写一个简单的框架
一、问题:
能不能写一个通用的查询框架,也就是我只写sql语句,什么加载驱动,创建连接,查询,封装......之类的全都封装到一起,然后我们可以打个jar包,以后无论查什么都可以通用, 好,下面开始干~
二、框架结构
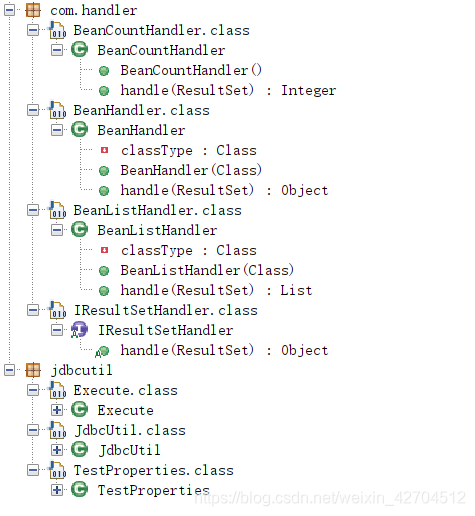
三、开始代码
1. 首先创建jdbcutil.JdbcUtil类,这个类主要是为了加载驱动,获取连接,返回连接,以及关闭连接。
package jdbcutil; import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSourceFactory; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.Properties; import javax.sql.DataSource; public class JdbcUtil { static DataSource ds = null; static { Properties p = new Properties(); InputStream in = null; ds = null; try { in = JdbcUtil.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties"); p.load(in); ds = DruidDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(p); } catch (Exception e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } } public static Connection getConn() { try { return ds.getConnection(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); return null; } } public static void close(ResultSet rset, PreparedStatement pstmt, Connection conn) { try { if (rset != null) rset.close(); if (pstmt != null) pstmt.close(); if (conn != null) conn.close(); } catch (SQLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2. 执行实际的sql语句类jdbcutil.Execute

package jdbcutil; import com.handler.IResultSetHandler; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; public class Execute { public int executeUpdata(String sql, Object... params) { Connection conn = JdbcUtil.getConn(); PreparedStatement pstmt = null; try { pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) pstmt.setObject(i + 1, params[i]); return pstmt.executeUpdate(); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtil.close(null, pstmt, conn); } return 0; } public <T> T executeQuery(String sql, IResultSetHandler<T> rh, Object... params) { Connection conn = JdbcUtil.getConn(); PreparedStatement pstmt = null; ResultSet rs = null; try { pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql); for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) pstmt.setObject(i + 1, params[i]); rs = pstmt.executeQuery(); return (T)rh.handle(rs); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { JdbcUtil.close(rs, pstmt, conn); } return null; } }
3. handler 主要是对数据的查询和封装 com.handler.BeanCountHandler
package com.handler; import java.sql.ResultSet; public class BeanCountHandler implements IResultSetHandler<Integer> { public Integer handle(ResultSet rs) throws Exception { if (rs.next()) return Integer.valueOf(rs.getInt(1)); return null; } }
4.com.handler.BeanHandler
package com.handler; import java.beans.BeanInfo; import java.beans.Introspector; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.sql.ResultSet; public class BeanHandler<T> implements IResultSetHandler<T> { private Class<T> classType; public BeanHandler(Class<T> classType) { this.classType = classType; } public T handle(ResultSet rs) throws Exception { if (rs.next()) { T obj = this.classType.newInstance(); BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(this.classType, Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] pds = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); byte b; int i; PropertyDescriptor[] arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1; for (i = (arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1 = pds).length, b = 0; b < i; ) { PropertyDescriptor pd = arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1[b]; Object val = rs.getObject(pd.getName()); pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(obj, new Object[] { val }); b++; } return obj; } return null; } }
5. com.handler.BeanListHandler
package com.handler; import java.beans.BeanInfo; import java.beans.Introspector; import java.beans.PropertyDescriptor; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class BeanListHandler<T> implements IResultSetHandler<List<T>> { private Class<T> classType; public BeanListHandler(Class<T> classType) { this.classType = classType; } public List<T> handle(ResultSet rs) throws Exception { List<T> list = new ArrayList<T>(); while (rs.next()) { T obj = this.classType.newInstance(); BeanInfo beanInfo = Introspector.getBeanInfo(this.classType, Object.class); PropertyDescriptor[] pds = beanInfo.getPropertyDescriptors(); byte b; int i; PropertyDescriptor[] arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1; for (i = (arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1 = pds).length, b = 0; b < i; ) { PropertyDescriptor pd = arrayOfPropertyDescriptor1[b]; Object val = rs.getObject(pd.getName()); pd.getWriteMethod().invoke(obj, new Object[] { val }); b++; } list.add(obj); } return list; } }
6.com.handler.IResultSetHandler
package com.handler; import java.sql.ResultSet; public interface IResultSetHandler<T> { T handle(ResultSet paramResultSet) throws Exception; }
至此已经完成,打个jar包 和jdbc jar包一起导入就可以用了
四、 jdbcUtil使用
1. 导入jar包,不想敲代码的同学,这里放上连接。
链接:[https://share.weiyun.com/sWGwc44z]密码:999999 导入后需要在你的项目里创建resource 文件夹以及里面的 db.properties
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc\:mysql\://localhost\:3306/test username=root password=root
1. 首先需要继承Execute类 或者创建Execute对象也行
2. 然后写自己的方法
/*
Execute类中有两个方法
1.executeQuery(); 执行查询操作
2.executeUpdata(); 执行修改操作
而里面的参数是可变的 具体根据自己的情况传参
3. 若执行查询操作 需要把接获及处理器传进去
结果集处理器有三种
- new BeanListHandler<泛型>(类的反射) 例如:new BeanListHandler(Address.class);
- new BeanBeanHandler 例如:new BeanHandler(Address.class)
- new BeanCountHandler() 这个是当执行统计总数时用的处理器 返回值为int类型
*/public 返回结果类型 方法名(参数类型) { String sql = "这里写要执行的sql语句"; return executeQuery(sql, 结果集处理器, 这里是sql语句里?对应的值); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号