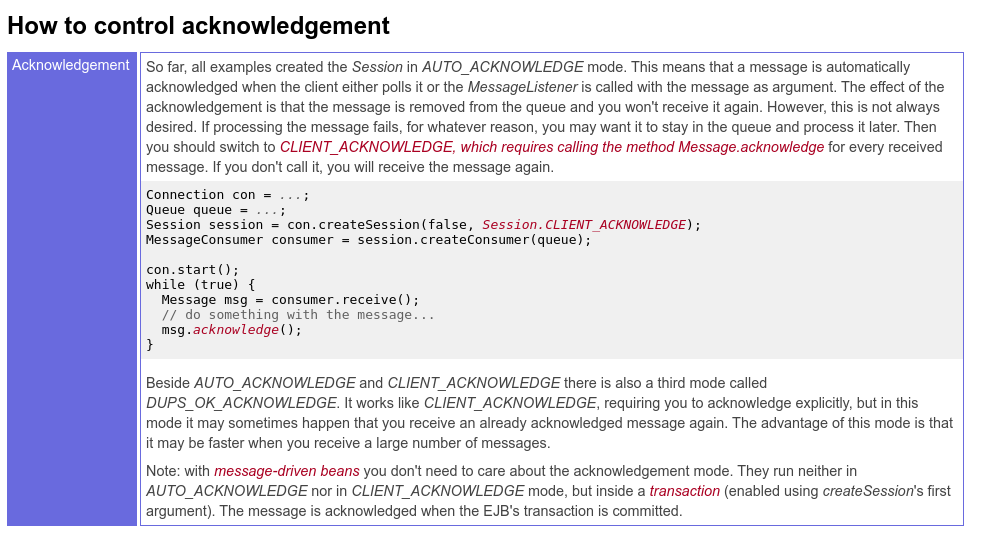
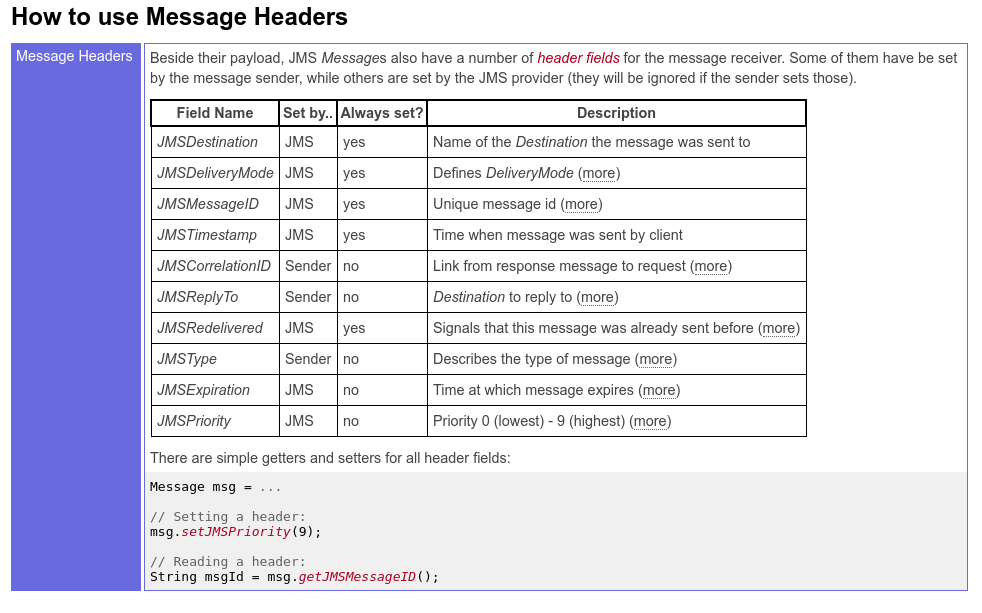
MQ的ack
老外总结的真是好.
https://timjansen.github.io/jarfiller/guide/jms/standaloneclient.xhtml#activemqsetup
Sending and Receiving Messages (Standalone Client)
ConnectionFactory factory =
new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://localhost:61616"); // ActiveMQ-specific (more)
Connection con = factory.createConnection();
try {
Session session =
con.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // non-transacted session (more)
Queue queue = session.createQueue("test.queue"); // only specifies queue name (more)
MessageProducer producer = session.createProducer(queue);
Message msg = session.createTextMessage("hello queue"); // text message (more)
producer.send(msg);
}
finally {
con.close(); // free all resources (more)
}
ConnectionFactory factory =
new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://localhost:61616"); // ActiveMQ-specific (more)
Connection con = factory.createConnection();
try {
Session session =
con.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // non-transacted session (more)
Queue queue = session.createQueue("test.queue"); // only specifies queue name (more)
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queue);
con.start(); // start the connection (more)
while (true) { // run forever
Message msg = consumer.receive(); // blocking! (more)
if (! (msg instanceof TextMessage))
throw new RuntimeException("Expected a TextMessage");
TextMessage tm = (TextMessage) msg;
System.out.println(tm.getText()); // print message content
}
}
finally {
con.close(); // free all resources (more)
}
ConnectionFactory factory =
new ActiveMQConnectionFactory("tcp://localhost:61616"); // ActiveMQ-specific (more)
Connection con = factory.createConnection();
try {
Session session =
con.createSession(false, Session.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE); // non-transacted session (more)
Queue queue = session.createQueue("test.queue"); // only specifies queue name (more)
MessageConsumer consumer = session.createConsumer(queue);
consumer.setMessageListener(new MessageListener() {
public void onMessage(Message msg) {
try {
if (! (msg instanceof TextMessage))
throw new RuntimeException("no text message");
TextMessage tm = (TextMessage) msg;
System.out.println(tm.getText()); // print message
}
catch (JMSException e) {
System.err.println("Error reading message");
}
}
});
con.start(); // start the connection (more)
Thread.sleep(60 * 1000); // receive messages for 60s (more)
finally {
con.close(); // free all resources (more)
}
Getting the ConnectionFactory via JNDI
The only (relatively) non-implementation-specific way to obtain the JMS implementation's ConnectionFactory and Destinations is to get them from a JNDI server. This is usually only possibly if you write your program as client for an application server. The following example shows how to do this with JBoss:
Hashtable<String,String> env = new Hashtable<String, String>();
env.put("java.naming.factory.initial", // JBoss-specific (more)
"org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory");
env.put("java.naming.provider.url", "jnp://localhost:1099"); // host address
env.put("java.naming.factory.url.pkgs",
"org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces");
Context ctx = new InitialContext(env);
ConnectionFactory factory = (ConnectionFactory)
ctx.lookup("/ConnectionFactory"); // obtain factory (more)
Queue queue = (Queue)
ctx.lookup("/queue/JarfillerQueue"); // obtain queue (more)
...
How to set up ActiveMQ
Setting up a ActiveMQ server is fairly easy:
- Download a ActiveMQ distribution from activemq.apache.org and unpack it somewhere
- You can start the server immediately, running unsecured on localhost, using the script bin/activemq
- When it is running, you can access your local server's console on http://localhost:8161/admin/
- Configure it by modifying conf/activemq.xml
In order to compile and run the client, just include the JAR files from the server's lib directory in your CLASSPATH.
How to set up Websphere MQ
Setting up a client for a Websphere MQ server is similar to ActiveMQ. You only need to create a MQConnectionFactory instance and configure it. The configuration of Websphere MQ is a bit more complicated that ActiveMQ's, because you need to create a queue manager and a channel in the server, and then specify it in the client. But once the client has obtained the ConnectionFactory, the usage is exactly like Active MQ's:
import com.ibm.mq.jms.*;
...
MQConnectionFactory factory = new MQConnectionFactory();
factory.setHostName("localhost"); // server IP address / name
factory.setTransportType(JMSC.MQJMS_TP_CLIENT_MQ_TCPIP); // for TCP/IP
factory.setChannel("my.channel"); // server connection channel to use
factory.setQueueManager("my.queue.manager"); // queue manager to use
In order to compile and run the client, you only need two JAR files: com.ibm.mq.jar and com.ibm.mq.jms.jar. Both should ship with the Websphere MQ client distributions.
>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>
https://timjansen.github.io/jarfiller/guide/jms/achknowledgement.xhtml





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号