『笔记』M^2Det
『笔记』M^2Det
2022年上半年同样一篇LSS流派做纯视觉的multi-view images的三维目标检测。在这里做一个简单记录
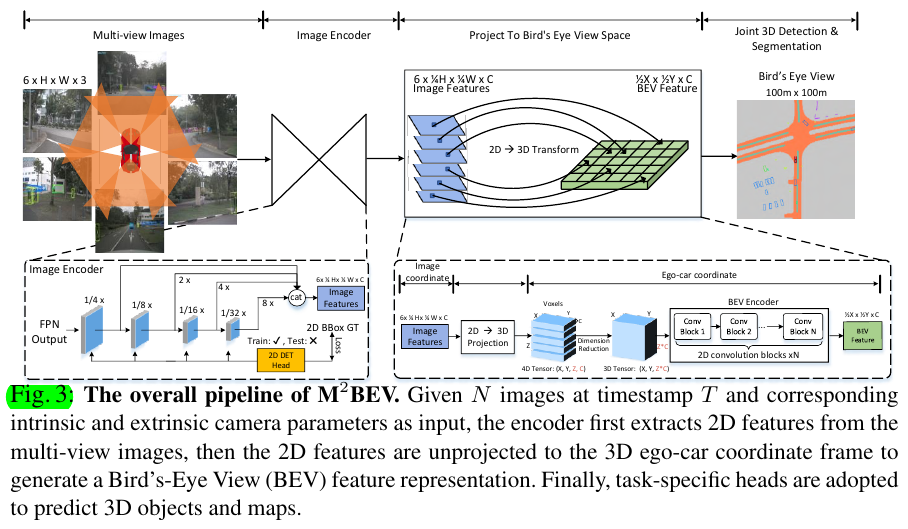
3 Method
3.1 M^2BEV Pipeline
Part1: 2D Image Encoder.
Part2: 2D→3D Projection.
Part3: 3D BEV Encoder.
Part4: 3D Detection Head.
Part5: BEV Segmentation Head.
3.2 Efficient 2D→3D Projection
Our Approach. Here, we assume the depth distribution along the ray is uniform, which means that all voxels along a camera ray are filled with the same features corresponding to a single pixel in P in 2D space. This uniform assumption increases the computational and memory efficiency by reducing the number of learned parameters
Comparison with LSS. The most related work to M2 BEV is LSS [27], which implicitly predicts a non-uniform depth distribution and lifts 2D features from H × W to H × W × D, typically with D ≥ 50, where D is the size of the categorical depth distribution. This step is very memory-expensive, prohibiting LSS from using a larger network or high-resolution images as input; We evaluate LSS and find the GPU memory of LSS is 3× higher than ours. Moreover, the image size of popular AV datasets, e.g. nuScenes, is 1600 × 900, and advanced monocular 3D detectors typically use ResNet- 101 as a backbone. However, LSS only uses a small backbone (EfficientNet-B0) and the input image size is only 128 × 384. In contrast, we do not implicitly estimate the depth when lifting 2D features to 3D as in LSS. As a result, our projection is more efficient and does not need learned parameters, which allows us to use a larger backbone (ResNet- 101) and higher resolution input (1600 × 900)
3.3 Improvement Designs
Efficient BEV Encoder. Spatial to Channel (S2C). It is impossible to build a heavy BEV encoder with 3D convolutions. However, S2C allows us to easily use and stack more 2D convolutions. (3D vs. S2C + 2D)
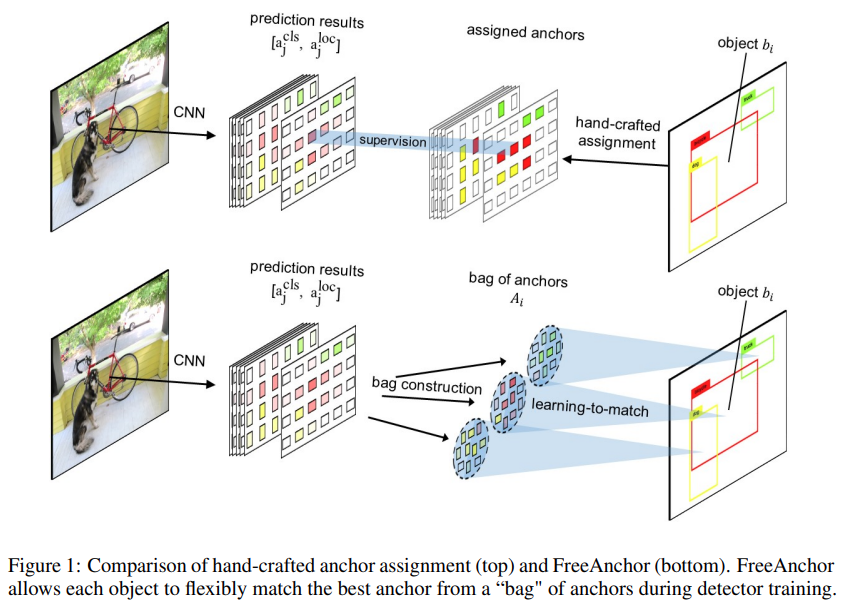
Dynamic Box Assignment. Many LiDAR-based works such as PointPillars [1] assign 3D anchors for ground-truth boxes using a fixed intersection-over-union (IoU) thresh- old. However, we argue that this hand-crafted assignment is suboptimal for our problem because our BEV feature does not consider the depth in LiDAR, thus the BEV representation may encode less-accurate geometric information. Insipred by FreeAnchor [30] that use learning-to-match assignment in 2D detection, we extend this assignment to 3D detection. The main difference is that we assigns 3D anchors in the BEV coordinate.
During training, we first predict the class \(a_j^{cls}\) and the location \(a_j^{loc}\) for each anchor \(aj ∈ A\) and select a bag of anchors for each ground-truth box based on IoU. We use a weighted sum of classification score and localization accuracy to distinguish the positive anchors; the intuition behind this practice is that, an ideal positive anchor should have high confidence in both classification and localization. The rest of the anchors with low classification scores or large localization errors are set as negative samples. Kindly refer to [30] for more details.
即采用了FreeAnchor文章中的target assignment方法。原文章的motivation在于经典的anchor匹配方法是根据IoU,很硬地匹配到给了grid每个位置上的anchors们,但是对于细长物体或者月牙形物体,包含了很多background内容,直接根据iou显然不合适。所以方法大概是,依然是用iou为每个gt分配到一小部分bag of anchors,然后它们再通过网络预测的形式得到cls和loc,把这两个预测和gt的比对loss给weight到一个式子中,目的是说一个好的anchor应该是cls和loc都很不错才对。我没有去看原文章,仅是通过这里的描述和其它只言片语进行了初步理解,以后如果有时间可以看。下图来自FreeAnchor
BEV Centerness. We extend the concept of “centerness” in a non-trivial distance-aware manner. The motivation is that area in BEV space farther away from the ego car correspond to fewer pixels in the images. So an intuitive idea is make the network pay more attention on the farther area. Errors in predictions for samples far away from the center are punished more.
即,说是叫什么centerness,其实不过就是给远处物体的检测loss加了更大weight
2D Detection Pre-training. We empirically found that pre-training the model on large- scale 2D detection dataset, e.g. nuImage dataset, could significantly improve the 3D accuracy. We pre-train a Cascade Mask R-CNN [32] on nuImage for 20 epoches.
2D Auxiliary Supervision. We add a 2D detection head on the features at different scales and calculating the losses with 2D GT bboxes. The 2D detection head is implemented in the same way as proposed in FCOS. 2D GT boxes are generated from 3D annotations. The 3D GT boxes from the ego-car coordinates are back-projected to the 2D image space. By using 2D detection as pre-training and auxiliary supervision, the image features are more aware of objects thus boosting up 3D accuracy.
个人总结:依然是LSS流派做bev检测的方法。主要的点在于,LSS部分我直接不做depth prediction了,之前是把每个ray的feature和每个预测的depth加权得到的feature赋给每个位置,现在直接把feature部分等同地直接作为了depth上各点的feature,节省资源和速度,于是可能用更大的backbone和image resolution. 另外,其它设计了一些小tricks,包括:S2C,FreeAnchor,不同距离不同loss weights,用nuImages对2d backbone预训练,增加2d objection作为auxiliary task


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号