UVA216 UVALive5155 Getting in Line【置换+回溯】
Computer networking requires that the computers in the network be linked.
This problem considers a “linear” network in which the computers are chained together so that each is connected to exactly two others except for the two computers on the ends of the chain which are connected to only one other computer. A picture is shown below. Here the computers are the black dots and their locations in the network are identified by planar coordinates (relative to a coordinate system not shown in the picture).
Distances between linked computers in the network are shown in feet.
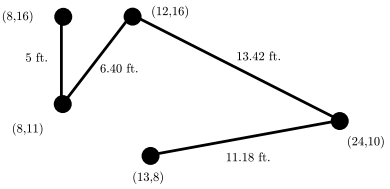
For various reasons it is desirable to minimize the length of cable used.
Your problem is to determine how the computers should be connected into such a chain to minimize the total amount of cable needed. In the installation being constructed, the cabling will run beneath the floor, so the amount of cable used to join 2 adjacent computers on the network will be equal to the distance between the computers plus 16 additional feet of cable to connect from the floor to the computers and provide some slack for ease of installation.
The picture below shows the optimal way of connecting the computers shown above, and the total length of cable required for this configuration is (4+16)+ (5+16) + (5.83+16) + (11.18+16) = 90.01 feet.

Input
The input file will consist of a series of data sets. Each data set will begin with a line consisting of a single number indicating the number of computers in a network. Each network has at least 2 and at most 8 computers. A value of 0 for the number of computers indicates the end of input.
After the initial line in a data set specifying the number of computers in a network, each additional line in the data set will give the coordinates of a computer in the network. These coordinates will be integers in the range 0 to 150. No two computers are at identical locations and each computer will be listed once.
Output
The output for each network should include a line which tells the number of the network (as determined by its position in the input data), and one line for each length of cable to be cut to connect each adjacent pair of computers in the network. The final line should be a sentence indicating the total amount of cable used.
In listing the lengths of cable to be cut, traverse the network from one end to the other. (It makes no difference at which end you start.) Use a format similar to the one shown in the sample output, with a line of asterisks separating output for different networks and with distances in feet printed to 2 decimal places.
Sample Input
6
5 19
55 28
38 101
28 62
111 84
43 116
5
11 27
84 99
142 81
88 30
95 38
3
132 73
49 86
72 111
0
Sample Output
Network #1
Cable requirement to connect (5,19) to (55,28) is 66.80 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (55,28) to (28,62) is 59.42 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (28,62) to (38,101) is 56.26 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (38,101) to (43,116) is 31.81 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (43,116) to (111,84) is 91.15 feet.
Number of feet of cable required is 305.45.
Network #2
Cable requirement to connect (11,27) to (88,30) is 93.06 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (88,30) to (95,38) is 26.63 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (95,38) to (84,99) is 77.98 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (84,99) to (142,81) is 76.73 feet.
Number of feet of cable required is 274.40.
Network #3
Cable requirement to connect (132,73) to (72,111) is 87.02 feet.
Cable requirement to connect (72,111) to (49,86) is 49.97 feet.
Number of feet of cable required is 136.99.
World Finals >> 1992 - Kansas City
问题链接:UVA216 UVALive5155 Getting in Line
问题简述:(略)
问题分析:
给定n个点(n<=8)的坐标,求连接这n个点最新距离。
暴力枚举各个点间的距离即可,可以用置换来求所有点之间的组合,再进行计算。但是,这种方法完全是穷举所有的可能,无法进行加快计算速度的剪枝,未必是最佳方案。
另外一种方法是用回溯法实现,回溯法也可以是一种穷尽搜索法,可以用DFS来实现。然而,回溯法可以加入剪枝条件来加快搜索速度。本问题中,求得一个暂时的最小距离之后,那么部分的距离之和只有小于这个最小距离才需要进一步搜索,否则可以回溯了。具体实现参见DFS代码的第37行。
程序说明:(略)
参考链接:(略)
题记:(略)
AC的C++程序(DFS)如下:
/* UVA216 UVALive5155 Getting in Line */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 8;
struct Point {
int x, y;
} p[N + 1];
int n;
double mind;
bool vis[N + 1];
int rec[N];
int ans[N];
double dist[N + 1][N + 1];
inline double getDist(Point& x, Point& y)
{
return sqrt((x.x - y.x) * (x.x - y.x) + (x.y - y.y) * (x.y - y.y)) + 16;
}
void dfs(int k, int cur, double d)
{
if(k == n) {
if(d < mind) {
mind = d;
memcpy(ans, rec, sizeof(ans));
}
} else {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) {
vis[i] = true;
rec[k] = i;
double nextd = d + dist[cur][i];
if(nextd < mind)
dfs(k + 1, i, nextd);
vis[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int caseno = 0;
while(~scanf("%d", &n) && n) {
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
memset(dist, 0, sizeof(dist));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = i; j <= n; j++)
if(i == j)
dist[i][j] = 0;
else
dist[j][i] = dist[i][j] = getDist(p[i], p[j]);
memset(vis, false, sizeof(vis));
mind = 1e60;
dfs(0, 0, 0);
printf("**********************************************************\n");
printf("Network #%d\n", ++caseno);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
printf("Cable requirement to connect (%d,%d) to (%d,%d) is %.2lf feet.\n",
p[ans[i - 1]].x, p[ans[i - 1]].y, p[ans[i]].x, p[ans[i]].y, dist[ans[i - 1]][ans[i]]);
printf("Number of feet of cable required is %.2lf.\n", mind);
}
return 0;
}
AC的C++程序(置换)如下:
/* UVA216 UVALive5155 Getting in Line */
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 8;
struct Point {
int x, y;
} p[N];
int rec[N];
int ans[N];
double dist[N][N];
inline double getDist(Point& x, Point& y)
{
return sqrt((x.x - y.x) * (x.x - y.x) + (x.y - y.y) * (x.y - y.y)) + 16;
}
int main()
{
int n, caseno = 0;
while(~scanf("%d", &n) && n) {
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d%d", &p[i].x, &p[i].y);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = i; j < n; j++)
if(i == j)
dist[i][j] = 0;
else
dist[j][i] = dist[i][j] = getDist(p[i], p[j]);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
rec[i] = i;
double minv = 1e60;
do {
double r = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++)
r += dist[rec[i - 1]][rec[i]];
if(r < minv) {
minv = r;
memcpy(ans, rec, sizeof(rec));
}
} while(next_permutation(rec, rec + n));
double ansv = 0;
printf("**********************************************************\n");
printf("Network #%d\n", ++caseno);
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
printf("Cable requirement to connect (%d,%d) to (%d,%d) is %.2lf feet.\n",
p[ans[i - 1]].x, p[ans[i - 1]].y, p[ans[i]].x, p[ans[i]].y, dist[ans[i - 1]][ans[i]]);
ansv += dist[ans[i - 1]][ans[i]];
}
printf("Number of feet of cable required is %.2lf.\n", ansv);
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号