------------恢复内容开始------------
一、
Spring-MVC 全称应该是spring-webmvc,即springmvc是spring框架的一个主要支持Javaweb的一个模块。
springMVC对servlet进行封装,避免繁琐的获取表单参数,多余的serlvet服务类等代码
二、
相较于struct2来说:
使用简单、性能安全性更加优秀、拓展性强
三、
优点:
清晰地角色划分
灵活的配置功能
提供了大量的控制器接口和实现类
国际化支持
面向接口编程
Spring提供了Web应用开发的一整套流程,不仅仅是MVC,他们之间可以很方便的结合一起。(意思就是springmvc是spring原生的,用起来不会有什么兼容问题)
四、核心类及接口
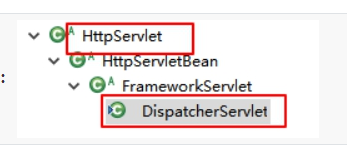
核心类:DispatcherServlet前端控制器 其父类是Httpservlet
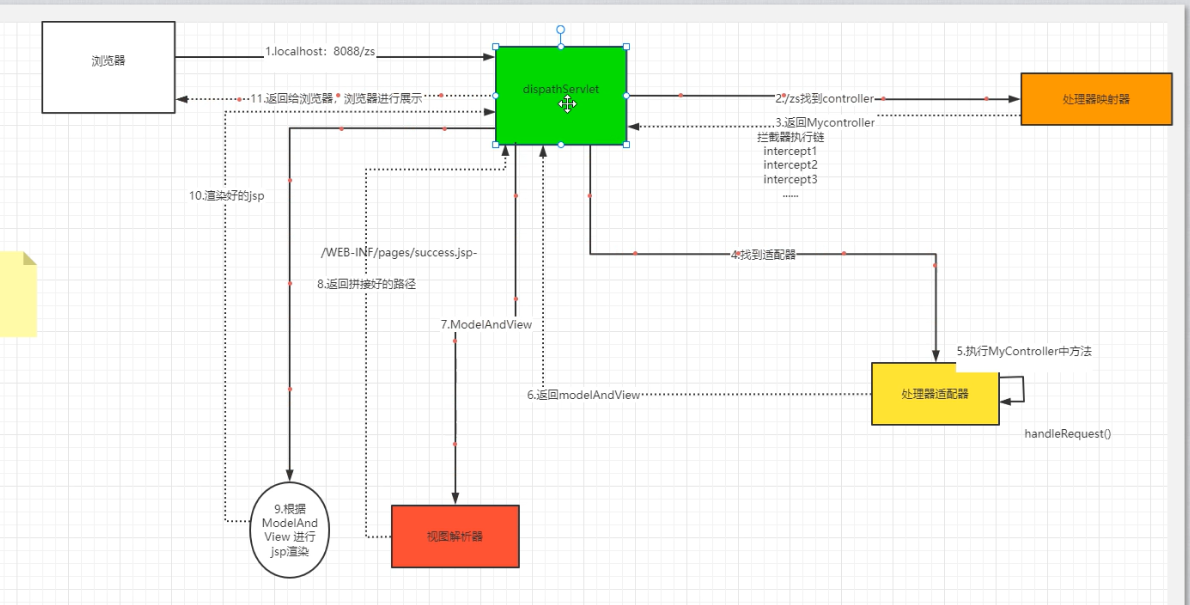
作用:接收请求,响应结果,相当于转发器,是SpringMVC的中央处理器。springMVC的入口
补图:
处理器():
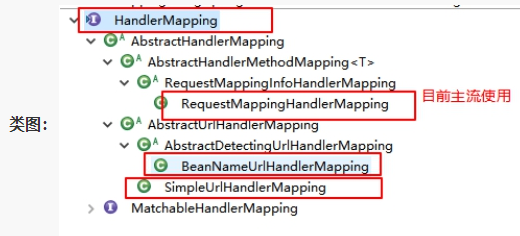
作用:前端控制器接收到请求,解析uri,HandlerMapping负责查找Handler处理器对象.(前后端的桥梁)
ModelAndView模型与视图对象

实战开始:
(这次写完发现了一个很白痴的错误,太久没写web项目不小心把lib放到项目下面导致一直报404浪费了快两小时排错,记得lib包要放到webinf下面)
1.搭建Web项目 略
2.lib包导入 略
3.controller层编写
package stu.adam.controller.impl; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; /** * @program: SpringMVC-1 * @description: * @author: adam * @create: 2021-12-16 19:42 **/ public class MsgControllerImpl implements Controller { @Override public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception { ModelAndView mav=new ModelAndView(); mav.setViewName("success"); mav.addObject("msg","你好~我是控制层"); return mav; } }
springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!--映射器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/> <!--适配器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"/> <!--视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> <!--spring 控制反转 bean给到容器中--> <bean name="/zs" class="stu.adam.controller.impl.MsgControllerImpl"/> </beans>
web.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <servlet> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:springmvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>dispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
效果:

上面那个是基础版本,开始改进(指使用注解 以及springxml处理映射器和处理器适配器的导入包改改,然后就是换成包扫描)
impl2
package stu.adam.controller.impl; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; /** * @program: SpringMVC-1 * @description: * @author: adam * @create: 2021-12-16 21:21 **/ @Controller public class MsgControllerImpl2 { @RequestMapping("/find") public ModelAndView findList(){ ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg"," annotation select find!"); return modelAndView; } @RequestMapping("/add") public ModelAndView addList(){ ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg"," annotation select add!"); return modelAndView; } }
springmvc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--包扫描--> <context:component-scan base-package="stu.adam.controller.impl"/> <!--映射器 变--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"/> <!--适配器 变--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"/> <!--视图解析器--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <!--前缀--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/pages/"/> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/> </bean> <!--spring 控制反转 bean给到容器中--> <!--<bean name="/zs" class="stu.adam.controller.impl.MsgControllerImpl"/>--> </beans>
web.xml不变 ,说实话比上一种好用多了
效果:

mapping补充以及优化测试:
- @GetMapping :只支持Get请求 - @DeleteMapping:只支持delete请求 - @PutMapping:只支持put请求 - @PostMapping:只支持post请求 - @RequestMapping : 支持 所有请求类型
接收请求类型(服务器类别,这些类别是汽车标签,TCP是汽车,服务器/客户端是运输公司)
HTTP只是个行为准则,而TCP才是GET和POST怎么实现的基本。
GET,
HEAD,
POST,
PUT,
PATCH,
DELETE,
OPTIONS,
TRACE;
//写到这看到了一篇好文,分享下,原博主(大概)链接:javaweb开发之get与post请求的区别 - 魔笛手 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
GET和POST是HTTP请求的两种基本方法,要说它们的区别,接触过WEB开发的人都能说出一二。
最直观的区别就是GET把参数包含在URL中,POST通过request body传递参数。
你可能自己写过无数个GET和POST请求,或者已经看过很多权威网站总结出的他们的区别,你非常清楚知道什么时候该用什么。
当你在面试中被问到这个问题,你的内心充满了自信和喜悦。
你轻轻松松的给出了一个“标准答案”:
GET在浏览器回退时是无害的,而POST会再次提交请求。
GET产生的URL地址可以被Bookmark,而POST不可以。
GET请求会被浏览器主动cache,而POST不会,除非手动设置。
GET请求只能进行url编码,而POST支持多种编码方式。
GET请求参数会被完整保留在浏览器历史记录里,而POST中的参数不会被保留。
GET请求在URL中传送的参数是有长度限制的,而POST么有。
对参数的数据类型,GET只接受ASCII字符,而POST没有限制。
GET比POST更不安全,因为参数直接暴露在URL上,所以不能用来传递敏感信息。
GET参数通过URL传递,POST放在Request body中。
(本标准答案参考自w3schools)
“很遗憾,这不是我们要的回答!”
请告诉我真相。。。
如果我告诉你GET和POST本质上没有区别你信吗?
让我们扒下GET和POST的外衣,坦诚相见吧!
GET和POST是什么?HTTP协议中的两种发送请求的方法。
HTTP是什么?HTTP是基于TCP/IP的关于数据如何在万维网中如何通信的协议。
HTTP的底层是TCP/IP。所以GET和POST的底层也是TCP/IP,也就是说,GET/POST都是TCP链接。GET和POST能做的事情是一样一样的。你要给GET加上request body,给POST带上url参数,技术上是完全行的通的。
那么,“标准答案”里的那些区别是怎么回事?
在我大万维网世界中,TCP就像汽车,我们用TCP来运输数据,它很可靠,从来不会发生丢件少件的现象。但是如果路上跑的全是看起来一模一样的汽车,那这个世界看起来是一团混乱,送急件的汽车可能被前面满载货物的汽车拦堵在路上,整个交通系统一定会瘫痪。为了避免这种情况发生,交通规则HTTP诞生了。HTTP给汽车运输设定了好几个服务类别,有GET, POST, PUT, DELETE等等,HTTP规定,当执行GET请求的时候,要给汽车贴上GET的标签(设置method为GET),而且要求把传送的数据放在车顶上(url中)以方便记录。如果是POST请求,就要在车上贴上POST的标签,并把货物放在车厢里。当然,你也可以在GET的时候往车厢内偷偷藏点货物,但是这是很不光彩;也可以在POST的时候在车顶上也放一些数据,让人觉得傻乎乎的。HTTP只是个行为准则,而TCP才是GET和POST怎么实现的基本。
但是,我们只看到HTTP对GET和POST参数的传送渠道(url还是requrest body)提出了要求。“标准答案”里关于参数大小的限制又是从哪来的呢?
在我大万维网世界中,还有另一个重要的角色:运输公司。不同的浏览器(发起http请求)和服务器(接受http请求)就是不同的运输公司。 虽然理论上,你可以在车顶上无限的堆货物(url中无限加参数)。但是运输公司可不傻,装货和卸货也是有很大成本的,他们会限制单次运输量来控制风险,数据量太大对浏览器和服务器都是很大负担。业界不成文的规定是,(大多数)浏览器通常都会限制url长度在2K个字节,而(大多数)服务器最多处理64K大小的url。超过的部分,恕不处理。如果你用GET服务,在request body偷偷藏了数据,不同服务器的处理方式也是不同的,有些服务器会帮你卸货,读出数据,有些服务器直接忽略,所以,虽然GET可以带request body,也不能保证一定能被接收到哦。
好了,现在你知道,GET和POST本质上就是TCP链接,并无差别。但是由于HTTP的规定和浏览器/服务器的限制,导致他们在应用过程中体现出一些不同。
你以为本文就这么结束了?
我们的大BOSS还等着出场呢。。。
这位BOSS有多神秘?当你试图在网上找“GET和POST的区别”的时候,那些你会看到的搜索结果里,从没有提到他。他究竟是什么呢。。。
GET和POST还有一个重大区别,简单的说:
GET产生一个TCP数据包;POST产生两个TCP数据包。
长的说:
对于GET方式的请求,浏览器会把http header和data一并发送出去,服务器响应200(返回数据);
而对于POST,浏览器先发送header,服务器响应100 continue,浏览器再发送data,服务器响应200 ok(返回数据)。
也就是说,GET只需要汽车跑一趟就把货送到了,而POST得跑两趟,第一趟,先去和服务器打个招呼“嗨,我等下要送一批货来,你们打开门迎接我”,然后再回头把货送过去。
因为POST需要两步,时间上消耗的要多一点,看起来GET比POST更有效。因此Yahoo团队有推荐用GET替换POST来优化网站性能。但这是一个坑!跳入需谨慎。为什么?
1. GET与POST都有自己的语义,不能随便混用。
2. 据研究,在网络环境好的情况下,发一次包的时间和发两次包的时间差别基本可以无视。而在网络环境差的情况下,两次包的TCP在验证数据包完整性上,有非常大的优点。
3. 并不是所有浏览器都会在POST中发送两次包,Firefox就只发送一次。
参数测试:
package stu.adam.controller.impl;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import stu.adam.entity.MyUser;
import stu.adam.entity.MyUserList;
import stu.adam.entity.User;
import javax.xml.bind.SchemaOutputResolver;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import static com.sun.xml.internal.ws.api.model.wsdl.WSDLBoundOperation.ANONYMOUS.required;
/**
* @program: SpringMVC-1
* @description:
* @author: adam
* @create: 2021-12-16 21:21
**/
@Controller
public class MsgControllerImpl2 {
@RequestMapping("/find")
public ModelAndView findList() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", " annotation select find!");
return modelAndView;
}
@GetMapping("/add")
public ModelAndView addList() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", " annotation select add!");
return modelAndView;
}
/*
* get和Post的区别
* 最直观的区别就是GET把参数包含在URL中,POST通过request body传递参数。
*
*
GET在浏览器回退时是无害的,而POST会再次提交请求。
GET产生的URL地址可以被Bookmark,而POST不可以。
GET请求会被浏览器主动cache,而POST不会,除非手动设置。
GET请求只能进行url编码,而POST支持多种编码方式。
GET请求参数会被完整保留在浏览器历史记录里,而POST中的参数不会被保留。
GET请求在URL中传送的参数是有长度限制的,而POST么有。
对参数的数据类型,GET只接受ASCII字符,而POST没有限制。
GET比POST更不安全,因为参数直接暴露在URL上,所以不能用来传递敏感信息。
GET参数通过URL传递,POST放在Request body中。
(本标准答案参考自w3schools)
* */
//这么写会出bug
@DeleteMapping("/delete")
public ModelAndView deleteList() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", " annotation select delete!");
return modelAndView;
}
//这么写会出bug
@PutMapping(value = "/update")
public ModelAndView updateList() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", "annotation select update!");
return modelAndView;
}
//这么写会出bug 现在暂时不行
//对于GET方式的请求,浏览器会把http header和data一并发送出去,服务器响应200(返回数据);
//而对于POST,浏览器先发送header,服务器响应100 continue,浏览器再发送data,服务器响应200 ok(返回数据)。
@RequestMapping(value = "/update2", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ModelAndView updateList2() {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg", "annotation select update!");
return modelAndView;
}
//===========================================================================================================================
/*
* 参数类型接收
* */
// 基本参数类型
@GetMapping("/common")
public ModelAndView CsTest(String username){
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",username);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//基本参数类型 别名注解使用
@GetMapping("/common2")
public ModelAndView CsTest2(@RequestParam("asd1") String username){
ModelAndView modelAndView=new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",username);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//传数组
@GetMapping("/array")
public ModelAndView arraytest(String[] array1){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg", Arrays.toString(array1));
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//传对象(自定义类型)
@GetMapping("Object")
public ModelAndView arraytest(User user){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",user);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//传对象(包装自定义类型2 就是套娃 对象里面套对象)
@GetMapping("Object2")
public ModelAndView arraytest2(MyUser user){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",user);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//传list集合
@GetMapping("list")
public ModelAndView list(MyUserList userlist){
System.out.println(userlist);
System.out.println(userlist.toString());
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",userlist);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
//传map
@GetMapping("map")
public ModelAndView map(stu.adam.entity.Map map){
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.addObject("msg",map);
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView;
}
/**/
//传json
// 使用Postmapping会出错
// @PostMapping("/json")
// @GetMapping(value = "/json")
@RequestMapping(value = "json",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView json(@RequestBody User user){
System.out.println("user====>" +user);
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
modelAndView.addObject("msg",user);
return modelAndView;
}
}
太多了 懒得写了:
<%-- Created by IntelliJ IDEA. User: Administrator Date: 2021/12/16 Time: 19:50 To change this template use File | Settings | File Templates. --%> <%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %> <html> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1 style="background-color: #ffa2d9">我是success页面</h1> ${msg} <form action="/common" method="get"> 姓名:<input type="text" name="asd"> <input type="submit" value="commit"> </form> <%--<form action="/common" method="get">--%> <%--姓名:<input type="text" name="asd">--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/common2" method="get">--%> <%--姓名:<input type="text" name="asd1">--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/array" method="get">--%> <%--兴趣:--%> <%--<input type="text" name="array1" value="1 篮球">--%> <%--<input type="text" name="array1" value="2 足球">--%> <%--<input type="text" name="array1" value="3 乒乓球">--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/Object" method="get">--%> <%--用户:--%> <%--<input type="text" name="id" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="username" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="pwd" >--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/Object2" method="get">--%> <%--用户:--%> <%--<input type="text" name="User.id" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="User.username" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="User.pwd" >--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/list" method="get">--%> <%--用户list:--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[0].id" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[0].username" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[0].pwd" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[1].id" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[1].username" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="userlist[1].pwd" >--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/map" method="get">--%> <%--用户:--%> <%--<input type="text" name="map['id']" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="map['name']" >--%> <%--<input type="text" name="map['qwe']" >--%> <%--<input type="submit" value="commit">--%> <%--</form>--%> <%--<form action="/json" method="get">--%> <%--123--%> <%--</form>--%> </body> </html>
package com.javasm.springmvc.controller; import com.javasm.springmvc.entity.*; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.Map; /** * @Author:liulei * @Version:1.0 * @Date:2021/12/16-11:38 * @Since:jdk1.8 * @Description: */ @Controller public class SecondController { // /zs @RequestMapping("/select") public ModelAndView findList(String username,@RequestParam("userage") Integer age) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { // String s = new String(username.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "utf-8"); System.out.println("username==="+username); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 System.out.println("userage===="+age); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 select "+username+"---------"+age); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/add") public ModelAndView add(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 add"); return modelAndView; } @PutMapping("/update") public ModelAndView update(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 update"); return modelAndView; } @DeleteMapping("/delete") public ModelAndView delete(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 delete"); return modelAndView; } //使用 @RequestMapping,只接收post请求 @RequestMapping(value = "/addUser",method = RequestMethod.POST) public ModelAndView addUser(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 addUser"); return modelAndView; } //使用 @RequestMapping,只接收post请求 @RequestMapping(value = "/updateUser",method = RequestMethod.PUT) public ModelAndView updateUser(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 updateUser"); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/array") public ModelAndView array(@RequestParam("hobby") String [] hobby1){ System.out.println("hobby==="+Arrays.toString(hobby1)); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 array=== "+Arrays.toString(hobby1)); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/dilraba") public ModelAndView dilraba(Dilraba dilraba) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { // String name = dilraba.getName(); // String name1 = new String(name.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"), "utf-8"); System.out.println("dilraba==="+dilraba); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 dilraba=== "+dilraba); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/myDilraba") public ModelAndView myDilraba(MyDilraba myDilraba){ System.out.println("myDilraba==="+myDilraba); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 myDilraba=== "+myDilraba); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/myCustomer") public ModelAndView myCustomer(MyCustomer myCustomer){ System.out.println("myCustomer==="+myCustomer); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 myCustomer=== "+myCustomer); return modelAndView; } @GetMapping("/myMap") public ModelAndView myMap(MyMap myMap){ System.out.println("myMap==="+myMap); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 myMap=== "+myMap); return modelAndView; } @PostMapping("/user") // User user 接收的是 key=value 的,不能接收json格式 //接收json格式 :因为json格式的字符串在 请求体里,所以加@RequestBody 去接收 public ModelAndView user(@RequestBody User user){ System.out.println("user==="+user); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 user=== "+user); return modelAndView; } @PostMapping("/userMap") // User user 接收的是 key=value 的,不能接收json格式 //接收json格式 :因为json格式的字符串在 请求体里,所以加@RequestBody 去接收 public ModelAndView map(@RequestBody Map<String,Object> map){ System.out.println("map==="+map); //age不能接收到,因为与 前端传过来的 userage 不一致,封装不上 //springMVC帮我们自动封装了接收参数,但是要求 后台的接收参数名与前端传过来的变量名一致 ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("success"); modelAndView.addObject("msg","springMVC 优化 map=== "+map); return modelAndView; } }
------------恢复内容结束------------


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号