用RNN来做像素分类,输入是一系列相近的像素,长度人为指定为l,相近是利用像素相似度或是范围相似度得到的,计算个欧氏距离或是SAM。
数据是两个高光谱数据
1、Pavia University,Reflective Optics System Imaging Spectrometer (ROSIS) sensor得到,102个波段,1.3米空间分辨率,总大小610*340像素,9类地物
2、Salinas image,Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS),204个有效波段,3.7米空间分辨率,总大小512*217像素,16类地物
网络结构:
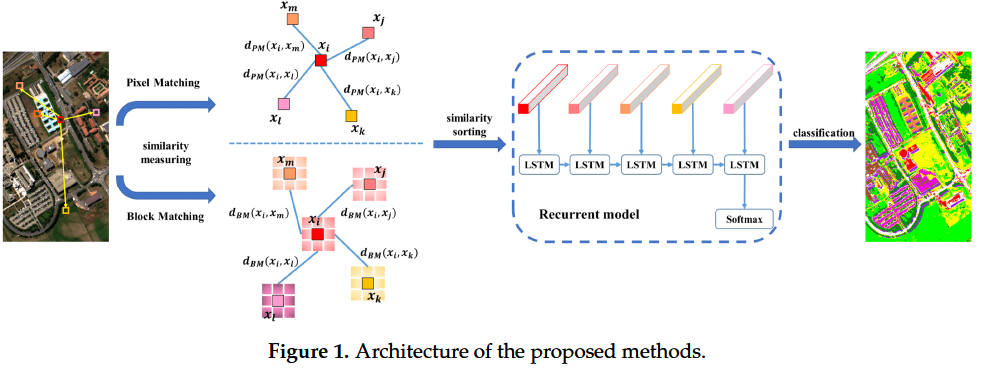
主要亮点在于像素点的选择吧,通过 Pixel Matching 和 Block Matching 来计算相似度距离,将距离按升序排列,选前n个距离最小的作为LSTM的输入,得到结果
参考文献:
42. Ienco, D.; Gaetano, R.; Dupaquier, C.; Maurel, P. Land cover classification via multitemporal spatial data by
deep recurrent neural networks. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 14, 1685–1689. [CrossRef]
43. Sharma, A.; Liu, X.; Yang, X. Land cover classification from multi-temporal, multi-spectral remotely sensed
imagery using patch-based recurrent neural networks. Neural Netw. 2018, 105, 346–355. [CrossRef]
44. Mou, L.; Ghamisi, P.; Zhu, X.X. Deep recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification.
IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 3639–3655. [CrossRef]
45. Wu, H.; Prasad, S. Convolutional recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral data classification. Remote Sens.
2017, 9, 298. [CrossRef]
46. Shi, C.; Pun, C.M. Multi-scale hierarchical recurrent neural networks for hyperspectral image classification.
Neurocomputing 2018, 294, 82–93. [CrossRef]
47. Romera-Paredes, B.; Torr, P.H.S. Recurrent instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the
European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–16 October 2016; Springer:
Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 312–329.



