引用数据类型:Scanner、Random
1、Scanner类:该类来完成用户键盘录入,获取到录入的数据。
固定格式:
数据类型 变量名 = new 数据类型();
Scanner i = new Scanner(System.in);
Scanner使用步骤:
导包:import java.util.Scanner;
创建对象实例:Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
调用方法:
int i = sc.nextInt(); 用来接收控制台录入的数字
String s = sc.next(); 用来接收控制台录入的字符串
例如:当x>3时,计算y=2*x+1
当-1<x<3时,计算y=2*x
当x<=-1时。计算y=2*x-1的值
import java.util.Scanner;
class zhezhi
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x=sc.nextInt();
int y =0;
if(x>=3){
y=2 * x + 1;
System.out.println(y);
}else if(-1<x&x<3){
y = 2 * x;
System.out.println(y);
}else if(x<=-1){
y = 2 * x - 1;
System.out.println(y);
}
}
}

2、随机数类:获取随机数
固定格式:
Random使用方式:
import导包:所属包java.util.Random
创建实例格式:Random 变量名 = new Random();
方法简介
public int nextInt(int maxValue) 产生[0,maxValue)范围的随机整数,包含0,不包含maxValue;
public double nextDouble() 产生[0,1)范围的随机小数,包含0.0,不包含1.0。
例如:获取10以内的随机整数和随机小数
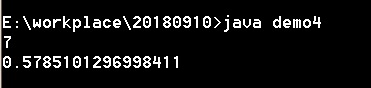
import java.util.Random;
class demo4
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Random r=new Random();
int s=r.nextInt(10);
double b=r.nextDouble();
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
3、流程控制语句
(1)选择结构
-----------------------------if语句:
if (条件语句){
执行语句;
}
-------------------------------if else语句
if (判断条件){
执行语句1
}else{
执行语句2
}
------------------------------if…else if…else语句
public class IfDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int grade = 75; // 定义学生成绩
if (grade > 80) {
// 满足条件 grade > 80
System.out.println("该成绩的等级为优");
} else if (grade > 70) {
// 不满足条件 grade > 80 ,但满足条件 grade > 70
System.out.println("该成绩的等级为良");
} else if (grade > 60) {
// 不满足条件 grade > 70 ,但满足条件 grade > 60
System.out.println("该成绩的等级为中");
} else {
// 不满足条件 grade > 60
System.out.println("该成绩的等级为差");
}
}
}
-----------------if语句和三元运算符
int x = 0;
int y = 1;
int max=0;
if (x > y) {
max = x;
} else {
max = y;
}
int max = x > y ? x : y;
(2)循环语句while
while(循环条件){
执行语句
}
public class WhileDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1; // 定义变量x,初始值为1
while (x <= 4) { // 循环条件
System.out.println("x = " + x); // 条件成立,打印x的值
x++; // x进行自增
}
}
}

(3)循环for
for(初始化表达式; 循环条件; 操作表达式){
执行语句
}
分别用①表示初始化表达式、②表示循环条件、③表示操作表达式、④表示循环体,通过序号来具体分析for循环的执行流程。具体如下:
for(① ; ② ; ③){
④
}
第一步,执行①
第二步,执行②,如果判断结果为true,执行第三步,如果判断结果为false,执行第五步
第三步,执行④
第四步,执行③,然后重复执行第二步
第五步,退出循环
class demo5
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//打印1-4之间的自然数
int i=1;
while (i<=4)
{
System.out.println(i);
i++;
}
for(int j=1;j++;j<=4){
System.out.println(j);
}
int q=1;
do{
System.out.println(q);
q++;
}while(q<=4);
}
}
(4) 循环语句do…while
do {
执行语句
………
} while(循环条件);
(5)无限循环
while(true){}
或
for(;;){}
(6)循环嵌套
for(初始化表达式; 循环条件; 操作表达式) {
………
for(初始化表达式; 循环条件; 操作表达式) {
执行语句
………
}
………
}
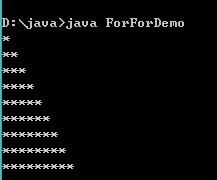
打印三角形:
1public class ForForDemo {
2 public static void main(String[] args) {
3 int i, j; // 定义两个循环变量
4 for (i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { // 外层循环
5 for (j = 1; j <= i; j++) { // 内层循环
6 System.out.print("*"); // 打印*
7 }
8 System.out.print("\n"); // 换行
9 }
10 }
11}
4、 跳转语句(break、continue)
(1) break语句:终止该循环
例如:
public class BreakDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 1; // 定义变量x,初始值为1
while (x <= 4) { // 循环条件
System.out.println("x = " + x); // 条件成立,打印x的值
if (x == 3) {
break;
}
x++; // x进行自增
}
}
}
(2)标记:
当break语句出现在嵌套循环中的内层循环时,它只能跳出内层循环,如果想使用break语句跳出外层循环则需要对外层循环添加标记。
public class BreakDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, j; // 定义两个循环变量
aaa: for (i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { // 外层循环标记
for (j = 1; j <= i; j++) { // 内层循环
if (i > 4) { // 判断i的值是否大于4
break aaa; // 跳出外层循环
}
System.out.print("*"); // 打印*
}
System.out.print("\n"); // 换行
}
}
}
(3)continue语句:终止本次循环,执行下次循环
例如:
public class ContinueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0; // 定义变量sum,用于记住和
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0) { // i是一个偶数,不累加
continue; // 结束本次循环
}
sum += i; // 实现sum和i的累加
}
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
}
}
5、猜数字小游戏
l 后台预先生成一个1-100之间的随机数,用户键盘录入猜数字
l 如果猜对了,打印“恭喜您,答对了”
l 如果猜错了
猜大了:打印“sorry,您猜大了!”
猜小了:打印“sorry,您猜小了!”
l 直到数字猜到为止
public class GuessNumber {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.通过Random类中方法nextInt(),生成一个1-100之间的随机数
int randomNumber = new Random().nextInt(100);
System.out.println("随机数已生成!");
//2.输入猜的数字
System.out.println("----请输入您猜的数字:----");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int enterNumber = sc.nextInt();
//3.通过while循环,进行猜数字对错判断
//猜对,跳出循环,游戏结束
while(enterNumber != randomNumber){
//猜错了,根据结果,给出提示,接着猜数字,游戏继续
if(enterNumber>randomNumber) {
//如果猜大了,打印sorry,您猜大了!继续下一次循环
System.out.println("sorry,您猜大了!继续下一次循环");
}else {
//如果猜小了,打印sorry,您猜小了!继续下一次循环
System.out.println("sorry,您猜小了!继续下一次循环");
}
//输入猜的数字
System.out.println("----请输入您猜的数字:----");
enterNumber = sc.nextInt();
}
System.out.println("恭喜您,答对了!");
}
}
6、流程控制语句:
Switch
switch 条件语句,它只能针对某个表达式的值作出判断,从而决定程序执行哪一段代码。
switch语句的基本语法格式:
switch (表达式){
case 目标值1:
执行语句1
break;
case 目标值2:
执行语句2
break;
......
case 目标值n:
执行语句n
break;
default:
执行语句n+1
break;
}
例如:输入1-7之间的数字,1-5为工作日,6-7为休息日,输入一个1-7之间的数看看是什么
public class SwitchDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int week = 5;
switch (week) {
case 1:
System.out.println("星期一");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("星期二");
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("星期三");
break;
case 4:
System.out.println("星期四");
break;
case 5:
System.out.println("星期五");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("星期六");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("星期天");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入的数字不正确...");
break;
}
}
}






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号