leetcode刷题记录:回溯算法注意事项
leetcode 46题:
给定一个 没有重复 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
输入: [1,2,3] 输出: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
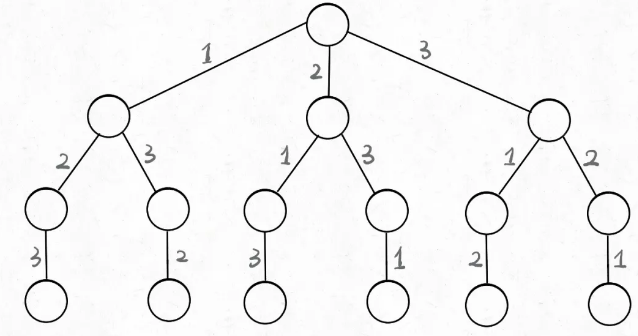
思路就是按照这张图进行穷举 ,对于回溯的问题,画图可以快速找到思路
class Solution { private List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) { List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>(); backTrack(path, nums); return res; } private void backTrack(List<Integer> path, int[] nums){ if(path.size() == nums.length){ res.add(new ArrayList<>(path)); // 注意要对path进行复制 return; } for(int num : nums){ if(path.contains(num)) continue; path.add(num); backTrack(path, nums); path.remove(path.size() - 1); } } }
代码按照回溯算法的典型框架实现,但是需要注意的是,在递归结束的时候,很容易犯如下错误
if(path.size() == nums.length){ res.add(path); return; }
这样的话,代码的输出结果为[[],[],[],[],[],[],[]]
当按照1->2->3这条路线遍历到最底层的时候,path = [1,2,3]确实被存进了res中,但是被忘了存的是path这个指针,在后来的遍历过程中path指向的堆内存的内容会一直修改,因为回溯算法的精髓是通过
path.remove(path.size() - 1)
将路径的最后一个节点删除去返回上一个节点,返回一次删一个,最终返回到最高层的时候,path指向的内容就为空了,所以为了保存遍历的结果,要讲path的内容复制一份。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号