static关键字
static关键字
静态属性
若类中有静态变量,可直接使用类名访问:
public class Student {
private static int age;//静态变量
private double score;//非静态变量
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(Student.age);//直接使用类名访问静态变量age
//System.out.println(Student.score);//会报错
System.out.println(s1.age);
System.out.println(s1.score);
}
}
静态变量对于这个类而言,在内存中只有一个,能被当前类所有实例共享
(例如一个类创建了多个不同的对象,每个对象会被分配不同的内存空间,但所有对象中的类变量只会被分配到一个相同的内存空间,即能被所有对象共享)
静态方法
非静态方法可以直接访问当前类中的静态方法
静态方法可以调用静态方法但不能调用非静态方法
public class Student {
private static int age;//静态变量
private double score;//非静态变量
public void run(){
}
public static void go(){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
go();
Student.go();
//run();//报错
//调用方式
Student student = new Student();
student.run();
}
}
静态代码块
public class Person {
{
//匿名代码块(一般不建议)
}
static{
//静态代码块(加载一些初始化的数据)
}
}
public class Person {
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
static{
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
public Person(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
}
}
输出结果:
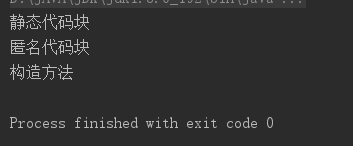
-
匿名代码块:
创建对象时自动创建,在构造器之前
可以用于赋初始值
-
静态代码块:
类一加载就执行,永久只执行一次
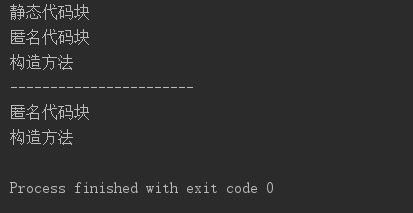
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person = new Person();
System.out.println("-----------------------");
Person person1 = new Person();
}
输出结果:
静态导入包
平时:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Math.random());
}
}
采用静态导入包:
//静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.random;
import static java.lang.Math.PI;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(random());//可直接使用方法
System.out.println(PI);
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号