深度学习(yolo11训练)
这里记录一下用yolo11训练coco数据集。
1、下载coco数据集:https://cocodataset.org/#download,下载这三个文件即可:2017 Train images [118K/18GB],2017 Val images [5K/1GB],2017 Train/Val annotations [241MB]。
2、使用下面脚本将coco数据集label转为yolo能识别地格式,json_path和label_path改为自己的目录,val和train分别执行一次。
import os import json from tqdm import tqdm import argparse # 生成训练集标签(换成自己的路径) json_path = '/home/tc/Downloads/coco/annotations_trainval2017/annotations/instances_val2017.json' label_path = '/home/tc/Downloads/coco/label/val' parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() parser.add_argument('--json_path', default=json_path, type=str, help="input: coco format(json)") parser.add_argument('--save_path', default=label_path, type=str, help="specify where to save the output dir of labels") arg = parser.parse_args() def convert(size, box): dw = 1. / (size[0]) dh = 1. / (size[1]) x = box[0] + box[2] / 2.0 y = box[1] + box[3] / 2.0 w = box[2] h = box[3] x = x * dw w = w * dw y = y * dh h = h * dh return (x, y, w, h) if __name__ == '__main__': json_file = arg.json_path # COCO Object Instance 类型的标注 ana_txt_save_path = arg.save_path # 保存的路径 data = json.load(open(json_file, 'r')) if not os.path.exists(ana_txt_save_path): os.makedirs(ana_txt_save_path) print(list(data)) id_map = {} for i, category in enumerate(data['categories']): id_map[category['id']] = i # 通过事先建表来降低时间复杂度 max_id = 0 for img in data['images']: max_id = max(max_id, img['id']) img_ann_dict = [[] for i in range(max_id + 1)] for i, ann in enumerate(data['annotations']): img_ann_dict[ann['image_id']].append(i) for img in tqdm(data['images']): filename = img["file_name"] img_width = img["width"] img_height = img["height"] img_id = img["id"] head, tail = os.path.splitext(filename) ana_txt_name = head + ".txt" f_txt = open(os.path.join(ana_txt_save_path, ana_txt_name), 'w') for ann_id in img_ann_dict[img_id]: ann = data['annotations'][ann_id] box = convert((img_width, img_height), ann["bbox"]) f_txt.write("%s %s %s %s %s\n" % (id_map[ann["category_id"]], box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3])) f_txt.close()
3、使用下面脚本将val和train的文件名导出为单独的文件val.txt和train.txt,同样是val和train各执行一次。
import os # 指定要读取的文件夹路径 folder_path = "/home/tc/Downloads/coco/images/val2017" # 替换为你的文件夹路径 output_file = "val.txt" # 存储结果的txt文件 # 获取文件夹中所有文件的绝对路径 file_paths = [os.path.join(folder_path, f) for f in os.listdir(folder_path) if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(folder_path, f))] # 将文件路径按行写入txt文件 with open(output_file, "w") as f: for file_path in file_paths: f.write(file_path + "\n") print(f"文件路径已存储在 {output_file} 中。")
4、配置yolo训练yaml文件,根据自己的路径修改配置,文件是yolo工程自带的。
# Ultralytics 🚀 AGPL-3.0 License - https://ultralytics.com/license # COCO 2017 dataset https://cocodataset.org by Microsoft # Documentation: https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/detect/coco/ # Example usage: yolo train data=coco.yaml # parent # ├── ultralytics # └── datasets # └── coco ← downloads here (20.1 GB) # Train/val/test sets as 1) dir: path/to/imgs, 2) file: path/to/imgs.txt, or 3) list: [path/to/imgs1, path/to/imgs2, ..] path: /home/tc/Downloads/coco # dataset root dir train: train2017.txt # train images (relative to 'path') 118287 images val: val2017.txt # val images (relative to 'path') 5000 images test: test-dev2017.txt # 20288 of 40670 images, submit to https://competitions.codalab.org/competitions/20794 # Classes names: 0: person 1: bicycle 2: car 3: motorcycle 4: airplane 5: bus 6: train 7: truck 8: boat 9: traffic light 10: fire hydrant 11: stop sign 12: parking meter 13: bench 14: bird 15: cat 16: dog 17: horse 18: sheep 19: cow 20: elephant 21: bear 22: zebra 23: giraffe 24: backpack 25: umbrella 26: handbag 27: tie 28: suitcase 29: frisbee 30: skis 31: snowboard 32: sports ball 33: kite 34: baseball bat 35: baseball glove 36: skateboard 37: surfboard 38: tennis racket 39: bottle 40: wine glass 41: cup 42: fork 43: knife 44: spoon 45: bowl 46: banana 47: apple 48: sandwich 49: orange 50: broccoli 51: carrot 52: hot dog 53: pizza 54: donut 55: cake 56: chair 57: couch 58: potted plant 59: bed 60: dining table 61: toilet 62: tv 63: laptop 64: mouse 65: remote 66: keyboard 67: cell phone 68: microwave 69: oven 70: toaster 71: sink 72: refrigerator 73: book 74: clock 75: vase 76: scissors 77: teddy bear 78: hair drier 79: toothbrush
5、执行训练脚本:
from ultralytics import YOLO import multiprocessing if __name__ == "__main__": multiprocessing.freeze_support() model = YOLO("yolo11l.pt") # load a pretrained model (recommended for training) # Train the model results = model.train(data="coco.yaml", epochs=10, imgsz=640)
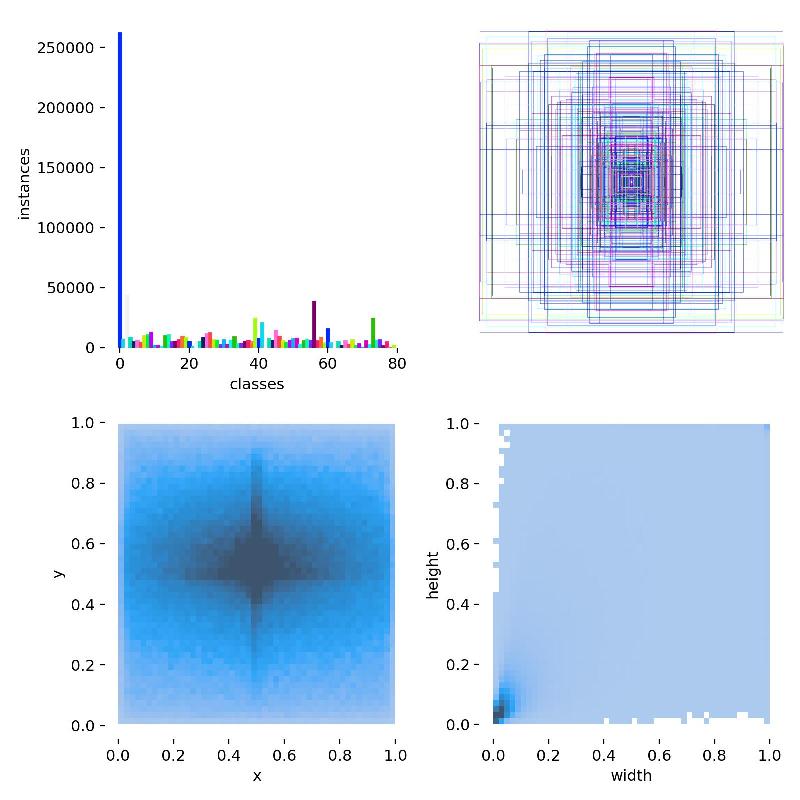
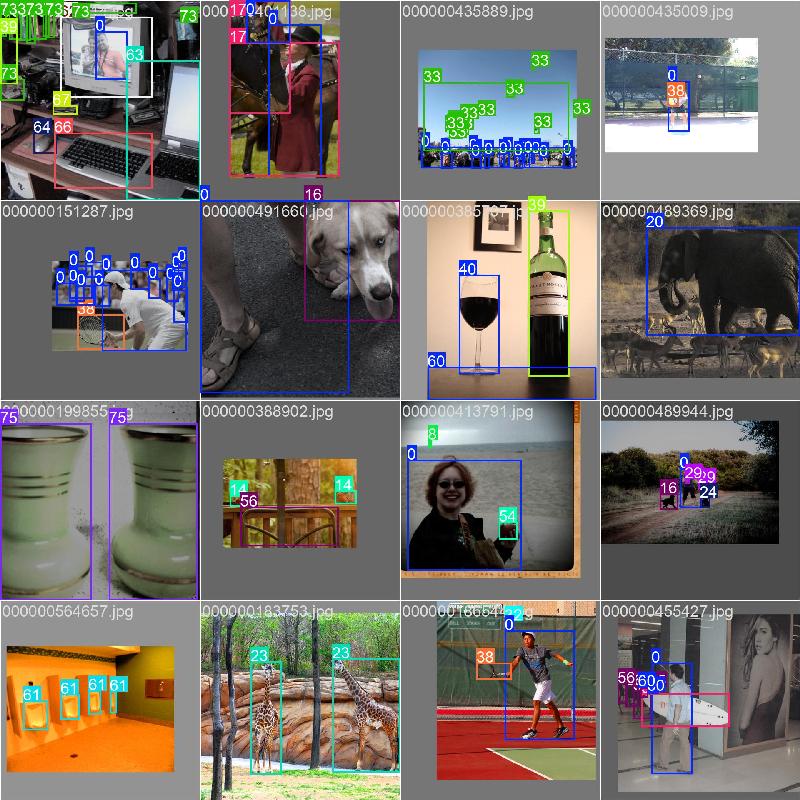
6、如果一切顺利,就可以等训练结束,训练后在./runs/detect/train/下有中间结果和模型文件,下面是中间生成的一些结果:





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号