Bert源码阅读笔记
BERT实际上就是tranformer的编码器部分
按照Google的bert源码,做一个MRPC的任务,地址:https://github.com/google-research/bert
官方提供的训练数据长这个样子:每条数据包含两句话及其ID,如果这两句话有关系,quality为1,否则为0,测试数据除了没有quality其他和训练数据一样

代码结构如下:
主程序为run_classifier.py,在训练之前,需要对数据预处理,nlp的第一步对句子进行分词,把词表示为字典中的序号
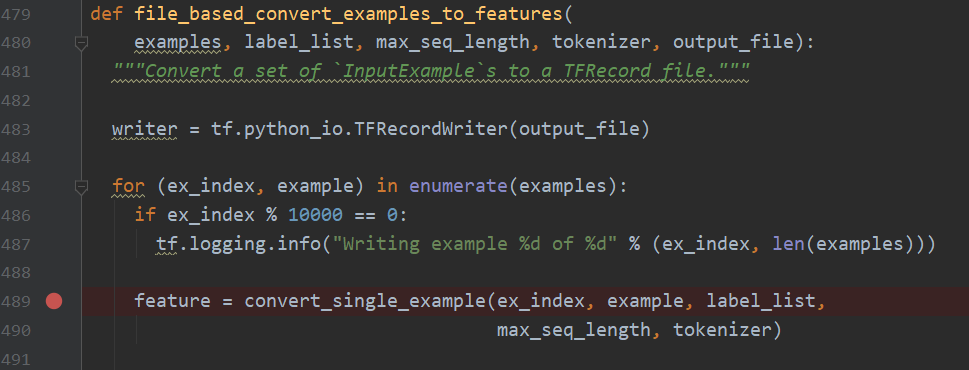
先把数据读到recordwrite,方便tensorflow操作,然后按行读取的训练数据,ex_index是序号,example包含a,b两句话,label_list是["0","1"],然后重点是convert_single_example,它的作用就是把文本表示为字典中的序号,看看它里边有什么:
def convert_single_example(ex_index, example, label_list, max_seq_length, tokenizer): """Converts a single `InputExample` into a single `InputFeatures`.""" if isinstance(example, PaddingInputExample): return InputFeatures( input_ids=[0] * max_seq_length, input_mask=[0] * max_seq_length, segment_ids=[0] * max_seq_length, label_id=0, is_real_example=False) label_map = {} for (i, label) in enumerate(label_list): # 把标签表示为字典格式 label_map[label] = i tokens_a = tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_a) # 对句子a进行分词 tokens_b = None if example.text_b: # 如果有第二句话,也对句子b分词 tokens_b = tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_b) if tokens_b: # Modifies `tokens_a` and `tokens_b` in place so that the total # length is less than the specified length. # Account for [CLS], [SEP], [SEP] with "- 3" _truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a, tokens_b, max_seq_length - 3) # 如果句子分词数超过了最大长度,进行截断操作,-3是因为要留下开头的[cls],两句话中间的[SEP],
第二句话最后的[SEP]] else: # Account for [CLS] and [SEP] with "- 2" if len(tokens_a) > max_seq_length - 2: # 如果只有一句话,则没有中间的[SEP],只需要-2 tokens_a = tokens_a[0:(max_seq_length - 2)] # The convention in BERT is: # (a) For sequence pairs: # tokens: [CLS] is this jack ##son ##ville ? [SEP] no it is not . [SEP] # 这里写的很清楚,下面的几句代码就是给句子加上[cls],[SEP], # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 # 并且创建一个句子类型的列表,[CLS]、第一句话的词、第一句话最后的[SEP]是0, # (b) For single sequences: 第二句话的词和最后的[SEP]是1 # tokens: [CLS] the dog is hairy . [SEP] # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 # # Where "type_ids" are used to indicate whether this is the first # sequence or the second sequence. The embedding vectors for `type=0` and # `type=1` were learned during pre-training and are added to the wordpiece # embedding vector (and position vector). This is not *strictly* necessary # since the [SEP] token unambiguously separates the sequences, but it makes # it easier for the model to learn the concept of sequences. # # For classification tasks, the first vector (corresponding to [CLS]) is # used as the "sentence vector". Note that this only makes sense because # the entire model is fine-tuned. tokens = [] segment_ids = [] tokens.append("[CLS]") segment_ids.append(0) for token in tokens_a: tokens.append(token) segment_ids.append(0) tokens.append("[SEP]") segment_ids.append(0) if tokens_b: for token in tokens_b: tokens.append(token) segment_ids.append(1) tokens.append("[SEP]") segment_ids.append(1) input_ids = tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens) # 把词转换为词典中对应的序号 # The mask has 1 for real tokens and 0 for padding tokens. Only real # tokens are attended to. input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids) # 下边会对长度不够的句子后边补零,但是补的零对训练没有,所以要用input_mask标记那些是有用的序号,有用的标1,没用的标0 # Zero-pad up to the sequence length. while len(input_ids) < max_seq_length: # 对长度不够的句子后边补零,input_mask也补零 input_ids.append(0) input_mask.append(0) segment_ids.append(0) assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_length assert len(input_mask) == max_seq_length assert len(segment_ids) == max_seq_length label_id = label_map[example.label] # 打印结果 if ex_index < 5: tf.logging.info("*** Example ***") tf.logging.info("guid: %s" % (example.guid)) tf.logging.info("tokens: %s" % " ".join( [tokenization.printable_text(x) for x in tokens])) tf.logging.info("input_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in input_ids])) tf.logging.info("input_mask: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in input_mask])) tf.logging.info("segment_ids: %s" % " ".join([str(x) for x in segment_ids])) tf.logging.info("label: %s (id = %d)" % (example.label, label_id)) feature = InputFeatures( input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, segment_ids=segment_ids, label_id=label_id, is_real_example=True) return feature
数据数据处理完看模型部分
def create_model(bert_config, is_training, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, labels, num_labels, use_one_hot_embeddings): """Creates a classification model.""" model = modeling.BertModel( config=bert_config, # 从预训练文件中读取神经网络设置,包括隐藏层神经元数量,dropout大小啥的 is_training=is_training, # 是否使用dropout input_ids=input_ids, # 数据处理后的结果,大小是(batch_size, max_seq_length), 这里是(8,128) input_mask=input_mask, # 数据处理后的结果,(8, 128) token_type_ids=segment_ids, # 数据处理后的结果, (8, 128) use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings) # TPU需要用这个,其他机器先不用管
首先调用了BertModel,看看这个里面干了啥
class BertModel(object):
def __init__(self,
config,
is_training,
input_ids,
input_mask=None,
token_type_ids=None,
use_one_hot_embeddings=False,
scope=None):
config = copy.deepcopy(config)
if not is_training: # 判断是否使用dropout
config.hidden_dropout_prob = 0.0
config.attention_probs_dropout_prob = 0.0
input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids, expected_rank=2)
batch_size = input_shape[0] # 8
seq_length = input_shape[1] # 128
if input_mask is None: # 如果没有输入input_mask, 默认全都是1, 即没有补零
input_mask = tf.ones(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
if token_type_ids is None: # 如果没有输入token_type_ids, 默认全都是0, 即都来自第一句话
token_type_ids = tf.zeros(shape=[batch_size, seq_length], dtype=tf.int32)
with tf.variable_scope(scope, default_name="bert"):
with tf.variable_scope("embeddings"):
# Perform embedding lookup on the word ids.
(self.embedding_output, self.embedding_table) = embedding_lookup(
input_ids=input_ids,
vocab_size=config.vocab_size,
embedding_size=config.hidden_size,
initializer_range=config.initializer_range,
word_embedding_name="word_embeddings",
use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings)
# 这部分通过查表做embedding,输入是(8,128), 输出是(8,128,768),即每个词embedding后的维度是768
看一下embedding_lookup里干了啥
def embedding_lookup(input_ids, # (8,128) vocab_size, # 预训练模型中包含的词汇数30522 embedding_size=128, initializer_range=0.02, word_embedding_name="word_embeddings", # embedding表的名称 use_one_hot_embeddings=False): if input_ids.shape.ndims == 2: # 因为输出维度是三维, 所以先把输入维度变成(8,128,1) input_ids = tf.expand_dims(input_ids, axis=[-1]) embedding_table = tf.get_variable( # 定义embedding表,(30522,768)batch里的词的embedding是从这里边查出来的 name=word_embedding_name, shape=[vocab_size, embedding_size], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) flat_input_ids = tf.reshape(input_ids, [-1]) # 把输入变成(8*128,1)=(1024, 1) if use_one_hot_embeddings: one_hot_input_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_input_ids, depth=vocab_size) output = tf.matmul(one_hot_input_ids, embedding_table) else: output = tf.gather(embedding_table, flat_input_ids) # 查表,得到输入对应的embedding,大小为(1024, 768) input_shape = get_shape_list(input_ids) output = tf.reshape(output, input_shape[0:-1] + [input_shape[-1] * embedding_size]) # 把embedding大小改为(8,128,768) return (output, embedding_table)
除了词本身的embedding,还要考虑词的类型,即token_type_id, 因为对于这个任务, 需要知道这个词是第一句还是第二句,代码如下
def embedding_postprocessor(input_tensor, use_token_type=False, token_type_ids=None, token_type_vocab_size=16, token_type_embedding_name="token_type_embeddings", use_position_embeddings=True, # 是否考虑位置信息,这个位置是说在每个batch中,长度不是128嘛,每个token的位置0-128 position_embedding_name="position_embeddings", initializer_range=0.02, max_position_embeddings=512, dropout_prob=0.1): """Performs various post-processing on a word embedding tensor. Args: input_tensor: float Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length, embedding_size]. use_token_type: bool. Whether to add embeddings for `token_type_ids`. token_type_ids: (optional) int32 Tensor of shape [batch_size, seq_length]. Must be specified if `use_token_type` is True. token_type_vocab_size: int. The vocabulary size of `token_type_ids`. token_type_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable for token type ids. use_position_embeddings: bool. Whether to add position embeddings for the position of each token in the sequence. position_embedding_name: string. The name of the embedding table variable for positional embeddings. initializer_range: float. Range of the weight initialization. max_position_embeddings: int. Maximum sequence length that might ever be used with this model. This can be longer than the sequence length of input_tensor, but cannot be shorter. dropout_prob: float. Dropout probability applied to the final output tensor. Returns: float tensor with same shape as `input_tensor`. Raises: ValueError: One of the tensor shapes or input values is invalid. """ input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3) # (8,128,786) batch_size = input_shape[0] seq_length = input_shape[1] width = input_shape[2] output = input_tensor if use_token_type: if token_type_ids is None: raise ValueError("`token_type_ids` must be specified if" "`use_token_type` is True.") token_type_table = tf.get_variable( 类型的embedding表,因为type只有0和1,所以大小是(2, 786) name=token_type_embedding_name, shape=[token_type_vocab_size, width], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # This vocab will be small so we always do one-hot here, since it is always # faster for a small vocabulary. flat_token_type_ids = tf.reshape(token_type_ids, [-1]) # (1024) one_hot_ids = tf.one_hot(flat_token_type_ids, depth=token_type_vocab_size) # 把0,1变成one-hot编码,大小是 (1024,2) token_type_embeddings = tf.matmul(one_hot_ids, token_type_table) # 相乘,做位置的embedding token_type_embeddings = tf.reshape(token_type_embeddings, # 把形状调整成和输入一样的,方便相加 [batch_size, seq_length, width]) output += token_type_embeddings # 输入和位置embedding相加 if use_position_embeddings: 如果考虑位置, 加上位置的embedding assert_op = tf.assert_less_equal(seq_length, max_position_embeddings) with tf.control_dependencies([assert_op]): full_position_embeddings = tf.get_variable( 位置embedding的大小(512,786),这块给多了,后面会切分 name=position_embedding_name, shape=[max_position_embeddings, width], initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # Since the position embedding table is a learned variable, we create it # using a (long) sequence length `max_position_embeddings`. The actual # sequence length might be shorter than this, for faster training of # tasks that do not have long sequences. # # So `full_position_embeddings` is effectively an embedding table # for position [0, 1, 2, ..., max_position_embeddings-1], and the current # sequence has positions [0, 1, 2, ... seq_length-1], so we can just # perform a slice. position_embeddings = tf.slice(full_position_embeddings, [0, 0], # 切分为(128,768) [seq_length, -1]) num_dims = len(output.shape.as_list()) # Only the last two dimensions are relevant (`seq_length` and `width`), so # we broadcast among the first dimensions, which is typically just # the batch size. position_broadcast_shape = [] for _ in range(num_dims - 2): position_broadcast_shape.append(1) position_broadcast_shape.extend([seq_length, width]) # 扩展为(1,128,768),方便加减 position_embeddings = tf.reshape(position_embeddings, position_broadcast_shape) output += position_embeddings # 对8个batch,都加上相同的位置embedding output = layer_norm_and_dropout(output, dropout_prob) # 加dropout后输出 return output
至此,BERT的第一步embedding完成
然后是mask部分
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"): # This converts a 2D mask of shape [batch_size, seq_length] to a 3D # mask of shape [batch_size, seq_length, seq_length] which is used # for the attention scores. attention_mask = create_attention_mask_from_input_mask( # 把mask从2D变成3D的,原来对于每个batch,都对应一个二维的mask[1,1,1....0,0],现在把这个mask立起来,放到每个batch里的每个 input_ids, input_mask) 元素上,最后的大小是(8,128,128)
Transformor部分
self.all_encoder_layers = transformer_model( input_tensor=self.embedding_output, # 之前算的embedding attention_mask=attention_mask, # 之前算的mask hidden_size=config.hidden_size, num_hidden_layers=config.num_hidden_layers, num_attention_heads=config.num_attention_heads, # 12头的self-attention intermediate_size=config.intermediate_size, intermediate_act_fn=get_activation(config.hidden_act), hidden_dropout_prob=config.hidden_dropout_prob, attention_probs_dropout_prob=config.attention_probs_dropout_prob, initializer_range=config.initializer_range, do_return_all_layers=True)
看看里边干了啥
def transformer_model(input_tensor, attention_mask=None, hidden_size=768, num_hidden_layers=12, num_attention_heads=12, intermediate_size=3072, intermediate_act_fn=gelu, hidden_dropout_prob=0.1, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_all_layers=False): if hidden_size % num_attention_heads != 0: # 先判断768够不够12个头分 raise ValueError( "The hidden size (%d) is not a multiple of the number of attention " "heads (%d)" % (hidden_size, num_attention_heads)) attention_head_size = int(hidden_size / num_attention_heads) # 768/12 = 64 input_shape = get_shape_list(input_tensor, expected_rank=3) batch_size = input_shape[0] seq_length = input_shape[1] input_width = input_shape[2] # The Transformer performs sum residuals on all layers so the input needs # to be the same as the hidden size. if input_width != hidden_size: # 因为最后要做残差连接,所以输入和输出维度要相同 raise ValueError("The width of the input tensor (%d) != hidden size (%d)" % (input_width, hidden_size)) # We keep the representation as a 2D tensor to avoid re-shaping it back and # forth from a 3D tensor to a 2D tensor. Re-shapes are normally free on # the GPU/CPU but may not be free on the TPU, so we want to minimize them to # help the optimizer. prev_output = reshape_to_matrix(input_tensor) # 为了方便TPU,做reshape all_layer_outputs = [] for layer_idx in range(num_hidden_layers): with tf.variable_scope("layer_%d" % layer_idx): layer_input = prev_output with tf.variable_scope("attention"): attention_heads = [] with tf.variable_scope("self"): attention_head = attention_layer( from_tensor=layer_input, # 因为是self-attention, 所以from tensor和to tensor 一样 to_tensor=layer_input, attention_mask=attention_mask, num_attention_heads=num_attention_heads, size_per_head=attention_head_size, attention_probs_dropout_prob=attention_probs_dropout_prob, initializer_range=initializer_range, do_return_2d_tensor=True, batch_size=batch_size, from_seq_length=seq_length, to_seq_length=seq_length) attention_heads.append(attention_head) attention_output = None if len(attention_heads) == 1: attention_output = attention_heads[0] else: # In the case where we have other sequences, we just concatenate # them to the self-attention head before the projection. attention_output = tf.concat(attention_heads, axis=-1) # Run a linear projection of `hidden_size` then add a residual # with `layer_input`. with tf.variable_scope("output"): attention_output = tf.layers.dense( attention_output, hidden_size, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) attention_output = dropout(attention_output, hidden_dropout_prob) attention_output = layer_norm(attention_output + layer_input) # 残差连接和layer_norm # The activation is only applied to the "intermediate" hidden layer. with tf.variable_scope("intermediate"): # 再经过两层全连接层 intermediate_output = tf.layers.dense( attention_output, intermediate_size, activation=intermediate_act_fn, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # Down-project back to `hidden_size` then add the residual. with tf.variable_scope("output"): layer_output = tf.layers.dense( intermediate_output, hidden_size, kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) layer_output = dropout(layer_output, hidden_dropout_prob) layer_output = layer_norm(layer_output + attention_output) prev_output = layer_output all_layer_outputs.append(layer_output) if do_return_all_layers: final_outputs = [] for layer_output in all_layer_outputs: final_output = reshape_from_matrix(layer_output, input_shape) final_outputs.append(final_output) return final_outputs else: final_output = reshape_from_matrix(prev_output, input_shape) return final_output
看一下attention里干了啥
def attention_layer(from_tensor, to_tensor, attention_mask=None, num_attention_heads=1, size_per_head=512, query_act=None, key_act=None, value_act=None, attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.0, initializer_range=0.02, do_return_2d_tensor=False, batch_size=None, from_seq_length=None, to_seq_length=None): def transpose_for_scores(input_tensor, batch_size, num_attention_heads, seq_length, width): output_tensor = tf.reshape( input_tensor, [batch_size, seq_length, num_attention_heads, width]) output_tensor = tf.transpose(output_tensor, [0, 2, 1, 3]) return output_tensor from_shape = get_shape_list(from_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3]) # (1024,768) to_shape = get_shape_list(to_tensor, expected_rank=[2, 3]) #(1024,768) if len(from_shape) != len(to_shape): raise ValueError( "The rank of `from_tensor` must match the rank of `to_tensor`.") if len(from_shape) == 3: batch_size = from_shape[0] from_seq_length = from_shape[1] to_seq_length = to_shape[1] elif len(from_shape) == 2: if (batch_size is None or from_seq_length is None or to_seq_length is None): raise ValueError( "When passing in rank 2 tensors to attention_layer, the values " "for `batch_size`, `from_seq_length`, and `to_seq_length` " "must all be specified.") # Scalar dimensions referenced here: # B = batch size (number of sequences) # F = `from_tensor` sequence length # T = `to_tensor` sequence length # N = `num_attention_heads` # H = `size_per_head` from_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(from_tensor) (1024,,768) to_tensor_2d = reshape_to_matrix(to_tensor) # `query_layer` = [B*F, N*H] query_layer = tf.layers.dense( # 定义query矩阵,注意输入是from tensor from_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=query_act, name="query", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # `key_layer` = [B*T, N*H] key_layer = tf.layers.dense( # 定义key矩阵, 输入是to tensor to_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=key_act, name="key", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # `value_layer` = [B*T, N*H] value_layer = tf.layers.dense( # 定义value矩阵,输入是to tensor to_tensor_2d, num_attention_heads * size_per_head, activation=value_act, name="value", kernel_initializer=create_initializer(initializer_range)) # `query_layer` = [B, N, F, H] query_layer = transpose_for_scores(query_layer, batch_size, # reshape成(8,12,128,64),这样方便做內积 num_attention_heads, from_seq_length, size_per_head) # `key_layer` = [B, N, T, H] key_layer = transpose_for_scores(key_layer, batch_size, num_attention_heads, to_seq_length, size_per_head) # Take the dot product between "query" and "key" to get the raw # attention scores. # `attention_scores` = [B, N, F, T] attention_scores = tf.matmul(query_layer, key_layer, transpose_b=True) # (8,12,128,128) attention_scores = tf.multiply(attention_scores, 1.0 / math.sqrt(float(size_per_head))) # 在softmax之前除以根号64 if attention_mask is not None: # `attention_mask` = [B, 1, F, T] attention_mask = tf.expand_dims(attention_mask, axis=[1]) # Since attention_mask is 1.0 for positions we want to attend and 0.0 for # masked positions, this operation will create a tensor which is 0.0 for # positions we want to attend and -10000.0 for masked positions. adder = (1.0 - tf.cast(attention_mask, tf.float32)) * -10000.0 # 把1变成0,把0变成-10000 # Since we are adding it to the raw scores before the softmax, this is # effectively the same as removing these entirely. attention_scores += adder # 加到分值上,这样mask里为1的位置不变,为0的位置变成一个极小的负数,一会要做sofemax,极小的负数会变成0 表示不考虑后来补的0 # Normalize the attention scores to probabilities. # `attention_probs` = [B, N, F, T] attention_probs = tf.nn.softmax(attention_scores) # This is actually dropping out entire tokens to attend to, which might # seem a bit unusual, but is taken from the original Transformer paper. attention_probs = dropout(attention_probs, attention_probs_dropout_prob) # `value_layer` = [B, T, N, H] value_layer = tf.reshape( value_layer, [batch_size, to_seq_length, num_attention_heads, size_per_head]) # (8,128,12,64) # `value_layer` = [B, N, T, H] value_layer = tf.transpose(value_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3]) # `context_layer` = [B, N, F, H] context_layer = tf.matmul(attention_probs, value_layer) # value和分数相乘得到结果 # `context_layer` = [B, F, N, H] context_layer = tf.transpose(context_layer, [0, 2, 1, 3]) if do_return_2d_tensor: # `context_layer` = [B*F, N*H] # 因为要算好几层,把最后的结果变成(1024,768) context_layer = tf.reshape( context_layer, [batch_size * from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]) else: # `context_layer` = [B, F, N*H] context_layer = tf.reshape( context_layer, [batch_size, from_seq_length, num_attention_heads * size_per_head]) return context_layer
最后回到代码主程序
def create_model(bert_config, is_training, input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, labels, num_labels, use_one_hot_embeddings): """Creates a classification model.""" model = modeling.BertModel( config=bert_config, is_training=is_training, input_ids=input_ids, input_mask=input_mask, token_type_ids=segment_ids, use_one_hot_embeddings=use_one_hot_embeddings) # In the demo, we are doing a simple classification task on the entire # segment. # # If you want to use the token-level output, use model.get_sequence_output() # instead. output_layer = model.get_pooled_output() # 拿到每句话第一个词也就是[CLS]的编码,对训练来说其他的词不重要,知道结果就行了 hidden_size = output_layer.shape[-1].value output_weights = tf.get_variable( "output_weights", [num_labels, hidden_size], initializer=tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev=0.02)) output_bias = tf.get_variable( "output_bias", [num_labels], initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()) with tf.variable_scope("loss"): if is_training: # I.e., 0.1 dropout output_layer = tf.nn.dropout(output_layer, keep_prob=0.9) logits = tf.matmul(output_layer, output_weights, transpose_b=True) logits = tf.nn.bias_add(logits, output_bias) probabilities = tf.nn.softmax(logits, axis=-1) log_probs = tf.nn.log_softmax(logits, axis=-1) # 经过一个全连接层出概率 one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=num_labels, dtype=tf.float32) per_example_loss = -tf.reduce_sum(one_hot_labels * log_probs, axis=-1) # 交叉熵算损失 loss = tf.reduce_mean(per_example_loss) return (loss, per_example_loss, logits, probabilities)
BERT的主要部分就是这样

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号