Java第二次大作业
OK,这是第二次写Java作业总结,主要分析第4、5、6次大作业以及期中考试的代码并对其进行总结。话不多说直接展示题目及代码。
Java第四次大作业
7-1:菜单计价程序-3
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish\[\] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\\
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record\[\] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
### 输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
### 输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:桌号、菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等,在本系列的后续作业中会做要求。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 12/2/3
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 38
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 17/0/0
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1: 22
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2023/3/22 16/59/59
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
table 1 out of opening hours
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/5 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
5 delete
7 delete
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
7 delete
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
delete error;
table 2:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
table 1 out of opening hours
table 2: 63
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
table 1 2022/12/3 19/5/12
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
table 2 2022/12/3 15/03/02
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
1 4 麻婆豆腐 1 1
7 delete
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist table 2: 1 麻婆豆腐 36 2 油淋生菜 27 麻辣鸡丝 does not exist 4 table 2 pay for table 1 12 delete error; table 1: 63 table 2: 75
给出源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static class Dish {
String name;
int unit_price;
public Dish(String name, int unit_price) {
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
}
public int getPrice(int portion) {
if (portion == 1) {
return unit_price;
} else if (portion == 2) {
return (int) Math.round(unit_price * 1.5);
} else if (portion == 3) {
return unit_price * 2;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
public static class Menu {
Dish[] dishes;
public Menu(Dish[] dishes) {
this.dishes = dishes;
}
public Dish searchDish(String dishName) {
for (Dish dish : dishes) {
if (dish.name.equals(dishName)) {
return dish;
}
}
return null;
}
}
public static class Record {
Dish dish;
int portion;
public Record(Dish dish, int portion) {
this.dish = dish;
this.portion = portion;
}
public int getPrice() {
return dish.getPrice(portion);
}
}
public static class Order {
Record[] records;
public Order() {
this.records = new Record[0];
}
public void addRecord(String dishName, int portion) {
Menu menu = new Menu(new Dish[]{
new Dish("西红柿炒蛋", 15),
new Dish("清炒土豆丝", 12),
new Dish("麻婆豆腐", 12),
new Dish("油淋生菜", 9),
});
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish != null) {
Record record = new Record(dish, portion);
Record[] newRecords = new Record[records.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(records, 0, newRecords, 0, records.length);
newRecords[records.length] = record;
records = newRecords;
} else {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
}
}
public int getTotalPrice() {
int totalPrice = 0;
for (Record record : records) {
totalPrice += record.getPrice();
}
return totalPrice;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Order order = new Order();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
if (line.equals("end")) {
break;
}
String[] parts = line.split(" ");
String dishName = parts[0];
int portion = Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
order.addRecord(dishName, portion);
}
System.out.println(order.getTotalPrice());
}
}
设计与分析:
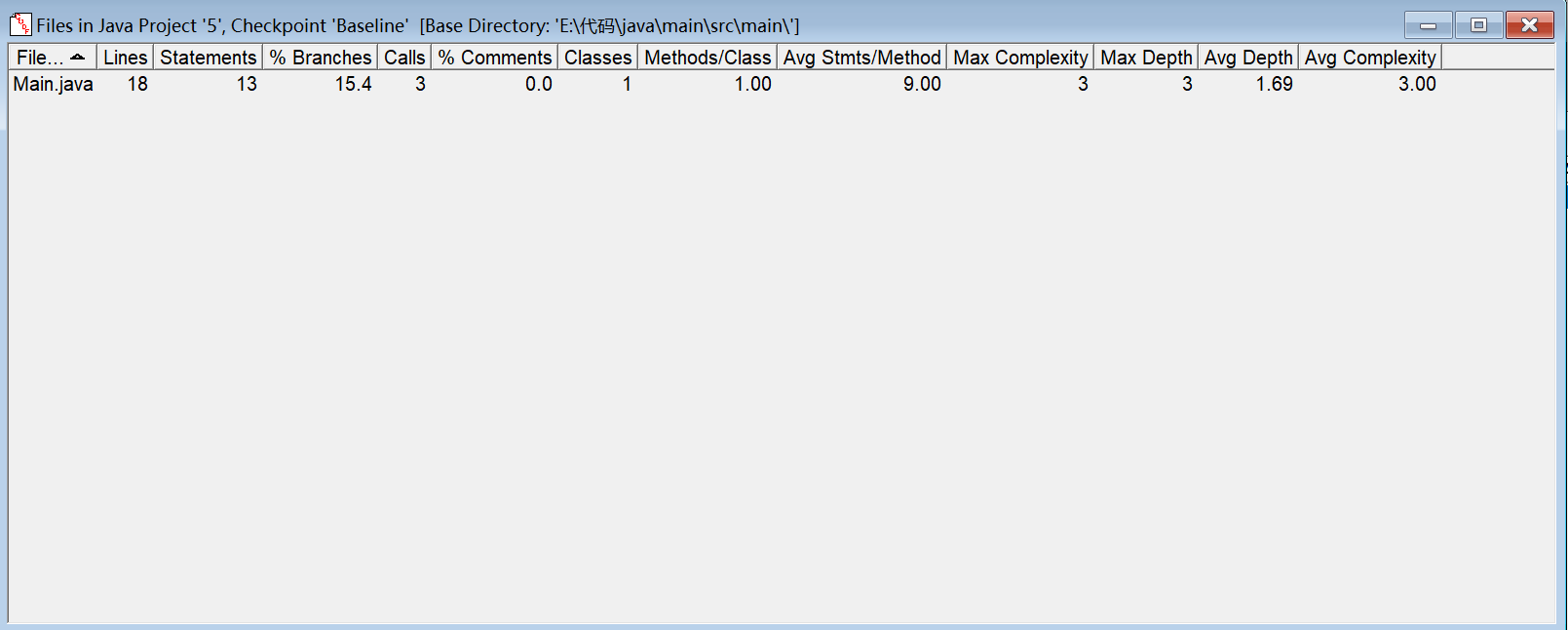
SourceMonitor分析:
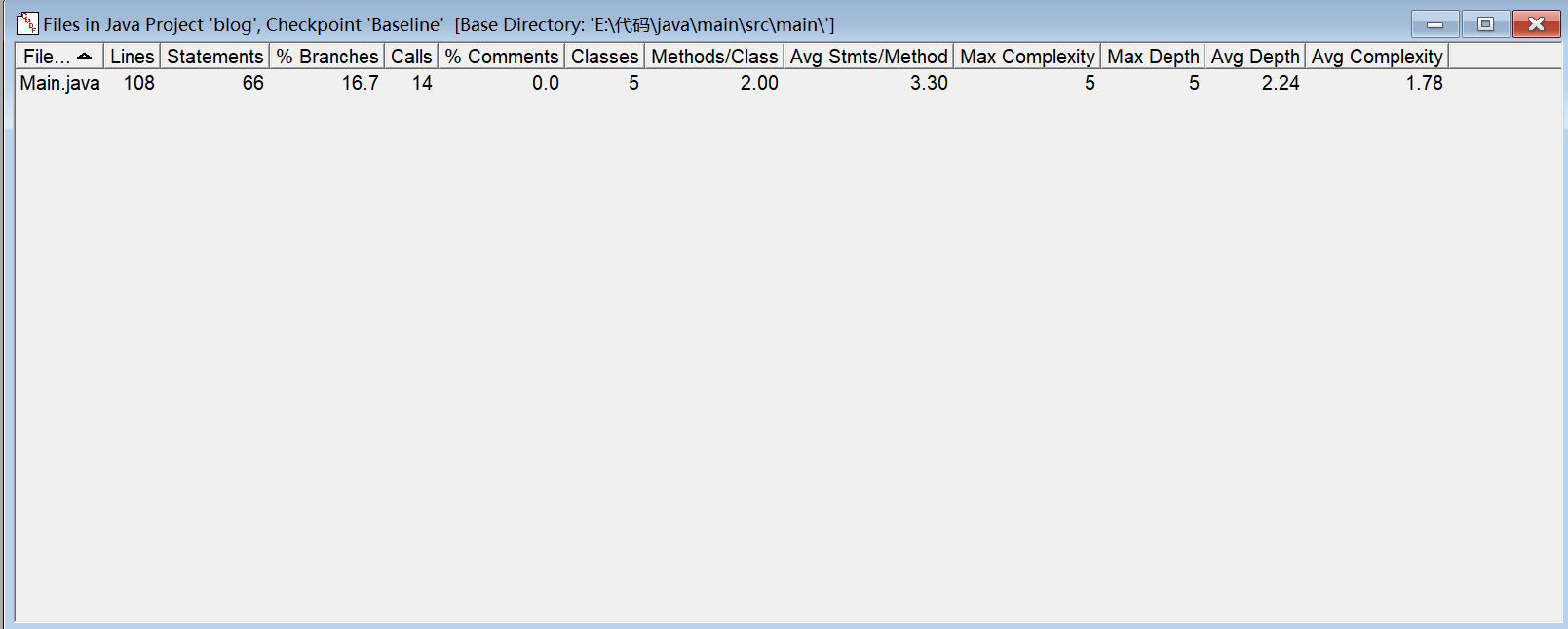
Powerdesigner分析:
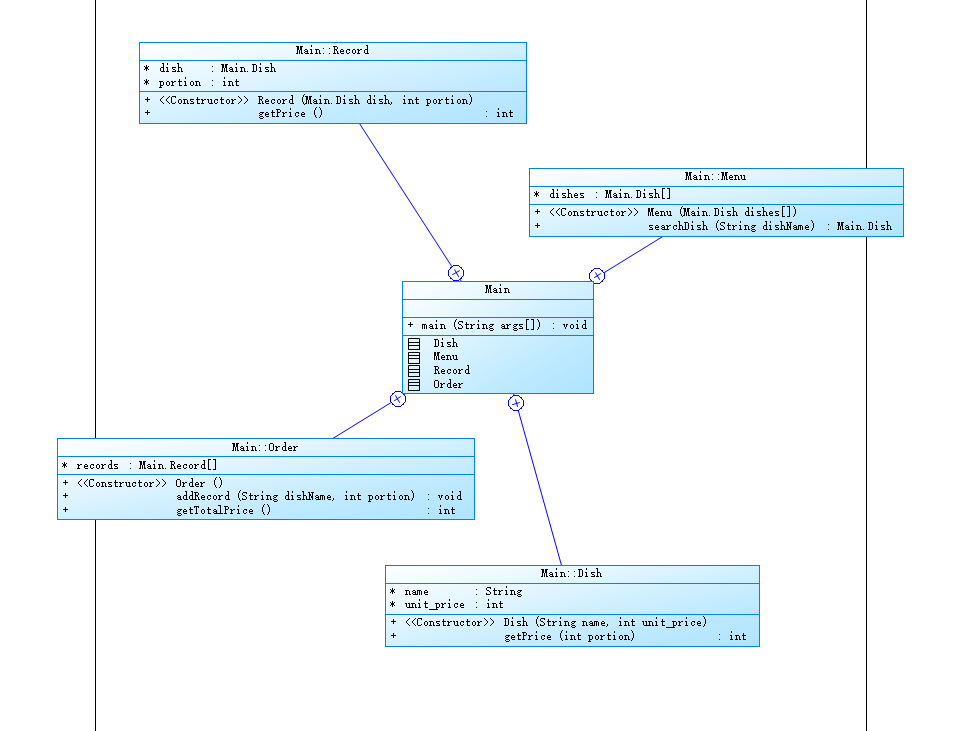
总结分析:
根据题目需求,这里我们可以设计一个点菜计价程序。首先,我们需要建立几个类来表示菜品、菜谱、点菜记录和订单。
菜品类 Dish:表示菜谱上的一道菜品的信息。包含菜名和基础价格,以及计算菜品价格的方法。
菜谱类 Menu:包含饭店提供的所有菜品信息,能够根据菜名查找菜品信息,并能够添加新的菜品信息。
点菜记录类 Record:保存订单上的一道菜品记录,包含序号、菜品、份额和计价方法。
订单类 Order:保存用户点的所有菜的信息,包含订单上每一道的记录,能够计算订单的总价,添加一条菜品信息到订单中,以及根据序号删除一条记录。
接下来是程序的主要逻辑:
读取输入信息并构建菜单和订单。
根据订单内容进行点菜、删除、代点菜等操作。
按照时间和折扣规则计算每一桌的总价,并输出处理信息和总价。
对于输入输出格式的处理,我们可以使用适当的分割和解析方法,将输入内容转换为程序内部的数据结构,然后根据输出规则构造相应的输出结果。
7-2:单词统计与排序
从键盘录入一段英文文本(句子之间的标点符号只包括“,”或“.”,单词之间、单词与标点之间都以" "分割。
要求:按照每个单词的长度由高到低输出各个单词(重复单词只输出一次),如果单词长度相同,则按照单词的首字母顺序(不区分大小写,首字母相同的比较第二个字母,以此类推)升序输出。
输入格式:
一段英文文本。
输出格式:
按照题目要求输出的各个单词(每个单词一行)。
输入样例:
Hello, I am a student from China.
输出样例:
student China Hello from am a I
给出源代码:
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String text = scanner.nextLine();
scanner.close();
StringTokenizer sc = new StringTokenizer(text, ", . ");
List<String> tokens = new ArrayList<>();
while (sc.hasMoreTokens()) {
String s = sc.nextToken();
tokens.add(s);
}
TreeSet<String> wordSet = new TreeSet<>((a, b) -> {
if (a.length() != b.length()) {
return b.length() - a.length();
} else {
return a.compareToIgnoreCase(b);
}
});
Collections.addAll(wordSet, tokens.toArray(new String[0]));
// 按照要求输出单词
for (String word : wordSet) {
System.out.println(word);
}
}
}
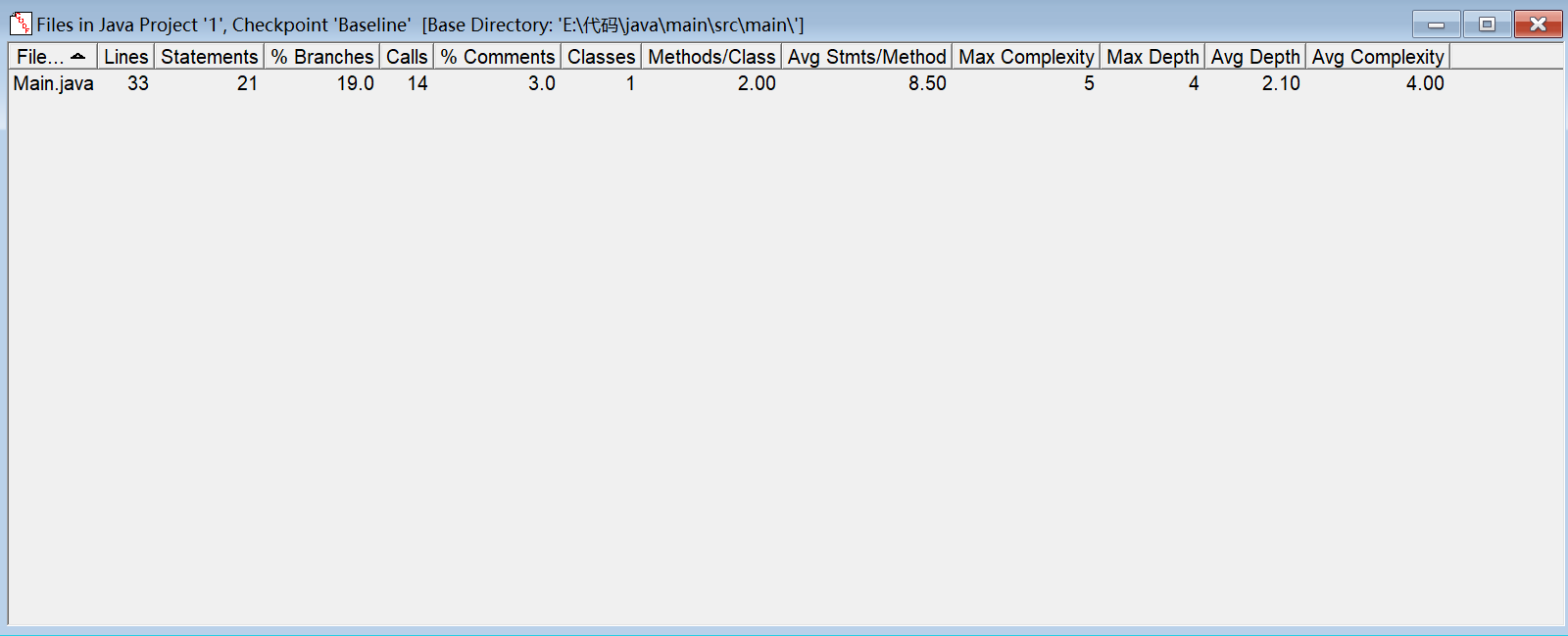
设计与分析:
SourceMonitor分析:
PowerDesigner分析:

代码分析与总结:这道题目较为简单,主要难点在于对输入文本进行分词,这里使用StringTokenizer对输入的文本进行分词,并将分词后的单词存储在tokens列表中。StringTokenizer会根据指定的分隔符(逗号、句号和空格)将文本进行分词。这里创建了一个TreeSet对象wordSet,用于存储单词并实现排序。在创建TreeSet时传入了一个Comparator对象,用于定义排序规则。Comparator中的compare方法定义了先按照单词长度降序排列,长度相同的情况下再按照字典顺序(不区分大小写)排列。再将分词后的单词列表tokens转换成数组,并将数组中的元素添加到wordSet中。最后通过for循环遍历输出。
7-3:判断两个日期的先后,计算间隔天数、周数
从键盘输入两个日期,格式如:2022-06-18。判断两个日期的先后,并输出它们之间间隔的天数、周数(不足一周按0计算)。
预备知识:通过查询Java API文档,了解Scanner类中nextLine()等方法、String类中split()等方法、Integer类中parseInt()等方法的用法,了解LocalDate类中of()、isAfter()、isBefore()、until()等方法的使用规则,了解ChronoUnit类中DAYS、WEEKS、MONTHS等单位的用法。
输入格式:
输入两行,每行输入一个日期,日期格式如:2022-06-18
输出格式:
第一行输出:第一个日期比第二个日期更早(晚)
第二行输出:两个日期间隔XX天
第三行输出:两个日期间隔XX周
输入样例1:
2000-02-18
2000-03-15
输出样例1:
第一个日期比第二个日期更早
两个日期间隔26天
两个日期间隔3周
输入样例2:
2022-6-18
2022-6-1
输出样例2:
第一个日期比第二个日期更晚 两个日期间隔17天 两个日期间隔2周
给出源码:
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
// 定义日期格式
DateTimeFormatter[] dateFormatters = {
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd"),
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-M-d")
};
// 输入第一个日期
String date1String = scanner.nextLine();
// 输入第二个日期
String date2String = scanner.nextLine();
LocalDate date1 = null;
LocalDate date2 = null;
// 尝试使用不同的日期格式进行解析
for (DateTimeFormatter dateFormatter : dateFormatters) {
try {
date1 = LocalDate.parse(date1String, dateFormatter);
date2 = LocalDate.parse(date2String, dateFormatter);
break;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 当前日期格式无法解析,继续下一个尝试
}
}
if (date1 == null || date2 == null) {
System.out.println("日期格式错误");
scanner.close();
return;
}
// 判断两个日期的先后关系
if (date1.isBefore(date2)) {
System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更早");
} else if (date1.isAfter(date2)) {
System.out.println("第一个日期比第二个日期更晚");
} else {
System.out.println("两个日期相等");
}
// 计算日期间隔天数
long days = Math.abs(ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(date1, date2));
System.out.println("两个日期间隔" + days + "天");
// 计算日期间隔周数(不足一周按0计算)
long weeks = Math.abs(ChronoUnit.WEEKS.between(date1, date2));
System.out.print("两个日期间隔" + weeks + "周");
}
}
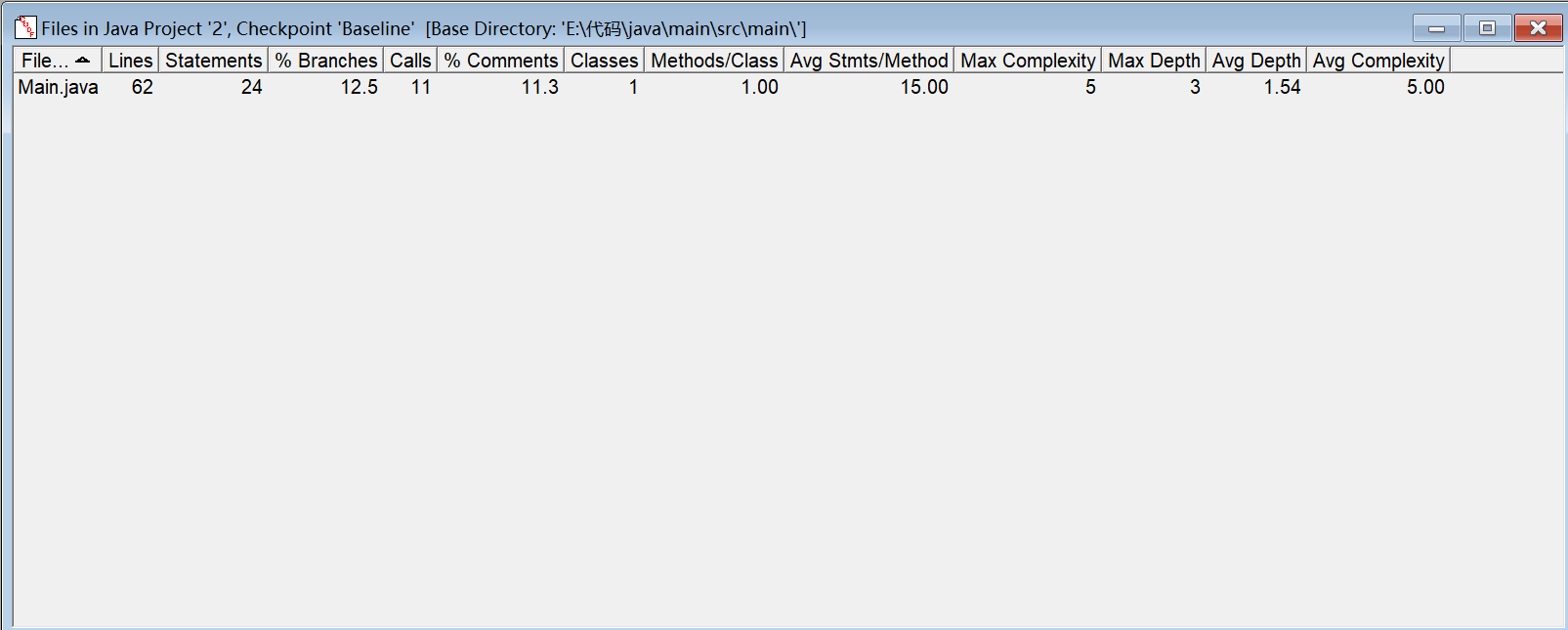
SourceMonitor分析:
PowerDesigner分析:

代码分析与总结:这个没有什么特别好分析的,主要在于应用Java8中的关于日期处理的相关类库,需要注意的是日期输入的格式问题,其他都比较简单。
7-4:菜单计价程序-2
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:点菜记录和删除信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。
份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:
小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。
中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。
小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。
如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
参考以下类的模板进行设计:
菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\
Dish d;//菜品\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
输入格式:
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:
序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数
注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按顺序输出每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。
如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“** does not exist”,**是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后输出订单上所有菜品的总价(整数数值),
本次题目不考虑其他错误情况,如:菜单订单顺序颠倒、不符合格式的输入、序号重复等。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
63
输入样例1:
订单中包含删除记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
1 delete
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
27
输入样例2:
订单中包含不存在的菜品记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
63
输入样例3:
订单中包含删除信息以及不存在的菜品记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
1 delete
7 delete
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
27
输入样例4:
订单中包含删除信息以及不存在的菜品记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9
1 麻婆豆腐 2 2
2 油淋生菜 1 3
3 麻辣鸡丝 1 2
5 delete
7 delete
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1 麻婆豆腐 36
2 油淋生菜 27
麻辣鸡丝 does not exist
delete error;
delete error;
63
给出源代码:
class Dish {
String name;
int unit_price;
public Dish(String name, int unit_price) {
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
}
public int getPrice(int portion) {
double price;
if (portion == 1) {
price = unit_price;
} else if (portion == 2) {
price = unit_price * 1.5;
} else if (portion == 3) {
price = unit_price * 2;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid portion: " + portion);
}
return (int) Math.round(price);
}
}
class Menu {
Dish[] dishes;
int i=0;
public Menu(Dish[] dishes) {
this.dishes = dishes;
}
public Dish searchDish(String dishName) {
for (Dish dish : dishes) {
if (dish != null) {
if (dish.name.equals(dishName)) {
return dish;
}
}
}
return null;
}
public void addmenu(String name,int price)
{
dishes[i] = new Dish(name,price);
i++;
}
}
class Record {
Dish dish;
int portion;
int no;
int number;
public Record(Dish dish, int portion,int number,int no) {
this.dish = dish;
this.portion = portion;
this.number = number;
this.no = no;
}
public int getPrice() {
return number*dish.getPrice(portion);
}
}
class Order {
Record[] records;
int size;
Menu menu;
public Order(int capacity, Dish[] dishes) {
records = new Record[capacity];
size = 0;
menu = new Menu(dishes);
}
public Record searchRecord(int no) {
for (Record record : records) {
if (record != null && no==record.no) {
return record;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addARecord(String dishName, int portion,int number,int no,Dish[] dishes) {
Menu menu = new Menu(dishes);
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish != null) {
Record record = new Record(dish, portion,number,no);
records[size] = record;
size++;
} else {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
}
}
public void delARecord(int no) {
Record record = searchRecord(no);
if (record != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (records[i] != null && records[i].no == no) {
for (int j = i; j < size - 1; j++) {
records[j] = records[j + 1];
}
records[size - 1] = null; // 将数组最后一个位置置为 null,避免产生错误
size--;
break;
}
}
} else {
System.out.println("delete error;");
}
}
public int getTotalPrice() {
int totalPrice = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
totalPrice += records[i].getPrice();
}
return totalPrice;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dish[] dishes = new Dish[10];
Order order = new Order(15, dishes);
java.util.Scanner scanner = new java.util.Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
String input = scanner.nextLine().trim();
if (input.equalsIgnoreCase("end")) {
break;
}
String[] parts = input.split(" ");
if(parts.length == 2&&(!parts[1].equalsIgnoreCase("delete")))
{
String name = parts[0];
int price =Integer.parseInt(parts[1]);
if(order.menu.searchDish(name)!=null)
order.menu.searchDish(name).unit_price = price;
else order.menu.addmenu(name,price);
}
if(parts.length == 4) {
int no = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]); String dishName = parts[1];
int portion = Integer.parseInt(parts[2]);
int number = Integer.parseInt(parts[3]);
order.addARecord(dishName, portion,number,no, order.menu.dishes);
if (order.searchRecord(no)!=null)
{
System.out.println(no+" "+dishName+" "+order.searchRecord(no).getPrice());
}
}
else
{
if(parts[1].equalsIgnoreCase("delete"))
{
int no = Integer.parseInt(parts[0]);
order.delARecord(no);
}
}
}
System.out.println( order.getTotalPrice());
}
}
SourceMonitor分析:
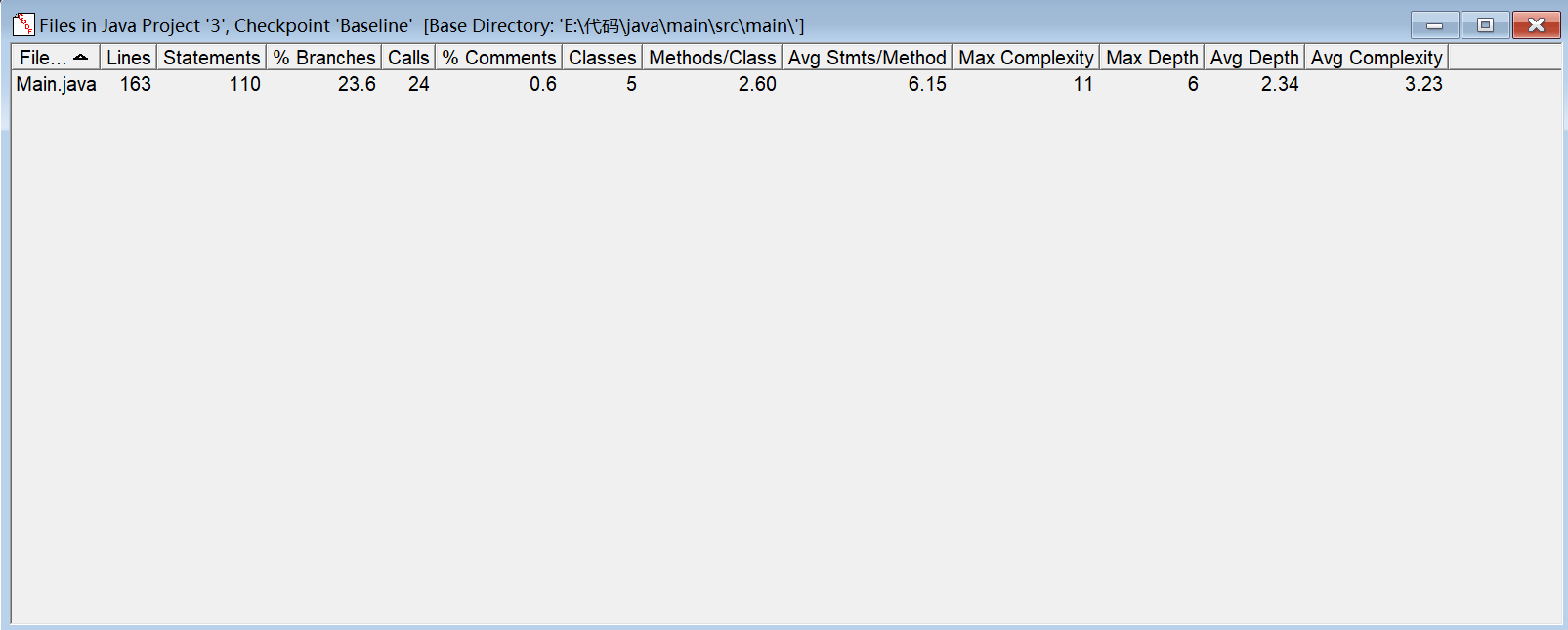
Powerdesigner分析:
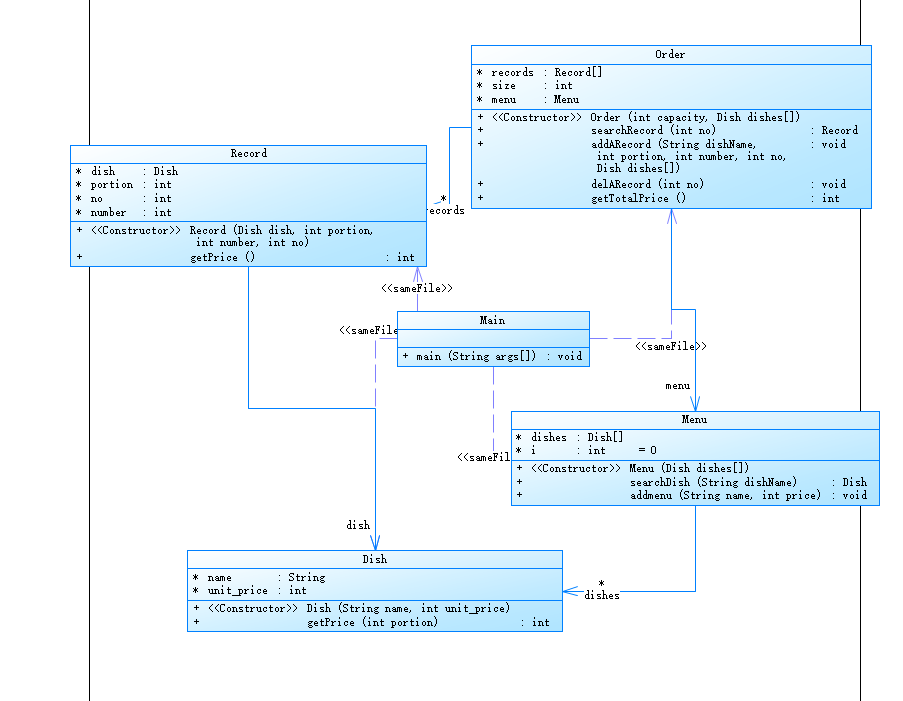
代码设计与分析:
在主函数main中,首先创建了一个空的菜品数组和一个订单对象。然后通过循环不断接收用户输入,根据输入内容进行相应的操作。如果输入是菜品名称和价格,则更新菜单中对应菜品的价格或者添加新菜品。如果输入是点餐记录的序号、菜品名称、份数和数量,则添加一条点餐记录,并打印出该条记录的总价。如果输入是要删除的点餐记录的序号,则删除相应的点餐记录。循环直到用户输入"end"为止,然后输出订单的总价。
Java第五次大作业
7-1:菜单计价程序-4
本体大部分内容与菜单计价程序-3相同,增加的部分用加粗文字进行了标注。
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 两个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 份额 分数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的桌号从小到大的顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计(本内容与计价程序之前相同,其他类根据需要自行定义):
菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
本次课题比菜单计价系列-3增加的异常情况:
1、菜谱信息与订单信息混合,应忽略夹在订单信息中的菜谱信息。输出:"invalid dish"
2、桌号所带时间格式合法(格式见输入格式部分说明,其中年必须是4位数字,月、日、时、分、秒可以是1位或2位数),数据非法,比如:2023/15/16 ,输出桌号+" date error"
3、同一桌菜名、份额相同的点菜记录要合并成一条进行计算,否则可能会出现四舍五入的误差。
4、重复删除,重复的删除记录输出"deduplication :"+序号。
5、代点菜时,桌号不存在,输出"Table number :"+被点菜桌号+" does not exist";本次作业不考虑两桌记录时间不匹配的情况。
6、菜谱信息中出现重复的菜品名,以最后一条记录为准。
7、如果有重复的桌号信息,如果两条信息的时间不在同一时间段,(时段的认定:周一到周五的中午或晚上是同一时段,或者周末时间间隔1小时(不含一小时整,精确到秒)以内算统一时段),此时输出结果按不同的记录分别计价。
8、重复的桌号信息如果两条信息的时间在同一时间段,此时输出结果时合并点菜记录统一计价。前提:两个的桌号信息的时间都在有效时间段以内。计算每一桌总价要先合并符合本条件的饭桌的点菜记录,统一计价输出。
9、份额超出范围(1、2、3)输出:序号+" portion out of range "+份额,份额不能超过1位,否则为非法格式,参照第13条输出。
10、份数超出范围,每桌不超过15份,超出范围输出:序号+" num out of range "+份数。份数必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
11、桌号超出范围[1,55]。输出:桌号 +" table num out of range",桌号必须为1位或多位数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
12、菜谱信息中菜价超出范围(区间(0,300)),输出:菜品名+" price out of range "+价格,菜价必须为数值,最高位不能为0,否则按非法格式参照第16条输出。
13、时间输入有效但超出范围[2022.1.1-2023.12.31],输出:"not a valid time period"
14、一条点菜记录中若格式正确,但数据出现问题,如:菜名不存在、份额超出范围、份数超出范围,按记录中从左到右的次序优先级由高到低,输出时只提示优先级最高的那个错误。
15、每桌的点菜记录的序号必须按从小到大的顺序排列(可以不连续,也可以不从1开始),未按序排列序号的输出:"record serial number sequence error"。当前记录忽略。(代点菜信息的序号除外)
16、所有记录其它非法格式输入,统一输出"wrong format"
17、如果记录以“table”开头,对应记录的格式或者数据不符合桌号的要求,那一桌下面定义的所有信息无论正确或错误均忽略,不做处理。如果记录不是以“table”开头,比如“tab le 55 2023/3/2 12/00/00”,该条记录认为是错误记录,后面所有的信息并入上一桌一起计算。
本次作业比菜单计价系列-3增加的功能:
菜单输入时增加特色菜,特色菜的输入格式:菜品名+英文空格+基础价格+"T"
例如:麻婆豆腐 9 T
菜价的计算方法:
周一至周五 7折, 周末全价。
注意:不同的四舍五入顺序可能会造成误差,请按以下步骤累计一桌菜的菜价:
计算每条记录的菜价:将每份菜的单价按份额进行四舍五入运算后,乘以份数计算多份的价格,然后乘以折扣,再进行四舍五入,得到本条记录的最终支付价格。
最后将所有记录的菜价累加得到整桌菜的价格。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”+英文空格
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“** does not exist”,**是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的原始总价+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 31 2023/2/1 14/20/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 16
2 油淋生菜 1 2
2 delete
2 delete
end
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 31:
1 num out of range 16
2 油淋生菜 18
deduplication 2
table 31: 0 0
输入样例1:
份数超出范围+份额超出范围。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 31 2023/2/1 14/20/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 16
2 油淋生菜 4 2
end
输出样例1:
份数超出范围+份额超出范围。例如:
table 31:
1 num out of range 16
2 portion out of range 4
table 31: 0 0
输入样例2:
桌号信息错误。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table a 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例3:
混合错误:桌号信息格式错误+混合的菜谱信息(菜谱信息忽略)。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 55 2023/3/31 12/000/00
麻辣香锅 15
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例4:
错误的菜谱记录。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12.0
油淋生菜 9 T
table 55 2023/3/31 12/00/00
麻辣香锅 15
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
table 55:
invalid dish
麻婆豆腐 does not exist
2 油淋生菜 14
table 55: 14 10
输入样例5:
桌号格式错误(以“table”开头)+订单格式错误(忽略)。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table a 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆 豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format
输入样例6:
桌号格式错误,不以“table”开头。例如:
麻婆豆腐 12
油淋生菜 9 T
table 1 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
tab le 2 2023/3/15 12/00/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1
2 油淋生菜 2 1
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1: 1 麻婆豆腐 12 2 油淋生菜 14 wrong format record serial number sequence error record serial number sequence error table 1: 26 17
给出源代码:
package self;
import java.util.*;
import java.time.YearMonth;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Menu menu = new Menu();
List<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>();
String input;
while (true) {
input = sc.nextLine();
if (input.equals("end")) {
break;
}
if (input.equals("")) {
System.out.println("wrong format");
continue;
}
String[] temp = input.split(" ");
int count = temp.length;
if (count == 2) {
if (input.matches("\\d delete")) {
int orderNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
deleteRecordByOrderNum(tables, orderNum);
} else if (input.matches("[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]{0,} \\d{0,}")) {
if (tables.isEmpty()) {
menu.addDish(temp[0], Integer.parseInt(temp[1]));
} else {
System.out.println("invalid dish");
}
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
} else if (count == 3) {
if (input.matches("[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]{0,} \\d{0,} [T]")) {
if (!tables.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("invalid dish");
continue;
}
menu.addDish(temp[0], Integer.parseInt(temp[1]), true);
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
} else if (count == 5) {
if (input.matches("([1-4][0-9]*|[5][0-5]*|[1-9]) \\d [\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]{1,} [123] ([1][0-5]|[1-9])")) {
int myTableNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[0]);
int anotherTableNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[1]);
int orderNum = Integer.parseInt(temp[3]);
int portion = Integer.parseInt(temp[4]);
Table myTable = findTableByTableNum(tables, myTableNum);
Table anotherTable = findTableByTableNum(tables, anotherTableNum);
if (myTable != null && anotherTable != null) {
Record record = anotherTable.getOrder().getRecordByOrderNum(orderNum);
if (record != null) {
myTable.getOrder().addRecord(record.getDish(), portion, record.getNum());
System.out.println(temp[1] + " table " + myTableNum + " pay for table " + temp[0] + " " + record.getPrice());
} else {
System.out.println("order " + orderNum + " does not exist");
}
} else {
System.out.println("Table number: " + anotherTableNum + " does not exist");
}
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
} else {
if (!tables.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
}
}
for (Table table : tables) {
if (!table.isToSum()) {
table.calculateTotalPrice();
}
}
}
private static void deleteRecordByOrderNum(List<Table> tables, int orderNum) {
for (Table table : tables) {
if (table.getOrder().deleteRecordByOrderNum(orderNum)) {
return;
}
}
System.out.println("delete error");
}
private static Table findTableByTableNum(List<Table> tables, int tableNum) {
for (Table table : tables) {
if (table.getTableNum() == tableNum) {
return table;
}
}
return null;
}
}
class Table {
private int tableNum;
private boolean inputIsValid = false;
private boolean isToSum = false;
private String tableDateTime;
private int sum = 0;
private int primeSum = 0;
private Order order = new Order();
private float discount = -1;
private float reDiscount = 1;
public Table(int tableNum) {
this.tableNum = tableNum;
}
public int getTableNum() {
return tableNum;
}
public boolean isToSum() {
return isToSum;
}
public Order getOrder() {
return order;
}
public void calculateTotalPrice() {
if (discount > 0) {
primeSum = order.getTotalPrice();
if (primeSum == 0) {
sum = 0;
}
System.out.println("table " + tableNum + ": " + primeSum + " " + sum);
}
}
public void processDateTime(String tableDateTime) {
this.tableDateTime = tableDateTime;
String[] temp = tableDateTime.split(" ");
String[] temp1 = temp[2].split("/");
String[] temp2 = temp[3].split("/");
int year = Integer.parseInt(temp1[0]);
int month = Integer.parseInt(temp1[1]);
int day = Integer.parseInt(temp1[2]);
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(year, month - 1, day);
int week = c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
if (week == 1) {
week = 7;
} else {
week--;
}
int hh = Integer.parseInt(temp2[0]);
int mm = Integer.parseInt(temp2[1]);
int ss = Integer.parseInt(temp2[2]);
if (year < 1000 || month < 1 || month > 12) {
inputIsValid = false;
return;
}
YearMonth myTime = YearMonth.of(year, month);
if (!myTime.isValidDay(day)) {
inputIsValid = false;
return;
}
if (year < 2022 || year > 2023) {
System.out.println("not a valid time period");
inputIsValid = false;
return;
}
if (week >= 1 && week <= 5) {
if (hh >= 17 && hh < 20) {
discount = 0.8F;
} else if ((hh == 20 && mm < 30) || (hh == 20 && mm == 30 && ss == 0)) {
discount = 0.8F;
} else if ((hh >= 11 && hh <= 13) || (hh == 10 && mm >= 30)) {
discount = 0.6F;
} else if ((hh == 14 && mm < 30) || (hh == 14 && mm == 30 && ss == 0)) {
discount = 0.6F;
}
} else {
if ((hh >= 10 && hh <= 20) || (hh == 9 && mm >= 30)) {
discount = 1.0F;
} else if ((hh == 21 && mm < 30) || (hh == 21 && mm == 30 && ss == 0)) {
discount = 1.0F;
}
}
inputIsValid = true;
}
public boolean isInputValid() {
return inputIsValid;
}
public boolean isDateValid() {
return inputIsValid && YearMonth.of(Integer.parseInt(tableDateTime.split(" ")[2].split("/")[0]), Integer.parseInt(tableDateTime.split(" ")[2].split("/")[1])).isValidDay(Integer.parseInt(tableDateTime.split(" ")[2].split("/")[2]));
}
public boolean isDateTimeInRange() {
int hh = Integer.parseInt(tableDateTime.split(" ")[3].split(":")[0]);
int mm = Integer.parseInt(tableDateTime.split(" ")[3].split(":")[1]);
if (hh >= 10 && hh <= 20) {
return true;
} else if (hh == 9 && mm >= 30) {
return true;
} else if ((hh == 21 && mm < 30) || (hh == 21 && mm == 30)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSameTime(Table table) {
if (tableNum != table.getTableNum()) {
return false;
}
if (isDateTimeInRange() && table.isDateTimeInRange()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
class Order {
private List<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();
public int getTotalPrice() {
int sum = 0;
for (Record record : records) {
sum += record.getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
public void addRecord(Dish dish, int portion, int num) {
boolean flag = true;
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.getDish().getName().equals(dish.getName()) && record.getPortion() == portion) {
flag = false;
}
}
if (flag) {
records.add(new Record(dish, portion, num));
}
}
public Record getRecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) {
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.getOrderNum() == orderNum) {
return record;
}
}
return null;
}
public boolean deleteRecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) {
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.getOrderNum() == orderNum) {
records.remove(record);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
class Record {
private int orderNum;
private Dish dish;
private int num;
private int portion;
private boolean noNeed = true;
private boolean isTaken = false;
private int exist = 1;
private float realDiscount = 1;
public Record(Dish dish, int portion, int num) {
this.dish = dish;
this.portion = portion;
this.num = num;
}
public int getOrderNum() {
return orderNum;
}
public Dish getDish() {
return dish;
}
public int getNum() {
return num;
}
public int getPortion() {
return portion;
}
public int getPrice() {
return dish.getPrice(portion) * num;
}
public float checkPortion(float discount) {
if (portion > 3 || portion < 1) {
System.out.println(orderNum + " portion out of range " + portion);
exist = 0;
noNeed = false;
} else if (num < 1 || num > 15) {
System.out.println(orderNum + " num out of range " + num);
exist = 0;
noNeed = false;
} else {
if (dish.isSpecial && (discount == 0.8F || discount == 0.6F)) {
realDiscount = 0.7F;
}
if (exist == 1 && !isTaken) {
System.out.println(orderNum + " " + dish.getName() + " " + getPrice());
}
}
return realDiscount;
}
public boolean isAheadValid() {
return num >= 1 && num <= 15 && portion >= 1 && portion <= 3;
}
}
class Menu {
private List<Dish> dishes = new ArrayList<>();
public void addDish(String name, int unitPrice) {
addDish(name, unitPrice, false);
}
public void addDish(String name, int unitPrice, boolean isSpecial) {
if (unitPrice < 1 || unitPrice > 300) {
System.out.println(name + " price out of range " + unitPrice);
return;
}
dishes.add(new Dish(name, unitPrice, isSpecial));
}
public Dish searchDish(String name) {
for (Dish dish : dishes) {
if (dish.getName().equals(name)) {
return dish;
}
}
System.out.println(name + " does not exist");
return null;
}
}
class Dish {
private String name;
private int unitPrice;
private boolean isSpecial;
public Dish(String name, int unitPrice, boolean isSpecial) {
this.name = name;
this.unitPrice = unitPrice;
this.isSpecial = isSpecial;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPrice(int portion) {
if (portion == 1) {
return unitPrice;
} else if (portion == 2) {
return Math.round(unitPrice * 1.5F);
} else if (portion == 3) {
return unitPrice * 2;
}
return 0;
}
}
SourceMonitor分析:
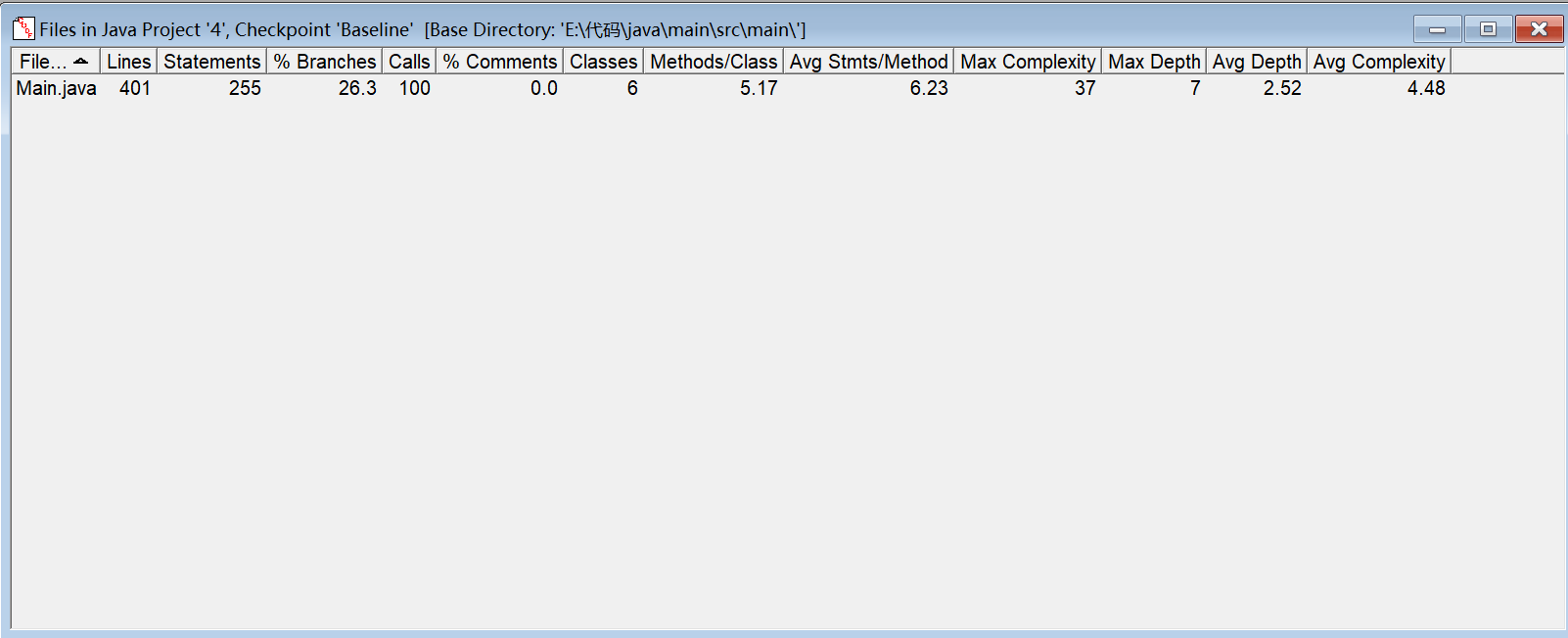
PowerDesigner分析:
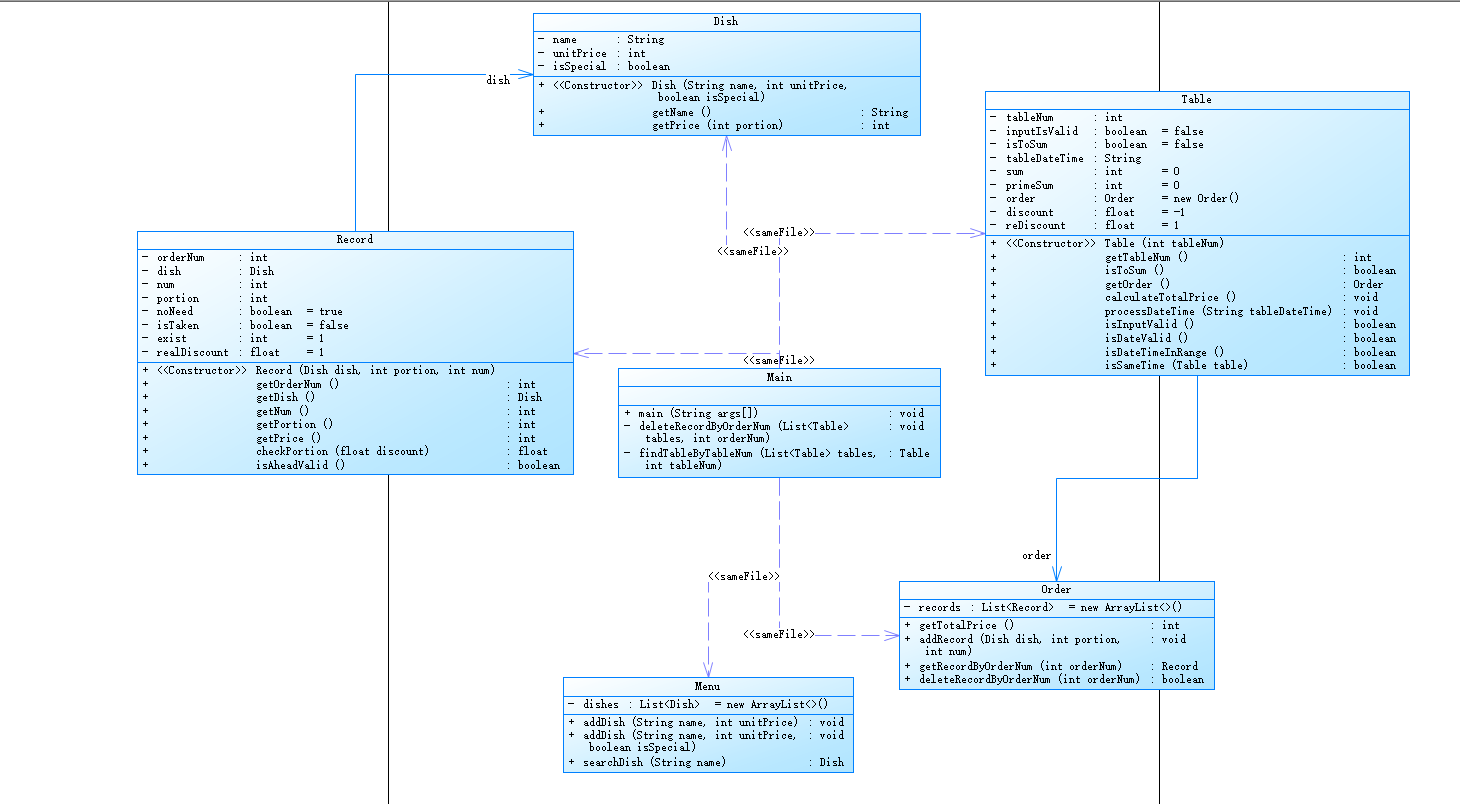
代码设计与分析:这次的菜单计价程序相比第三次主要是增加了特色菜这个板块,并且增加了周一至周五7折,周末全价的计价方式,主要代码思想还是没变,需要注意的是计算价格时需要先对菜品单价进行四舍五入后再乘以份数后再乘以折扣最后再进行四舍五入,不然答案很有可能错误!
期中考试
7-1测试1-圆类设计
创建一个圆形类(Circle),私有属性为圆的半径,从控制台输入圆的半径,输出圆的面积
输入格式:
输入圆的半径,取值范围为(0,+∞),输入数据非法,则程序输出Wrong Format,注意:只考虑从控制台输入数值的情况
输出格式:
输出圆的面积(保留两位小数,可以使用String.format(“%.2f”,输出数值)控制精度)
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2.35
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
17.35
给出源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double radius;
radius = scanner.nextDouble();
double area;
if (radius <= 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
area = radius * radius * Math.PI;
System.out.printf("%.2f", area);
}
}
}
SourceMonitor分析:
PowerDesigner分析:

代码设计与分析:这道题目属实简单了点,甚至不用创建类。。。要说难度的话只有计算面积时那个圆周率需要用到MATH.PI来写吧。有一个细节就是输出的时候有用printf而不是println,每次写这种保留几位小数输出的时候总会忘记导致编译错误,每次还又找半天不知道错哪了。
7-2测验2-类结构设计
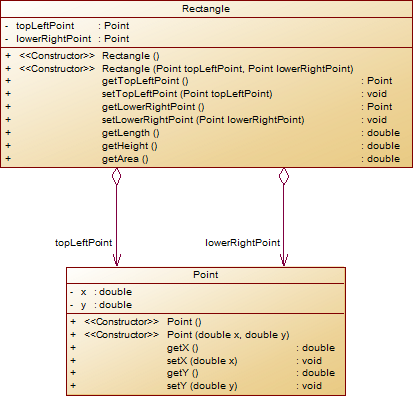
设计一个矩形类,其属性由矩形左上角坐标点(x1,y1)及右下角坐标点(x2,y2)组成,其中,坐标点属性包括该坐标点的X轴及Y轴的坐标值(实型数),求得该矩形的面积。类设计如下图:
输入格式:
分别输入两个坐标点的坐标值x1,y1,x2,y2。
输出格式:
输出该矩形的面积值(保留两位小数)。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
6 5.8 -7 8.9
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
40.30
给出源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
class Rectangle {
private double x1, y1, x2, y2;
public Rectangle(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
}
public double calculateArea() {
double Length = Math.abs(x2 - x1);
double Height = Math.abs(y2 - y1);
return Length * Height;
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
x1 = scanner.nextDouble();
y1 = scanner.nextDouble();
x2 = scanner.nextDouble();
y2 = scanner.nextDouble();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(x1, y1, x2, y2);
double area = rectangle.calculateArea();
System.out.printf("%.2f", area);
}
}
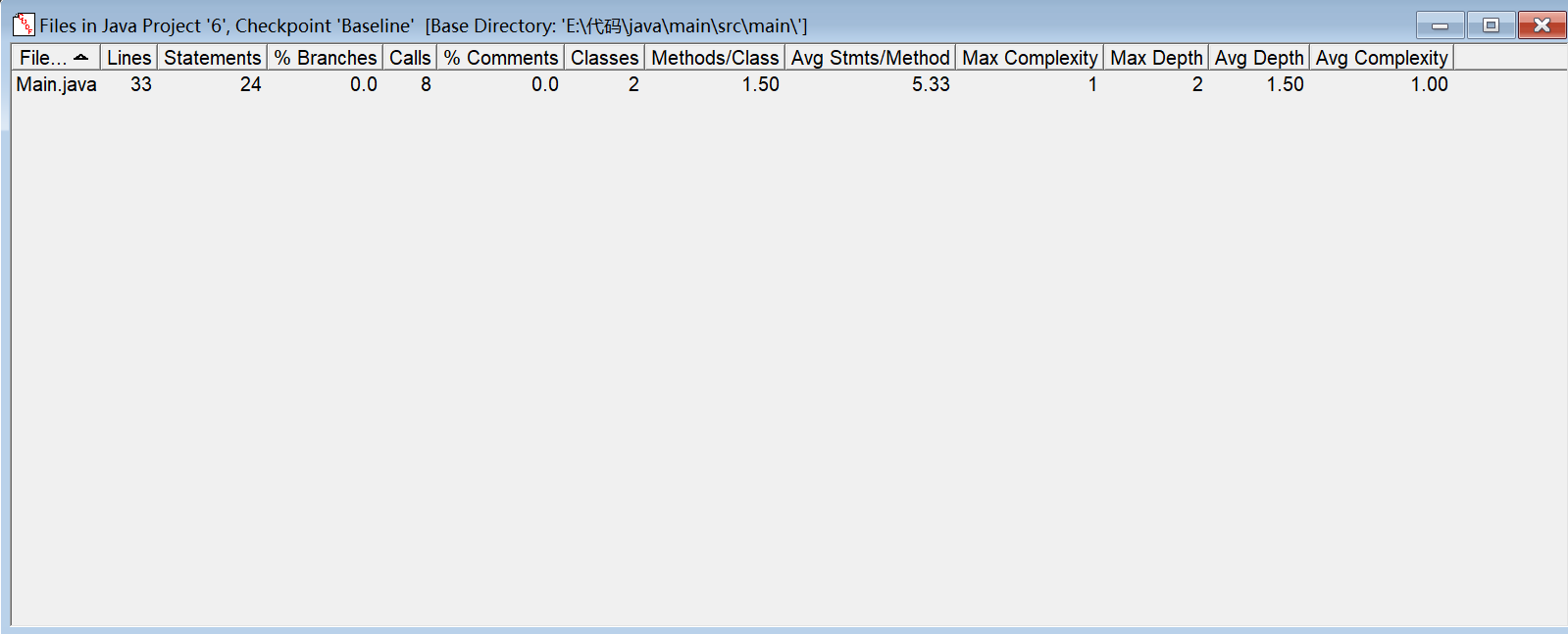
SourceMonitor分析:
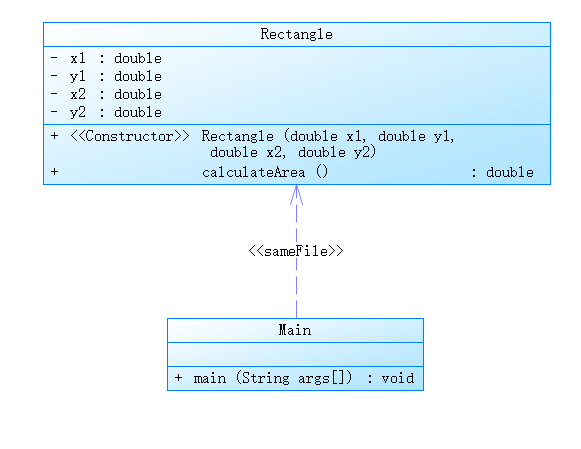
PowerDesigner分析:
代码设计与分析:这道题目难度也不算大,创建两个类嘛,一个有关位置坐标的,一个有关长方形长度高度的主要还是用同一类坐标相减得到,最后在主函数中计算出长方形面积即可,需要注意的是计算长度高度时要对结果进行求绝对值,不然结果会成为负数导致答案错误。
7-3测试三-继承与多态
将测验1与测验2的类设计进行合并设计,抽象出Shape父类(抽象类),Circle及Rectangle作为子类,类图如下所示:
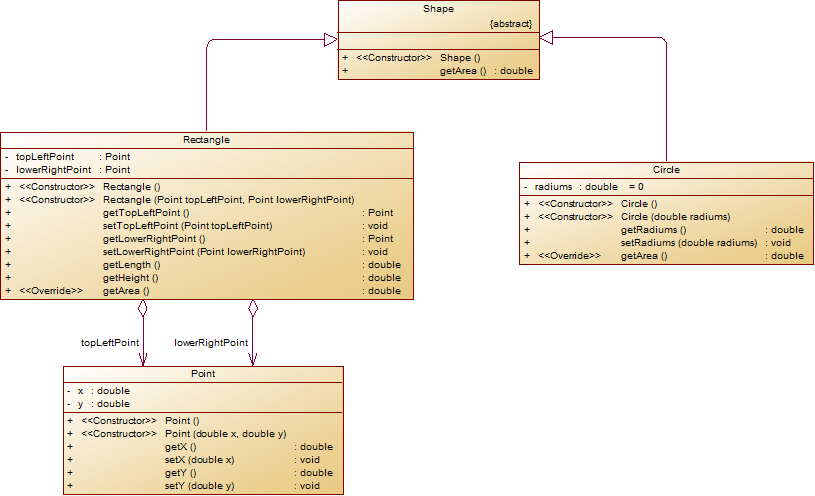
试编程完成如上类图设计,主方法源码如下(可直接拷贝使用):
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = input.nextInt();
switch(choice) {
case 1://Circle
double radiums = input.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radiums);
printArea(circle);
break;
case 2://Rectangle
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1);
Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint);
printArea(rectangle);
break;
}
}
其中,printArea(Shape shape)方法为定义在Main类中的静态方法,体现程序设计的多态性。
输入格式:
输入类型选择(1或2,不考虑无效输入)
对应图形的参数(圆或矩形)
输出格式:
图形的面积(保留两位小数)
输入样例1:
1
5.6
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
98.52
输入样例2:
2
5.6
-32.5
9.4
-5.6
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
102.22
给出源代码:
import java.util.Scanner;
abstract class Shape {
abstract double getArea();
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private Point TopLeftPoint;
private Point LowerRightPoint;
public Rectangle(Point TopLeftPoint, Point LowerRightPoint) {
this.TopLeftPoint = TopLeftPoint;
this.LowerRightPoint = LowerRightPoint;
}
double getArea() {
double Length = Math.abs(LowerRightPoint.getX() - TopLeftPoint.getX());
double Height = Math.abs(LowerRightPoint.getY() - TopLeftPoint.getY());
return Length * Height;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = input.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
double radius = input.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radius);
printArea(circle);
break;
case 2:
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point TopLeftPoint = new Point(x1, y1);
Point LowerRightPoint = new Point(x2, y2);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(TopLeftPoint, LowerRightPoint);
printArea(rectangle);
break;
}
}
public static void printArea(Shape shape) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", shape.getArea()));
}
}
SourceMonitor分析:
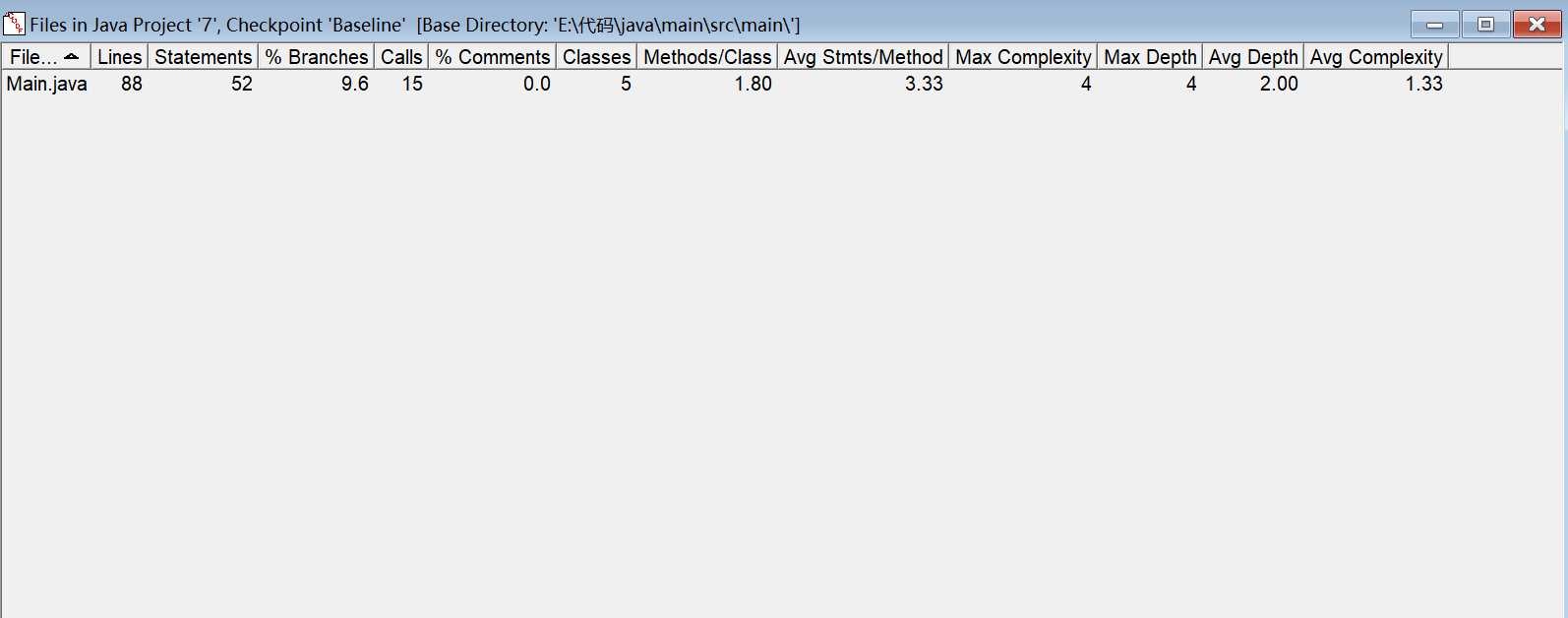
PowerDesignerf分析:
代码设计与分析:这道题目难度也不算很大,问题在于如何将圆类和矩形类结合在一起,这里我们选用case语句进行区分和判断,当你输入1时就计算圆的面积,输入2的话就计算矩形的面积。还有,在进行代码编写的时候,我们需要用到abstract语句,这个语句的作用在于将圆和矩形抽象化,由于抽象类不能被实例化,最大的好处就是通过方法的覆盖来实现多态的属性。也就是运行期绑定抽象类将事物的共性的东西提取出来,由子类继承去实现,代码易扩展、易维护。
7-4测试4-抽象类与接口
在测验3的题目基础上,重构类设计,实现列表内图形的排序功能(按照图形的面积进行排序)。
提示:题目中Shape类要实现Comparable接口。
其中,Main类源码如下(可直接拷贝使用):
public class Main {
public static void main(String\[\] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>();
int choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1://Circle
double radiums = input.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radiums);
list.add(circle);
break;
case 2://Rectangle
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1);
Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint);
list.add(rectangle);
break;
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());//正向排序
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea()) + " ");
}
}
}
输入格式:
输入图形类型(1:圆形;2:矩形;0:结束输入)
输入图形所需参数
输出格式:
按升序排序输出列表中各图形的面积(保留两位小数),各图形面积之间用空格分隔。
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1
2.3
2
3.2
3
6
5
1
2.3
0
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
5.60 16.62 16.62
这道题目需要解释一下,因为这个题目是在考试期间写的,时间来不及没写,故0分。。。
所以这道题并没有代码和分析,望见谅。
Java第六次大作业
7-1菜单计价程序5
本题在菜单计价程序-3的基础上增加了部分内容,增加的内容用加粗字体标识。
注意不是菜单计价程序-4,本题和菜单计价程序-4同属菜单计价程序-3的两个不同迭代分支。
设计点菜计价程序,根据输入的信息,计算并输出总价格。
输入内容按先后顺序包括两部分:菜单、订单,最后以"end"结束。
菜单由一条或多条菜品记录组成,每条记录一行
每条菜品记录包含:菜名、基础价格 三个信息。
订单分:桌号标识、点菜记录和删除信息、代点菜信息。每一类信息都可包含一条或多条记录,每条记录一行或多行。
桌号标识独占一行,包含两个信息:桌号、时间。
桌号以下的所有记录都是本桌的记录,直至下一个桌号标识。
点菜记录包含:序号、菜名、份额、份数。份额可选项包括:1、2、3,分别代表小、中、大份。
不同份额菜价的计算方法:小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格。中份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格1.5。小份菜的价格=菜品的基础价格2。如果计算出现小数,按四舍五入的规则进行处理。
删除记录格式:序号 delete
标识删除对应序号的那条点菜记录。
如果序号不对,输出"delete error"
代点菜信息包含:桌号 序号 菜品名称 口味度 份额 份数
代点菜是当前桌为另外一桌点菜,信息中的桌号是另一桌的桌号,带点菜的价格计算在当前这一桌。
程序最后按输入的先后顺序依次输出每一桌的总价(注意:由于有代点菜的功能,总价不一定等于当前桌上的菜的价格之和)。
每桌的总价等于那一桌所有菜的价格之和乘以折扣。如存在小数,按四舍五入规则计算,保留整数。
折扣的计算方法(注:以下时间段均按闭区间计算):
周一至周五营业时间与折扣:晚上(17:00-20:30)8折,周一至周五中午(10:30--14:30)6折,其余时间不营业。
周末全价,营业时间:9:30-21:30
如果下单时间不在营业范围内,输出"table " + t.tableNum + " out of opening hours"
参考以下类的模板进行设计:菜品类:对应菜谱上一道菜的信息。
Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
int unit_price; //单价
int getPrice(int portion)//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份) }
菜谱类:对应菜谱,包含饭店提供的所有菜的信息。
Menu {
Dish[] dishs ;//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName)//根据菜名在菜谱中查找菜品信息,返回Dish对象。
Dish addDish(String dishName,int unit_price)//添加一道菜品信息
}
点菜记录类:保存订单上的一道菜品记录
Record {
int orderNum;//序号\\
Dish d;//菜品\\
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)\\
int getPrice()//计价,计算本条记录的价格\\
}
订单类:保存用户点的所有菜的信息。
Order {
Record[] records;//保存订单上每一道的记录
int getTotalPrice()//计算订单的总价
Record addARecord(int orderNum,String dishName,int portion,int num)//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
delARecordByOrderNum(int orderNum)//根据序号删除一条记录
findRecordByNum(int orderNum)//根据序号查找一条记录
}
### 输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称+英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
### 输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+”:”
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
最后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的总价(整数数值)格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的总价
以上为菜单计价系列-3的题目要求,加粗的部分是有调整的内容。本次课题相比菜单计价系列-3新增要求如下:
1、菜单输入时增加特色菜,特色菜的输入格式:菜品名+英文空格+口味类型+英文空格+基础价格+"T"
例如:麻婆豆腐 川菜 9 T
菜价的计算方法:
周一至周五 7折, 周末全价。
特色菜的口味类型:川菜、晋菜、浙菜
川菜增加辣度值:辣度0-5级;对应辣度水平为:不辣、微辣、稍辣、辣、很辣、爆辣;
晋菜增加酸度值,酸度0-4级;对应酸度水平为:不酸、微酸、稍酸、酸、很酸;
浙菜增加甜度值,甜度0-3级;对应酸度水平为:不甜、微甜、稍甜、甜;
例如:麻婆豆腐 川菜 9 T
输入订单记录时如果是特色菜,添加口味度(辣/酸/甜度)值,格式为:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+口味度值+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数
例如:1 麻婆豆腐 4 1 9
单条信息在处理时,如果口味度超过正常范围,输出"spicy/acidity/sweetness num out of range : "+口味度值,spicy/acidity/sweetness(辣度/酸度/甜度)根据菜品类型择一输出,例如:
acidity num out of range : 5
输出一桌的信息时,按辣、酸、甜度的顺序依次输出本桌菜各种口味的口味度水平,如果没有某个类型的菜,对应的口味(辣/酸/甜)度不输出,只输出已点的菜的口味度。口味度水平由口味度平均值确定,口味度平均值只综合对应口味菜系的菜计算,不做所有菜的平均。比如,某桌菜点了3份川菜,辣度分别是1、3、5;还有4份晋菜,酸度分别是,1、1、2、2,辣度平均值为3、酸度平均值四舍五入为2,甜度没有,不输出。
一桌信息的输出格式:table+英文空格+桌号+:+英文空格+当前桌的原始总价+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价+英文空格+"川菜"+数量+辣度+英文空格+"晋菜"+数量+酸度+英文空格+"浙菜"+数量+甜度。
如果整桌菜没有特色菜,则只输出table的基本信息,格式如下,注意最后加一个英文空格:
table+英文空格+桌号+:+英文空格+当前桌的原始总价+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价+英文空格
例如:table 1: 60 36 川菜 2 爆辣 浙菜 1 微甜
计算口味度时要累计本桌各类菜系所有记录的口味度总和(每条记录的口味度乘以菜的份数),再除以对应菜系菜的总份数,最后四舍五入。
注:本题要考虑代点菜的情况,当前桌点的菜要加上被其他桌代点的菜综合计算口味度平均值。
2、考虑客户订多桌菜的情况,输入时桌号时,增加用户的信息:
格式:table+英文空格+桌号+英文空格+":"+英文空格+客户姓名+英文空格+手机号+日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
例如:table 1 : tom 13670008181 2023/5/1 21/30/00
约束条件:客户姓名不超过10个字符,手机号11位,前三位必须是180、181、189、133、135、136其中之一。
输出结果时,先按要求输出每一桌的信息,最后按字母顺序依次输出每位客户需要支付的金额。不考虑各桌时间段的问题,同一个客户的所有table金额都要累加。
输出用户支付金额格式:
用户姓名+英文空格+手机号+英文空格+支付金额
注意:不同的四舍五入顺序可能会造成误差,请按以下步骤累计一桌菜的菜价:
计算每条记录的菜价:将每份菜的单价按份额进行四舍五入运算后,乘以份数计算多份的价格,然后乘以折扣,再进行四舍五入,得到本条记录的最终支付价格。
将所有记录的菜价累加得到整桌菜的价格。
输入格式:
桌号标识格式:table + 序号 +英文空格+ 日期(格式:YYYY/MM/DD)+英文空格+ 时间(24小时制格式: HH/MM/SS)
菜品记录格式:
菜名+口味类型+英文空格+基础价格
如果有多条相同的菜名的记录,菜品的基础价格以最后一条记录为准。
点菜记录格式:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+辣/酸/甜度值+英文空格+份额+英文空格+份数 注:份额可输入(1/2/3), 1代表小份,2代表中份,3代表大份。辣/酸/甜度取值范围见题目中说明。
删除记录格式:序号 +英文空格+delete
代点菜信息包含:桌号+英文空格+序号+英文空格+菜品名称**+英文空格+辣/酸/甜度值+**英文空格+份额+英文空格+分数
最后一条记录以“end”结束。
输出格式:
按输入顺序输出每一桌的订单记录处理信息,包括:
1、桌号,格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格
2、按顺序输出当前这一桌每条订单记录的处理信息,
每条点菜记录输出:序号+英文空格+菜名+英文空格+价格。其中的价格等于对应记录的菜品\*份数,序号是之前输入的订单记录的序号。如果订单中包含不能识别的菜名,则输出“\*\* does not exist”,\*\*是不能识别的菜名
如果删除记录的序号不存在,则输出“delete error”
之后按输入顺序一次输出每一桌所有菜品的价格(整数数值),
格式:table+英文空格+桌号+“:”+英文空格+当前桌的计算折扣后总价+英文空格+辣度平均值+英文空格+酸度平均值+英文空格+甜度平均值+英文空格
最后按拼音顺序输出每位客户(不考虑客户同名或拼音相同的情况)的支付金额,格式: 用户姓名+英文空格+手机号+英文空格+支付总金额,按输入顺序排列。
输入样例1:
桌号时间超出营业范围。例如:
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
油淋生菜 9
麻辣鸡丝 10
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/1 21/30/00
1 麻婆豆腐 3 1 2
2 油淋生菜 2 1
3 麻婆豆腐 2 3 2
end
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1 out of opening hours
输入样例2:
一种口味的菜品。例如:
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
油淋生菜 9
麻辣鸡丝 10
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/1 20/30/00
1 麻婆豆腐 2 1 2
2 油淋生菜 2 1
3 麻婆豆腐 2 3 2
end
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 24
2 油淋生菜 14
3 麻婆豆腐 48
table 1: 86 62 川菜 4 稍辣
tom 13605054400 62
输入样例3:
辣度值超出范围。例如:
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
油淋生菜 9
麻辣鸡丝 10
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/1 18/30/00
1 麻婆豆腐 6 1 2
2 油淋生菜 1 1
3 麻婆豆腐 5 3 2
end
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
spicy num out of range :6
2 油淋生菜 9
3 麻婆豆腐 48
table 1: 57 41 川菜 2 爆辣
tom 13605054400 41
输入样例4:
同一用户对应多桌菜。例如:
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
油淋生菜 9
麻辣鸡丝 10
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/1 18/30/00
1 麻婆豆腐 1 1 2
2 油淋生菜 1 1
3 麻婆豆腐 2 2 2
table 2 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/6 18/30/00
1 麻婆豆腐 2 1 2
2 麻辣鸡丝 2 2
3 麻婆豆腐 2 1 1
end
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 麻婆豆腐 24
2 油淋生菜 9
3 麻婆豆腐 36
table 2:
1 麻婆豆腐 24
2 麻辣鸡丝 30
3 麻婆豆腐 12
table 1: 69 49 川菜 4 稍辣
table 2: 66 66 川菜 3 稍辣
tom 13605054400 115
输入样例5:
多用户多桌菜。例如:
东坡肉 浙菜 25 T
油淋生菜 9
蜜汁灌藕 浙菜 10 T
刀削面 晋菜 10 T
醋浇羊肉 晋菜 30 T
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
麻辣鸡丝 川菜 15 T
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/6 12/30/00
1 醋浇羊肉 4 1 1
3 刀削面 1 1 3
2 东坡肉 3 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 2 1 1
table 2 : jerry 18100334566 2023/5/1 12/30/00
1 醋浇羊肉 1 1 2
3 麻婆豆腐 2 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 2 3 3
table 3 : jerry 18100334566 2023/5/1 12/30/00
1 醋浇羊肉 2 1 1
3 蜜汁灌藕 1 1 2
2 东坡肉 2 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 5 1 1
end
输出样例5:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 醋浇羊肉 30
3 刀削面 30
2 东坡肉 38
4 麻辣鸡丝 15
table 2:
1 醋浇羊肉 60
3 麻婆豆腐 18
4 麻辣鸡丝 90
table 3:
1 醋浇羊肉 30
3 蜜汁灌藕 20
2 东坡肉 38
4 麻辣鸡丝 15
table 1: 113 113 川菜 1 稍辣 晋菜 4 稍酸 浙菜 1 甜
table 2: 168 118 川菜 4 稍辣 晋菜 2 微酸
table 3: 103 73 川菜 1 爆辣 晋菜 1 稍酸 浙菜 3 微甜
jerry 18100334566 191
tom 13605054400 113
输入样例6:
多用户多桌菜含代点菜。例如:
东坡肉 浙菜 25 T
油淋生菜 9
蜜汁灌藕 浙菜 10 T
刀削面 晋菜 10 T
醋浇羊肉 晋菜 30 T
麻婆豆腐 川菜 12 T
麻辣鸡丝 川菜 15 T
table 1 : tom 13605054400 2023/5/6 12/30/00
1 醋浇羊肉 4 1 1
3 刀削面 1 1 3
2 东坡肉 3 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 2 1 1
table 2 : jerry 18100334566 2023/5/1 12/30/00
1 1 醋浇羊肉 0 1 2
3 麻婆豆腐 2 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 2 3 3
table 3 : lucy 18957348763 2023/5/1 12/30/00
1 醋浇羊肉 2 1 1
3 蜜汁灌藕 1 1 2
2 东坡肉 2 2 1
4 麻辣鸡丝 5 1 1
end
输出样例6:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
table 1:
1 醋浇羊肉 30
3 刀削面 30
2 东坡肉 38
4 麻辣鸡丝 15
table 2:
1 table 2 pay for table 1 60
3 麻婆豆腐 18
4 麻辣鸡丝 90
table 3:
1 醋浇羊肉 30
3 蜜汁灌藕 20
2 东坡肉 38
4 麻辣鸡丝 15
table 1: 113 113 川菜 1 稍辣 晋菜 6 微酸 浙菜 1 甜
table 2: 168 118 川菜 4 稍辣
table 3: 103 73 川菜 1 爆辣 晋菜 1 稍酸 浙菜 3 微甜
jerry 18100334566 118
lucy 18957348763 73
tom 13605054400 113
输入样例7:
错误的菜品记录和桌号记录,用户丢弃。例如:
东坡肉 25 T
油淋生菜 9
table 1 : tom 136050540 2023/5/1 12/30/00
2 东坡肉 3 2 1
end
输出样例7:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
wrong format wrong format
给出源代码:
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Menu menu = new Menu();
// 读入菜单信息
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String menuLine = sc.nextLine();
while (!menuLine.startsWith("table")) {
String[] menuInfo = menuLine.split(" ");
if (menuInfo.length == 2) {
String name = menuInfo[0];
int unit_price = Integer.parseInt(menuInfo[1]);
if (menu.searchDish(name) == null) {
menu.addDish(name, unit_price);
}
} else if (menuInfo.length == 4 && menuLine.endsWith("T")) {
String name = menuInfo[0];
String type = menuInfo[1];
int unit_price = Integer.parseInt(menuInfo[2]);
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>() {
{
put("川菜", "Chuan");
put("晋菜", "Jin");
put("浙菜", "Zhe");
}
};
DishType dishType = DishType.valueOf(map.get(type));
if (menu.searchDish(name) == null) {
menu.addDish(name, unit_price, dishType);
}
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
menuLine = sc.nextLine();
}
ArrayList<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
// 读入订单信息
int tableId = 0;
String name = null;
String phone = null;
Date date = null;
Date time = null;
boolean legaltime = true;
boolean legalformat = true;
String orderLine = menuLine;
while (!orderLine.equals("end")) {
String[] orderInfo = orderLine.split(" ");
// 解析桌号标识
if (orderLine.startsWith("table")) {
legalformat = true;
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
SimpleDateFormat timeFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH/mm/ss");
tableId = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[1]);
name = orderInfo[3];
phone = orderInfo[4];
try {
date = dateFormat.parse(orderInfo[5]);
time = timeFormat.parse(orderInfo[6]);
} catch (Exception e) {
legalformat = false;
System.out.println("wrong format");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
String regex = "^1(80|81|89|33|35|36)\\d{8}$";
Table table = new Table(tableId, name, phone, date, time);
tables.add(table);
if (name.length() > 10 || !phone.matches(regex)) {
legalformat = false;
System.out.println("wrong format");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
if (!names.contains(name)) {
names.add(name);
}
if (table.getCoefficient(true) == 0) {
legaltime = false;
System.out.println("table " + table.tableId + " out of opening hours");
} else {
System.out.println(table.printId());
}
} else {
if (legalformat) {
int orderNum;
try {
orderNum = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[0]);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("wrong format");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
if (orderLine.endsWith("delete")) {
if (!tables.get(tableId - 1).delRecordByOrderNum(orderNum)) {
System.out.println("delete error");
}
} else {
if (orderInfo.length == 4) {
String dishName = orderInfo[1];
int portion = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[2]);
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[3]);
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish == null) {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
Record record = new Record(tableId, orderNum, dish, portion, quantity);
tables.get(tableId - 1).addRecord(record);
if (legaltime) {
System.out.println(record.print(tableId));
}
} else if (orderInfo.length == 5) {
String dishName = orderInfo[1];
int level = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[2]);
int portion = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[3]);
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[4]);
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish == null) {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
Record record = new Record(tableId, orderNum, dish, level, portion, quantity);
tables.get(tableId - 1).addRecord(record);
if (legaltime) {
System.out.println(record.print(tableId));
}
} else if (orderInfo.length == 6) {
int givenId = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[1]);
String dishName = orderInfo[2];
int level = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[3]);
int portion = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[4]);
int quantity = Integer.parseInt(orderInfo[5]);
Dish dish = menu.searchDish(dishName);
if (dish == null) {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
continue;
}
Record record1 = new Record(givenId, orderNum, dish, level, portion, quantity);
Record record2 = new Record(givenId, orderNum, dish, level, 0, quantity);
tables.get(tableId - 1).addRecord(record1);
tables.get(givenId - 1).addRecord(record2);
if (legaltime) {
System.out.println(record1.print(tableId));
}
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
}
}
}
// 读入下一个桌号标识
orderLine = sc.nextLine();
}
sc.close();
for (Table table : tables) {
if (table.flag && table.getTotalPrice() != 0) {
System.out.println(table.printInfo());
}
}
names.sort(new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String s1, String s2) {
return s1.compareTo(s2);
}
});
for (String costumName : names) {
int sum = 0;
String costumPhone = null;
for (Table table : tables) {
if (table.name.equals(costumName)) {
sum += table.getCheckedPrice();
costumPhone = table.phone;
}
}
if (sum != 0) {
System.out.println(costumName + " " + costumPhone + " " + sum);
}
}
}
}
enum DishType {
Chuan,
Jin,
Zhe,
}
class Dish {
public String name;
public int unit_price;
public DishType type;
public Dish(String name, int unit_price, DishType type) {
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
this.type = type;
}
public Dish(String name, int unit_price) {
this.name = name;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
class Menu {
public ArrayList<Dish> dishs = new ArrayList<>();
public Dish searchDish(String dishName) {
for (Dish dish : dishs) {
if (dish.name.equals(dishName)) {
return dish;
}
}
return null;
}
void addDish(String dishName, int unit_price) {
dishs.add(new Dish(dishName, unit_price));
}
void addDish(String dishName, int unit_price, DishType type) {
dishs.add(new Dish(dishName, unit_price, type));
}
}
class Record {
int orderNum;
Dish dish;
int portion;
int quantity;
int level;
boolean flag;
int givenId;
boolean check_level() {
switch (dish.type) {
case Chuan:
if (level > 5 || level < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
case Jin:
if (level > 4 || level < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
case Zhe:
if (level > 3 || level < 0) {
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
default:
return true;
}
}
public Record(int givenID, int orderNum, Dish dish, int portion, int quantity) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.dish = dish;
this.portion = portion;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.level = -1;
this.flag = true;
this.givenId = givenID;
}
public Record(int givenId, int orderNum, Dish dish, int level, int portion, int quantity) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.dish = dish;
this.portion = portion;
this.quantity = quantity;
this.level = level;
this.flag = check_level();
this.givenId = givenId;
}
int getPrice() {
if (!flag)
return 0;
double coefficient = 0;
switch (portion) {
case 1:
coefficient = 1;
break;
case 2:
coefficient = 1.5;
break;
case 3:
coefficient = 2;
break;
}
int price = (int) Math.round(dish.unit_price * coefficient) * quantity;
return price;
}
int getCheckedPrice(Double coefficient) {
return (int) Math.round(getPrice() * coefficient);
}
public String print(int tableId) {
if (flag == false) {
switch (dish.type) {
case Chuan:
return "spicy num out of range :" + level;
case Jin:
return "acidity num out of range :" + level;
case Zhe:
return "sweetness num out of range :" + level;
default:
return null;
}
} else {
if (givenId == tableId) {
return orderNum + " " + dish.toString() + " " + getPrice();
}
return orderNum + " table " + tableId + " pay for table " + givenId + " " + getPrice();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Record [orderNum=" + orderNum + ", dish=" + dish + ", portion=" + portion + ", quantity=" + quantity
+ ", level=" + level + ", flag=" + flag + ", givenId=" + givenId + "]";
}
}
class Table {
ArrayList<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();
int tableId;
String name;
String phone;
Date date;
Date time;
boolean flag;
public Table(int tableId, String name, String phone, Date date, Date time) {
this.name = name;
this.phone = phone;
this.date = date;
this.time = time;
this.tableId = tableId;
this.flag = true;
}
double getCoefficient(boolean Special) throws ParseException {
double coefficient = 0;
SimpleDateFormat sdfTime = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm");
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.setTime(date);
int dayOfWeek = cal.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
// 营业时间
if (dayOfWeek == 1 || dayOfWeek == 7) {
if (time.after(sdfTime.parse("9:29")) && time.before(sdfTime.parse("21:31"))) {
coefficient = 1;
}
} else {
if (time.after(sdfTime.parse("16:59")) && time.before(sdfTime.parse("20:31"))) {
if (Special) {
coefficient = 0.7;
} else {
coefficient = 0.8;
}
} else if (time.after(sdfTime.parse("10:29")) && time.before(sdfTime.parse("14:31"))) {
if (Special) {
coefficient = 0.7;
} else {
coefficient = 0.6;
}
}
}
if (coefficient == 0) {
flag = false;
}
return coefficient;
}
int getTotalPrice() {
int sum = 0;
for (Record record : records) {
sum += record.getPrice();
}
return sum;
}
int getCheckedPrice() throws ParseException {
int sum = 0;
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.level != -1) {
sum += record.getCheckedPrice(getCoefficient(true));
} else {
sum += record.getCheckedPrice(getCoefficient(false));
}
}
return sum;
}
String getAveLevel(DishType type) {
String[] spicy = { "不辣", "微辣", "稍辣", "辣", "很辣", "爆辣" };
String[] acidity = { "不酸", "微酸", "稍酸", "酸", "很酸" };
String[] sweetness = { "不甜", "微甜", "稍甜", "甜" };
double sum = 0;
double num = 0;
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.dish.type == type) {
if (record.flag && tableId == record.givenId) {
num += record.quantity;
sum += record.level * record.quantity;
}
}
}
if (num == 0) {
return "";
}
int ave = (int) Math.round(sum / num);
switch (type) {
case Chuan:
return " 川菜 " + (int) num + " " + spicy[ave];
case Jin:
return " 晋菜 " + (int) num + " " + acidity[ave];
case Zhe:
return " 浙菜 " + (int) num + " " + sweetness[ave];
default:
return null;
}
}
void addRecord(Record record) {
records.add(record);
}
boolean delRecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) {
return records.removeIf(record -> record.orderNum == orderNum);
}
Record findRecordByOrderNum(int orderNum) {
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.orderNum == orderNum) {
return record;
}
}
return null;
}
public String printId() {
return "table " + tableId + ": ";
}
public String printInfo() throws ParseException {
String chuan = getAveLevel(DishType.Chuan);
String jin = getAveLevel(DishType.Jin);
String zhe = getAveLevel(DishType.Zhe);
if (chuan == "" && jin == "" && zhe == "") {
return "table " + tableId + ": " + getTotalPrice() + " " + getCheckedPrice() + " ";
} else {
return "table " + tableId + ": " + getTotalPrice() + " " + getCheckedPrice() + chuan + jin + zhe;
}
}
SourceMonitor分析:
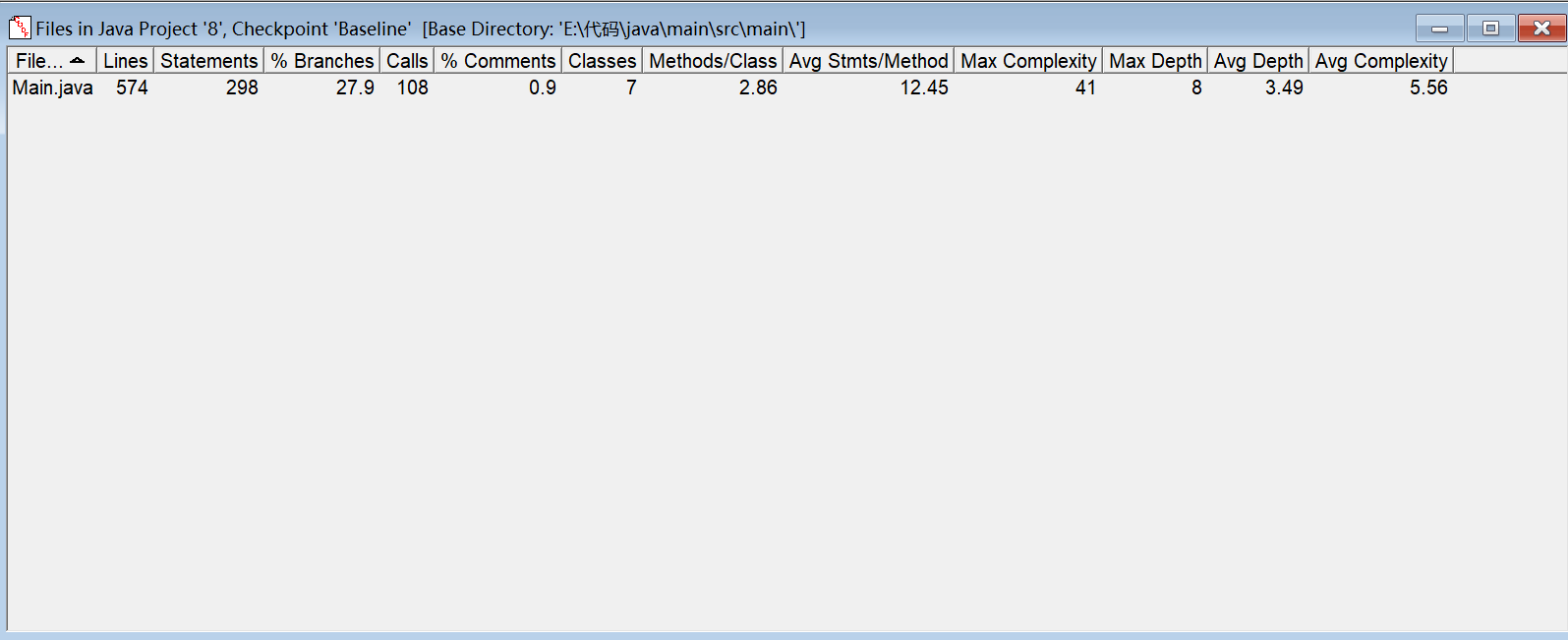
PowerDesigner分析:
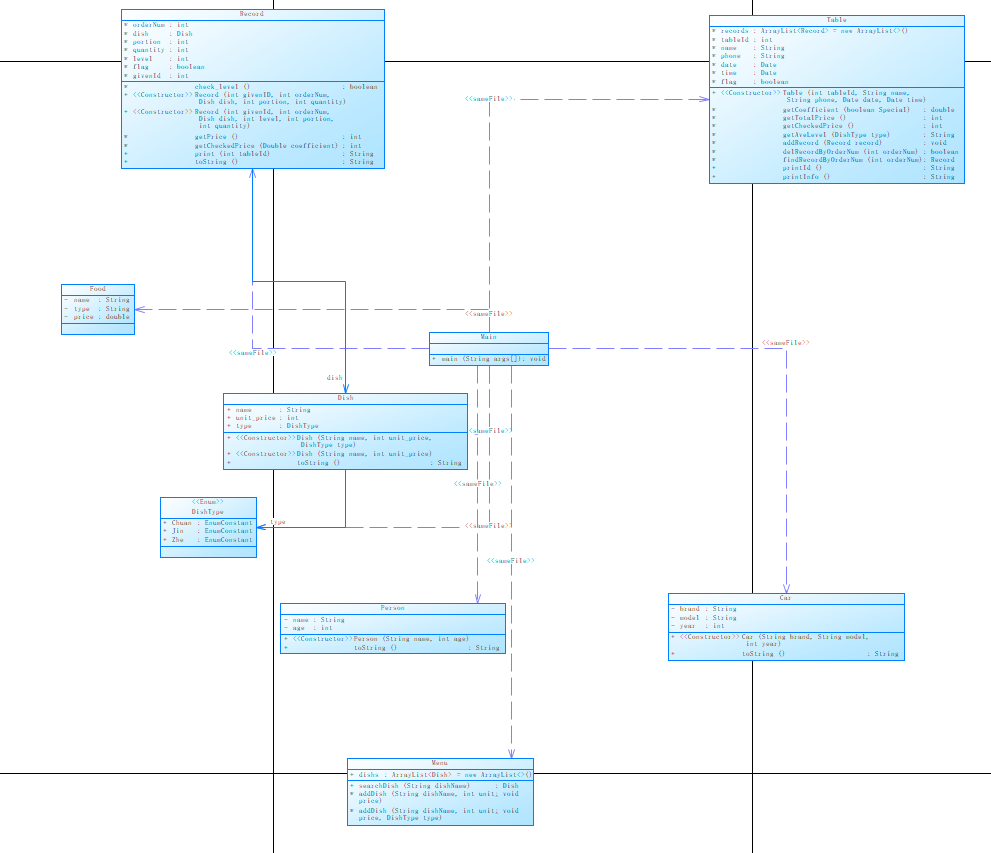
代码设计与分析:这道题目没得满分,测试点晋菜测试点单用户菜品的重复记录和单用户多菜系含错误记录这两个测试点没过去,后续太懒了也没想着去查明错误点在哪。本题对比菜单计价3新增了很多类的创建,包括一些输入格式等等。需要改进的部分肯定是错误的地方不能空放在那里不管啊。整体设计上,代码采用了面向对象的思想,将菜单、菜品、订单、餐桌等概念抽象成类,通过类与类之间的交互实现了餐厅点餐系统的功能。代码结构清晰,易于理解和维护。另外,代码实现了异常处理、日期时间解析、字符串格式化等功能,保证了系统的稳定性和健壮性。
总结:
OK啊,也是成功的写到了总结这一部分。对于6-11周这几次的代码作业,个人还是觉得比较头疼因为菜单计价程序确实很复杂,要写的东西有很多,但是从中也是能学到很多东西的,比如很多格式的输入输出,以及一个完整的菜单计价程序所需要的东西有哪些,哪些是需要你考虑的,类如最后的价格计算,四舍五入这方面的先后计算也挺重要的,很多细节需要自己慢慢琢磨,不是一蹴而就就能完成的。总的来说对于作业来说肯定是学习到了东西,但是还有其他应该改进的地方。比如老师布置的课堂作业总是忘记写导致超时课上也不够认真,希望下次能够注意!!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号