『论文』Deformable DETR
Deformable DETR
Deformable Detr: Deformable Transformers For End-To-End Object Detection
3 Revisiting Transformers And Detr
Multi-head attention module:
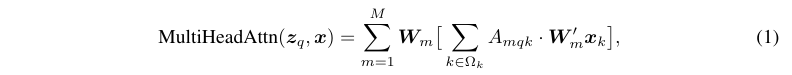
There are two known issues with Transformers.
- One is Transformers need long training schedules before convergence. 初始化时会依据0 mean和 1 variance的distribution,于是attention weights \(A_{mqk}\)基本等于\(\frac{1}{N_k}\),大家都一样,都很小。It will lead to ambiguous gradients for input features. Thus, long training schedules are required so that the attention weights can focus on specific keys.
- The computational and memory complexity for multi-head attention can be very high with numerous query and key elements. The multi-head attention module suffers from a quadratic complexity growth with the feature map size
DETR: built upon the Transformer encoder-decoder architecture, combined with a set-based Hungarian loss that forces unique predictions for each ground-truth bounding box via bipartite matching.
It also has its own issues.
- DETR has relatively low performance in detecting small objects. Modern object detectors use high-resolution feature maps to better detect small objects. However, high-resolution feature maps would lead to an unacceptable complexity for the self-attention module in the Transformer encoder of DETR
- DETR requires many more training epochs to converge.
4 Method
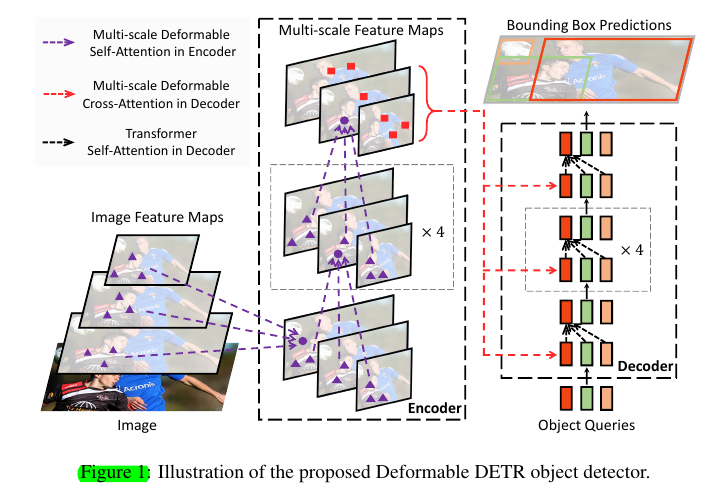
4.1 Deformable Transformers For End-To-End Object Detection
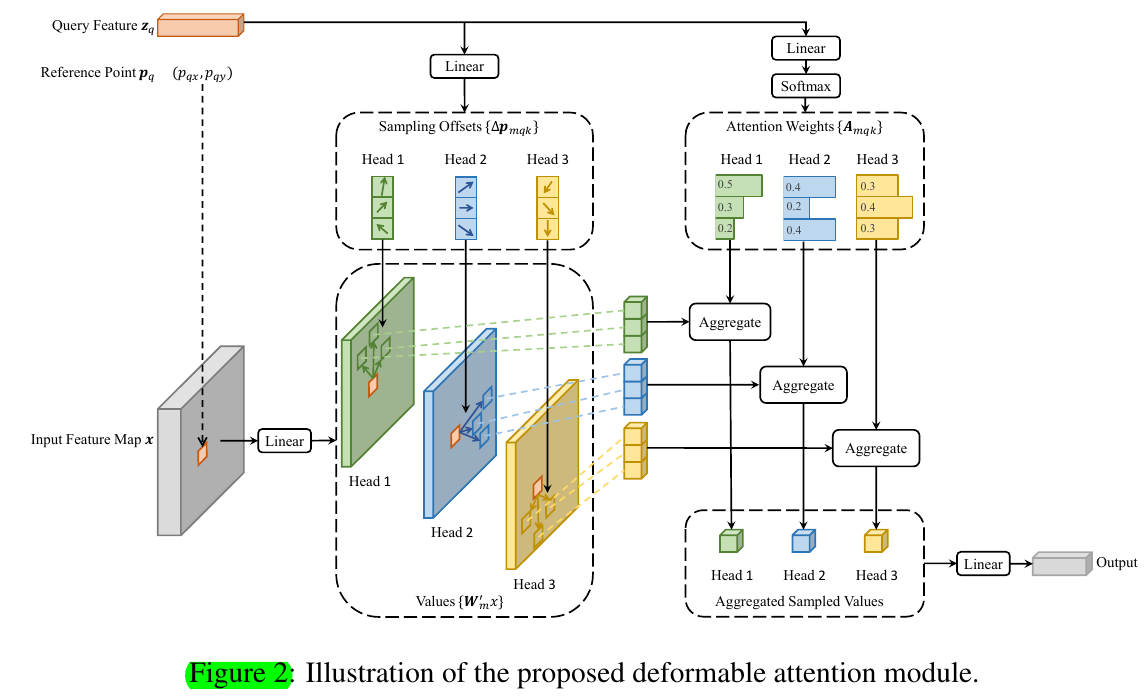
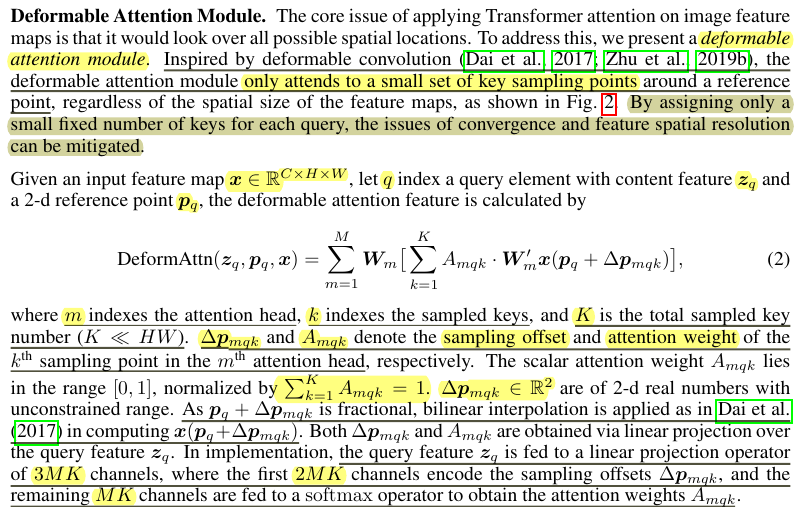
Deformable Attention Module.
Multi-scale Deformable Attention Module.
- Our proposed deformable attention module can be naturally extended for multi-scale feature maps.
Deformable Transformer Encoder.
- Both the input and output of the encoder are of multi-scale feature maps with the same resolutions.
- For each query pixel, the reference point is itself. To identify which feature level each query pixel lies in, we add a scale-level embedding, to the feature representation
Deformable Transformer Decoder.
- For each object query, the 2-d normalized coordinate of the reference point p̂_q is predicted from its object query embedding via a learnable linear projection followed by a sigmoid function.
4.2 Additional Improvements And Variants For Deformable Detr
Iterative Bounding Box Refinement.
- Here, each decoder layer refines the bounding boxes based on the predictions from the previous layer.
Two-Stage Deformable DETR. - We explore a variant of Deformable DETR for generating region proposals as the first stage. The generated region proposals will be fed into the decoder as object queries for further refinement
其他
Deformable DETR借鉴了DCN的思想,提出可变形注意力机制——每个特征像素不必与所有特征像素交互计算,只需要与部分基于采样获得的其它像素交互,并且这些采样点的位置是可学习的。这是一种局部(local)和稀疏(sparse)的高效注意力机制,能够解决DETR收敛慢与能够处理的特征分辨率受限的问题。与DETR详细对比的话,主要有以下不同:
1. 多尺度特征;
2. 新增scale-level embedding,用于区分不同特征层(由于第1点);
3. 使用了多尺度可变形注意力替代Encoder中的自注意力和Decoder中的交叉注意力;
4. 引入了参考点,某种程度上起到先验的作用;
5. 为自己开发了“高配”版:迭代的框校正策略 和 两阶段模式;
6. 检测头部的回归分支预测的是bbox偏移量而非绝对坐标值


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号