随便玩玩之C# 6 程序控制-条件判断if
随便玩玩之C# 6 程序控制-条件判断if
1.if
前面的内容中语句都是一条一条执行的。生活中又很多不确定的事情,就要做好各种打算。比如:如果明天下雨,在家打游戏。这里关键词就是“如果”,根据明天的实际情况,再确定要做的事情。这就是程序流程控制。
根据明天天气情况,打不打游戏的事情,文字描述的伪代码可以这样写:
如果(明天下雨)
{
在家玩游戏
}
如果(if)就是判断条件的开始。
括号中的“明天下雨”表示明天天气情况,在编程中当然不能直接写上天气情况,要用程序语言来描述。可以使用真(true)或假(false)表示。真假也是C#语言的一种数据类型。
大括号的内容即条件为真时执行的语句。所谓的条件为真或假就是下不下雨的问题。
C#语言的代码如下:
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
bool tomorrowWeather; //声明一个布尔类型的变量,表示明天天气情况。
//明天下雨为真(true),不下雨为假(false)。
tomorrowWeather = true;
if (tomorrowWeather==true)
{
Console.WriteLine("在假打游戏");
}
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
}
}
}
第10行中的语句表示声明一个布尔类型的变量,变量名称为tomorrowWeather,变量的值可能为真也可能为假。
第12行将明天的天气情况设定为下雨(true),即将真值赋给tomorrowWeather。
第14行判断代码开始,用if表示开始,之后跟小括号内的判断内容,判断明天天气情况,括号里的判断内容结果为真就执行后面大括号内的代码,否则跳过,执行大括号后吗的代码。其中的判断符号为“==”两个等号。一个等号是赋值,两个等号是判断。
运行结果:
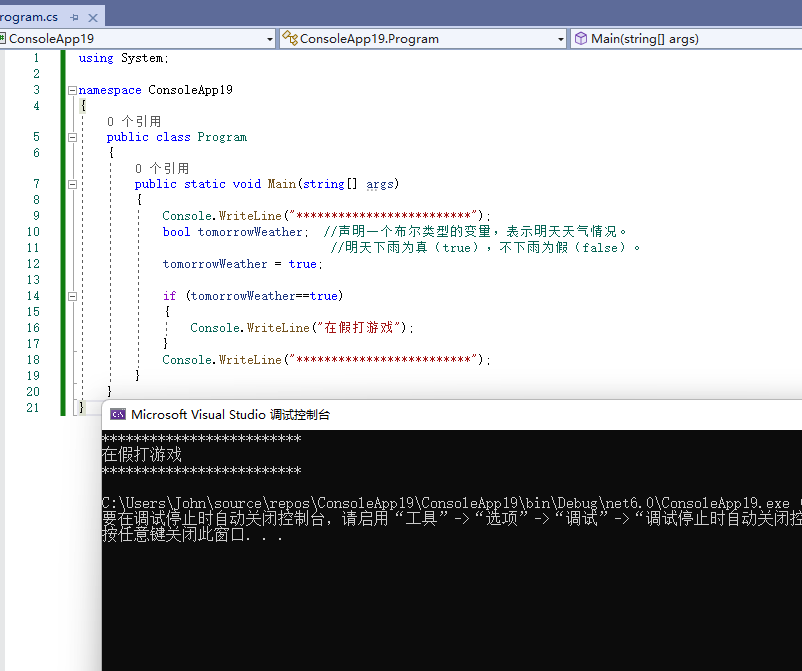
如果明天不下雨,大括号里的语句就不执行。修改天气为不下雨(false)。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
bool tomorrowWeather; //声明一个布尔类型的变量,表示明天天气情况。
//明天下雨为真(true),不下雨为假(false)。
tomorrowWeather = false;
if (tomorrowWeather==true)
{
Console.WriteLine("在假打游戏");
}
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
}
}
}
运行结果:
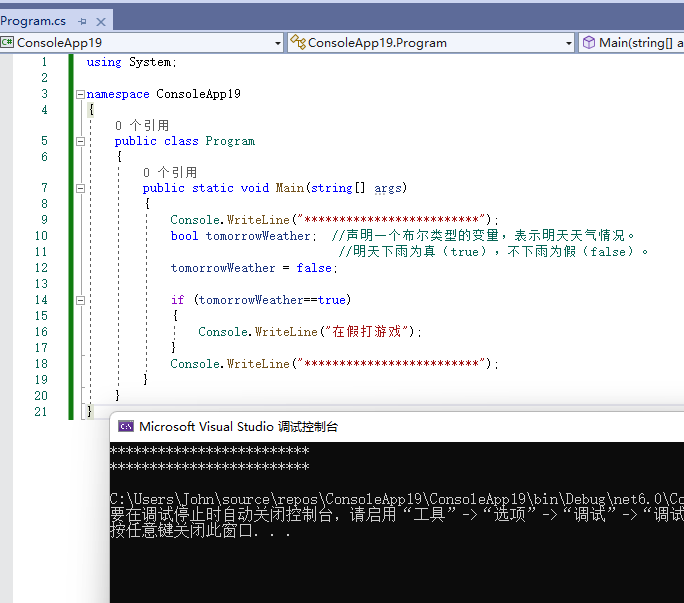
刚刚没想好不下雨去干啥,现在想好了,如果明天不下雨就去公园。那么就可以再写一个if判断语句。
using System;
namespace ConsoleApp19
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
bool tomorrowWeather; //声明一个布尔类型的变量,表示明天天气情况。
//明天下雨为真(true),不下雨为假(false)。
tomorrowWeather = false;
if (tomorrowWeather==true)
{
Console.WriteLine("明天下雨,在家打游戏");
}
if (tomorrowWeather == false)
{
Console.WriteLine("明天不下雨,去公园玩");
}
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
}
}
}
运行结果:
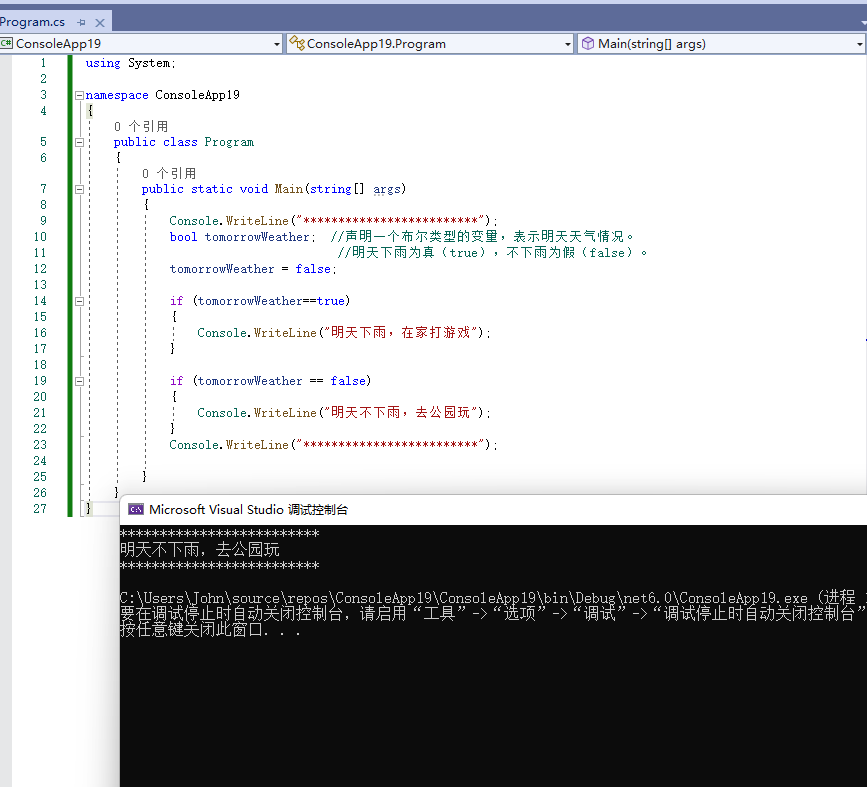
两个if,根据 tomorrowWeather的结果执行不同的语句。
using System;
namespace Week
{
public class Program
{
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
//声明变量
string weekNumber=Console.ReadLine();
//判断输出
if (weekNumber == "1") { Console.WriteLine("星期一"); }
if (weekNumber == "2") { Console.WriteLine("星期二"); }
if (weekNumber == "3") { Console.WriteLine("星期三"); }
if (weekNumber == "4") { Console.WriteLine("星期四"); }
if (weekNumber == "5") { Console.WriteLine("星期五"); }
if (weekNumber == "6") { Console.WriteLine("星期六"); }
if (weekNumber == "7") { Console.WriteLine("星期日"); }
//判断不符合要求的输入
if (weekNumber == null) { Console.WriteLine("你什么都没有输入"); }
Console.WriteLine("*************************");
}
}
}
运行结果:
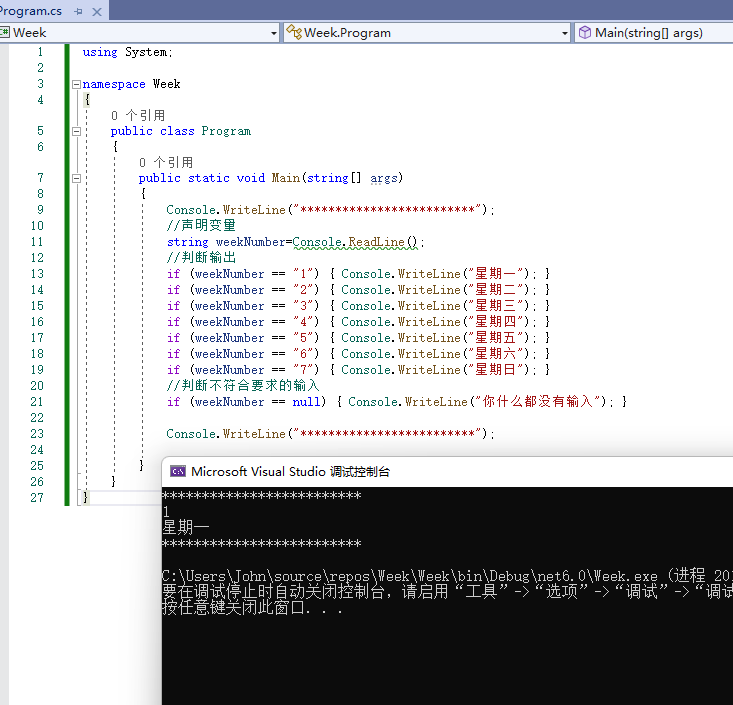
将工具箱中的Label控件拖放到WPF设计器的空白区域。选中WPF设计器中Label控件,将其名称修改为OutputLabel。
将工具箱中的Button控件拖放到WPF设计器的空白区域。选中WPF设计器中Button控件,将其Content属性修改为确定。
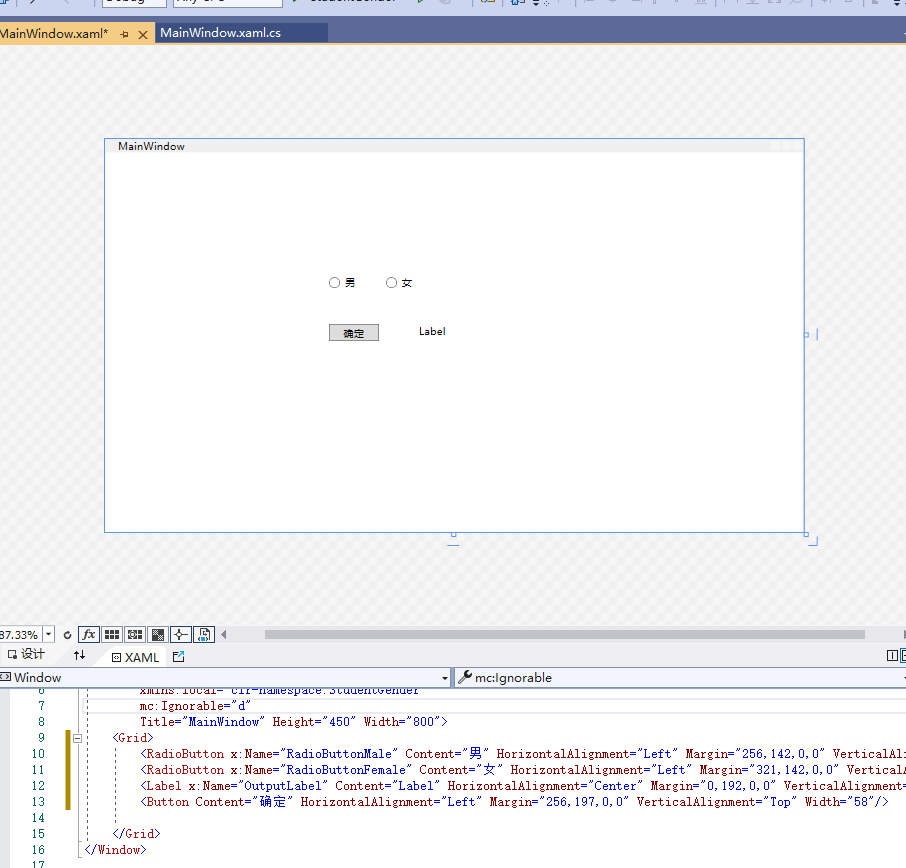
双击Button按钮,再Button_Click()中输入代码。
private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
// 判断RadioButton是否被选中,选中了就提示选中的RadioButton
// (bool)表示强制转换数据类型,RadioButtonMale.IsChecked表示是否被选中
if ((bool)RadioButtonMale.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "选择了性别:男"; }
if((bool)RadioButtonFemale.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "选择了性别:女"; }
}
运行个结果:

-----------------------------------------------------
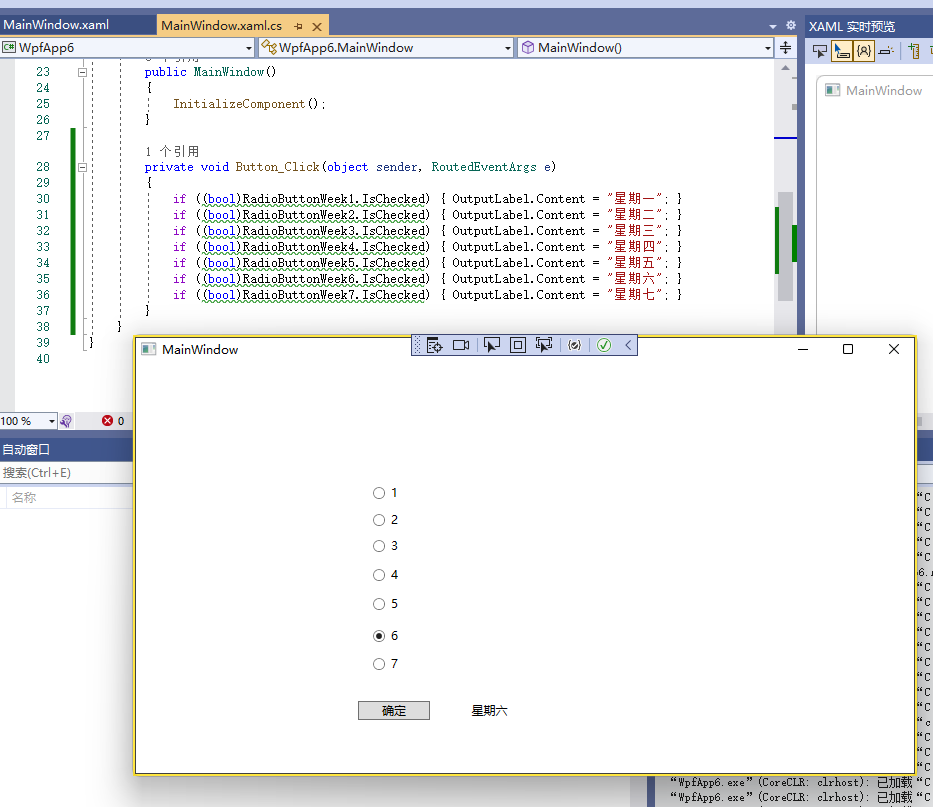
将工具箱中的Label控件拖放到WPF设计器的空白区域。选中WPF设计器中Label控件,将其名称修改为OutputLabel。
将工具箱中的Button控件拖放到WPF设计器的空白区域。选中WPF设计器中Button控件,将其Content属性修改为确定。

双击Button按钮,再Button_Click()中输入代码。
private void Button_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e)
{
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek1.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期一"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek2.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期二"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek3.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期三"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek4.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期四"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek5.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期五"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek6.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期六"; }
if ((bool)RadioButtonWeek7.IsChecked) { OutputLabel.Content = "星期七"; }
}
运行结果:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号