java---多线程
1. Thraed类和Runnable接口
(1)Thread类
static boolean holdsLock(Object obj) //当前线程是否占有obj对象锁
2. 实现线程的3种方式
(1)实现 java.lang.Runnable接口
1 public class TestRunnable implements Runnable{ 2 private int count = 10; 3 @Override 4 public void run() { 5 while(count-->0) { 6 System.out.println("TestRunnable run"); 7 } 8 } 9 }
TestRunnable b = new TestRunnable(); new Thread(b).start(); System.out.println("main end");
(2)继承 java.lang.Thread类
1 public class TestThread extends Thread{ 2 private int count = 10; 3 public void run(){ 4 while(count-->0) { 5 System.out.println("TestThread run"); 6 } 7 } 8 }
TestThread a = new TestThread(); a.start(); System.out.println("main end");
run和start的区别:
run封装了线程要执行的代码,直接调用是普通方法
start表示启动线程,由jvm去调用线程的run方法
(3)Callable
是Runnable的扩展,Callable可以抛出异常,且有返回值
import java.util.concurrent.*; public class Outer { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Future<Integer> f1 = pool.submit(new Thread1(100)); Future<Integer> f2 = pool.submit(new Thread1(200)); int i1 = f1.get(); int i2 = f2.get(); System.out.println(i1); System.out.println(i2); pool.shutdown(); } static class Thread1 implements Callable<Integer> { private int number; public Thread1(int number) {this.number = number;} @Override public Integer call() throws Exception { int sum = 0; for(int x = 1;x<=number;x++) { sum += x; } return sum; } } }
3. 线程生命周期
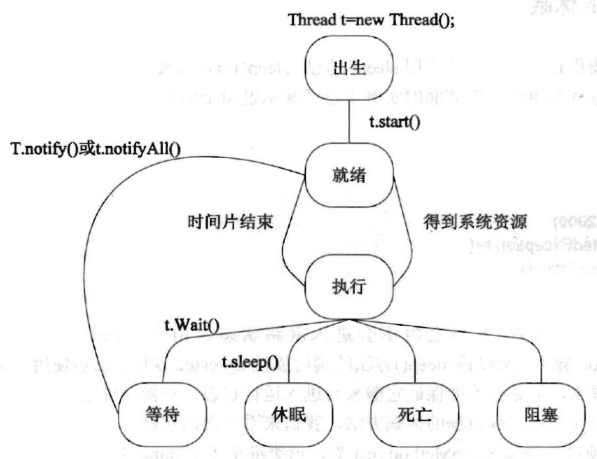
(1)休眠
static void sleep(long millis)
线程进入休眠状态,之后进入就绪状态
可能抛出 InterruptedException 异常
(2)线程加入
存在线程A和B,如果需要插入线程B,让线程B先执行完毕,然后执行线程A:在A的线程中调用B的join方法
void join() void join(long millis)
在A中调用 B.join()时,A会等待B结束,然后继续执行
若调用B.join(n),A线程尝试获得B的锁,然后等待n毫秒,如果n毫秒后B还没结束,则A继续往下执行(如果不能获得锁,则会一直等待)
(3)线程中断
void interrupt()
在线程外部调用,结束线程,抛出异常
(4)线程礼让
static void yield()
提醒正在运行的线程礼让资源给其它线程,不保证成功。
(5)线程优先级
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY 1 Thread.MAX_PRIORITY 2 Thread.NORM_PRIORITY 5
线程默认优先级为NORM_PRIORITY,子线程继承了父线程的优先级
void setPriority(int newPriority) int getPriority()
设置优先级的参数:1~10,参数不对会产生 IllegalArgumentException异常
4. 线程同步
(1)同步块
synchronized(Object) { // }
Object:检查对象标志位,如果为0,表明此同步块中存在其它线程在运行,如果为1,则线程可以执行到同步块中并设置标志位为0
(2)同步方法
synchronized void fun() {}
当某个对象调用了同步方法,该对象上其它同步方法必须等待该同步方法执行完毕才能被执行,必须将每个能访问共享资源的方法修饰为synchronized
5. 线程间通信
(1)等待
继承自Object:
void wait() void wait(long timeout)
调用wait,会释放该线程占有的锁(sleep不会)
(2)唤醒
继承自Object:
void notify() void notifyAll()
package com; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class Outer { static boolean flag =true; static Object lock = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Thread1(),"线程A"); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Thread2(),"线程B"); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } static class Thread1 implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { synchronized (lock) { while(flag) { //当前线程不满足执行条件 try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":flag is true.wait at " +new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); lock.wait(); //进入等待状态,释放锁lock }catch (InterruptedException e) { } } //条件满足,继续工作 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+":flag is false.running at " +new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); } } } static class Thread2 implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { synchronized (lock) { //另一个线程发出通知,当前代码块执行完才释放锁lock System.out.println(Thread.currentThread()+" hold lock.notify at " +new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date())); lock.notifyAll(); flag = false; } } } }
6. 守护线程
调用 Thread的成员方法setDaemon(true)
=======================================================================================




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号