作业二
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 班级的链接 |
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | 作业要求 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 了解使用nlp,学习python,加强对测试和性能分析的理解 |
论文查重项目报告
一、GitHub 仓库
https://github.com/Tsukilc/duplicate-checking
二、PSP 表格
| Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
| Planning 计划 | 10 | 10 |
| - Estimate 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 195 | 185 |
| Development 开发 | 170 | 160 |
| - Analysis 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 20 | 20 |
| - Design Spec 生成设计文档 | 20 | 20 |
| - Design Review 设计复审 | 10 | 20 |
| - Coding Standard 代码规范 | 10 | 10 |
| - Design 具体设计 | 10 | 10 |
| - Coding 具体编码 | 60 | 50 |
| - Code Review 代码复审 | 30 | 30 |
| - Test 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 10 | 10 |
| Reporting 报告 | 25 | 25 |
| - Test Report 测试报告 | 10 | 20 |
| - Size Measurement 计算工作量 | 5 | 5 |
| - Postmortem 总结及改进计划 | 10 | 20 |
| 合计 | 205 | 225 |
三、代码设计与实现
设计思路与优缺点
-
因为不能联网,考虑将大模型下载到本地,调用本地大模型进行语义层面的论文查重
-
利用jieba分词,转化为向量后提供给大模型进行处理
-
因为使用了大模型,所以速度没有单靠词频处理快
论文要如何识别番茄和西红柿,周五和星期五的差异?以及各种词在不同位置的出现等复杂的问题,第一个想法就是使用NLP来进行
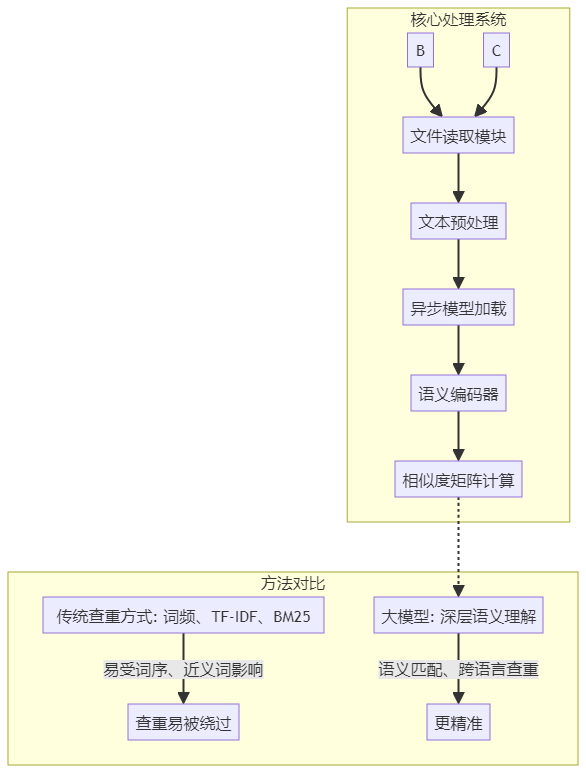
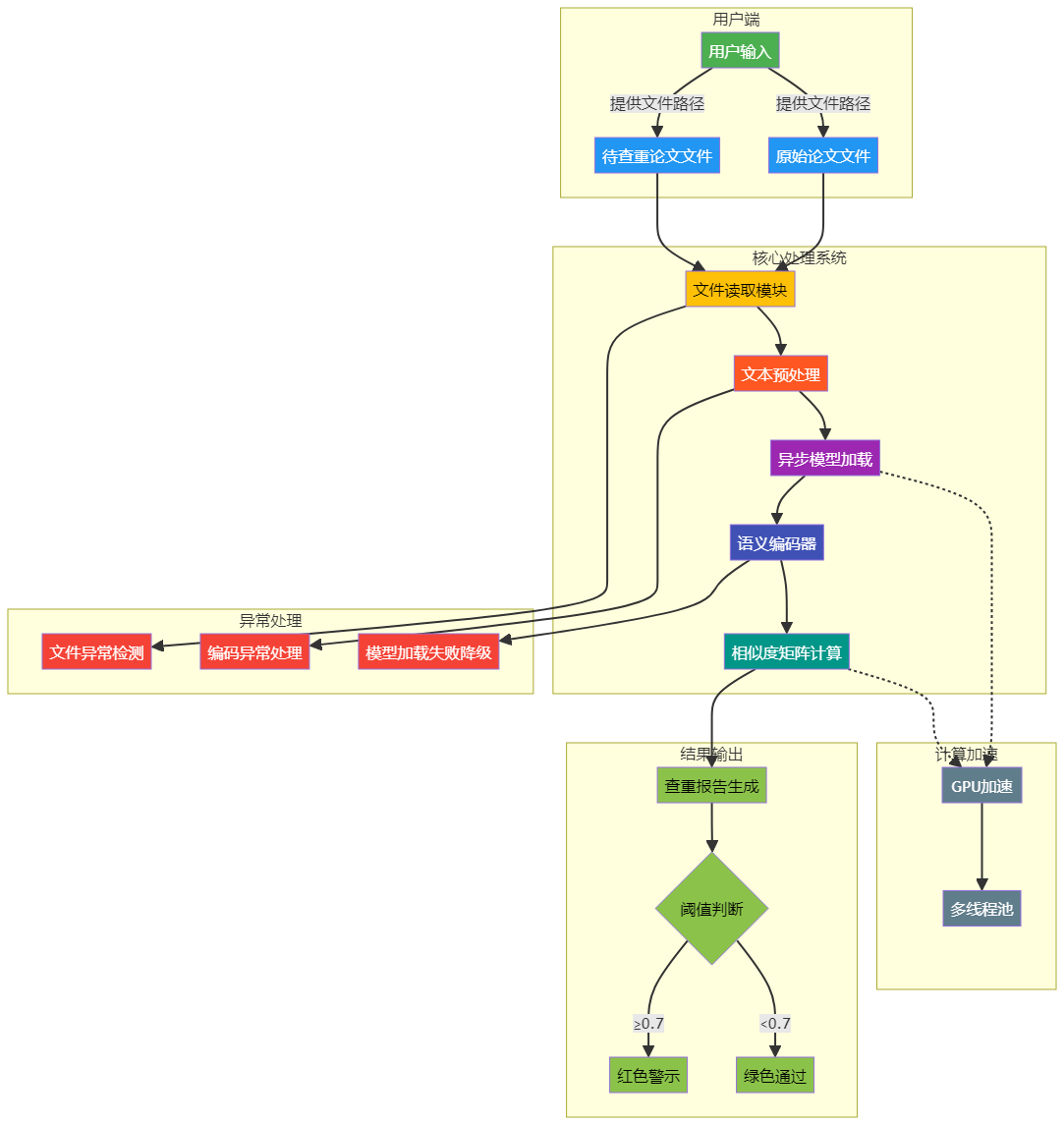
架构设计图
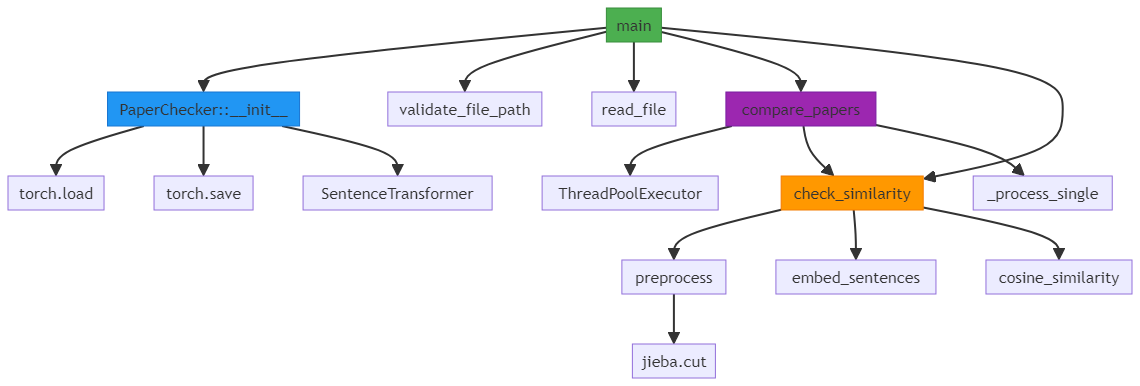
函数调用流程图
关键技术实现
- 文本比较
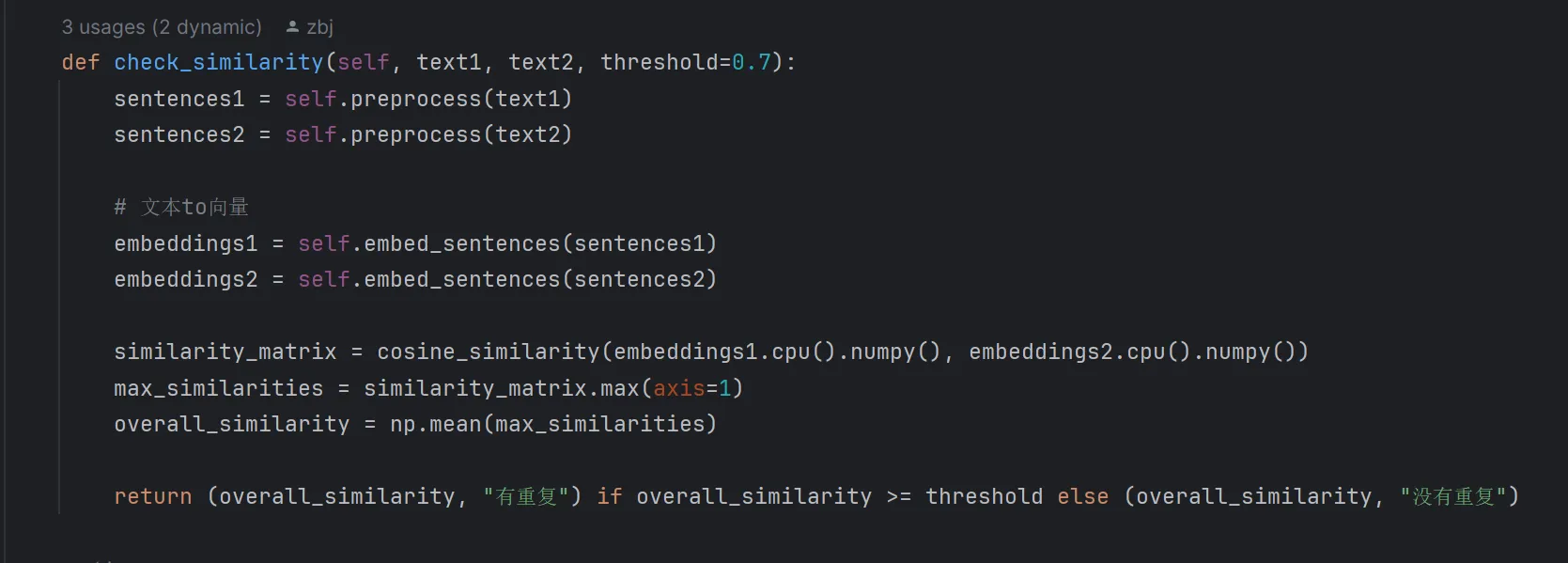
# 核心相似度计算流程(checker.py)
def check_similarity(self, text1, text2):
# 多粒度文本分割
sentences1 = self.preprocess(text1)
sentences2 = self.preprocess(text2)
# 文本to向量
embeddings1 = self.embed_sentences(sentences1)
embeddings2 = self.embed_sentences(sentences2)
# 调用大模型比较
similarity_matrix = cosine_similarity(embeddings1.cpu().numpy(), embeddings2.cpu().numpy())
max_similarities = similarity_matrix.max(axis=1)
overall_similarity = np.mean(max_similarities)
return (overall_similarity, "有重复") if overall_similarity >= threshold else (overall_similarity, "没有重复")
- 大模型初始化
def
__init__
(self, model_name="sentence-transformers/paraphrase-multilingual-MiniLM-L12-v2",
cache_dir="./models", use_gpu=True):
self.cache_dir = cache_dir
self.device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() and use_gpu else 'cpu'
if not os.path.exists(self.cache_dir):
os.makedirs(self.cache_dir)
fast_model_path = os.path.join(self.cache_dir, "fast_model.pt")
torch.set_num_threads(12)
if os.path.exists(fast_model_path):
# print("加载优化后的模型...")
self.model = torch.load(fast_model_path,
weights_only=False,
map_location=self.device)
else:
print("初始化新模型...")
self.model = SentenceTransformer(model_name)
# 保存为权重文件
torch.save(self.model.state_dict(), fast_model_path)
# print(f"模型加载完成,设备: {self.device}")
- 文本预处理
def preprocess(self, text):
"""文本预处理(分词+去除空白)"""
sentences = text.replace("\n", "。").split("。") # 以句号拆分
sentences = [s.strip() for s in sentences if s.strip()]
# # 分词并打印每个句子的分词结果
# for sentence in sentences:
# words = jieba.cut(sentence) # 分词
# word_list = ' '.join(words) # 将分词结果拼接成字符串
# print(f"分词结果:{word_list}") # 打印分词结果
# 返回分词后的句子
sentences = [' '.join(jieba.cut(sentence)) for sentence in sentences]
return sentences
四、性能分析与优化
使用cprofile生成的性能分析图

- 性能瓶颈分析
在论文查重过程中,主要的性能瓶颈包括:
-
模型加载时间:大模型通常占用大量显存,加载时间较长,影响查重速度。
-
文件 I/O 读写:当原文与查重文本较大时,文件读写速度成为性能瓶颈。
-
计算资源占用:语义编码与相似度计算较为耗时,影响整体响应速度。
-
消耗时长最大的函数
文本to向量,拆词,大模型计算。。。因此非常耗时。后续可以引进计算能力更强的大模型解决这个问题,但是响应的加载时长也会久。不用restful接口的话,每次请求都初始化大模型,很难突破5s的瓶颈。。。
- 主要优化策略
(1)异步流水线
-
优化点:文件读取、文本预处理和模型加载并行执行
-
优化方案:
-
使用
asyncio进行 文件读取 & 预处理并行化 -
在用户输入时 异步加载模型,减少等待时间
-
优化效果:减少同步等待,提高整体吞吐量
-
(2)多线程并行计算
-
优化点:加速语义编码和相似度计算
-
优化方案:
-
采用 ThreadPoolExecutor 进行多线程计算
-
优化效果:提高 CPU 利用率,减少计算时间
-
(3)模型选择权衡
-
优化点:兼顾查重精度与计算成本
-
优化方案:
-
考虑大模型加载速度慢,小模型效果差的问题
-
最终选用
paraphrase-xlm-r-multilingual-v1 -
该模型占用空间较大,但语义识别效果优秀
-
优化效果:保证查重精度,兼顾计算资源
-
五、单元测试设计
-
课堂发的单元测试
-
西红柿和番茄是不是重复的
-
文件操作测试
-
文件扩展名是否正确测试
异常处理说明
-
文件路径不能为空
-
文件不存在
-
路径指向的是目录
-
不支持的文件格式
-
文件名包含非法字符
-
模型加载失败
class TestExceptionHandling:
def test_invalid_encoding(self):
"""测试读取非UTF-8编码文件"""
from main import read_file
# 生成包含非法字节的文件
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode="wb", delete=False, suffix=".txt") as f:
f.write(b"\x80\xFFinvalid") # 直接写入二进制非法数据
bad_file = f.name
try:
with pytest.raises(UnicodeDecodeError):
read_file(bad_file)
finally:
os.unlink(bad_file)
@pytest.fixture
def checker():
"""测试用查重器实例"""
from main import PaperChecker
return PaperChecker(use_gpu=False)
@pytest.fixture
def sample_texts():
return {
"empty": "",
"short": "这是一个短文本。",
"normal": "自然语言处理是人工智能的重要领域。深度学习模型在其中发挥关键作用。",
"dup_part": "自然语言处理是AI的核心领域。深度学习模型非常重要。",
"full_dup": "自然语言处理是人工智能的重要领域。深度学习模型在其中发挥关键作用。"
}
# 测试工具函数
def create_temp_file(content, suffix=".txt"):
"""创建临时测试文件"""
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode="w", suffix=suffix, delete=False) as f:
f.write(content)
return f.name
# 测试预处理模块
class TestPreprocess:
def test_jieba_segment(self, checker):
text = "自然语言处理技术"
result = checker.preprocess(text)
assert result == ["自然语言 处理 技术"]
class TestModelLoading:
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
def clean_cache(self):
# 清理模型缓存
cache_path = os.path.join("./models", "fast_model.pt")
if os.path.exists(cache_path):
os.remove(cache_path)
yield
def test_cold_start(self):
"""测试无缓存时的模型加载"""
checker = PaperChecker(use_gpu=False)
assert checker.model is not None
def test_warm_start(self):
"""测试有缓存时的模型加载"""
# 先冷启动生成缓存
PaperChecker(use_gpu=False)
# 再次加载
checker = PaperChecker(use_gpu=False)
assert checker.model is not None
# 测试文件操作
class TestFileOperations:
def test_valid_file(self):
from main import validate_file_path
valid_file = create_temp_file("正常内容" * 100)
assert validate_file_path(valid_file) == os.path.abspath(valid_file)
def test_invalid_paths(self):
from main import validate_file_path
with pytest.raises(FileNotFoundError):
validate_file_path("non_existent.txt")
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as d:
with pytest.raises(IsADirectoryError):
validate_file_path(d)
def test_file_size_limit(self):
from main import validate_file_path
big_file = create_temp_file("a" * (10 * 1024 * 1024 + 1))
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
validate_file_path(big_file)
# 测试完整流程
class TestIntegration:
def test_full_workflow(self, checker, tmp_path):
"""测试完整流程并验证输出文件"""
from main import compare_papers
# 使用临时目录
output_dir = tmp_path / "output"
output_dir.mkdir()
os.chdir(output_dir)
# 生成测试内容
orig_content = "自然语言处理的基本原理。"
plag_content = "自然语言处理的基础理论。"
# 执行查重比较
results = compare_papers(
orig_text=orig_content,
plagiarism_texts=[("test.txt", plag_content)], # 文件名不影响测试
checker=checker,
threshold=0.5
)
# 异常处理测试
class TestExceptionHandling:
def test_invalid_encoding(self):
"""测试读取非UTF-8编码文件"""
from main import read_file
# 生成包含非法字节的文件
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode="wb", delete=False, suffix=".txt") as f:
f.write(b"\x80\xFFinvalid") # 直接写入二进制非法数据
bad_file = f.name
try:
with pytest.raises(UnicodeDecodeError):
read_file(bad_file)
finally:
os.unlink(bad_file)
# 清理临时文件
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
def cleanup():
yield
for f in os.listdir(tempfile.gettempdir()):
if f.startswith("tmp"):
try:
os.remove(os.path.join(tempfile.gettempdir(), f))
except:
pass
覆盖率
使用pytest进行模拟测试,行覆盖率百分之七十二
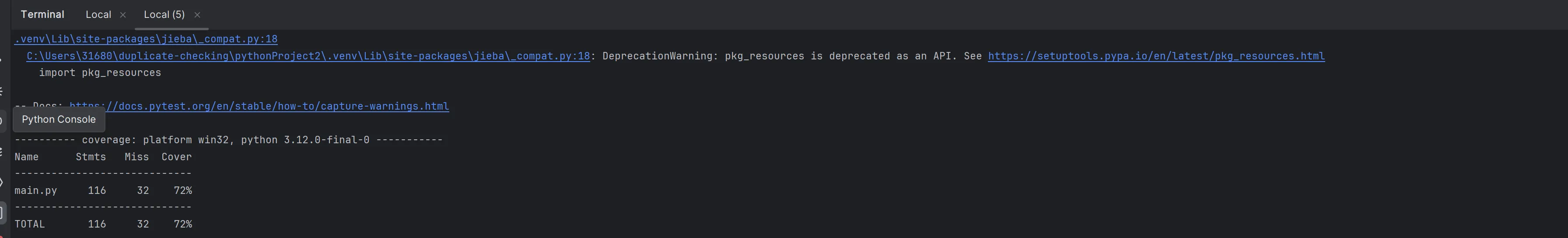
# 使用pytest-cov生成报告
pytest --cov=main test.py --cov-report=term
六、改进路线图
技术演进路径
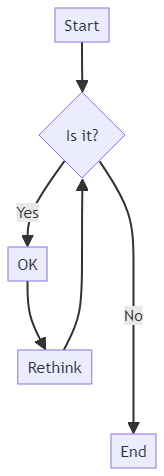
近期优化方向
既然是用到了模型,肯定不能请求一次生成一次模型,最理想的方式是引用restful接口,生成模型后提供接口给用户调用就行了,也可以选用更大型更快的模型。。
工程化改进:
-
构建Docker镜像
-
添加restful API支持



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号