JavaScript for C#Developers Study(3)
Object-Oriented JavaScript
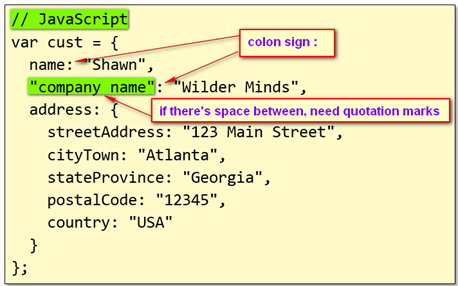
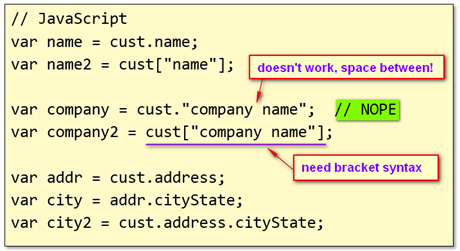
- Dynamic Objects
- Creating dynamic object is very similar in c# and JavaScript
-
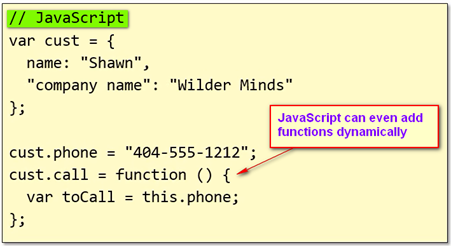
- Both c# and JavaScript can add new properties dynamically
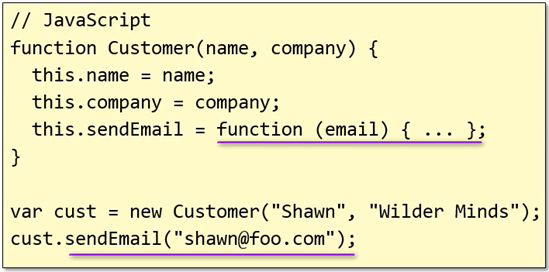
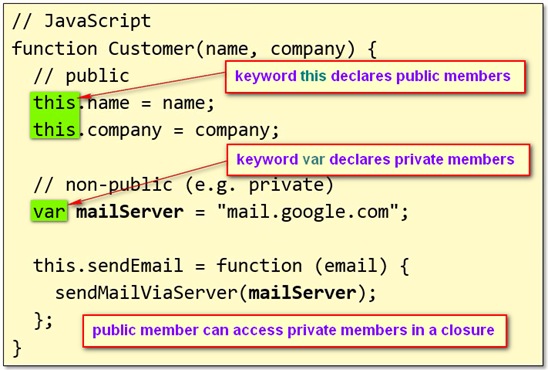
- In JavaScript, we use FUNCTION to define a class
- when using keyword new to initialize a class function, the owner of this function is the newly created object
-
- In a class function, function member can be declared as well
-
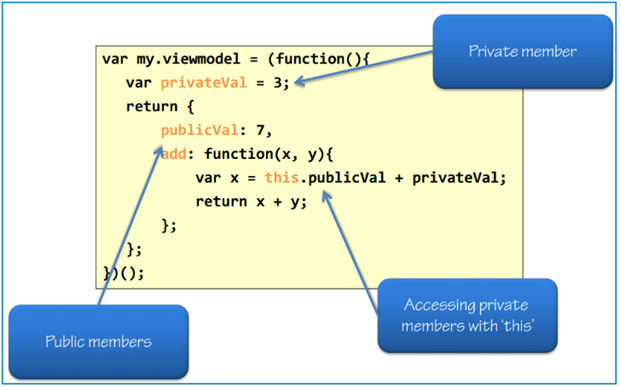
- In a function class, keyword “this” declares public members, while keyword “var” declares private ones
-
- An example of passing in an owner to a function
1 var my = my||{}; 2 3 my.Product = function (selectedItem) { 4 var self = this; 5 self.id = ko.observable(); 6 self.salePrice = ko.observable(); 7 self.photo = ko.observable(); 8 self.model = ko.observable(); 9 self.category = ko.observable(); 10 self.description = ko.observable(); 11 self.rating = ko.observable(); 12 self.isSelected = ko.computed(function () { 13 return selectedItem() === self; 14 }); 15 //this.shortDescription = ko.observable(); 16 self.shortDesc = ko.computed(function () { 17 return this.model() ? this.model().brand() + " " + this.model().name() : ""; 18 }, self), // passing self as owner of the function 19 self.photoUrl = ko.computed(function () { 20 return photoPath + this.photo(); 21 }, self); // passing self as owner of the function 22 };
-
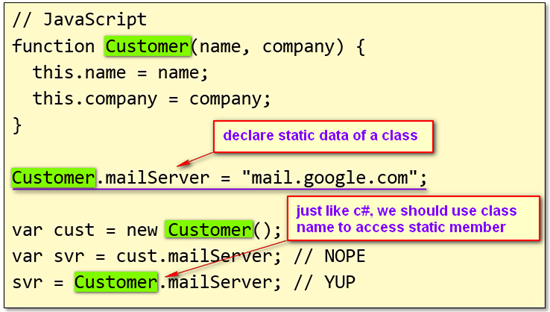
- Just like c#, we should use Class Name to access static member of a class
-
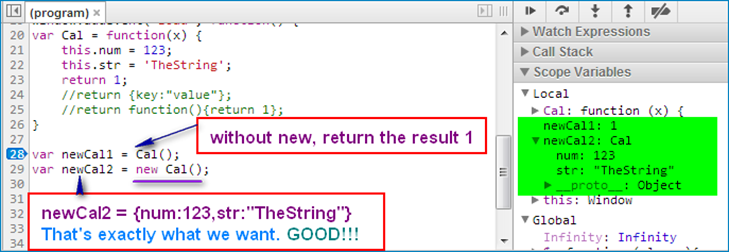
Go deeper for the keyword “new” applying to a constructor function
-
no return statement in constructor class (GOOD)
-
-
-
return non-object value in constructor class(GOOD)
-
-
-
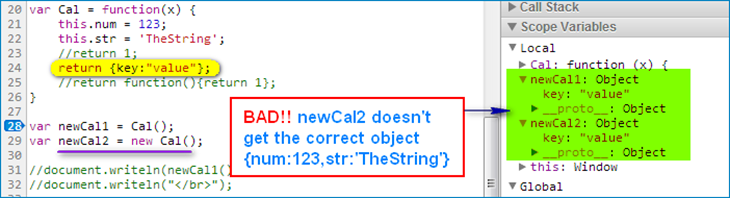
return an object in constructor class (BAD)
-
-
-
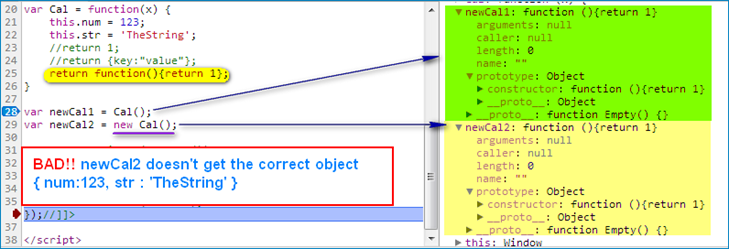
return a function in constructor class (BAD)
-
Run the code in jsFiddle
Conclusion:
-
Must use keyword “new” to instantiate a constructor class
-
Constructor class should not have a return statement
-
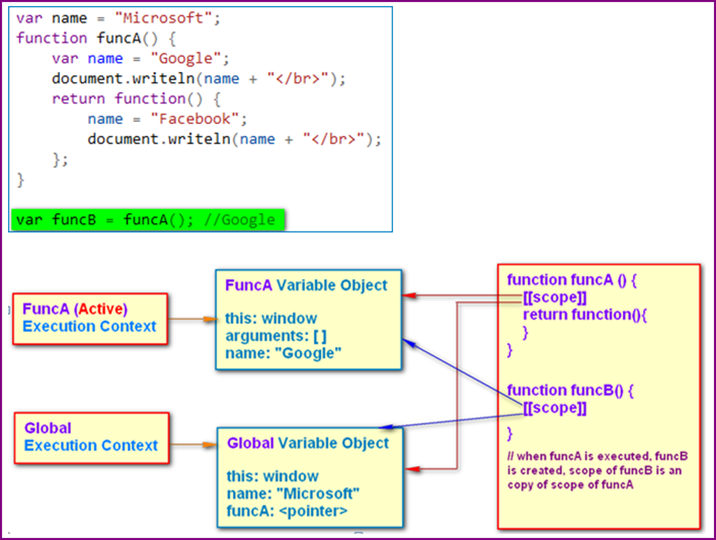
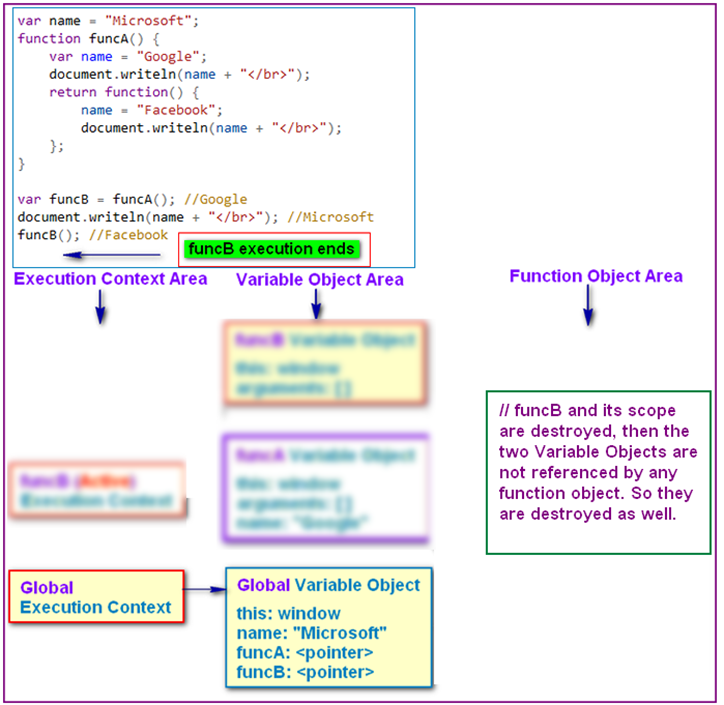
- Execution Context and Scope Chain
1 var name = "Microsoft"; 2 function funcA() { 3 var name = "Google"; 4 document.writeln(name + "</br>"); 5 return function() { 6 name = "Facebook"; 7 document.writeln(name + "</br>"); 8 }; 9 } 10 11 var funcB = funcA(); //Google 12 document.writeln(name + "</br>"); //Microsoft 13 funcB(); //Facebook
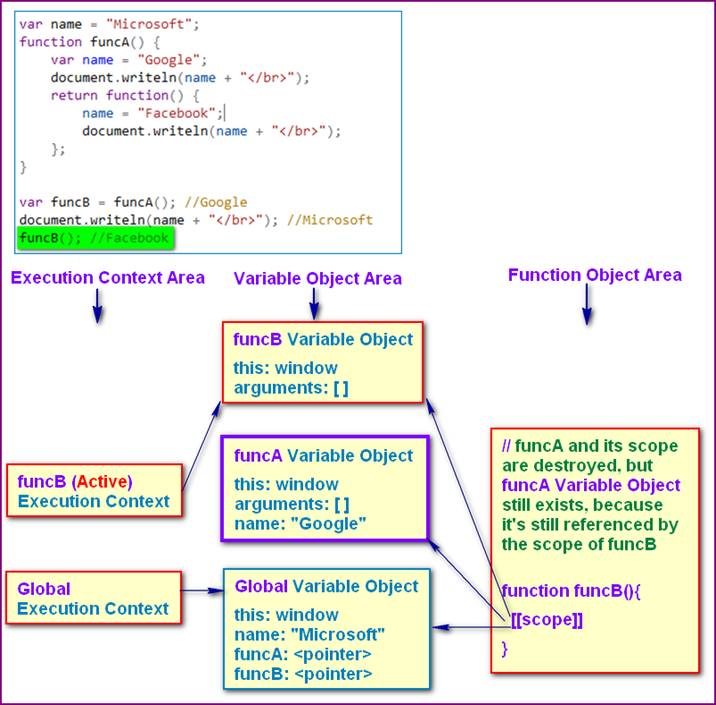
- A further example
1 var nameF = 'Facebook'; 2 function funcA() { 3 var nameM ='Microsoft'; 4 return function(){ 5 var name = 'Google'; 6 document.writeln(nameF +', '+ nameM +', ' + name+'</br>'); 7 }; 8 } 9 var funcB = funcA(); 10 funcB(); 11 12 //output: Facebook, Microsoft, Google
funcB can access nameM in funA scope, and nameF in Window scope









 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号