HBase的JavaAPI操作
HBase是一个分布式的NoSql数据库,在实际工作当中,我们一般都可以通过JavaAPI来进行各种数据的操作,包括创建表,以及数据的增删改查等等
1 创建maven工程
- 讲如下内容作为maven工程中pom.xml的repositories的内容
- 自动导包
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>XZK</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>HbaseApi1</artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-client</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-auth</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.hbase/hbase-client -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>6.14.3</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.testng</groupId>
<artifactId>testng</artifactId>
<version>6.14.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<filters>
<filter>
<artifact>*:*</artifact>
<excludes>
<exclude>META-INF/*.SF</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*.DSA</exclude>
<exclude>META-INF/*/RSA</exclude>
</excludes>
</filter>
</filters>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2 创建myuser表
- 创建myuser表,此表有两个列族f1和f2
//操作数据库 第一步:获取连接 第二步:获取客户端对象 第三步:操作数据库 第四步:关闭
/**
* 创建一张表 myuser 两个列族 f1 f2
*/
@Test
public void createTable() throws IOException {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
//连接HBase集群不需要指定HBase主节点的ip地址和端口号
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum","hadoop01:2181,hadoop02:2181,hadoop03:2181");
//创建连接对象
Connection connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);
//获取连接对象,创建一张表
//获取管理员对象,来对手数据库进行DDL的操作
Admin admin = connection.getAdmin();
//指定我们的表名
TableName myuser = TableName.valueOf("myuser");
HTableDescriptor hTableDescriptor = new HTableDescriptor(myuser);
//指定两个列族
HColumnDescriptor f1 = new HColumnDescriptor("f1");
HColumnDescriptor f2 = new HColumnDescriptor("f2");
hTableDescriptor.addFamily(f1);
hTableDescriptor.addFamily(f2);
admin.createTable(hTableDescriptor);
admin.close();
connection.close();
}
3 向表中添加数据
private Connection connection ;
private final String TABLE_NAME = "myuser";
private Table table ;
@Before
public void initTable () throws IOException {
Configuration configuration = HBaseConfiguration.create();
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum","node01:2181,node02:2181");
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(configuration);
table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
}
@After
public void close() throws IOException {
table.close();
connection.close();
}
/**
* 向myuser表当中添加数据
*/
@Test
public void addData() throws IOException {
//获取表
//Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
Put put = new Put("0001".getBytes());//创建put对象,并指定rowkey值
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),"zhangsan".getBytes());
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(), Bytes.toBytes(18));
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(), Bytes.toBytes(25));
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(), Bytes.toBytes("地球人"));
table.put(put);
table.close();
}
4 查询数据
- 初始化一批数据到HBase表当中,用于查询
![]()
/**
* hbase的批量插入数据
*/
@Test
public void batchInsert() throws IOException {
// 创建put对象,并指定rowkey
Put put = new Put("0002".getBytes());
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(1));
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("曹操"));
put.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(30));
put.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("沛国谯县"));
put.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("16888888888"));
put.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("helloworld"));
Put put2 = new Put("0003".getBytes());
put2.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(2));
put2.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("刘备"));
put2.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(32));
put2.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put2.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("幽州涿郡涿县"));
put2.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("17888888888"));
put2.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("talk is cheap , show me the code"));
Put put3 = new Put("0004".getBytes());
put3.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(3));
put3.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("孙权"));
put3.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(35));
put3.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put3.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("下邳"));
put3.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("12888888888"));
put3.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("what are you 弄啥嘞!"));
Put put4 = new Put("0005".getBytes());
put4.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(4));
put4.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("诸葛亮"));
put4.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(28));
put4.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put4.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("四川隆中"));
put4.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("14888888888"));
put4.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("出师表你背了嘛"));
Put put5 = new Put("0006".getBytes());
put5.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(5));
put5.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("司马懿"));
put5.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(27));
put5.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put5.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("哪里人有待考究"));
put5.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("15888888888"));
put5.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("跟诸葛亮死掐"));
Put put6 = new Put("0007".getBytes());
put6.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"id".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(5));
put6.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"name".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("xiaobubu—吕布"));
put6.addColumn("f1".getBytes(),"age".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes(28));
put6.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"sex".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("1"));
put6.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"address".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("内蒙人"));
put6.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"phone".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("15788888888"));
put6.addColumn("f2".getBytes(),"say".getBytes(),Bytes.toBytes("貂蝉去哪了"));
List<Put> listPut = new ArrayList<Put>();
listPut.add(put);
listPut.add(put2);
listPut.add(put3);
listPut.add(put4);
listPut.add(put5);
listPut.add(put6);
table.put(listPut);
}
4.1 Get查询
- 按照rowkey进行查询,获取所有列的所有值
- 查询主键rowkey为0003的人
/**
* 查询rowkey为0003的人
* get -> Result
*/
@Test
public void getData() throws IOException {
// Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
// 通过get对象,指定rowkey
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes("0001"));
get.addFamily("f1".getBytes());//限制只查询f1列族下面所有列的值
// 查询f2 列族 phone 这个字段
get.addColumn("f2".getBytes(), "phone".getBytes());
// 通过get查询,返回一个result对象,所有的字段的数据都是封装在result里面了
Result result = table.get(get);
List<Cell> cells = result.listCells(); //获取一条数据所有的cell,所有数据值都是在cell里面 的
if (cells != null) {
for (Cell cell : cells) {
// 获取列族名
byte[] familyName = CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell);
// 获取列名
byte[] columnName = CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell);
// 获取rowKey
byte[] rowKey = CellUtil.cloneRow(cell);
// 获取cell值
byte[] cellValue = CellUtil.cloneValue(cell);
// 需要判断字段的数据类型,使用对应的转换的方法,才能够获取到值
if ("age".equals(Bytes.toString(columnName)) || "id".equals(Bytes.toString(columnName))) {
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(familyName));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(columnName));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(rowKey));
System.out.println(Bytes.toInt(cellValue));
} else {
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(familyName));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(columnName));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(rowKey));
System.out.println(Bytes.toString(cellValue));
}
}
table.close();
}
}
4.2 Scan查询
/**
* 不知道rowkey的具体值,我想查询rowkey范围值是0003 到0006
* select * from myuser where age > 30 and id < 8 and name like 'zhangsan'
*
*/
@Test
public void scanData() throws IOException {
// 获取table
// Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
Scan scan = new Scan();// 没有指定startRow以及stopRow 全表扫描
// 只扫描f1列族
scan.addFamily("f1".getBytes());
// 只扫描f2列族: phone 这个字段
scan.addColumn("f2".getBytes(), "phone".getBytes());
scan.withStartRow("0003".getBytes());
scan.withStopRow("0007".getBytes()); // 前闭后开
// 通过getScanner查询获取到了表里面所有的数据,是多条数据
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
// 遍历ResultScanner 得到每一条数据,每一条数据都是封装在result对象里面了
for (Result result : scanner) {
List<Cell> cells = result.listCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
byte[] family_name = CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell);
byte[] qualifier_name = CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell);
byte[] rowkey = CellUtil.cloneRow(cell);
byte[] value = CellUtil.cloneValue(cell);
//判断id和age字段,这两个字段是整形值
if ("age".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name)) || "id".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name))) {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(family_name) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toInt(value));
} else {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(family_name) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toString(value));
}
}
}
table.close();
}
5 HBase过滤器查询
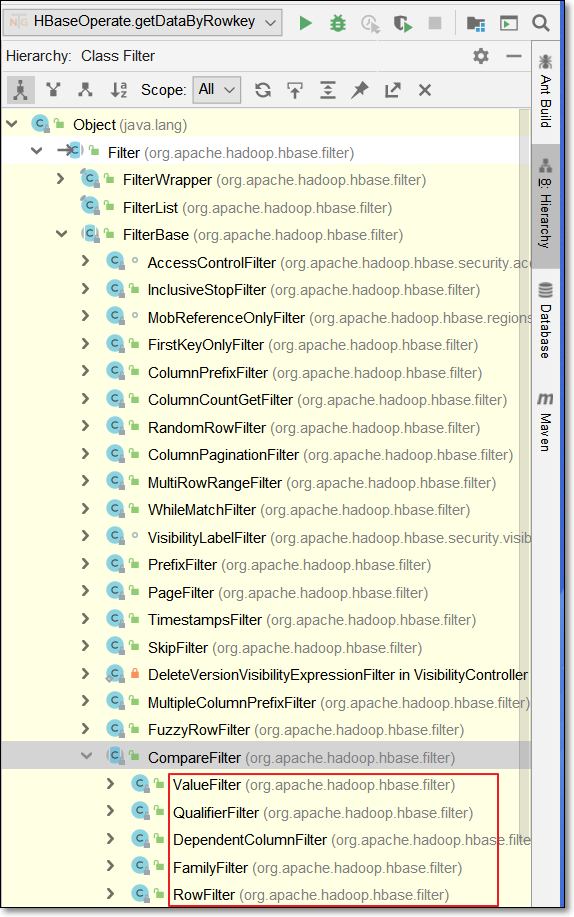
5.1 过滤器
- 过滤器的作用是在服务端判断数据是否满足条件,然后只将满足条件的数据返回给客户端
- 过滤器的类型很多,但是可以分为两大类
- 比较过滤器
- 专用过滤器
5.2 比较过滤器使用
- HBase过滤器的比较运算符:
LESS <
LESS_OR_EQUAL <=
EQUAL =
NOT_EQUAL <> 不等于
GREATER_OR_EQUAL >=
GREATER >
NO_OP 排除所有
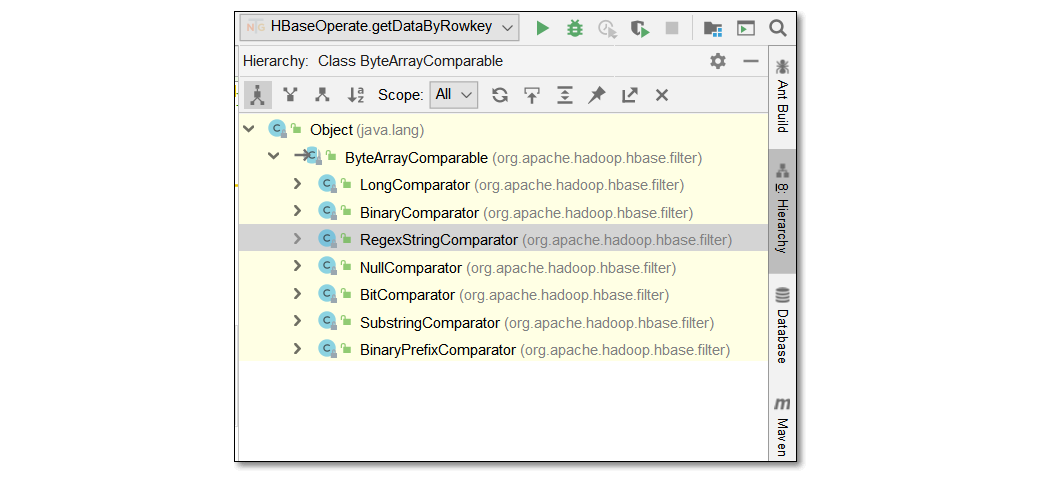
- HBase比较过滤器的比较器(指定比较机制):
BinaryComparator 按字节索引顺序比较指定字节数组,采用Bytes.compareTo(byte[])
BinaryPrefixComparator 跟前面相同,只是比较左端前缀的数据是否相同
NullComparator 判断给定的是否为空
BitComparator 按位比较
RegexStringComparator 提供一个正则的比较器,仅支持 EQUAL 和非EQUAL
SubstringComparator 判断提供的子串是否出现在中
- 比较过滤器
![]()
1、rowKey过滤器RowFilter
- 通过RowFilter过滤比rowKey 0003小的所有值出来
/**
* 查询所有的rowkey比0003小的所有的数据
*/
@Test
public void rowFilter() throws IOException {
// Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
Scan scan = new Scan();
// 获取我们比较对象
BinaryComparator binaryComparator = new BinaryComparator("0003".getBytes());
/*
* rowFilter需要加上两个参数
* 第一个参数就是我们的比较规则
* 第二个参数就是我们的比较对象
*/
RowFilter rowFilter = new RowFilter(CompareFilter.CompareOp.LESS, binaryComparator);
// 为我们的scan对象设置过滤器
scan.setFilter(rowFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : scanner) {
List<Cell> cells = result.listCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
byte[] family_name = CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell);
byte[] qualifier_name = CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell);
byte[] rowkey = CellUtil.cloneRow(cell);
byte[] value = CellUtil.cloneValue(cell);
// 判断id和age字段,这两个字段是整形值
if ("age".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name)) || "id".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name))) {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(family_name) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toInt(value));
} else {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(family_name) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toString(value));
}
}
}
}
2、列族过滤器FamilyFilter
- 查询列族名包含f2的所有列族下面的数据
/**
* 通过familyFilter来实现列族的过滤
* 需要过滤,列族名包含f2
* f1 f2 hello world
*/
@Test
public void familyFilter() throws IOException {
// Table table = connection.getTable(TableName.valueOf(TABLE_NAME));
Scan scan = new Scan();
SubstringComparator substringComparator = new SubstringComparator("f2");
// 通过familyfilter来设置列族的过滤器
FamilyFilter familyFilter = new FamilyFilter(CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, substringComparator);
scan.setFilter(familyFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : scanner) {
List<Cell> cells = result.listCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
byte[] familyName = CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell);
byte[] qualifierName = CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell);
byte[] rowKey = CellUtil.cloneRow(cell);
byte[] value = CellUtil.cloneValue(cell);
// 判断id和age字段,这两个字段是整形值
if ("age".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifierName)) || "id".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifierName))) {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowKey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(familyName) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifierName) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toInt(value));
} else {
System.out.println("数据的rowkey为" + Bytes.toString(rowKey) + "======数据的列族为" + Bytes.toString(familyName) + "======数据的列名为" + Bytes.toString(qualifierName) + "==========数据的值为" + Bytes.toString(value));
}
}
}
}
3、列过滤器QualifierFilter
- 只查询列名包含
name的列的值
/**
* 列名过滤器 只查询包含name列的值
*/
@Test
public void qualifierFilter() throws IOException {
Scan scan = new Scan();
SubstringComparator substringComparator = new SubstringComparator("name");
// 定义列名过滤器,只查询列名包含name的列
QualifierFilter qualifierFilter = new QualifierFilter(CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, substringComparator);
scan.setFilter(qualifierFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner);
}
public void printResult(ResultScanner scanner) {
for (Result result : scanner) {
List<Cell> cells = result.listCells();
for (Cell cell : cells) {
byte[] family_name = CellUtil.cloneFamily(cell);
byte[] qualifier_name = CellUtil.cloneQualifier(cell);
byte[] rowkey = CellUtil.cloneRow(cell);
byte[] value = CellUtil.cloneValue(cell);
//判断id和age字段,这两个字段是数值
if("age".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name)) || "id".equals(Bytes.toString(qualifier_name))){
System.out.println("rowkey: " + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + ";列族: " + Bytes.toString(family_name) + ";列名: " + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + ";数据: " + Bytes.toInt(value));
}else{
System.out.println("rowkey: " + Bytes.toString(rowkey) + ";列族: " + Bytes.toString(family_name) + ";列名: " + Bytes.toString(qualifier_name) + ";数据: " + Bytes.toString(value));
}
}
}
}
4、列值过滤器ValueFilter
- 查询所有列当中包含8的数据
/**
* 查询哪些字段值 包含数字8
*/
@Test
public void contains8() throws IOException {
Scan scan = new Scan();
SubstringComparator substringComparator = new SubstringComparator("8");
// 列值过滤器,过滤列值当中包含数字8的所有的列
ValueFilter valueFilter = new ValueFilter(CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, substringComparator);
scan.setFilter(valueFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner);
}
5.3 专用过滤器使用
1、单列值过滤器 SingleColumnValueFilter
- SingleColumnValueFilter会返回满足条件的cell。所在行的所有cell的值
- 查询f1 列族 name 列 值为刘备的数据
/**
* 单列值过滤器过滤
*/
@Test
public void singleColumnValueFilter() throws IOException {
// 查询 f1 列族 name 列 值为刘备的数据
Scan scan = new Scan();
// 单列值过滤器,过滤 f1 列族 name 列 值为刘备的数据
SingleColumnValueFilter singleColumnValueFilter = new SingleColumnValueFilter("f1".getBytes(), "name".getBytes(), CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, "刘备".getBytes());
scan.setFilter(singleColumnValueFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner);
}
2、列值排除过滤器SingleColumnValueExcludeFilter
- 与SingleColumnValueFilter相反
- 如果指定列的值符合filter条件,则会排除掉row中指定的列,其他的列全部返回
- 如果列不存在或不符合filter条件,则不返回row中的列
3、rowkey前缀过滤器PrefixFilter
- 查询以00开头的所有前缀的rowkey
/**
* 查询rowkey前缀以 00开头的所有的数据
*/
@Test
public void prefixFilter() throws IOException {
Scan scan = new Scan();
//过滤rowkey以 00开头的数据
PrefixFilter prefixFilter = new PrefixFilter("00".getBytes());
scan.setFilter(prefixFilter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner);
}
4、分页过滤器PageFilter
- 通过pageFilter实现分页过滤器
/**
* HBase当中的分页
*/
@Test
public void hbasePageFilter() throws IOException {
int pageNum = 3;
int pageSize = 2;
Scan scan = new Scan();
String startRow = "";
// 扫描数据的调试 扫描五条数据
int scanDatas = (pageNum - 1) * pageSize + 1;
scan.setMaxResultSize(scanDatas);//设置一步往前扫描多少条数据
PageFilter filter = new PageFilter(scanDatas);
scan.setFilter(filter);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
for (Result result : scanner) {
// 获取rowkey
byte[] row = result.getRow();
// 最后一次startRow的值就是0005
startRow = Bytes.toString(row);// 循环遍历我们所有获取到的数据的rowkey
// 最后一条数据的rowkey就是我们需要的起始的rowkey
}
// 获取第三页的数据
scan.withStartRow(startRow.getBytes());
scan.setMaxResultSize(pageSize);//设置我们扫描多少条数据
PageFilter filter1 = new PageFilter(pageSize);
scan.setFilter(filter1);
ResultScanner scanner1 = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner1);
}
5 多过滤器综合查询FilterList
- 需求:使用SingleColumnValueFilter查询f1列族,name为刘备的数据,并且同时满足rowkey的前缀以00开头的数据(PrefixFilter)
/**
* 查询 f1 列族 name 为刘备数据值
* 并且rowkey 前缀以 00开头数据
*/
@Test
public void filterList() throws IOException {
Scan scan = new Scan();
SingleColumnValueFilter singleColumnValueFilter = new SingleColumnValueFilter("f1".getBytes(), "name".getBytes(), CompareFilter.CompareOp.EQUAL, "刘备".getBytes());
PrefixFilter prefixFilter = new PrefixFilter("00".getBytes());
FilterList filterList = new FilterList();
filterList.addFilter(singleColumnValueFilter);
filterList.addFilter(prefixFilter);
scan.setFilter(filterList);
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
printResult(scanner);
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号