深度学习(RepVGG重参数化)
RepVGG的核心思想是:在训练网络时使用复杂结构以获得更优的性能,在推理网络时则将其等价转换为一个简单结构以提高速度。
网络核心结构如下图:
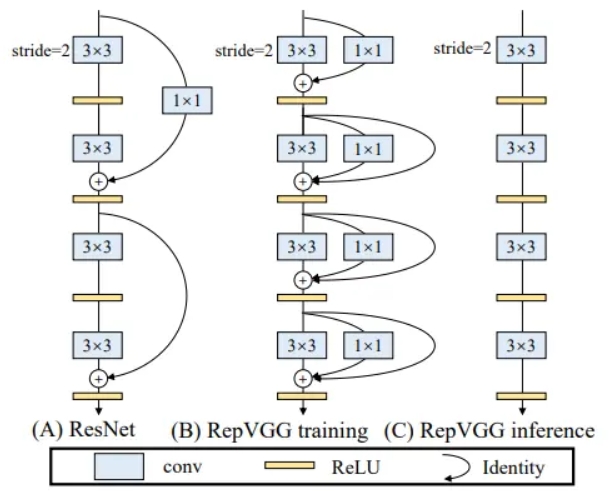
如果是ResNet这样的网络,短连接中间有一个非线性层,则没有办法重参数化。
所以RepVGG中将3*3结构,1*1结构和直连结构并联在一起,从而在训练时能够学到更多参数。
在推理时则将三个分支参数合并为3*3结构,从而提高推理速度。
下面代码是按照自己的理解实现的重参数化Block,分为训练和部署两个分支,结果通过了allclose验证。
import torch import torch.nn as nn class RepVGGBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, channels, deploy): super(RepVGGBlock, self).__init__() self.deploy = deploy self.channels = channels self.conv3x3 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True) self.bn3x3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels) self.conv1x1 = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True) self.bn1x1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels) self.bn = nn.BatchNorm2d(channels) if(deploy==False): self.conv3x3.weight.data = torch.randn(channels,channels,3,3) self.conv3x3.bias.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn3x3.weight.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn3x3.bias.data = torch.randn(channels) self.conv1x1.weight.data = torch.randn(channels,channels,1,1) self.conv1x1.bias.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn1x1.weight.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn1x1.bias.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn.weight.data = torch.randn(channels) self.bn.bias.data = torch.randn(channels) # Fusion conv self.fusion_conv = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) def forward(self, x): if self.deploy==False: x1 = self.conv3x3(x) x1 = self.bn3x3(x1) x2 = self.conv1x1(x) x2 = self.bn1x1(x2) x = self.bn(x) x = x1 + x2 + x else: x = self.fusion_conv(x) return self.relu(x) def reparam3x3(self): conv_w = self.conv3x3.weight conv_b = self.conv3x3.bias bn_w = self.bn3x3.weight bn_b = self.bn3x3.bias bn_w = bn_w.div(torch.sqrt(self.bn3x3.eps + self.bn3x3.running_var)) fusion_w = torch.mm(torch.diag(bn_w), conv_w.view(self.channels, -1)).view(self.channels,self.channels,3,3) fusion_b = bn_w * (conv_b - self.bn3x3.running_mean) + bn_b print(fusion_w.shape,fusion_b.shape) return fusion_w, fusion_b def reparam1x1(self): conv_w = self.conv1x1.weight conv_b = self.conv1x1.bias bn_w = self.bn1x1.weight bn_b = self.bn1x1.bias bn_w = bn_w.div(torch.sqrt(self.bn1x1.eps + self.bn1x1.running_var)) fusion_w = torch.mm(torch.diag(bn_w), conv_w.view(self.channels, -1)).view(self.channels,self.channels,1,1) w = torch.zeros(self.channels, self.channels, 3, 3) w[:,:,1,1] = fusion_w.squeeze(2).squeeze(2) fusion_b = bn_w * (conv_b - self.bn1x1.running_mean) + bn_b print(w.shape,fusion_b.shape) return w , fusion_b def reparamBn(self): bn_w = self.bn.weight bn_b = self.bn.bias bn_w = bn_w.div(torch.sqrt(self.bn.eps + self.bn.running_var)) bn_w = torch.diag(bn_w).view(self.channels,self.channels,1,1) w = torch.zeros(self.channels, self.channels, 3, 3) w[:,:,1,1] = bn_w.squeeze(2).squeeze(2) print(w.shape,bn_b.shape) return w, bn_b def reparam(self): w_3x3, b_3x3 = self.reparam3x3() w_1x1, b_1x1 = self.reparam1x1() w, b = self.reparamBn() self.fusion_conv.weight.data = (w_3x3 + w_1x1+w).clone() self.fusion_conv.bias.data = (b_3x3 + b_1x1+b).clone() x = torch.randn(1, 20, 224, 224) net1 = RepVGGBlock(20,deploy=False) torch.save(net1.state_dict(), "repvgg.pth") net1.eval() y1 = net1(x) net2 = RepVGGBlock(20,deploy=True) net2.load_state_dict(torch.load("repvgg.pth")) net2.reparam() net2.eval() y2 = net2(x) print(y1.shape,y2.shape) print(torch.allclose(y1, y2, atol=1e-4)) torch.onnx.export(net1, x, "repvgg.onnx", input_names=['input'], output_names=['output']) torch.onnx.export(net2, x, "repvgg_deploy.onnx", input_names=['input'], output_names=['output'])




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号