Vue-router就是WebApp的链接路径管理系统。简单可以理解为路径的跳转。 那么我们为什么不能用 a 标签,这是因为用 Vue 做的都是单页应用(当你的项目准备 打包时,运行 npm run build 时,就会生成 dist 文件夹,这里面只有静态资源和一个 index.html 页面),所以我们写的<a></a>标签是不起作用的,必须使用 Vue-router 来进行管理。

选择不自动安装 vue-router。
npm install vue-router
npm install --save vue-router //进入项目根目录进行安装路由依赖
通过上述命令安装完路由依赖后,路由使用步骤如下:
(1) 在 src 目录下建立 router/index.js 文件,此文件专门用于管理路由核心文件,使用 Vue.use()加载路由插件,代码如下:
// 引入 vue 框架
import Vue from 'vue'
// 引入 vue-router 路由依赖
import Router from 'vue-router'
// 引入页面组件,命名为 HelloWorld。@代表绝对路径
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
// Vue 全局使用 Router Vue.use(Router)
// 定义路由配置,注意 export 导出,只要道出了别的文件才能 import 导入
export default new Router({
routes: [ //配置路由,这里是个数组
{ //每一个链接都是一个对象
// 引入vue框架 import Vue from 'vue' // 引入vue-router路由依赖 import Router from 'vue-router' // 引入页面组件,命名为HelloWorld。@代表绝对路径 import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' import Home from '@/components/Home' import News from '@/components/News' import Hi from '../components/Hi' /*导入页面1 页面2*/ import One from '@/pages/One' import Two from '@/pages/Two' import Three from '@/pages/Three' // Vue全局使用Router Vue.use(Router) // 定义路由配置,注意export导出,只要道出了别的文件才能import导入 export default new Router({ mode:'history', // 去掉路由地址的# routes: [ //配置路由,这里是个数组 { //每一个链接都是一个对象 path: '/', name: 'HelloWorld', //路由名称, component: HelloWorld //对应的组件模板 }, { path: '/home', name: 'Home', component: Home, children:[ // 嵌套子路由 { path:'one', // 子页面1 name:'One', component:One }, { path:'two/:id/:name', // 子页面2 component:Two }, { path:'three/:id/:name', // 子页面3 name: 'three', component:Three } ] }, { path: '/hi', name: 'Hi', component: Hi }, { path: '/news', name: 'News', component: News } ] })
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- <img src="./assets/logo.png">-->
<Nav></Nav>
<!--路由占位符:将路由路径所指定的组件渲染到页面中-->
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld'
import Nav from '@/components/Nav'
export default {
name: 'App',
components:{
Nav
}
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: 'Avenir', Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
<template>
<div id="hello">
<h1>HelloWorld.vue组件</h1>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
data () { //在组件中必须为data函数,这是vue特性
return {
msg: 'Welcome to Your Vue.js App',
}
},
created() {
this.$axios.get('http://rap2api.taobao.org/app/mock/23080/resources/search',{
params: {
id: 5
}
})
.then(res => {
console.log('数据是:', res);
})
.catch((e) => {
console.log('获取数据失败');
});
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
(5) 运行 npm run dev 启动服务,访问 http://localhost:8080/页面
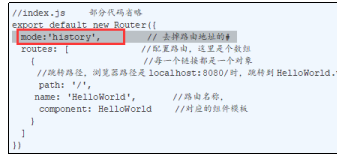
Vue为我们提供了一个属性mode:"history",可以去掉地址栏中的#,如图所示:
每个页面对应一个组件,也就是对应一个.vue文件。在components目录下创建Hi.vue文件,代码如下 <template> <div id="hi"> <h1>Hi.vue 组件</h1> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Hi" } </script>
再回到 index.js 里,完成路由的配置,代码如下:
//引入 Hi 组件
import Hi from '../components/Hi'
// Vue 全局使用 Router
Vue.use(Router) // 定义路由配置,注意 export 导出,只要道出了别的文件才能 import 导入
export default new Router({
mode:'history', // 去掉路由地址的#
routes: [ //配置路由,这里是个数组
//...
{
path: '/hi',
name: 'Hi',
component: Hi
}
]
})
启动服务,在浏览器中访问 http://localhost:8080/和 http://localhost:8080/hi 就可以分别访 问 HelloWorld.vue 和 Hi.vue 组件页面。
ES6 语法提示:
ES6 新增了 let 和 const 命令来声明变量,代替了 var。它们的用法类似于 var,但是所 声明的变量只在代码块内有效,如下面代码:
{
let a=123;
var b=234;
}
console.log(a); //报错 a is not defined
console.log(b); //234
let 和 const 的主要区别是,const 声明一个只读的常量。一旦声明,常量的值就不能改 变。
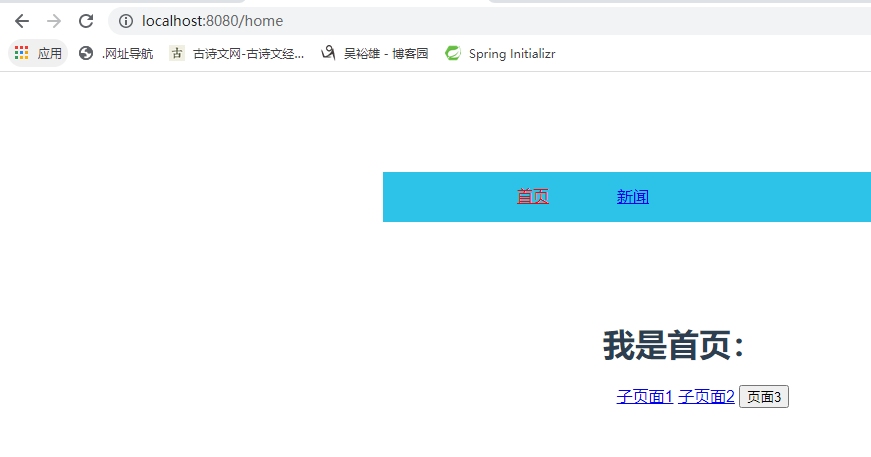
在 components 目录下创建 Home.vue(首页)和 News.vue(新闻页)两个文件,代码如下:
<template> <div id="Home"> <h1>我是首页:</h1> <ul> <!--路径要写完整路径:父路径+子路径--> <span><router-link :to="{name: 'One', params:{username:'beixi'}}">子页面1</router-link></span> <span><router-link to="/home/two/666/贝西奇谈" >子页面2</router-link></span> <button @click="toThreePage">页面3</button> </ul> <!-- 子页面展示部分 --> <router-view/> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home", methods: { toThreePage() { this.$router.push({name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name: 'beixi'}}) } } } </script> <style scoped> .router-link-active{ color: red; } </style>
<template> <div id="News"> <h3>{{title}}</h3> <ul class="ulnews"> <li v-for="(data,index) in newslist">{{data}}</li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "News", data(){ return{ title:'新闻栏目', newslist:[ '新闻1', '新闻2', '新闻3' ] } } } </script> <style scoped> .ulnews li{ display: block; } </style>
这样我们可以在地址栏输入不同的路径访问对应的页面,但一般页面上需要有个导航链接,我们只要点击就可以实现页面内容的变化。在 components 目录下创建 Nav.vue 导航页 面,代码如下:
<template> <div id="box"> <ul> <li><router-link to="/home" active-class="router-link-active">首页</router-link></li> <!--v-bind动态设置--> <!-- <li><router-link v-bind:to="home">首页</router-link></li>--> <!--同上--> <!-- <li><router-link :to="{ path: 'home' }">首页</router-link></li>--> <!-- <button @click="goHome">首页</button>--> <li><router-link to="/news" >新闻</router-link></li> </ul> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "nav", data(){ return { home:'/home' } }, methods: { goHome(){ this.$router.push('/home'); } } } </script> <!--scoped该样式只能适用于当前组件元素--> <style scoped> .router-link-active{ color: red; } *{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } ul{ list-style: none; overflow: hidden; } #box{ width: 600px; margin: 100px auto; } #box ul{ padding: 0 100px; background-color: #2dc3e8; } #box ul li { display: block; width: 100px; height: 50px; background-color: #2dc3e8; color: #fff; float: left; line-height:50px; text-align: center; } #box ul li:hover{ background-color: #00b3ee; } </style>
导航页面构建完成后,在跟实例App.vue组件中导入 <template> <div id="app"> <Nav></Nav> <router-view/> <!--路由占位符:将路由路径所指定的组件渲染到页面中--> </div> </template> <script> import Nav from '@/components/Nav' export default { name: 'App', components:{ Nav } } </script>
接着介绍 vue.js 通过路由跳转页面方式: (1) router-link 标签跳转,它会被渲染成<a>标签,使用方式如下
<template> <div id="box"> <ul> <li><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link></li> <li><router-link to="/news">新闻</router-link></li> </ul> </div> </template>
<router-link> 标签中的属性介绍: to: 表示目标路由的链接。当然也可以用 v-bind 动态设置链接路 径,代码如下: <li><router-link to="/home">首页</router-link></li> <!--v-bind动态设置--> <li><router-link v-bind:to="home">首页</router-link></li> <!--同上--> <li><router-link :to="{ path: 'home' }">首页</router-link></li>
replace 使用 replace 属性导航后不会留下 history 记录,所以导航后不能用后退键返回到上一 个页面,如<router-link to="/home" replace>。
tag 有时想要 <router-link> 渲染成某种标签,例如 <li>。代码如下: <router-link to="/foo" tag="li">foo</router-link>
(2) JS 代码内部跳转 实际项目中,很多时候都是通过在 JS 代码内部进行导航的跳转,使用方式如下: this.$router.push('/xxx') 具体的用法步骤如下: 在页面中添加敲击事件,代码如下: <button @click="goHome">首页</button> 在<script>模块里加入 goHome 方法, 并用 this.$router.push(‘/’)导航到首页,
export default {
name: 'app',
methods: {
goHome(){
this.$router.push('/home');
}
}
}
路由嵌套 子路由,也叫路由嵌套,一般应用都会出现二级导航这种情况,这时就得使用路由嵌套 这种写法,采用在 children 后跟路由数组来实现,数组里和其他配置路由基本相同,需要配 置 path 和 component,然后在相应部分添加<router-view/>来展现子页面信息,相当于嵌入 iframe。具体如下面的示例: (1) Src/components/Home.vue(父页面),代码如下: <template> <div id="Home"> <h1>我是首页:</h1> <ul> <!--路径要写完整路径:父路径+子路径--> <span><router-link to="/home/one" >子页面 1</router-link></span> <span><router-link to="/home/two" >子页面 2</router-link></span> </ul> <!-- 子页面展示部分 --> <router-view/> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Home" } </script> <style scoped> .router-link-active{ color: red; } </style>
(2) src/pages/One.vue(子页面 1),代码如下:
<template> <div id="one"> <h3>{{msg}}</h3> <h2>{{$route.params.username}}</h2> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "One", data(){ return { msg:'这是第一个子页面' } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
(3) src/pages/Two.vue(子页面 2),代码如下:
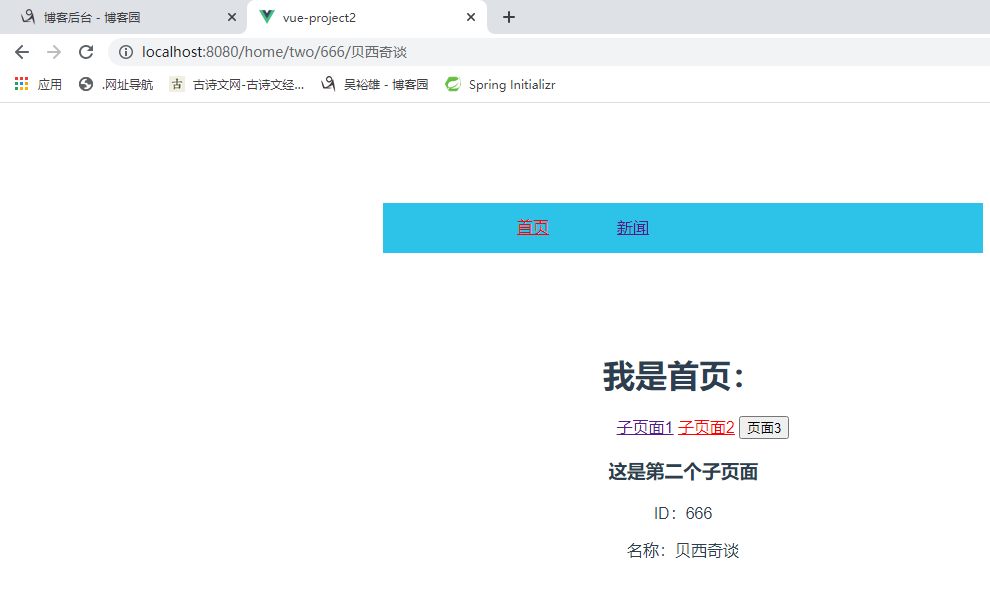
<template> <div id="two"><h3>{{msg}}</h3> <p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p> <p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p> </div> </template> <script> export default { name: "Two", data(){ return { msg:'这是第二个子页面' } } } </script> <style scoped> </style>
(4) src/router/index.js(路由配置),代码如下:
//部分代码省略
/*导入页面 1 页面 2*/
import One from '@/pages/One'
import Two from '@/pages/Two'
export default new Router({
routes: [
//...
{
path: '/home',
name: 'Home',
component: Home,
children:[ // 嵌套子路由
{
path:'one', // 子页面 1
component:One
},
{
path:'two', // 子页面 2
component:Two
},
]
}
]
})
注意:子页面显示的位置是在其父级页面中,所以一定要在父级页面中加 <router-view/>标签。
路由参数传递 路由传递参数有三种方式: 1. 通过<router-link> 标签中的 to 传参, <router-link :to="{name:xxx, params: {key:value}}">valueString</router-link> 上面 to 前面是带冒号,值为对象形式的字符串: name:对应的是路由配置文件中起的 name 值,叫做路由名称。 params:要传的参数,它是对象形式,在对象里可以传递多个值。
具体实例如下: (1)在 src/components/Home.vue 里面导航中添加如下代码: <router-link :to="{name: 'One', params:{username:'beixi'}}"> 子页面 1</router-link> (2)在 src/router/indes.js 中添加如下代码: { path:'one', // 子页面 1 name:'One', //name 属性不能少 component:One } (3)在 src/pages/One.vue 里面接受参数,代码如下: <h2>{{$route.params.username}}</h2>
2. url 中传递参数 (1)在路由中以冒号形式传递,在 src/router/index.js中添加如下代码: { path:'two/:id/:name', // 子页面 2 component:Two } (2)接受参数,在 src/pages/Two.vue 中添加如下代码: <p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p> <p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p> (3)路由跳转,在 src/components/Home.vue 中添加如下代码: <router-link to="/home/two/666/贝西奇谈" >子页面 2</router-link>
3. 编程式导航 params 传递参数 (1)在 src/router/index.js 页面添加如下代码: { path:'three/:id/:name', // 子页面 3 name: 'three', component:Three } (2)在 src/pages/Three.vue 页面添加如下代码: <p>ID:{{ $route.params.id}}</p> <p>名称:{{ $route.params.name}}</p> (3)在 src/components/Home.vue 中添加如下代码: // template 部分代码省略 <button @click="toThreePage">页面 3</button> // script methods: { toThreePage() { this.$router.push({name: 'three', params: {id: 1, name:'beixi'}}) } }
代码说明:
动态路由使用 params 传递参数,在 this.$router.push() 方法中 path 不能和 params 一起使用,否则 params 将无效。需要用 name 来指定页面。
以上方式参数不会显示到浏览器的地址栏中,如果刷新一次页面,就获取不到参数 了,改进方式如下:
{
path:'/home/three/:id/:name', // 子页面 3
name: 'three',
component:Three
}
路由中 router 和 route 的区别:
(1)router 是 VueRouter 的一个对象,通过 Vue.use(VueRouter)和 VueRouter 构造函数 得到一个 router 的实例对象,这个对象中是一个全局的对象,他包含了所有的路由并且也包 含了许多关键的对象和属性,如下所示:
$router.push({path:'home'});// 切换路由,有 history 记录
$router.replace({path:'home'});//替换路由,没有历史记录
(2)route 是一个跳转的路由对象,每一个路由都会有一个 route 对象,是一个局部的 对象,可以获取对应的 name,path,params,query 等。
$route.path,,$route.params,$route.name, $route.query 这几个属性很容易理解,主要 用于接收路由传递的参数。