实验7
task1
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 80
#define M 100
typedef struct {
char name[N]; // 书名
char author[N]; // 作者
} Book;
void write();
void read();
int main() {
printf("测试1: 把图书信息写入文本文件\n");
write();
printf("\n测试2: 从文本文件读取图书信息, 打印输出到屏幕\n");
read();
return 0;
}
void write() {
Book x[] = { {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"},
{"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"},
{"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"},
{"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"},
{"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"},
{"《上学记》", "何兆武"},
{"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} };
int n, i;
FILE *fp;
// 计算数组x中元素个数
n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
// 以写的方式打开文本文件data1.txt
fp = fopen("data1.txt", "w");
// 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to write\n");
return;
}
// 将结构体数组x中的图书信息格式化写到fp指向的文件data1.txt
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
fprintf(fp, "%-40s %-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author);
fclose(fp);
}
void read() {
Book x[M];
int i, n;
FILE *fp;
// 以读的方式打开文本文件data1.txt
fp = fopen("data1.txt", "r");
// 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to read\n");
return;
}
// 从文件中读取图书信息,保存到结构体数组x中
i = 0;
while(fscanf(fp, "%s%s", x[i].name, x[i].author) != EOF)
++i;
// 将图书信息打印输出到屏幕上
n = i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d. %-40s%-20s\n", i+1, x[i].name, x[i].author);
fclose(fp);
}


task2
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define N 80
#define M 100
typedef struct {
char name[N]; // 书名
char author[N]; // 作者
} Book;
void write();
void read();
int main() {
printf("测试1: 把图书信息以数据块方式写入二进制文件\n");
write();
printf("\n测试2: 从二进制文件读取图书信息, 打印输出到屏幕\n");
read();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void write() {
Book x[] = { {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"},
{"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"},
{"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"},
{"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"},
{"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"},
{"《上学记》", "何兆武"},
{"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} };
int n, i;
FILE *fp;
// 计算数组x中元素个数
n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
// 以写的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat
fp = fopen("data2.dat", "wb");
// 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to write\n");
return;
}
// 将结构体数组x中的图书信息以数据块方式写入二进制文件data2.dat
fwrite(x, sizeof(Book), n, fp);
fclose(fp);
}
void read() {
Book x[M];
int i, n;
FILE *fp;
// 以读的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat
fp = fopen("data2.dat", "rb");
// 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to read\n");
return;
}
// 从二进制文件data2.dat以数据块方式读取图书信息存储到结构体数组x
i = 0;
while(fread(&x[i], sizeof(Book), 1, fp) == 1)
++i;
// 在屏幕上打印输出
n = i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d. %-40s%-20s\n", i+1, x[i].name, x[i].author);
fclose(fp);
}


task3
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define N 100
#define M 80
void write();
void read_str();
void read_char();
int main() {
printf("测试1: 把一组字符信息以字符串方式写入文本文件\n");
write();
printf("\n测试2: 从文件以字符串方式读取, 输出到屏幕\n");
read_str();
printf("\n测试3: 从文件以单个字符方式读取, 输出到屏幕\n");
read_char();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void write() {
char *ptr[] = { "Working\'s Blues",
"Everything Will Flow",
"Streets of London",
"Perfect Day",
"Philadelphia"};
int i, n;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("data3.txt", "w");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to write\n");
return;
}
n = sizeof(ptr)/sizeof(ptr[0]);
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
fputs(ptr[i], fp);
fputs("\n", fp);
}
fclose(fp);
}
void read_str() {
char songs[N][M];
int i, n;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("data3.txt", "r");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to read\n");
return;
}
i = 0;
while(i < N && (fgets(songs[i], M, fp) != NULL))
++i;
n = i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d. %s", i+1, songs[i]);
fclose(fp);
}
void read_char() {
int ch;
FILE *fp;
fp = fopen("data3.txt", "r");
if(fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file to read\n");
return;
}
while((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF)
putchar(ch);
fclose(fp);
}

思考
1.'是转义字符,代表'。
2.i<N的作用是判断读取的数据有没有超过数组的最大行,防止文件的行数过多产生越界。
task4
源代码
点击查看代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
//读取文件
//统计行数
//统计字符数
int main(){
FILE *fp;
int l=0,w=0;
char ch;
if((fp=fopen("C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Downloads\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\data4.txt","r"))==NULL){
printf("fail to open fail to read\n");
return 1;
}
while((ch=fgetc(fp))!=EOF){
if(ch=='\n')
l++;
if((ch!='\n')&&(ch!=' ')&&ch!=('\t'))
w++;
}
printf("data4.txt统计结果\n");
printf("行数\t%d\t\n",l);
printf("字符数(不计空白符)\t%d\t\n",w);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

task5
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define N 10
typedef struct {
long id; // 准考证号
char name[20]; // 姓名
float objective; // 客观题得分
float subjective; // 操作题得分
float sum; // 总分
char result[10]; // 考试结果
} STU;
// 函数声明
void read(STU st[], int n);
void write(STU st[], int n);
void output(STU st[], int n);
int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]);
int main() {
STU stu[N], stu_pass[N];
int cnt;
double pass_rate;
printf("从文件读入%d个考生信息...\n", N);
read(stu, N);
printf("\n对考生成绩进行统计...\n");
cnt = process(stu, N, stu_pass);
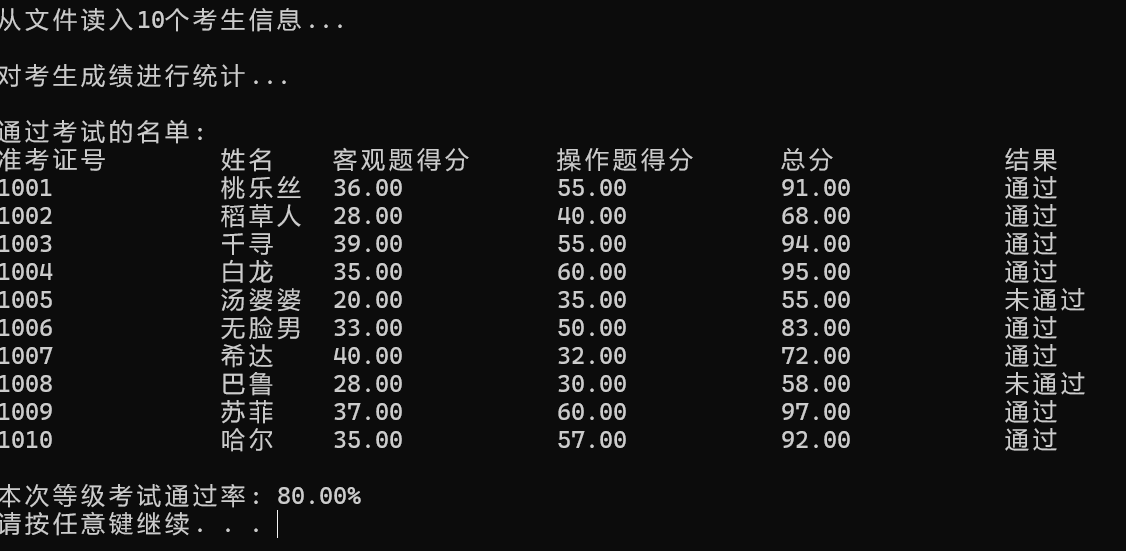
printf("\n通过考试的名单:\n");
output(stu, N); // 输出所有考生完整信息到屏幕
write(stu, N); // 输出考试通过的考生信息到文件
pass_rate = 1.0 * cnt / N;
printf("\n本次等级考试通过率: %.2f%%\n", pass_rate*100);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 把所有考生完整信息输出到屏幕上
// 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果
void output(STU st[], int n) {
int i;
printf("准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t结果\n");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
printf("%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n", st[i].id, st[i].name, st[i].objective, st[i].subjective, st[i].sum, st[i].result);
}
// 从文本文件examinee.txt读入考生信息:准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分
void read(STU st[], int n) {
int i;
FILE *fin;
fin = fopen("C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Downloads\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\examinee.txt", "r");
if (!fin) {
printf("fail to open file\n");
return;
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
fscanf(fin, "%ld %s %f %f", &st[i].id, st[i].name, &st[i].objective, &st[i].subjective);
fclose(fin);
}
// 把通过考试的考生完整信息写入文件list_pass.txt
// 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果
void write(STU s[], int n) {
FILE *fpass;
int i;
if((fpass=fopen("list_pass.txt","w+"))==NULL){
printf("fail to open to write");
return;
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i].sum>=60)
fwrite(&s[i],sizeof(STU),1,fpass);
}
fclose(fpass);
}
// 对考生信息进行处理:计算每位考生考试总分、结果;统计考试通过的人数
int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]) {
int i,j=0,stu_pass=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
st[i].sum=st[i].objective+st[i].subjective;
if(st[i].sum>=60){
strcpy(st[i].result,"通过");
stu_pass++;
st_pass[j++]=st[i];
}
if(st[i].sum<60)
strcpy(st[i].result,"未通过");
}
return stu_pass;
}
task6
源代码
点击查看代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <time.h>
#define STUDENT_NUM 80
#define INFO_LEN 100
void readStudents(char students[STUDENT_NUM][INFO_LEN], const char *filename) {
FILE *fp = fopen("C:\\Users\\Lenovo\\Downloads\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\实验7数据文件及部分代码_gbk\\list.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file\n");
exit(1);
}
int i = 0;
while (i < STUDENT_NUM && fgets(students[i], INFO_LEN, fp) != NULL) {
int len = strlen(students[i]);
if (students[i][len - 1] == '\n') {
students[i][len - 1] = '\0';
}
i++;
}
fclose(fp);
}
void randomSelect(int selected[], int total, int count) {
int flag[5] = {0};
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
int i = 0;
while (i < count) {
int randIdx = rand() % total;
if (flag[randIdx] == 0) {
selected[i] = randIdx;
flag[randIdx] = 1;
i++;
}
}
}
void showAndSave(char students[STUDENT_NUM][INFO_LEN], int selected[], int count, const char *saveFile) {
// 显示中奖名单
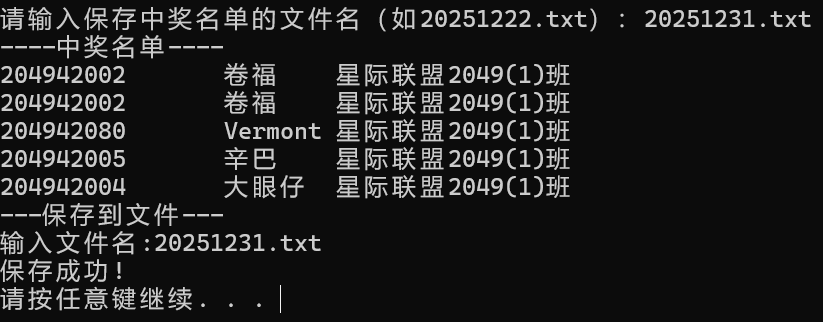
printf("----中奖名单----\n");
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
printf("%s\n", students[selected[i]]);
}
// 写入文件
FILE *fp = fopen(saveFile, "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("fail to open file for writing\n");
exit(1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
fprintf(fp, "%s\n", students[selected[i]]);
}
fclose(fp);
printf("---保存到文件---\n");
printf("输入文件名:%s\n", saveFile);
printf("保存成功!\n");
}
int main() {
char students[STUDENT_NUM][INFO_LEN];
int selected[5];
char saveFile[50];
readStudents(students, "list.txt");
randomSelect(selected, STUDENT_NUM, 5);
printf("请输入保存中奖名单的文件名(如20251222.txt):");
scanf("%s", saveFile);
showAndSave(students, selected, 5, saveFile);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号