Spring注解驱动开发--属性值的自动装配
前言
Spring的自动装配指的是Spring利用依赖注入(DI),完成对IOC容器中各个组件的依赖关系赋值。很基础的东西,希望对大家能有帮助。
自动装配自定义组件
1.使用@Autowried自动注入
1)、默认优先按照类型去容器中找对应的组件:applicationContext.getBean(BookDao.class);找到就赋值
2)、如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性的名称作为组件的id去容器中查找
applicationContext.getBean("bookDao")
3)、@Qualifier("bookDao"):使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的组件的id,而不是使用属性名
4)、自动装配默认一定要将属性赋值好,没有就会报错;可以使用@Autowired(required=false);
5)、@Primary:让Spring进行自动装配的时候,默认使用首选的bean;也可以继续使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的bean的名字
6)、 @Autowired:构造器,参数,方法,属性;都是从容器中获取参数组件的值
①[标注在方法位置]:@Bean+方法参数;参数从容器中获取;默认不写@Autowired效果是一样的;都能自动装配
②[标在构造器上]:如果组件只有一个有参构造器,这个有参构造器的@Autowired可以省略,参数位置的组件还是可以自动从容器中获取
③放在参数位置:
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface Autowired { /** * Declares whether the annotated dependency is required. * <p>Defaults to {@code true}. */ boolean required() default true; }
2.Spring还支持使用@Resource(JSR250)和@Inject(JSR330)[java规范的注解]
@Resource:
可以和@Autowired一样实现自动装配功能;默认是按照组件名称进行装配的;
没有能支持@Primary功能没有支持@Autowired(reqiured=false);
@Inject:
需要导入javax.inject的包,和Autowired的功能一样。没有required=false的功能;
@Autowired:Spring定义的; @Resource、@Inject都是java规范
自定义bean
public class BookService { //@Qualifier("bookDao") //@Autowired(required=false) //@Resource(name="bookDao2") @Inject private BookDao bookDao; public void print(){ System.out.println(bookDao); } @Override public String toString() { return "BookService [bookDao=" + bookDao + "]"; } } @Repository public class BookDao { private String lable = "1"; public String getLable() { return lable; } public void setLable(String lable) { this.lable = lable; } @Override public String toString() { return "BookDao [lable=" + lable + "]"; } }
@Controller public class BookController { @Autowired private BookService bookService; }
@Repository public class BookDao { private String lable = "1"; public String getLable() { return lable; } public void setLable(String lable) { this.lable = lable; } @Override public String toString() { return "BookDao [lable=" + lable + "]"; } }
配置中心
@Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.atguigu.service","com.atguigu.dao", "com.atguigu.controller","com.atguigu.bean"}) public class MainConifgOfAutowired { @Primary @Bean("bookDao2") public BookDao bookDao(){ BookDao bookDao = new BookDao(); bookDao.setLable("2"); return bookDao; } /** * @Bean标注的方法创建对象的时候,方法参数的值从容器中获取 * @param car * @return */ @Bean public Color color(Car car){ Color color = new Color(); color.setCar(car); return color; } }
测试类
public class IOCTestAutowired { @Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConifgOfAutowired.class); BookService bookService = applicationContext.getBean(BookService.class); System.out.println(bookService); //BookDao bean = applicationContext.getBean(BookDao.class); //System.out.println(bean); Boss boss = applicationContext.getBean(Boss.class); System.out.println(boss); Car car = applicationContext.getBean(Car.class); System.out.println(car); Color color = applicationContext.getBean(Color.class); System.out.println(color); System.out.println(applicationContext); applicationContext.close(); } }
自动装配Spring底层组件
上面讲解了如何注入自定义组件,在开发中,自定义组件中有时需要注入Spring底层组件:可以使用以上方式注入spring底层组件,下面我们看看另一种方式
自定义组件实现xxxAware(ApplicationContext,BeanFactory,xxx)接口在创建对象的时候,会调用接口规定的方法注入相关组件,把Spring底层一些组件注入到自定义的Bean中。
每一个xxxAware:都有对应的xxxProcessor后置处理器来完成属性的注入
ApplicationContextAware==》ApplicationContextAwareProcessor;
@Component public class Red implements ApplicationContextAware,BeanNameAware,EmbeddedValueResolverAware { private ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("传入的ioc:"+applicationContext); this.applicationContext = applicationContext; } @Override public void setBeanName(String name) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub System.out.println("当前bean的名字:"+name); } @Override public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) { // spring中string的表达式的解析都是通过StringValueResolver 来完成的 String resolveStringValue = resolver.resolveStringValue("你好 ${os.name} 我是 #{20*18}"); System.out.println("解析的字符串:"+resolveStringValue); } }
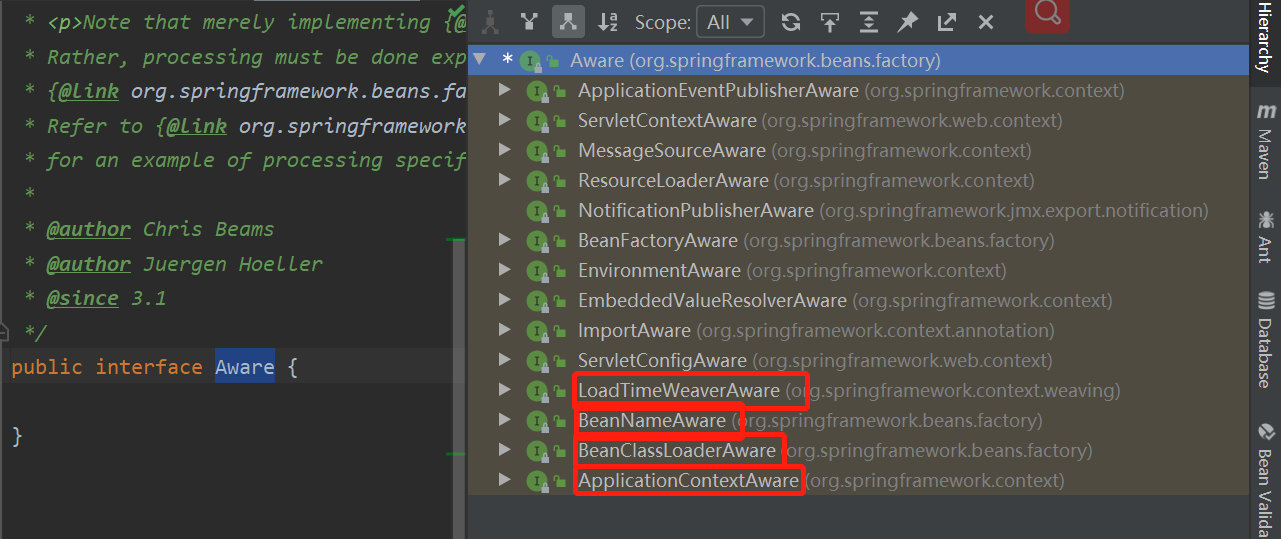
Aware的实现接口
Profile注解
Spring为我们提供的可以根据当前环境,动态的激活和切换一系列组件的功能
比如不同的环境中连接的数据源不同
开发环境、测试环境、生产环境根据配置获取自己的数据源
@Profile:指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,不指定,任何环境下都能注册这个组件
1)、加了环境标识的bean,只有这个环境被激活的时候才能注册到容器中。默认是default环境
2)、写在配置类上,只有是指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能开始生效
3)、没有标注环境标识的bean在,任何环境下都是加载的;
dbconfig.properties文件
db.user=root db.password=123456 db.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
配置文件
@PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfProfile implements EmbeddedValueResolverAware{
@Value("${db.user}")
private String user;
private StringValueResolver valueResolver;
private String driverClass;
@Bean
public Yellow yellow(){
return new Yellow();
}
@Profile("test")
@Bean("testDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceTest(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean("devDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceDev(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_crud");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("prod")
@Bean("prodDataSource")
public DataSource dataSourceProd(@Value("${db.password}")String pwd) throws Exception{
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(pwd);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/scw_0515");
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Override
public void setEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver resolver) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
this.valueResolver = resolver;
driverClass = valueResolver.resolveStringValue("${db.driverClass}");
}
}
激活Profile的方式
①使用代码的方式
在使用代码的方式激活环境之前,先看看spring的构造
public class AnnotationConfigApplicationContext extends GenericApplicationContext implements AnnotationConfigRegistry { private final AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader reader; private final ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner; public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() { this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); } public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) { super(beanFactory); this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this); this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this); }
//一个构造,将所有的一切包含在其中,体会这种设计 public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class<?>... componentClasses) { this(); this.register(componentClasses); this.refresh(); } public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(String... basePackages) { this(); this.scan(basePackages); this.refresh(); } public void setEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { super.setEnvironment(environment); this.reader.setEnvironment(environment); this.scanner.setEnvironment(environment); } public void setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator) { this.reader.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); this.scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(beanNameGenerator); this.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationBeanNameGenerator", beanNameGenerator); } public void setScopeMetadataResolver(ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver) { this.reader.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); this.scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(scopeMetadataResolver); } public void register(Class<?>... componentClasses) { Assert.notEmpty(componentClasses, "At least one component class must be specified"); this.reader.register(componentClasses); } public void scan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); this.scanner.scan(basePackages); } public <T> void registerBean(@Nullable String beanName, Class<T> beanClass, @Nullable Supplier<T> supplier, BeanDefinitionCustomizer... customizers) { this.reader.registerBean(beanClass, beanName, supplier, customizers); } }
代码的方式激活
@Test public void test01(){ AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(); //1、创建一个applicationContext //2、设置需要激活的环境 applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("dev"); //3、注册主配置类 applicationContext.register(MainConfigOfProfile.class); //4、启动刷新容器(再此之前,激活相应的环境,而有参的构造直接刷新了整个容器) applicationContext.refresh(); String[] namesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class); for (String string : namesForType) { System.out.println(string); } applicationContext.close(); }
②指定运行时参数
使用命令行动态参数: 在虚拟机参数位置加载 -Dspring.profiles.active=test



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号