树的直径
证明
求树的直径的方法:
- 选择树上任意一点,从该点dfs,求其它所有点到x的距离distx[]
- 从distx[]中选择一个最大的距离所对应的点y,从y开始再次dfs求一个disty[]
- disty[]中的最大值就是树的直径
求树的直径的bfs/dfs方法的正确性证明:
问题就在第一点:距离x最远的y点在树的直径上。
现在证明这个结论
反正法:
假设y不在直径上,那么有以下情况:
- 树的直径和\(x -> y\)的路径存在交点。
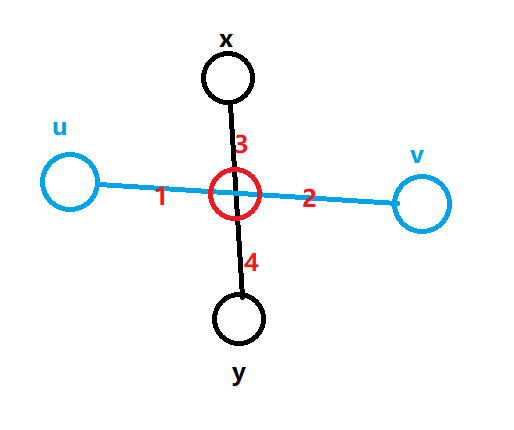
此时\(u -> v\)为树的直径
而\(dist(x, y) \ge dist(x, u)\)它们存在公共部分\(3\), 所以有\(1 \le 4\)
从而\(1 + 2 \le 4 + 2\), 所以有\(dist(u, v) \le dist(y, v)\)
那么\(dist(y, v)\)就成了直径,\(y\)成了直径的端点,与假设矛盾。
- 树的直径和\(x -> y\)的路径不存在交点。
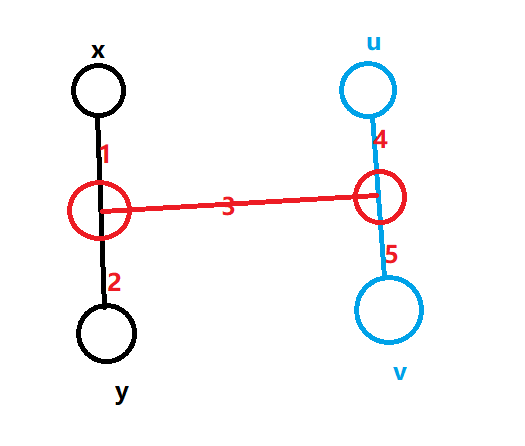
此时\(u -> v\)
为树的直径
因为\(dist(x, y) \ge dist(x, v)\)
所以有\(1 + 3 + 5 \le 1 + 2\)
\(\to 3 + 5 \le 2\)
\(\to 2 + 3 \ge 5\)
\(\to 2 + 3 + 4 \ge 5 + 4\)
\(\to dist(y, u) \ge dist(u, v)\)
所以\(dist(y, u)\)为树的直径,所以\(y\)为树的直径上的端点,与假设矛盾。
综上,结论“距离x最远的y点在树的直径上”结论获证。
代码
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 100010, M = 200010;
int h[N], e[M], ne[M], w[M], idx;
int n;
int dist[N], st[N];
int add(int a, int b, int c){
e[idx] = b, ne[idx] = h[a], w[idx] = c, h[a] = idx ++;
}
void dfs(int u){
for(int i = h[u]; ~i; i = ne[i]){
int j = e[i];
if(st[j]) continue;
st[j] = 1;
dist[j] = dist[u] + w[i];
dfs(j);
}
}
int main(){
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i ++){
int a, b, c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
add(a, b, c);
add(b, a, c);
}
st[1] = 1;
dfs(1);
int k = 1;
for(int i = 2, maxv = dist[1]; i <= n; i ++)
if(maxv < dist[i]){
maxv = dist[i];
k = i;
}
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
st[k] = 1;
dist[k] = 0;
dfs(k);
int res = dist[1];
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i ++)
res = max(res, dist[i]);
cout << res << endl;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号