python自动化_day3_文件操作及编码的补充
1、文件操作:如何用python处理一个文件
打开方法:1、文件路径,2、编码方式:utf-8,3、动作mode,读,读写,写读,。。。。
1 #f1 = open('路径',mode='r',encoding='utf-8') 2 #content = f1.read() 3 print(content)
f1,文件句柄,文件对象,file,f_handle,file_handle,f_obj
open 不是python的指令,是win的指令
windows 默认编码方式gbk,linux默认编码方式utf-8,mac默认编码方式utf-8
1、打开文件,产生文件句柄,
2、操作文件句柄
3、关闭文件。f1.close()
默认文件操作以读为主,所以默认mode=‘r’可以不写
读:r rb r+ r+b
read read(n) readline readlines for循环
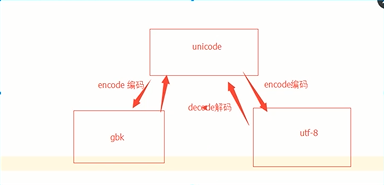
unicode 转换成bytes类型用 encode()
bytes转换成unicode 用decode()
#编码解码 s1是gbk的bytes类型,转换成utf-8的bytes类型 s1 =b'\xd6\xd0\xb9\xfa' s2 = s1.decode('gbk').encode('utf-8')
1 f2 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='r') 2 print(f2.read()) 3 f2.close() 4 5 f2 = open('log2',mode='rb') #rb模式不用带编码方式,非文字类文件打开 6 print(f2.read()) 7 f2.close() 8 9 #r 模式的五种读模式:read,read(n),readline(),readlines(),for循环读取 10 #readline 一行一行读取 11 f2 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='r') 12 print(f2.readline())#每次打印一行 13 print(f2.readline())#每次打印一行 14 print(f2.readline())#每次打印一行 15 f2.close() 16 #readlines 将每一行当成列表的一个元素并返回这个列表 17 f2 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='r') 18 print(f2.readlines()) 19 f2.close() 20 #for 循环 21 f2 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='r') 22 for i in f2: 23 print(i) 24 f2.close() 25 26 #read(n) r模式按照字符读取,rb模式按照字节读取 27 f2 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='r') 28 print(f2.read(5)) 29 f2.close()
写:w wb w+ w+b
追加:a ab a+ a+b
seek tell truncates,wratable readable等等
#tell 告诉指针的位置 #seek(参数),seek(0,2)调至最后 按照字节去调整光标 f1 = open('log2',encoding='utf-8',mode='w') f1.write('221321312321') print(f1.tell()) print(f1.seek()) f1.close()
#with open() as: with open('log1', encoding='utf-8') as f1,\ open('log2', encoding='utf-8', mode='w')as f2: print(f1.read()) f2.write('777')
文件的改。
#1、打开原文件 #2、创建新文件,产生文件句柄 #3、读取原文件,进行修改写入新文件 #4、将原文件删除 #5、新文件重命名 import os with open('file_test',encoding='utf-8') as f1,\ open('file_test.bak',encoding='utf-8',mode='w') as f2: old_content = f1.read() new_content = old_content.replace('alex','SB') f2.write(new_content) os.remove('file_test') os.rename('file_test.bak','file_test') import os with open('file_test',encoding='utf-8') as f1,\ open('file_test.bak',encoding='utf-8',mode='w') as f2: for line in f1: new_line = line.replace('SB','alex') os.remove('file_test') os.rename('file_test.bak','file_test')






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号