最小生成树
最小生成树
题目描述
如题,给出一个无向图,求出最小生成树,如果该图不连通,则输出 orz。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数 \(N,M\),表示该图共有 \(N\) 个结点和 \(M\) 条无向边。
接下来 \(M\) 行每行包含三个整数 \(X_i,Y_i,Z_i\),表示有一条长度为 \(Z_i\) 的无向边连接结点 \(X_i,Y_i\)。
输出格式
如果该图连通,则输出一个整数表示最小生成树的各边的长度之和。如果该图不连通则输出 orz。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4 5
1 2 2
1 3 2
1 4 3
2 3 4
3 4 3
样例输出 #1
7
提示
数据规模:
对于 \(20\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 5\),\(M\le 20\)。
对于 \(40\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 50\),\(M\le 2500\)。
对于 \(70\%\) 的数据,\(N\le 500\),\(M\le 10^4\)。
对于 \(100\%\) 的数据:\(1\le N\le 5000\),\(1\le M\le 2\times 10^5\),\(1\le Z_i \le 10^4\)。
样例解释:
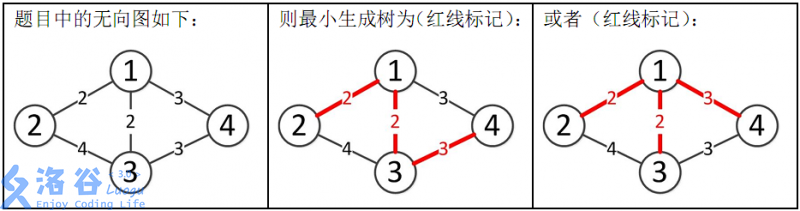
所以最小生成树的总边权为 \(2+2+3=7\)。
朴素Prim
dist[i] = INF
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
1.找到集合外距离最近的点 t
2.用t更新其他点到集合的距离
3.st[t] = true
代码:
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.StreamTokenizer;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
static final int N = 5010, INF = 0x3f3f3f;
static int n, m;
static int[] dist = new int[N];
static boolean[] st = new boolean[N];
static List<int[]>[] g = new List[N];
static StreamTokenizer in = new StreamTokenizer(new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
n = nextInt();
m = nextInt();
int x, y, z;
Arrays.setAll(g, a -> new ArrayList<>());
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
x = nextInt();
y = nextInt();
z = nextInt();
g[x].add(new int[]{y, z});
g[y].add(new int[]{x, z});
}
Arrays.fill(dist, INF);
int res = prim();
if (res == -1) System.out.println("orz");
else System.out.println(res);
}
public static int prim() {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int t = -1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!st[j] && (t == -1 || dist[j] < dist[t])) {
t = j;
}
}
if (i > 0 && dist[t] == INF) return -1;
if (i > 0) res += dist[t];
st[t] = true;
for (int[] nei : g[t]) {
int x = nei[0], w = nei[1];
dist[x] = Math.min(dist[x], w);
}
}
return res;
}
public static int nextInt() throws IOException {
in.nextToken();
return (int) in.nval;
}
}
Kruskal算法
1.所有边按权重从小到大排序 O(mlogm)
2.枚举每条边a,b 权重c
if(a,b不连通)
将这条边加入集合中


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号