获取时间的函数有很多,具体包括如下:
一、gettimeofday()获取当前微秒(us)等级的时间
time()/gettimeofday()等等,下面是获取具体到usecond的时间程序:
#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <time.h> #include <sys/time.h> using namespace std; int main() { struct tm *tm; struct timeval tv; gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); tm = localtime(&tv.tv_sec); printf("[%d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d:%02d]\n",tm->tm_year + 1900,tm->tm_mon + 1,tm->tm_mday,tm->tm_hour,tm->tm_min,tm->tm_sec,tv.tv_usec); return 0; }
程序中需要引入对应的头文件:
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
程序中调用了gettimeofday函数,函数获得的结果保存在结构体tv中,函数会把得到从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到现在的秒数返回到第一个参数指向的结构体中,第二个参数是关于时区,如果不考虑填入NULL。
struct timeval结构体的成员如下所示:
/* A time value that is accurate to the nearest microsecond but also has a range of years. */ struct timeval { __time_t tv_sec; /* Seconds. */ __suseconds_t tv_usec; /* Microseconds. */ };
包括了两个部分,第一部分是second秒,第二部分是毫秒usecond。
二、localtime()将当前秒级时间转化为年月日时分秒结构
localtime函数的作用是将秒second转换为year、month、day、hour、minute、second。并把转换的结果保存在tm结构体中。
struct tm结构的成员如下:
/* Used by other time functions. */ struct tm { int tm_sec; /* Seconds. [0-60] (1 leap second) */ int tm_min; /* Minutes. [0-59] */ int tm_hour; /* Hours. [0-23] */ int tm_mday; /* Day. [1-31] */ int tm_mon; /* Month. [0-11] */ int tm_year; /* Year - 1900. */ int tm_wday; /* Day of week. [0-6] */ int tm_yday; /* Days in year.[0-365] */ int tm_isdst; /* DST. [-1/0/1]*/ # ifdef __USE_MISC long int tm_gmtoff; /* Seconds east of UTC. */ const char *tm_zone; /* Timezone abbreviation. */ # else long int __tm_gmtoff; /* Seconds east of UTC. */ const char *__tm_zone; /* Timezone abbreviation. */ # endif };
三、time()获取当前秒(s)等级的时间
time()函数:获取到当前时间的秒数,这里需要注意的是时间变量类型 time_t 这个变量目前是 unsigned 64Bits 的空间大小了,能够足够存储从1970年以来的us级别的时间值
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <time.h> 6 #include <sys/time.h> 7 8 int main(void) 9 { 10 time_t tt; 11 tt = time(NULL); 12 printf("Time: %ld\n",tt); 13 14 time(&tt); 15 printf("Time: %ld\n",tt); 16 }
四、字符串与时间之间的转换 strftime() 和 strptime()
1. strptime() 函数:把时间格式字符串,按一定格式存储到tm结构体中。
函数声明:char *strptime(const char *buf,const char *format,struct tm *timeptr)
该函数有三个参数:
- 时间格式字符串,
- 时间格式。
- tm 结构体的指针
2. strftime() 函数:把timeptr指向的结构体内容,根据format格式转换,并且存储在str中。
函数声明:size_t strftime(char *str, size_t maxsize, const char *format, const struct tm *timeptr)
该函数有四个参数,
- str -- 这是指向目标数组的指针,用来复制产生的 C 字符串。
- maxsize -- 这是被复制到 str 的最大字符数。
- format -- 这是 C 字符串,包含了普通字符和特殊格式说明符的任何组合。这些格式说明符由函数替换为表示 tm 中所指定时间的相对应值
- timeptr -- 这是由localtime函数返回的指向tm结构体的指针。
3. 用例程序如下C++(C)
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <iostream> // #include <time.h> // Add this if C 3 4 using namespace std; // Remove if C 5 6 #define str_time "2021-11-13 18:30:22" 7 8 int main(void) 9 { 10 struct tm tm; 11 char buf[255]; 12 13 strptime(str_time, "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm); 14 strftime(buf, sizeof(buf), "%d %b %Y %H:%M", &tm); 15 puts(buf); 16 return 0; 17 }
运行结果:
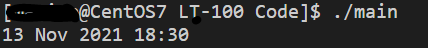
4. format中的格式如下:
|
%a |
星期几的简写形式 |
|
%A |
星期几的全称 |
|
%b |
月份的简写形式 |
|
%B |
月份的全称 |
|
%c |
日期和时间 |
|
%d |
月份中的日期,0-31 |
|
%H |
小时,00-23 |
|
%I |
12进制小时钟点,01-12 |
|
%j |
年份中的日期,001-366 |
|
%m |
年份中的月份,01-12 |
|
%M |
分,00-59 |
|
%p |
上午或下午 |
|
%S |
秒,00-60 |
|
%u |
星期几,1-7 |
|
%w |
星期几,0-6 |
|
%x |
当地格式的日期 |
五. 这里封装一个时间相关的函数库方便调用

1 time_t get_timestamp_ms(void) 2 { 3 time_t timestamp_ms = 0; 4 struct timeval tv; 5 6 gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); 7 timestamp_ms = tv.tv_sec * 1000 + tv.tv_usec / 1000; 8 return timestamp_ms; 9 } 10 11 time_t get_timestamp_us(void) 12 { 13 time_t timestamp_ms = 0; 14 struct timeval tv; 15 16 gettimeofday(&tv,NULL); 17 timestamp_ms = tv.tv_sec * 1000000 + tv.tv_usec; 18 return timestamp_ms; 19 }
未完待续!





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号