数学——Euler方法求解微分方程详解(python3)
数学——Euler方法求解微分方程详解(python3)
分享是最快乐的一件事儿,写出好文章,分享新知识,是一件费时费力的事儿,一分耕耘一分收获,希望自己从菜鸟逐渐转变为技术原创大神,大家的支持、点赞以及打赏是我持续耕耘的动力。谢谢每一位读者!
算法的数学描述图解
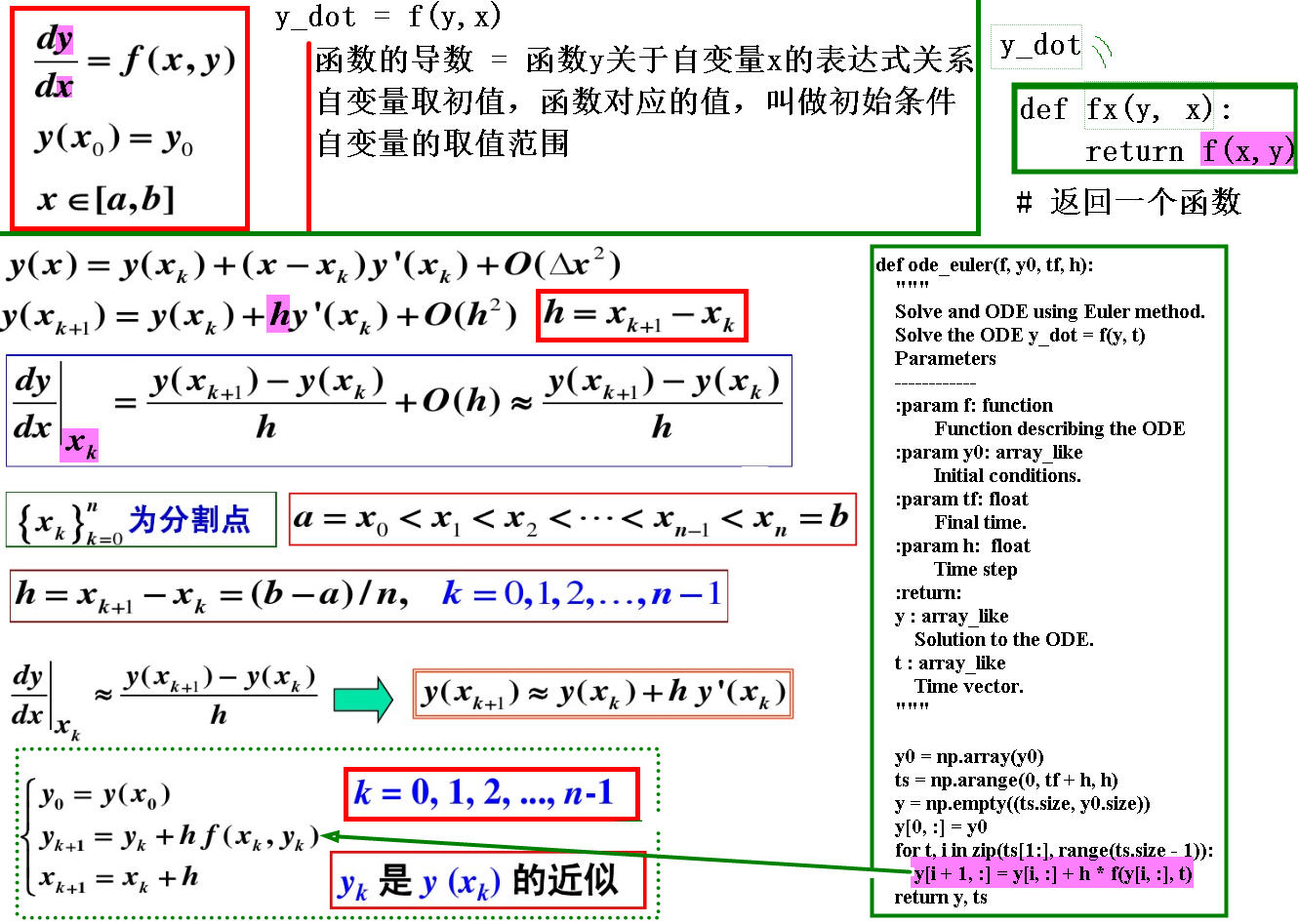
实例
用Euler算法求解初值问题
dydx=y+2xy2dydx=y+2xy2
初始条件y(0)=1y(0)=1,自变量的取值范围x∈[0,2]x∈[0,2]
算法Python3代码求解
# 导入包
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义求解函数 y_dot = y + 2*x/(y*y)
def fx(y, x):
return y + 2*x/(y*y)
# 算法定义
def ode_euler(f, y0, tf, h):
"""
Solve and ODE using Euler method.
Solve the ODE y_dot = f(y, t)
Parameters
------------
:param f: function
Function describing the ODE
:param y0: array_like
Initial conditions.
:param tf: float
Final time.
:param h: float
Time step
:return:
y : array_like
Solution to the ODE.
t : array_like
Time vector.
"""
y0 = np.array(y0)
ts = np.arange(0, tf + h, h)
y = np.empty((ts.size, y0.size))
y[0, :] = y0
for t, i in zip(ts[1:], range(ts.size - 1)):
y[i + 1, :] = y[i, :] + h * f(y[i, :], t)
return y, ts
# 实例应用案例
def newton_cooling_example():
print('Solving Newton Cooling ODE...')
y, ts = ode_euler(fx, 1, 2, 0.01)
print('Done.')
plt.figure()
plt.plot(ts, y)
plt.xlabel('time [s]')
plt.title('Solution to the Newton cooling equation')
plt.show()代码中的部分函数理解
numpy.array
numpy.array(object, dtype=None, copy=True, order='K', subok=False, ndmin=0)
参考numpy.array
output:创建一个array,返回类型为ndarray
实例
np.array([1, 2, 3.0]) # array([1., 2., 3.])
np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) # array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
np.array([1, 2, 3], dtype=complex) # array([1.+0.j, 2.+0.j, 3.+0.j])numpy.arange
参考numpy.arangenumpy.arange([start, ]stop, [step, ]dtype=None)
作用:在给定间隔内返回均匀间隔的值。
值在半开区间[start, stop)内生成(换句话说,包括开始但不包括终止)。返回的是ndarray而不是列表。
np.arange()函数返回一个有终点和起点的固定步长的排列,如[1,2,3,4,5],起点是1,终点是5,步长为1。
参数个数情况: np.arange()函数分为一个参数,两个参数,三个参数三种情况 :
1. 一个参数时,参数值为终点,起点取默认值0,步长取默认值1。
2. 两个参数时,第一个参数为起点,第二个参数为终点,步长取默认值1。
3. 三个参数时,第一个参数为起点,第二个参数为终点,第三个参数为步长。其中步长支持小数。案例
np.arange(3,7) # array([3, 4, 5, 6])
np.arange(3,7,2) # array([3, 5])numpy.ma.size
numpy.ma.size(obj, axis=None)
参考
案例
a = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]])
np.size(a) # 6
np.size(a,1) # 3
np.size(a,0) # 2numpy.empty
参考numpy.empty(shape, dtype=float, order='C')
shape : int or tuple of int Shape of the empty array, e.g., (2, 3) or 2.
out : ndarray
案例
np.empty([2, 2])
# 结果
array([[ -9.74499359e+001, 6.69583040e-309],
[ 2.13182611e-314, 3.06959433e-309]]) #random
np.empty([2, 2], dtype=int)
# 结果
array([[-1073741821, -1067949133],
[ 496041986, 19249760]]) #random

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号