1.2 40 msec 60 msec 48 msec
2 10.10.56.1 [AS 65001] 40 msec 468 msec 288 msec
3 10.10.1.9 [AS 65001] 908 msec 520 msec *
② 用10.14.4.1 traceroute 10.20.5.1
R4#show ip route
B 10.20.0.0/16 [200/0] via 10.10.0.2, 02:44:04
O 10.10.0.2/32 [110/201] via 10.10.1.10, 03:17:45, Serial0/1
[110/201] via 10.10.1.5, 03:17:45, Serial0/0
C 10.10.1.8/30 is directly connected, Serial0/1
C 10.10.1.4/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
数据包到达R2
R2#show ip route
B 10.20.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.1, 02:36:58
C 10.10.12.0/30 is directly connected, Serial0/0
从s0/0出到达R1
R1#show ip route
C 10.20.5.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet1/1
到达目的地
查看traceroute 结果
R4# traceroute 10.20.5.1 sour 10.14.4.1
1 10.10.1.10 60 msec
10.10.1.5 28 msec
10.10.1.10 380 msec
2 10.10.1.1 120 msec
10.10.1.13 60 msec
10.10.1.1 52 msec
3 10.10.12.1 484 msec 764 msec *
4) BGP路由策略部署(方案二:MED)
R1(config)#
ip prefix-list p5 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
!
route-map as65002-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p5
set metric 1000
!
route-map as65002-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set metric 2000
!
route-map as65002-out permit 30
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65002-out out
R6(config)#
ip prefix-list p5 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
route-map as65002-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p5
set metric 2000
!
route-map as65002-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set metric 1000
!
route-map as65002-out permit 30
!
neighbor 10.10.56.1 route-map as65002-out out
R2(config)#
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
!
route-map as65001-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3
set metric 1000
!
route-map as65001-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set metric 2000
!
route-map as65001-out permit 30
neighbor 10.10.12.1 route-map as65001-out out
R5(config)#
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
!
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
!
route-map as65001-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3 //实验中因为把P3写成了3导致med发布错误
set metric 2000
!
route-map as65001-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set metric 1000
!
neighbor 10.10.56.2 route-map as65001-out out
R1#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.10.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 0 65001 i
*> 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 1000 0 65001 i
* i10.14.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 2000 100 0 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 2000 0 65001 i
* i10.15.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 2000 100 0 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 2000 0 65001 i
* i10.20.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i10.30.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
查看各设备的BGP表
R1#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.10.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 0 65001 i
*> 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 1000 0 65001 i
*>i10.14.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 1000 100 0 65001 i
//自己从EBGP邻居R2处收到的路由MED是2000,而从IBGP邻居收到的MED值是1000,选择从IBGP即R6处收到的路由
* 10.10.12.2 2000 0 65001 i
*>i10.15.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 1000 100 0 65001 i
* 10.10.12.2 2000 0 65001 i
R2# show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*> 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.12.1 1000 0 65002 i
* i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 1000 100 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.5 1000 100 0 65002 i
* 10.10.12.1 2000 0 65002 i
R5#show ip bgp
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.56.2 2000 0 65002 i
* i 10.10.0.2 1000 100 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.2 1000 100 0 65002 i
*> 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.56.2 1000 0 65002 i
R6# show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.10.0.0/16 10.20.0.1 0 100 0 65001 i
*>i10.13.0.0/16 10.20.0.1 1000 100 0 65001 i
* 10.10.56.1 2000 0 65001 i
*> 10.14.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 1000 0 65001 i
*> 10.15.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 1000 0 65001 i
R6#trace 10.13.3.1 source e1/1
1 10.20.1.1 44 msec 40 msec 32 msec
2 10.10.12.2 [AS 65001] 72 msec 144 msec 192 msec
3 10.10.1.2 [AS 65001] 172 msec * 760 msec
R6#trace 10.14.4.1 source e1/1
1 10.10.56.1 [AS 65001] 192 msec 200 msec 24 msec
2 10.10.1.9 [AS 65001] 120 msec * 232 msec
R3#traceroute 10.30.6.1 source e1/1
1 10.10.1.6 48 msec
10.10.1.1 56 msec
//在这里有个IGP的负载均衡,如果下一跳选择10.10.1.1,那么就会到达R2,R2从R1收到的关于10.30.0.0/16网段的MED是3000,而从R5收到的该网段的MED是2000,所以会选择下一跳是R5(10.10.1.14)
10.10.1.6 236 msec
//如果下一跳选择10.10.1.6 ,那么数据包到达R4,R4上关于10.30.0.0/16网段的路由下一跳是R5<原因:R4通过查找路由表 ,通过BGP显示下一跳是R5,再通过IGP递归查找 <<话说又为什么是R5呢,顺便来说一下为什么10.30.0.0/16只有这么一条,怎么就没有从R2反射过来的MED值较大的放进BGP表中呢?答案是这样的,因为R2根本就没有把10.30.0.0/16这个网段传播出去,因为它从R4那里收到了一条更优的也就是MED值更小的关于该网段的路由,所以无论是经过比较谁最优还是基于IBGP的水平分割,它都不应该把这条路由传播出去,所以R4的BGP表中只有一条关于该网段的路由>>>
2 10.10.1.14 668 msec
10.10.1.10 276 msec
10.10.1.14 388 msec
3 10.10.56.2 120 msec 520 msec *
达到了要求
1.2.8 BGP路由策略部署(方案三:Local_Prefence+MED)
以下思路版权归spring所有
R1:首先解决别人进来的时候怎么选路问题
在R1上调整MED值,10.20.0.0/16网段的MED 2000,10.30.0.0/16网段的MED 3000 ,然后 应用在neighbor的出方向上<调整好之后发出去供别人比较>
其次解决自己出去的时候怎么选路问题
在R1上调整别人进来时的本地优先级,10.13.0.0/16网段的本地优先级300,10.14.0.0/16和10.15.0.0/16网段的本地优先级200,然后应用在neighbor的in方向上 <你一进来我就该你优先级供我本AS系统比较使用>
在R6上面与R1完全相反的思路配置即可
BGP配置
R1:
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p5 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
route-map as65001-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3
set local-preference 300
route-map as65001-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set local-preference 200
route-map as65001-in permit 30
route-map as65002-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p5
set metric 1000
route-map as65002-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set metric 2000
route-map as65002-out permit 30
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65001-in in
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65002-out out
R6:
ip prefix-list p3 seq 5 permit 10.13.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 5 permit 10.14.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p4 seq 10 permit 10.15.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p5 seq 5 permit 10.20.0.0/16
ip prefix-list p6 seq 5 permit 10.30.0.0/16
route-map as65001-in permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p3
set local-preference 200
route-map as65001-in permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p4
set local-preference 300
route-map as65001-in permit 30
route-map as65002-out permit 10
match ip address prefix-list p5
set metric 2000
route-map as65002-out permit 20
match ip address prefix-list p6
set metric 1000
route-map as65002-out permit 30
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.10.56.1 route-map as65001-in in
neighbor 10.10.56.1 route-map as65002-out out
查看各设备的BGP表
R1#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* i10.10.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 100 0 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 0 65001 i
*> 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
*>i10.14.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 300 0 65001 i
* 10.10.12.2 200 0 65001 i
*>i10.15.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 300 0 65001 i
* 10.10.12.2 200 0 65001 i
* i10.20.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
* i10.30.0.0/16 10.30.0.5 0 100 0 i
*> 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
R2#show ip bgp
*> 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.12.1 1000 0 65002 i
* i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 1000 100 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.5 1000 100 0 65002 i
* 10.10.12.1 2000 0 65002 i
总结:我本来想看一下R1自己设置的MED,可是我没看见,却在R2上看见了,这个实验现象表明:MED太残忍了,它对自己人进行各种蹂躏,最后却把结果发出去给别人使用,自己都看不见,晕~~
R6和R5上面我就不用看了吧,亲,大同小异啦
为了展示偶的才华,偶觉得traceroute一下纸
R1#traceroute 10.14.4.1 source 10.20.5.1
1 10.20.1.2 32 msec 316 msec 56 msec
2 10.10.56.1 [AS 65001] 204 msec 148 msec 312 msec
3 10.10.1.9 [AS 65001] 632 msec 368 msec 1288 msec
好吧,我决定分析一下这个路径,告诉你们为什么它这样走撒
首先呢,R1收到R2发来的10.14.0.0/16网段,自己将其优先级改为了200
然后呢,R1收到R6发来的10.14.0.0/16网段的优先级是300
最后呢,R1选择由R6发来的路由优先
当数据包到达R6之后,R6由要选路了
晕,这个就没什么可选的啦,只有一条,那就是它的EBGP邻居发来滴,你若要问我为什么,晕,难道它有其他选择吗?R1发来的关于这个网段的路由的优先级是200!!
当数据包到R5之后,R5又开始选路啦
也没什么可选的 就R4了,不解释
R3#traceroute 10.30.6.1 source e1/1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Tracing the route to 10.30.6.1
1 10.10.1.1 64 msec
10.10.1.6 192 msec
10.10.1.1 376 msec
2 10.10.1.10 316 msec
10.10.1.14 88 msec
10.10.1.10 32 msec
3 10.10.56.2 336 msec * 700 msec
1.2.9 bgp 缺省路由
向邻居发布缺省路由
R2(config)#router bgp 65001
R2(config-router)#nei 10.10.12.1 default-originate
R1#show ip bgp
*> 0.0.0.0 10.10.12.2 0 0 65001 i
R1# show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:01:08
向全网发布缺省路由
R3(config)#ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 null 0
R3(config)#router bgp 65001
R3(config-router)#net 0.0.0.0
R1# show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:06
R2#show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 10.10.0.3, 00:00:25
R3#show ip route
S* 0.0.0.0/0 is directly connected, Null0
R4#show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 10.10.0.3, 00:00:37
R5# show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [200/0] via 10.10.0.3, 00:02:39
R6#show ip route
B* 0.0.0.0/0 [20/0] via 10.10.56.1, 00:00:12
1.3 组网二:BGP路由策略与选路控制(二)
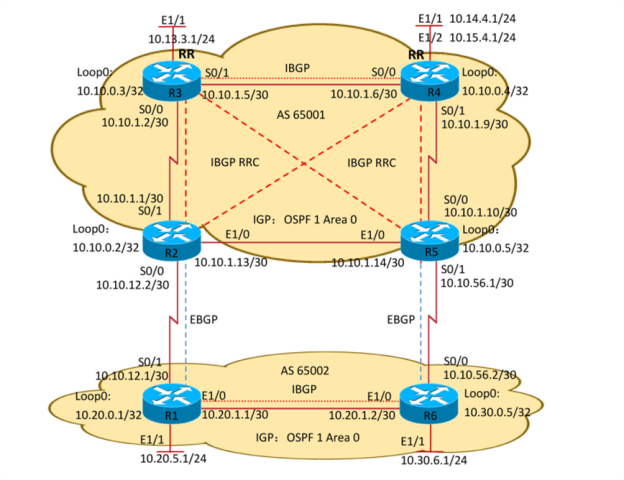
1.3.1 组网需求
1) AS65001边界网段发布:R2,R5重发布直连路由至ospf(metric 1000 type 1)
2) R3,R4发布业务网段至ospf1 area0 (10.13.3.0/24、10.14.4.0/24、10.15.4.0/24)
3) R1发布AS65002的汇总路由至BGP:10.20.0.0/16
4) R6发布 AS65003的汇总路由至BGP: 10.30.0.0/16
5) R2,R3,R4,R5都运行BGP;R3,R4为同簇RR(簇ID为R3loopback0),R2,R5都分别为R3,R4 的客户端,且R3与R4之间建立普通的IBGP邻居
6) R3,R4发布AS65001的汇总路由至BGP:10.10.0.0/16、10.13.0.0/16、10.14.0.0/16、10.15.0.0/16
7) BGP配置要求
No synchronization
No auto-summary
Neighbor<IBGP邻居>update-source loopback0
Neighbor<IBGP邻居>next-hop-self
1.3.2组网拓扑
1.3.3 选路需求
AS 65002(R1)去往其他AS的主路径走R1—R2;AS 65003 (R6)去往其他AS的主路径走R6—R5;即 AS65002—AS65003 的链路(R1—R6)只用作备份链路.
AS 65001 (R2,R3,R4,R5)去往10.20.0.0/16的主路径走R2—R1
AS 65001 (R2,R3,R4,R5)去往10.30.0.0/16的主路径走R5—R6
1.3.4 基本连通性测试
1.3.5 1.3.5 BGP配置及调测
BGP配置
查看各设备的BGP邻居状态,BGP表,全局路由表
不做任何属性的配置
R1#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 10.13.0.0/16 10.20.1.2 0 6500365001i
*> 10.10.12.2 0 65001 i
//选择AS_path最大unde路由
R6#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 10.14.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 0 65001 i
* 10.15.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 0 65001 i
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.56.1 0 65001 65002 i
*> 10.20.1.1 0 0 65002 i
//选择as_path最短的路由
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
*>i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 100 0 65003 i
* i 10.10.0.5 0 100 0 65003 i
* 10.10.12.1 0 65002 65003 i
R5#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.56.2 0 65003 65002 i
* i 10.10.0.2 0 100 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.2 0 100 0 65002 i
*> 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.56.2 0 0 65003 i
//选择AS_path最短的路由,<R5只选择了AS号为65002的路由>
//选择router id最小的BGP邻居通告的路由<两个一样的路由中其中被选择的那一条是R3反射的路由,所以选择它>
//BGP只把最优的路由通告给它的邻居,记忆基于邻居的水平分割<10.30.0.0/16网段没有收到其IBGP邻居R2通告的路由,是因为R2同时收到R6通告给自己的路由,发现自己所拥有的那条路由不是最优的,所以不会通告给R6>
//从IBGP学到的路由不通告给其他的IBGP邻居<R2是个文明人那,收到了R6发来的最优路由也不说在通告回去,恩,值得表扬>
R3#show ip bgp
*>i10.20.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 100 0 65002 i
*>i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 100 0 65003 i
R4#show ip bgp
*>i10.20.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 100 0 65002 i
*>i10.30.0.0/16 10.10.0.5 0 100 0 65003 i
由以上可知,在没有配置任何BGP路由策略的情况下,AS65001已经达到了选路需求
.png)
.png)
.png)
1.4 BGP路由策略部署(方案一 :增加AS_PATH长度)
1) 在R1,R6上,操控AS_path来实现需求
R6将向AS65002通的路由的AS AS_path增加2个长度(即向AS_PATH中增加两个AS号,一般增加自己的AS号)
R1将向AS65003通的路由的AS AS_path增加2个长度(即向AS_PATH中增加两个AS号,一般增加自己的AS号)
R1:
route-map add-as permit 10
set as-path prepend 65002 65002
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.20.1.2 route-map add-as out
R2:
route-map add-as permit 10
set as-path prepend 65003 65003
router bgp 65003
neighbor 10.20.1.1 route-map add-as out
2) 查看各设备的BGP表
R1#show ip bgp
*> 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 0 65001 65003 i
* 10.20.1.2 0 0 65003 65003 65003 i
//选择了as_path短的路由
R6#show ip bgp
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 0 65002 65002 65002 i
*> 10.10.56.1 0 65001 65002 i
//选择了as_path短的路由
跟踪测试:
.png)
成功!!!!!
1.5 BGP路由策略部署(方案二:local_preference)
1) 在R1,R6上,操控local_preference来实现选路需求
2) 在R1,R6上,将从AS65001收到的路由的local-preference设置为300,从其他AS收到的路由的本地优先级采用默认值
R1:
route-map as65001-in permit 10
set local-preference 300
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.10.12.2 route-map as65001-in in
r6:
route-map as65001-in permit 10
set local-preference 300
router bgp 65003
nei 10.10.56.1 route-m as65001-in
3) 查看各设备的BGP表
R1#show ip bgp
* 10.10.0.0/16 10.20.1.2 0 65003 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
* 10.13.0.0/16 10.20.1.2 0 65003 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
* 10.14.0.0/16 10.20.1.2 0 65003 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
* 10.15.0.0/16 10.20.1.2 0 65003 65001 i
*> 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 i
*> 10.20.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
*> 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.12.2 300 0 65001 65003 i
* 10.20.1.2 0 0 65003 i
//从AS65001过来的路由优先级都变为300, 也正因为如此,在去往10.30.0.0/16这条路的时候,不直接走R6的缘故
R6#show ip bgp
Network Next Hop Metric LocPrf Weight Path
* 10.10.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
* 10.13.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
* 10.14.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
* 10.15.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 65002 65001 i
*> 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 i
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.20.1.1 0 0 65002 i
*> 10.10.56.1 300 0 65001 65002 i
*> 10.30.0.0/16 0.0.0.0 0 32768 i
跟踪结果:
.png)
都饶了一大圈儿…..
1.5 BGP补充实验
1.6.1 BGP负载均衡
实验拓扑就是在下面这个图上面的R1和R2之间加一条广域网链路,都是S0/2
1.6.1 负载均衡组网需求:
BGP只把最优的路由通告给邻居,故BGP不能向邻居通告等价路由
如图,怎样实现在R2—R1之间的两条链路上实现负载均衡
1.6.2 解决办法一:将R2—R1之间的两条链路上进行捆绑,捆绑成一条链路使用
以太网链路使用手动捆绑或者LACP捆绑,PPP链路使用PPP multi-link
1.6.3 解决办法二:每条链路建立一个EBGP邻居,进行BGP本地负载均衡
R1:
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.10.12.2 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.12.6 remote-as 65001
maximum-paths 2
R2:
router bgp 65001
neighbor 10.10.12.1 remote-as 65002
neighbor 10.10.12.5 remote-as 65002
maximum-paths 2
查看BGP表
R2#show ip bgp
* 10.20.0.0/16 10.10.12.5 0 0 65002 i
*> 10.10.12.1 0 300 0 65002 i
* 10.30.0.0/16 10.10.12.5 0 0 65002 i
* i 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
*>i 10.10.0.5 0 300 0 65002 i
* 10.10.12.1 0 200 0 65002 i
R1#show ip route
B 10.10.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.6, 00:00:04
[20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:04
B 10.14.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.6, 00:00:04
[20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:04
B 10.15.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.6, 00:00:04
[20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:04
B 10.13.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.6, 00:00:04
[20/0] via 10.10.12.2, 00:00:04
R2# show ip route
B 10.30.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.5, 00:00:37
[20/0] via 10.10.12.1, 00:00:37
B 10.20.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.12.5, 00:00:37
[20/0] via 10.10.12.1, 00:00:37
R6#show ip route
B 10.13.0.0/16 [200/0] via 10.20.0.1, 00:01:46
R6# show ip bgp
*>i10.13.0.0/16 10.20.0.1 0 100 0 65001 i
//R1选择一条最优的通告给R6
BGP负载均衡只在本地有效:如果配置了maximum-paths N,BGP可将N相同网段且LP ,AS_PATH,ORIGIN,MEN,WEIGH都完全相同的外部AS路由,形成负载均衡路由安装到全局路由表;但最终还是会选出其中一条最优的路由通告给邻居
1.6.4 法三:使用loopback来建多跳EBGP邻居及静态路由解决负载均衡问题
R1:
ip route 10.10.0.2 255.255.255.255 Serial0/1 10.10.12.2
ip route 10.10.0.2 255.255.255.255 Serial0/2 10.10.12.6
router bgp 65002
neighbor 10.10.0.2 remote-as 65001
neighbor 10.10.0.2 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.10.0.2 update-source Loopback0
R2:
ip route 10.20.0.1 255.255.255.255 Serial0/0 10.10.12.1
ip route 10.20.0.1 255.255.255.255 Serial0/2 10.10.12.5
router bgp 65001
neighbor 10.20.0.1 remote-as 65002
neighbor 10.20.0.1 ebgp-multihop 2
neighbor 10.20.0.1 update-source Loopback0
R2#show ip bgp
*> 10.20.0.0/16 10.20.0.1 0 0 65002 i
R2show ip bgp
B 10.20.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.20.0.1, 00:02:39 //下一跳负载均衡
S 10.20.0.1/32 [1/0] via 10.10.12.5, Serial0/2
[1/0] via 10.10.12.1, Serial0/0
R1#show ip bgp
*> 10.13.0.0/16 10.10.0.2 0 65001 i
R1#show ip route
B 10.13.0.0/16 [20/0] via 10.10.0.2, 00:03:30 //下一跳负载均衡
S 10.10.0.2/32 [1/0] via 10.10.12.6, Serial0/2
[1/0] via 10.10.12.2, Serial0/1





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号