Python用Keras的LSTM神经网络进行时间序列预测天然气价格例子
原文链接:http://tecdat.cn?p=26519
原文出处:拓端数据部落公众号
一个简单的编码器-解码器LSTM神经网络应用于时间序列预测问题:预测天然气价格,预测范围为 10 天。“进入”时间步长也设置为 10 天。) 只需要 10 天来推断接下来的 10 天。可以使用 10 天的历史数据集以在线学习的方式重新训练网络。
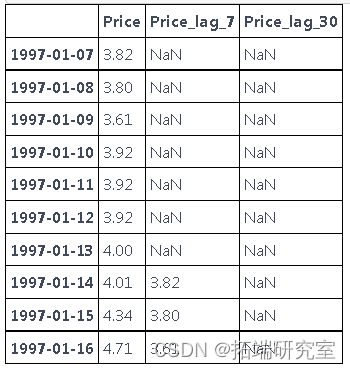
- 日期(从 1997 年到 2020 年)- 为 每天数据
- 以元计的天然气价格
读取数据并将日期作为索引处理
-
-
# 固定日期时间并设置为索引
-
dftet.index = pd.DatetimeIndex
-
-
# 用NaN来填补缺失的日期(以后再补)
-
dargt = f_arget.reindex(ales, fill_value=np.nan)
-
-
# 检查
-
print(d_tret.dtypes)
-
df_aget.head(10)
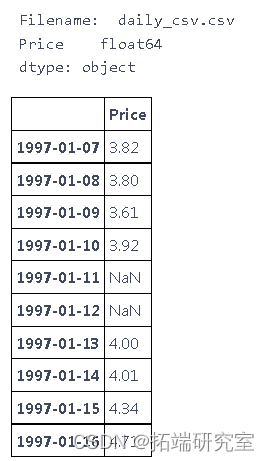
处理缺失的日期
-
# 数据归纳(,使用 "向前填充"--根据之前的值进行填充)。
-
dfaet.fillna(method='ffill', inplace=True)
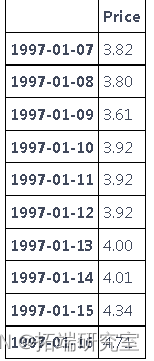
特征工程
因为我们正在使用深度学习,所以特征工程将是最小的。
- One-hot 编码“is_weekend”和星期几
- 添加行的最小值和最大值(可选)
通过设置固定的上限(例如 30 倍中位数)修复异常高的值
-
-
-
# 在df_agg中修复任何非常高的值 - 归一化为中值
-
for col in co_to_fi_ies:
-
dgt[col] = fixnaes(dftget[col])
添加滞后
-
-
# 增加每周的滞后性
-
df_tret = addag(d_aget, tare_arble='Price', step_ak=7)
-
# Add 30 day lag
-
df_get = ad_ag(df_ret, tagt_able='Price', sep_bck=30)
-
# 合并后删除任何有NA值的列
-
d_gt.dropna(inplace=True)
-
print(dfget.shape)
-
-
tie_nx = df_art.index
![]()
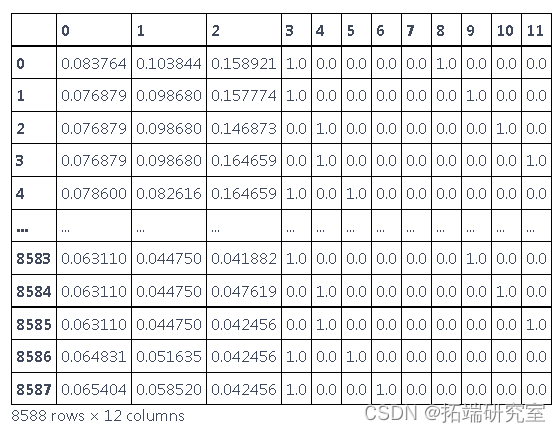
归一化
- 归一化或最小-最大尺度(需要减小较宽的数值范围,以便 LSTM 收敛)。
-
# 标准化训练数据[0, 1]
-
sclr = prcsing.Maxcaer((0,1))
准备训练数据集
- 时间步数 = 1
- 时间步数 = nsteout小时数(预测范围)
在这里,我们将数据集从 [samples, features] 转换为 [samples, steps, features] - 与算法 LSTM 一起使用的形状。下面的序列拆分使用“walk-forward”方法来创建训练数据集。
-
# 多变量多步骤编码器-解码器 lstm 示例
-
# 选择一个时间步骤的数量
-
-
-
-
# 维度变成[样本数、步骤、特征]
-
X, y = splices(datasformed, n_ep_in, n_ep_out)
-
-
# 分成训练/测试
-
et_ut = int(0.05*X.shpe[0])
-
X_tain, X_est, ytrain, y_tst = X[:-tetaont], X[-tes_ont:], y[:-tstmunt], y[-es_unt:]

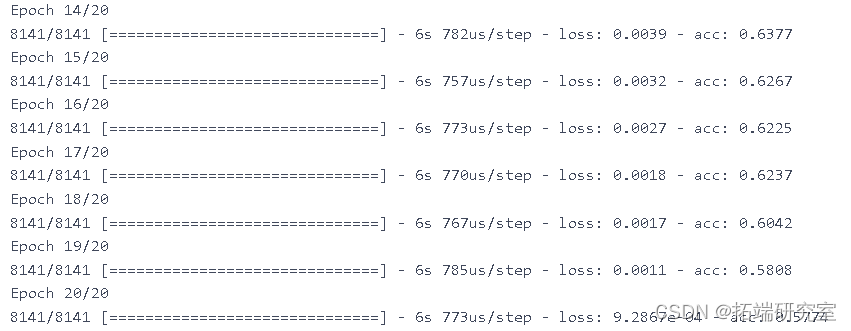
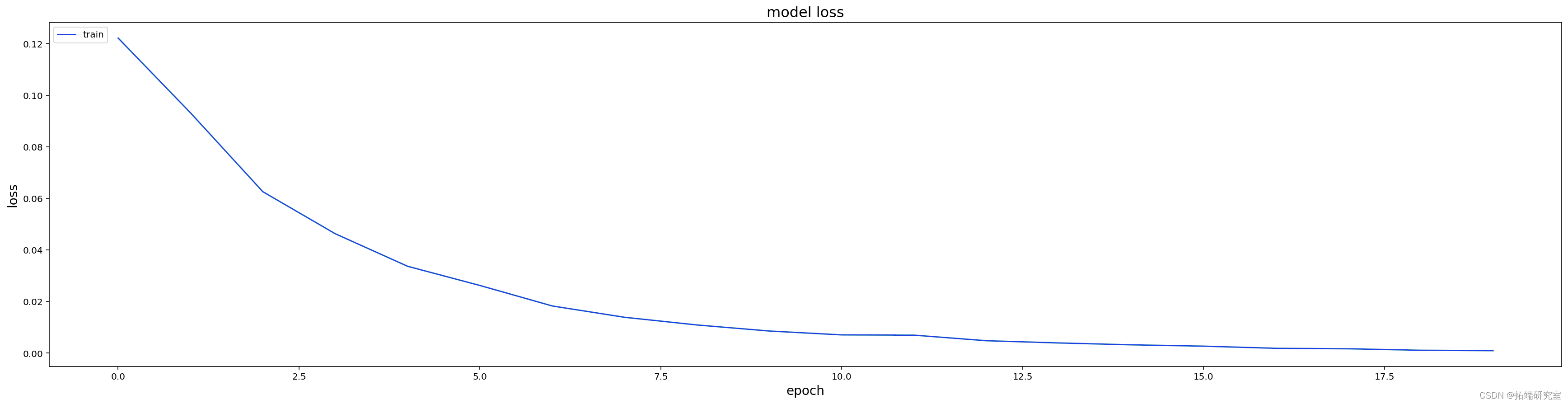
训练模型
这利用了长期短期记忆算法。
-
# 实例化和训练模型
-
print
-
model = cre_odel(n_tps_in, n_tep_out, n_feures, lerig_rate=0.0001)
探索预测
-
%%time
-
#加载特定的模型
-
-
model = lod_id_del(
-
n_stepin,
-
n_sep_out,
-
X_tan.shape[2])

-
# 展示对一个样本的预测
-
testle_ix = 0
-
yat = mdel.predict(X_tet[est_amle_ix].reshape((1,n_sep_in, nfatues)),erbose=Tue)
-
# 计算这一个测试样本的均方根误差
-
rmse = math.sqrt
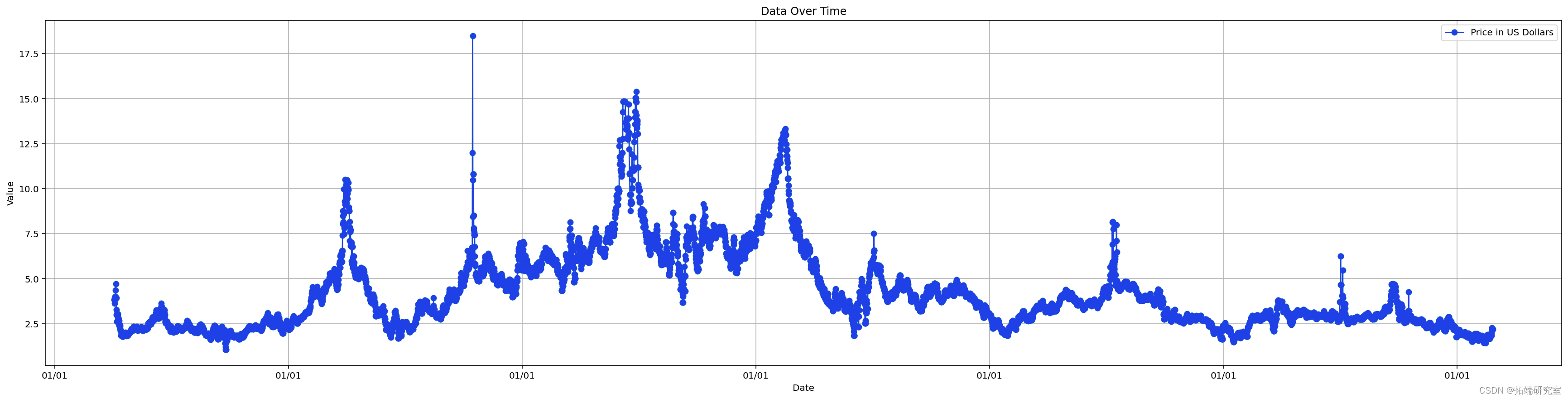
![]()
plot_result(yhat[0], scaler, saved_columns)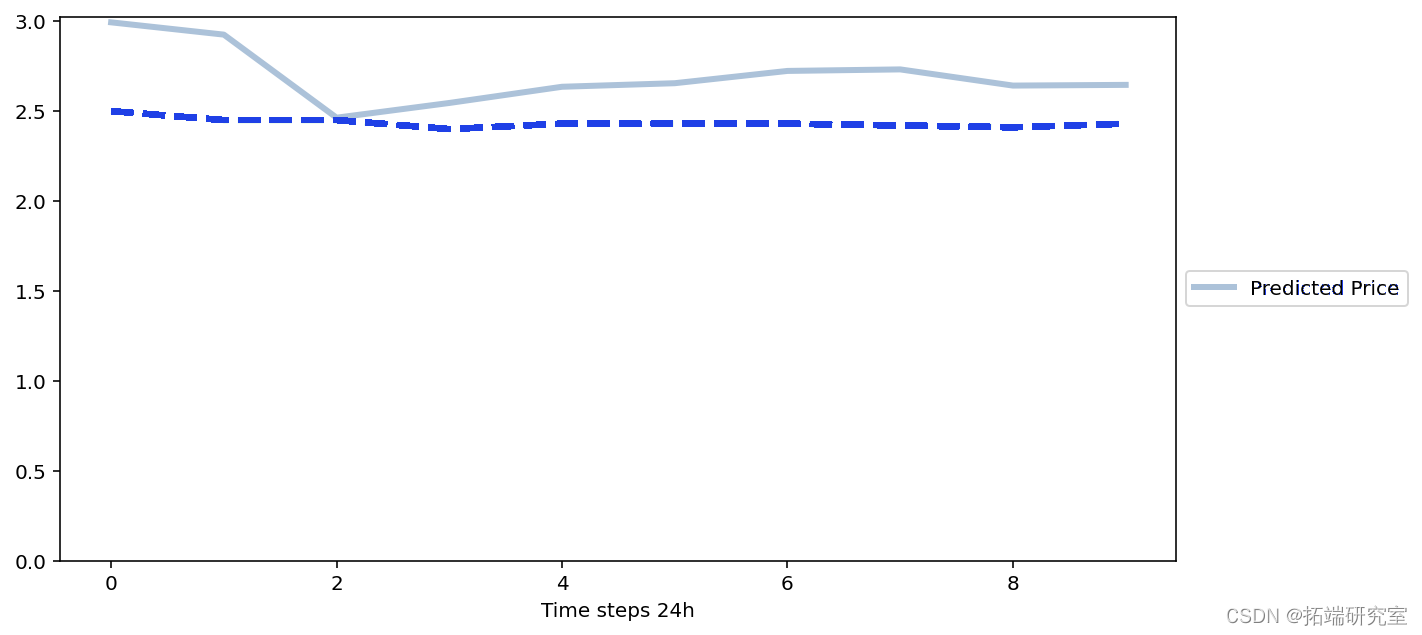
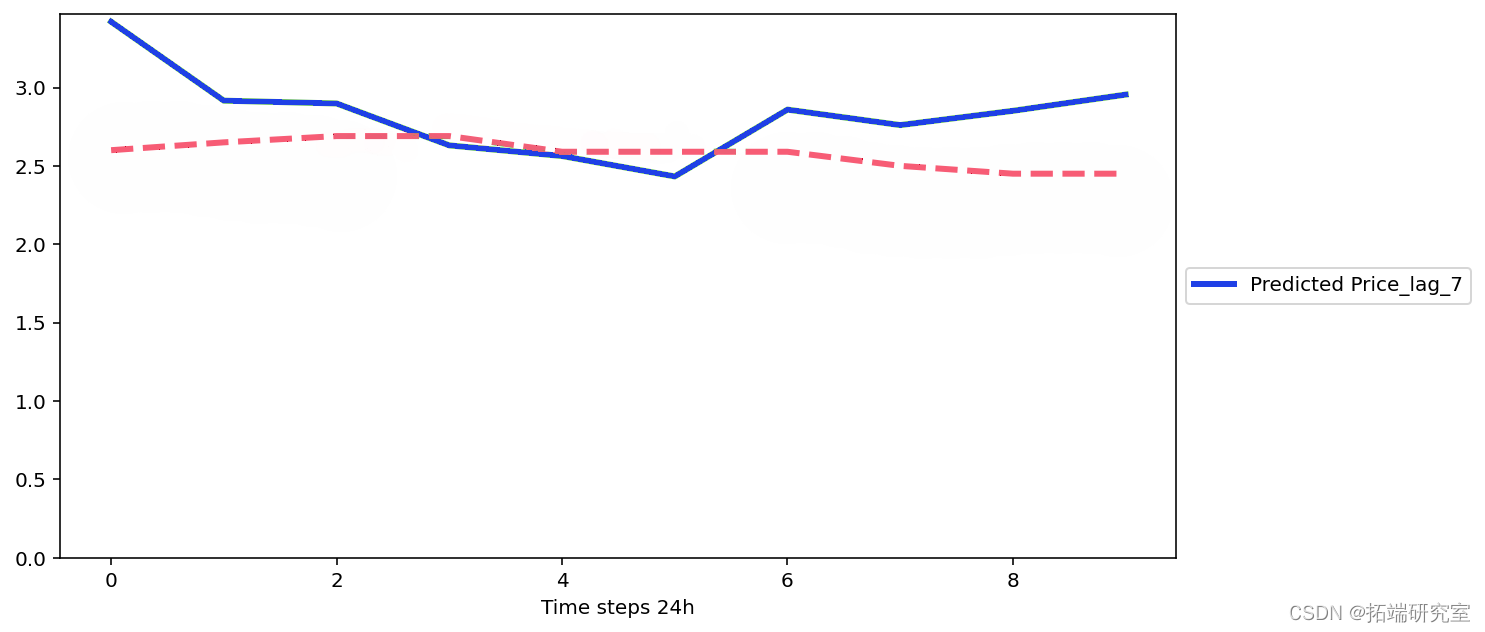
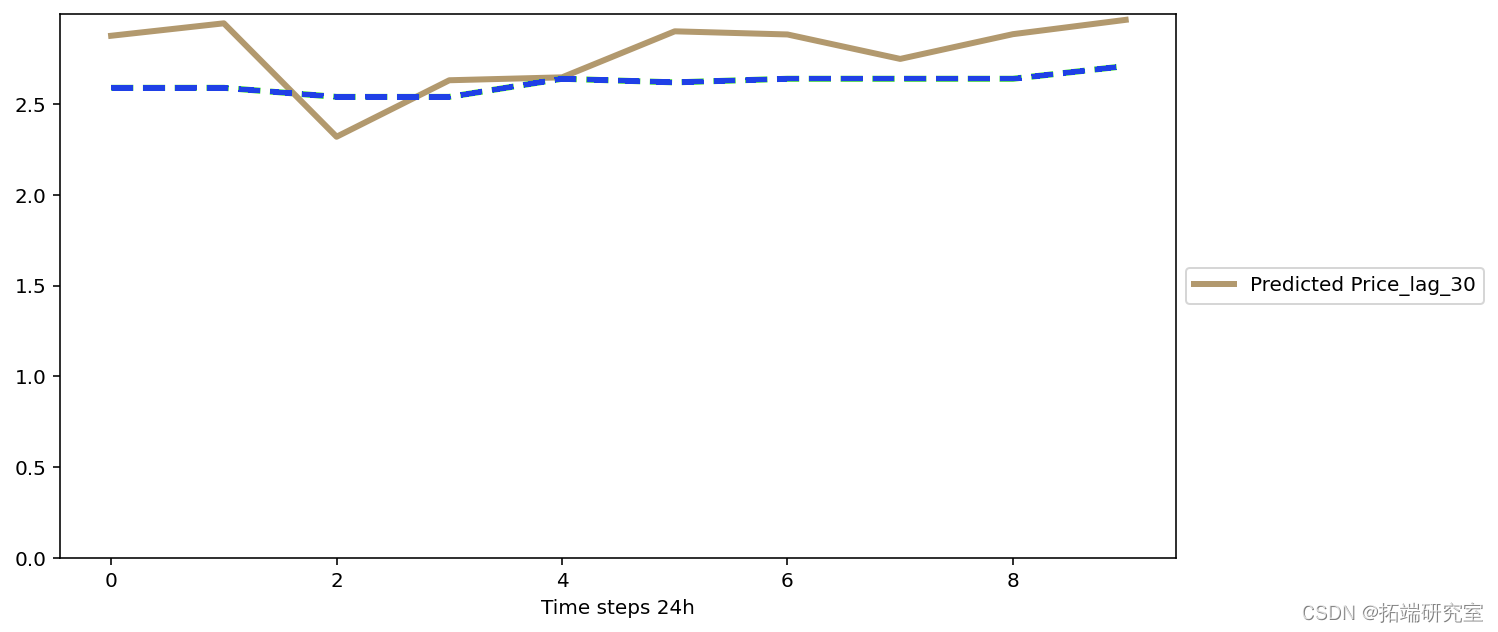
平均 RMSE
-
# 收集所有的测试RMSE值
-
rmesores = []
-
for i in range:
-
yhat = oel.predict(Xtet[i].reshape((1, _stes_in, _faues)), verbose=False)
-
# 计算这一个测试样本的均方根误差
-
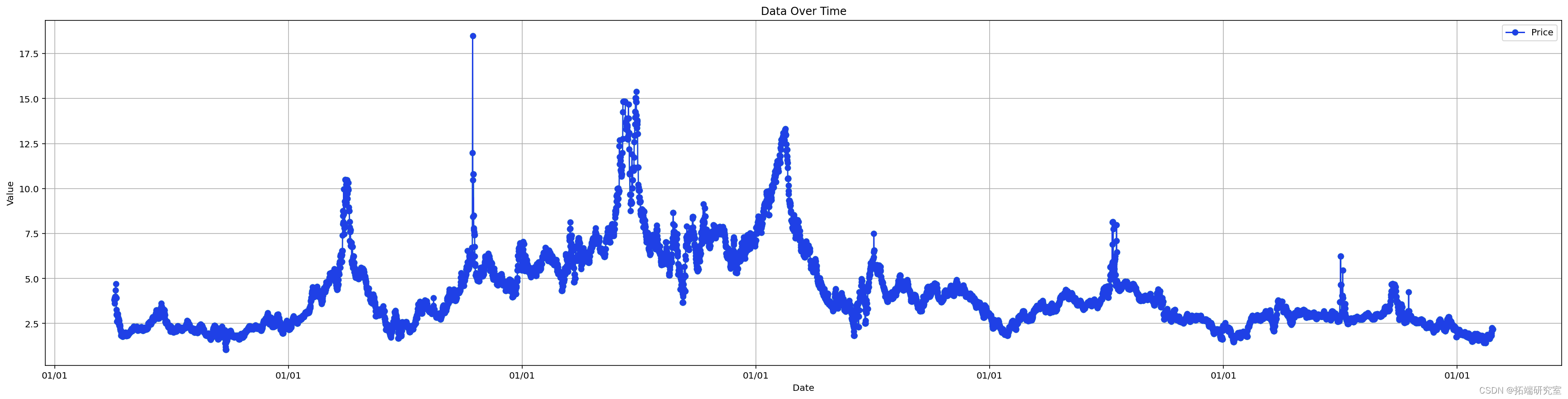
rmse = math.sqrt(mensqaerror(yhat[0], y_test[i]))
![]()
训练整个数据集
-
#在所有数据上实例化和训练模型
-
modl_l = cret_mel(nsep_in, steps_ou, n_etures,learnnrate=0.0001)
-
mde_all, ru_ime, weighfie = trin(md_all, X, y, batcsie=16, neohs=15)

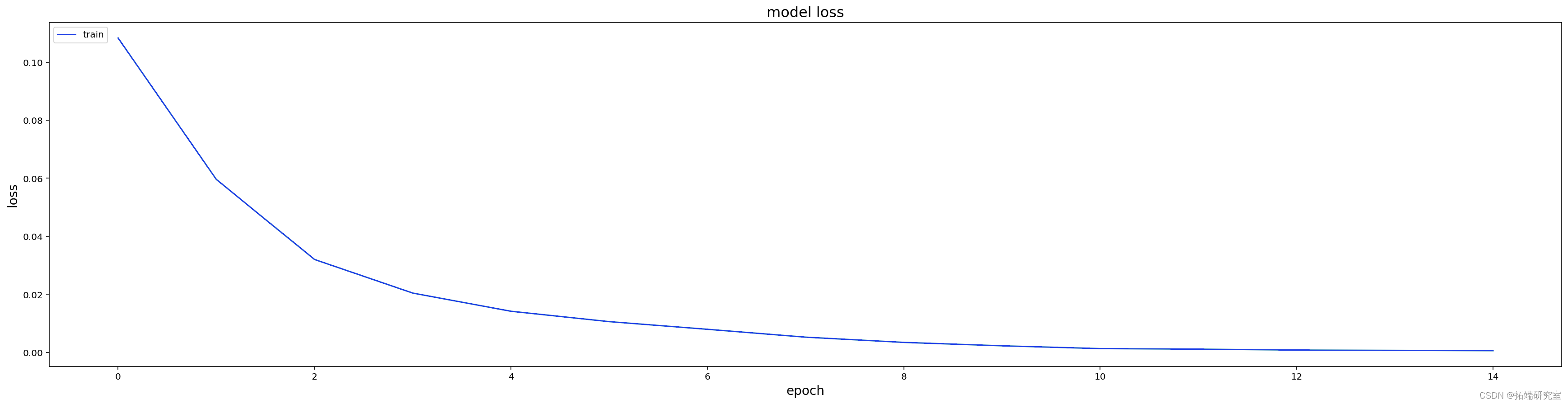
样本内预测
注意:模型已经“看到”或训练了这些样本,但我们希望确保它与预测一致。如果它做得不好,模型可能会欠拟合或过拟合。要尝试的事情:
- 增加或减少批量大小
- 增加或减少学习率
- 更改网络中 LSTM 的隐藏层数
-
-
# 获得10个步
-
da_cent = dfret.iloc[-(ntes_in*2):-nsps_in]
-
-
# 标准化
-
dta_ectormed = sclr.rasfrm(daareent)
-
-
# 维度变成[样本数、步骤、特征]
-
n_res = dtcentorm.shape[1]
-
X_st = data_recn_trsrd.reshape((1, n_tps_n, n_feares))
-
-
# 预测
-
foecst = mlll.predict(X_past)
-
-
# 扩大规模并转换为DF
-
forcast = forast.resape(n_eaturs))
-
foect = saer.inese_transform(forecast)
-
fuure_dtes df_targe.ide[-n_steps_out:]
-
-
# 绘图
-
histrcl = d_aet.ioc[-100:, :1] # 获得历史数据的X步回溯
-
for i in ane(oisae[1]):
-
fig = plt.igre(fgze=(10,5))
-
-
# 绘制df_agg历史数据
-
plt.plot(.iloc[:,i]
-
-
# 绘制预测图
-
plt.plot(frc.iloc[:,i])
-
-
# 标签和图例
-
plt.xlabel
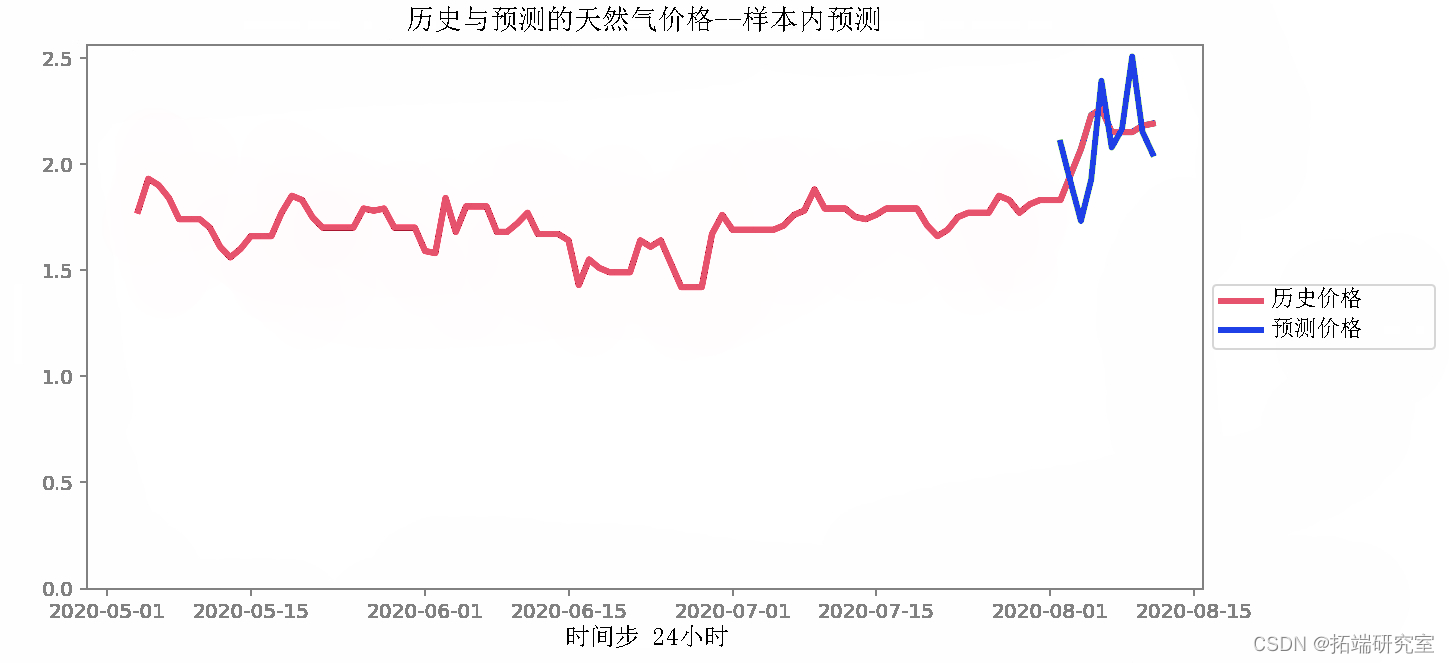
预测样本外
-
-
# 获取最后10步
-
dtareent = dfargt.iloc[-nstpsin:]。
-
-
# 缩放
-
dta_ecntranfomed = scaler.trasorm(data_recent)
-
-
-
# 预测
-
forct = meall.rict(_past)
-
-
# 扩大规模并转换为DF
-
foreast = foecs.eshape(_seps_ut, n_eatures))
-
foreast = sclerinvers_tranorm(focast)
-
futur_daes = pd.daternge(df_argetinex[-1], priods=step_out, freq='D')
-
-
-
# 绘图
-
htrical = df_taet.iloc[-100:, :1] # 获得历史数据的X步回溯
-
# 绘制预测图
-
plt.plot(fectoc[:,i])
-

最受欢迎的见解
1.在python中使用lstm和pytorch进行时间序列预测
2.python中利用长短期记忆模型lstm进行时间序列预测分析
▍关注我们
【大数据部落】第三方数据服务提供商,提供全面的统计分析与数据挖掘咨询服务,为客户定制个性化的数据解决方案与行业报告等。
▍咨询链接:http://y0.cn/teradat
▍联系邮箱:3025393450@qq.com




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号