SpringBoot
Spring Boot
1.微服务
1.1什么是微服务架构
微服务是一种架构风格(可以对比mvc三层架构,mvvm前端架构对比),要求我们在开发一个应用的时候,这个应用必须构建成一系列小的服务组合。可以通过http的方式进行互通。其演变过程:
1.1.1单体应用架构
单体应用架构(all in one)是指,将一个应用中的所有应用服务都封装在一个应用中
好处:易于开发和测试,方便部署
缺点:修改任何一处都需要关掉服务器,重新打包和部署。不利于大型项目的维护和分工
1.1.2微服务架构
打破all in one的架构方式,每个工功能元素独立起来。独立的元素动态组合,需要哪一些功能元素就拿来组合,
简而言之,微服务架构样式[1]是一种将单个应用程序开发为一组小服务的方法,每个小服务都在自己的进程中运行并与轻量级机制(通常是HTTP资源API)进行通信。这些服务围绕业务功能构建,并且可以由全自动部署机制独立部署。这些服务的集中管理几乎没有,可以用不同的编程语言编写并使用不同的数据存储技术。
相关文献推荐:微服务论文(马丁·福勒) - 简书 (jianshu.com)
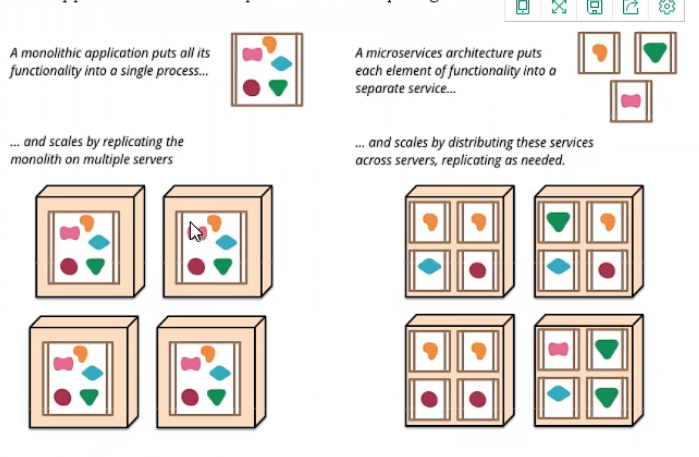
一个大型系统的微服务架构,就像一个复杂交织的神经网络,每个神经元就是一个功能元素,他们各自完成自己的功能,然后通过http相互请求调用,但是这种庞大的系统架构给部署和运维带来很大的难度,即spring带来了大型分布式服务的全套,全程产品
- springboot构建一个个独立的微服务应用单元,帮我们快速构建一个应用
- springcloud完成大型分布式网络服务调用,实现分布式
- spring cloud data flow在分布式中间进行流式数据计算,批处理
组件是独立可替换和可升级的软件单元。
我们将库定义 为链接到程序中并使用内存中函数调用进行调用的组件
而服务则是进程外组件,它们通过某种机制(例如Web服务请求或远程过程调用)进行通信。(这与许多OO程序中的服务对象的概念不同[3]。)
2.第一个Spring Boot程序
springboot提供快速生成的网站,官网下载后解压导入idea
同时idea也集成了该网站功能,直接使用idea创建一个springboot项目
也可生成一个空白的springboot项目,然后导入web包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
在application.properties包里,基本配置可以更改端口号:
server.port=8081
2.1自动装配原理
springboot是通过main方法下的SpringApplication.run方法启动的,启动的时候他会调用refshContext方法,先刷新容器,然后根据解析注解或者解析配置文件的形式祖册bean,而它是通过启动类的SpringBootApplication注解进行开始解析的,他会根据EnableAutoConfiguration开启自动化配置,里面有个核心方法ImportSelect选择性的导入,根据loadFanctoryNames根据classpash路径以MATA-INF/spring.factorces下面以什么什么EnableAutoConfiguration开头的key去加载里面所有对应的自动化配置,他并不是把这一百二十多个自动化配置全部导入,在他每个自动化配置里面都有条件判断注解,先判断是否引入相互的jar包,再判断容器是否有bean再进行注入到bean容器
pom.xml
-
核心依赖都在父工程中 <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.7.4</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent>
启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 启动器:就是springboot的启动场景。如spring-boot-starter-web会自动导入web环境所有依赖
- springboot会将所有功能场景,编程一个个启动器。需要什么功能,只需要找到所需要启动器即可
主程序(@SpringBootApplication 主程序类标志)
springboot所有的自动配置文件都是在启动的时候扫描并加载:
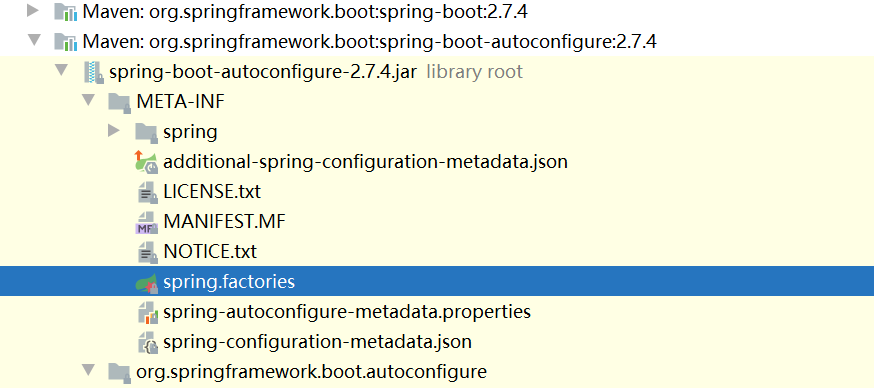
spring.factories所有的自动配置类都在这里,但是不一定生效,因为需要满足ConditionalOnClass()里面所有的条件,其中就必须包括启动类,只有导入了相关的star启动器,这些自动装配的包才有效
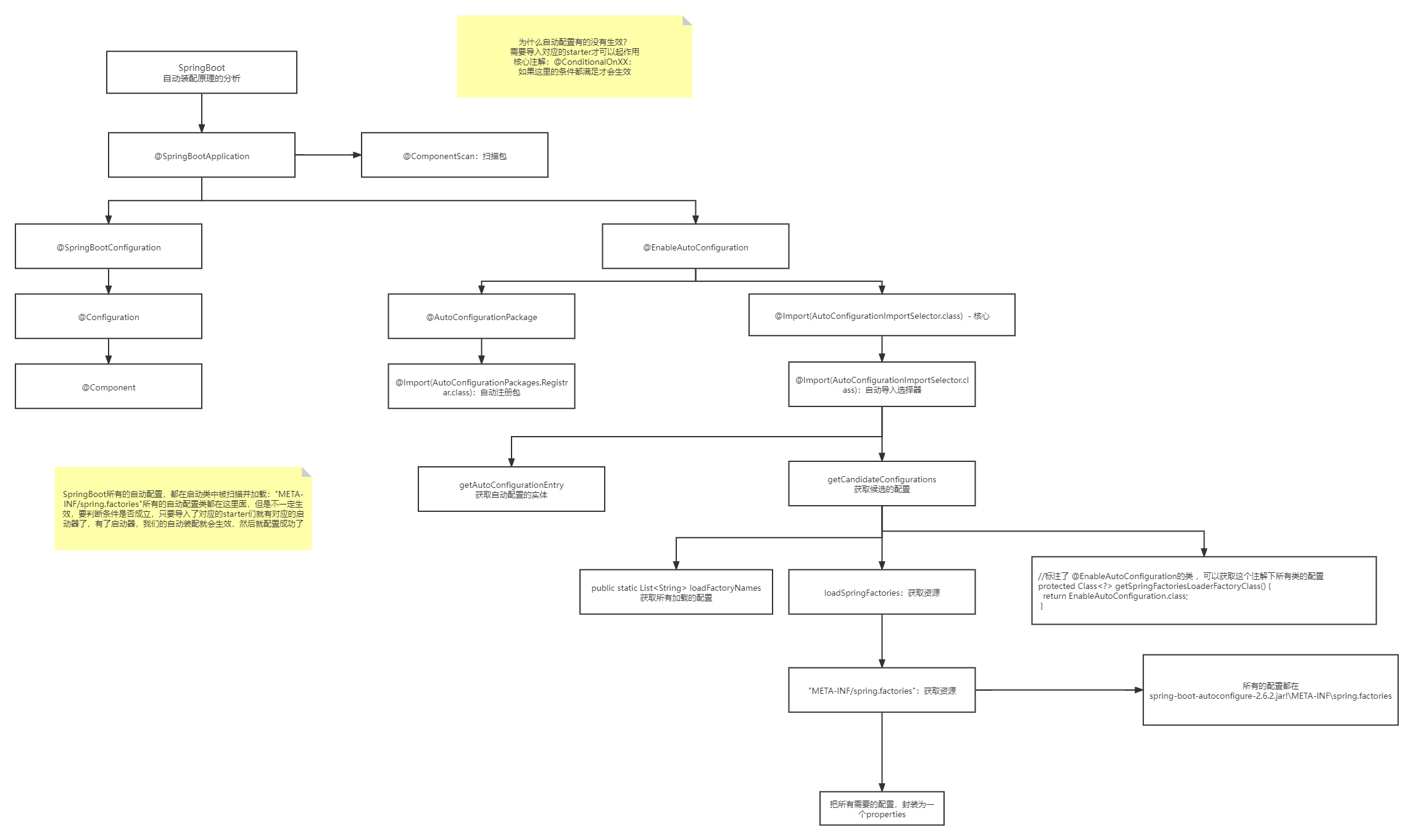
-
SpringBoot在启动的时候,从类路径下/META-INF/spring.factories获取指定的值
-
将这些自动配置的类导入容器,自动配置类就会生效,帮我们进行自动配置
-
以前我们需要自动配置的东西,现在不需要了
-
整合javaEE,解决方案和自动配置的东西都在Spring-boot-autoconfigure下
-
它会把所有需要导入的组件,以类名的方式返回这些组件,这些组件就会被添加到容器
-
容器中也会存在非常多的XXXAutoConfigure的文件(@Bean),就是这个类给容器导入了这个场景所需要的所有组件并自动配置
2.2主程序
SpringApplication.run()
1.推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是web项目
2.查找并加载所有可用初始化器,设置到initializers属性中
3.找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners中
4.推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类(加载主类)
3.配置文件
yaml是一种标记语言(对空格的要求十分严格),语法: k: v
# 普通的key-value
name: tzf
#对象
student:
name: tzf
age: 18
#行内写法
student: {name: tzf , age: 18}
#数组
pets:
-cat
-dog
-pig
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
xxxconfigeration组件装配了大量的xxxpropertiesz自动装配类,我们在yaml的配置其实就是在给xxxpropertiesz自动装配类的属性赋值,以达到自动配置的效果。
另外我们可以通过在yaml配置debug=true在控制台输出查看哪些配置以及开启,哪些还未开启
还有就是并不是所有的xxxautoconfigeration自动装配都会起作用,因为这些自动装配类内部都有@ConditionalOneClass(xxx,xxx,xxx),只有满足@ConditionalOneClass这个注解里面所有条件,被注解的配置类才会起作用,而这些条件就包括一个个的start启动类
3.1个属性赋值的几种方式
1.使用@Value("...")注解
@Value("旺财")
private String name;
@Value("1")
private Integer age;
2.使用yml配置文件对对象赋值
注意:实体类需要用到@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person"),与配置文件yaml里的对象相对应
Person
@Component
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
yaml
person:
name: tzf
age: 18
happy: true
birth: 2022/10/14
map: {k1: v1,k2: v2}
lists:
- cat
- dag
- girl
dog:
name: 旺财
age: 1
测试类
@SpringBootTest
class Spring01HelloworldApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
3.使用.propertysource配置文件(了解,这里不做详细介绍)
3.2配置文件的优先级
1.file:./config/ (根目录下的config包下的配置文件)
2.file:./ (根目录下的配置文件)
3.classpath:/config/ (java/resource下的config下的配置文件)
4.classpath:/ (java/resource下的配置文件)
3.3springboot的多环境配置文件,可以选择激活哪一个配置文件
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: test
#最后测试的结果用的是8082端口号
下一个问题,配置文件能配那些设置?
其实xxx.properties或xxx.yml文件能配置的东西是固定,@ConfigurationProperties()与你写的配置文件绑定,其默认值都写在@xxxproperties里面,如果想修改默认值,按照对应配置规则去配置
精髓:
1、SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
2、我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
3、我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件;(只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
4、给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置文件中指定这些属性的值即可;
xxxxAutoConfigurartion:自动配置类;给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties:封装配置文件中相关属性;
3.4读取yaml数据方式
方式一:
使用@Value读取单个数据,属性名引用方式:${一级属性名.二级属性名……}
lesson: SpringBoot
server:
port: 82
enterprise:
name: itcast
age: 16
tel: 4006184000
subject:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Value("${lesson}")
private String lessonName;
@Value("${server.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${enterprise.subject[1]}")
private String[] subject_01;
}
baseDir: /usr/local/fire
center:
dataDir: ${baseDir}/data
tmpDir: ${baseDir}/tmp
logDir: ${baseDir}/log
msgDir: ${baseDir}/msgDir
方式二:
封装全部数据到Environment对象
lesson: SpringBoot
server:
port: 82
enterprise:
name: itcast
age: 16
tel: 4006184000
subject:
- Java
- 前端
- 大数据
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public String getById(@PathVariable Integer id){
System.out.println(env.getProperty("lesson"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("enterprise.subject[0]"));
return "hello , spring boot!";
}
}
方式四:
自定义对象封装指定数据的作用
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm_db?serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: root
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "datasource")
public class DataSource {
private String driverClassName;
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
}
4.JSR303数据校验
松散绑定:即"ab"可以用“a-b"表示
JSR303数据校验 : 这个就是我们可以在字段是增加一层过滤器验证 , 可以保证数据的合法性
使用需要先添加依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.hibernate.validator/hibernate-validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate.validator</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>6.0.16.Final</version>
</dependency>
- 类似于html页面的input的type属性,指定类型
<input type="text">
springboot中使用jsp303需要@Validated注解
Bean Validation 中内置的 constraint
Hibernate Validator 附加的 constraint
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email(message = "邮件文件格式错误")
private String email;//属性email必须符合邮件格
}
静态资源导入:
1.在springboot中,我们可以使用一下方式处理静态资源
- webjars localhost:8080/webjars/
- public,static,/**,resources localhost:8080/
优先级:resources>static(默认)>public
5.Thymeleaf引擎模板
之前我们收到前端的html页面,会把它转换成jsp页面,jsp页面可以很轻松把后台数据显示到前端上面,并且实现交互,但是springboot项目 是以jar包,不是以war包,并且我们使用的嵌入式的tomcat不支持jsp。然而纯静态页面无法实现交互,所以springboot推荐我们使用模板引擎,如freemarker,其实jsp也是一种模板引擎,以及springboot推荐我们使用的thymeleaf。
1.导入相关启动器依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.创建templates包,将静态网页放在templates中
原因:约定大于配置,springboot的配置文件ThymeleafProperties表明文件的前缀和后缀
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
首页面模式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<title>Good Thymes Virtual Grocery</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" media="all"
href="../../css/gtvg.css" th:href="@{/css/gtvg.css}" />
</head>
<body>
<p th:text="#{home.welcome}">Welcome to our grocery store!</p>
</body>
</html>
3.语法表达式
具体参考官网:Tutorial: Using Thymeleaf
-
- Variable Expressions:
${...}变量 - Selection Variable Expressions:
*{...}选择 - Message Expressions:
#{...}消息 - Link URL Expressions:
@{...}URL - Fragment Expressions:
~{...}
- Variable Expressions:
所有的html元素都被thymeleaf接管替代,格式为:th:元素名
例如:th:class="" th:style=""
<div th:text="${name}"></div>
取后端传来的参数‘name'的值,属性为text,使用时为:th:text=""
字符转义(可识别标签):th:utext=""
遍历的两种方式
<div th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}"></div>
<div th:each="user:${users}">[[${user}]]</div>
6.拓展使用springMVC
springboot在自动配置的时候会用到很多组件,会首先看容器中有没有用户配置的文件(如果用户自己配置@Bean),如果有优先使用用户配置文件,没有才会使用默认配置。有些配置存在多个,比如视图解析器,用户配置和默认配置可以结合使用。
扩展MVC使用即我们自己要编写一个@Configeration注解的类,并且类型为WebMvcConfigurer,还不能加@EnableWebMvc注解,如:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.ViewControllerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/tzf").setViewName("success");
}
}
注意:springboot中有很多的xxxConfiguration配置类帮助我们扩展配置,只要我们看到这个类型的类,就说明它在修改和扩展原来的配置功能。
7.整合jdbc
补充@Autowired与@Resource区别
- @Autowired注解是Spring提供的,而@Resource注解是J2EE本身提供的
- @Autowird注解默认通过byType方式注入,而@Resource注解默认通过byName方式注入
- @Autowired注解注入的对象需要在IOC容器中存在,否则需要加上属性required=false,表示忽略当前要注入的bean,如果有直接注入,没有跳过,不会报错
yaml配置数据库DataSource:
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=tru&characterEncoding=utf-8
password: 123456
username: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
@RestController
public class JdbcController {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/userList")
public List<Map<String,Object>> userList(){
String sql="select * from user1";
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList(sql);
return maps;
}
@RequestMapping("/userAdd")
public String addUser(){
String sql="insert into user1 values(3,'aa','12345')";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql);
return "add-Success";
}
@RequestMapping("/userupdate/{id}")
public String updateUser(@PathVariable("id")int id){
String sql="update user1 set name = ?,pwd=? where id="+id;
Object[] objects = new Object[2];
objects[0]="tzf6";
objects[1]="520";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,objects);
return "add-Success";
}
}
8.自定义数据源(DruidDataSource)
第一种自定义整合:
Druid是阿里开源平台数据库连接池的实现,结合了数据库线程池和日志监控
导包:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/druid -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.15</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j</artifactId>
<version>1.2.17</version>
</dependency>
yaml配置data数据源为的druid
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
password: 123456
username: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# 数据源其他配置
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数
initial-size: 5
#最小连接池数量
min-idle: 5
#最大连接池数量 maxIdle已经不再使用
max-active: 20
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒
max-wait: 60000
#申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
test-while-idle: true
#既作为检测的间隔时间又作为testWhileIdel执行的依据
time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000
#销毁线程时检测当前连接的最后活动时间和当前时间差大于该值时,关闭当前连接
min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 30000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql 必须是一个查询语句
#mysql中为 select 'x'
#oracle中为 select 1 from dual
validation-query: select 'x'
#申请连接时会执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,开启会降低性能,默认为true
test-on-borrow: false
#归还连接时会执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,开启会降低性能,默认为true
test-on-return: false
# 是否缓存preparedStatement
pool-prepared-statements: true
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
#配置监拉统计挡成的filters. stat: 监控统计、Log4j:日志记录、waLL: 防御sqL注入
#如果启用日志记录时报错java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: org.apache.log4j.Priority
#则导入Log4j 依赖即时,Maven 地址: https://mvnrepository. com/artifact/log4j/log4
filters: stat,wall,1og4j
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20
use-global-data-source-stat: true
connect-properties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
虽然我们配置了druid连接池的其他属性但是不会生效,因为默认使用的是java.sql.Datasource的类来获取属性的,有些属性datasource没有。如果想要配置生效需要手动创建Druid的配置文件
* 描述: Spring Boot 手动整合 Druid 连接池
*/
// @Deprecated
@Configuration
public class MyDataSourceConfig {
/**
* 配置 Druid 数据源。(Spring Boot 会在 IoC 容器自动读取类型为 DataSource 的对象。故这个 bean 注入后,即与Spring Boot整合好了)
* @return DruidDataSource 数据源
* @throws SQLException
*/
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource",ignoreUnknownFields = false) // 读取配置文件中的数据源信息。Druid会以此建立数据库连接
public DataSource dataSource() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setFilters("stat"); // 开启
return druidDataSource;
}
/**
* (非必要)开启前台监控页面对应的 Servlet,并设置密码(通过 http://域名/druid/index.html 即可访问监控页面)
* 此 Servlet 是由 Druid 提供的 StatViewServlet
* @return
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> druidServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> statViewServletServletRegistrationBean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(new StatViewServlet(), "/druid/*");
statViewServletServletRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("loginUsername","root");
statViewServletServletRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("loginPassword","131121");
return statViewServletServletRegistrationBean;
}
/**
* (非必要)配置Druid的Filter,用于记录 web 请求记录。
* 此 Filter 是由 Druid 提供的 WebStatFilter
* @return
*/
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean<WebStatFilter> druidFilter(){
WebStatFilter webStatFilter = new WebStatFilter();
FilterRegistrationBean<WebStatFilter> webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(webStatFilter);
// 除以下路径的访问不记录,其它都会进行记录
webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("exclusions","*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*");
// 记录 session 时,记录下 session 中记录的用户名
webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("principalSessionName","userName");
return webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean;
}
}
第二种方法使用starter:
导资源包:
此时就不需要Druid的依赖了,starter中已经包含druid的包了
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.2.16</version>
</dependency>
配置数据源:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
password: 123456
username: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
# 连接池配置:
druid:
initial-size: 2 # 初始化时建立物理连接的个数。默认0
max-active: 10 # 最大连接池数量,默认8
min-idle: 1 # 最小连接池数量
max-wait: 2000 # 获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。
pool-prepared-statements: false # 是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache。PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle。在mysql下建议关闭。
max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: -1 # 要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
# ……druid节点下的其它参数见官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/DruidDataSource%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE%E5%B1%9E%E6%80%A7%E5%88%97%E8%A1%A8
# 启用Druid内置的Filter,会使用默认的配置。可自定义配置,见下方的各个filter节点。
filters: stat,wall
# StatViewServlet监控器。开启后,访问http://域名/druid/index.html
stat-view-servlet:
enabled: true # 开启 StatViewServlet,即开启监控功能
login-username: daniel # 访问监控页面时登录的账号
login-password: 1234 # 密码
url-pattern: /druid/* # Servlet的映射地址,不填写默认为"/druid/*"。如填写其它地址,访问监控页面时,要使用相应的地址
reset-enable: false # 是否允许重置数据(在页面的重置按钮)。(停用后,依然会有重置按钮,但重置后不会真的重置数据)
allow: 192.168.1.2,192.168.1.1 # 监控页面访问白名单。默认为127.0.0.1。与黑名单一样,支持子网掩码,如128.242.127.1/24。多个ip用英文逗号分隔
deny: 18.2.1.3 # 监控页面访问黑名单
# 配置 WebStatFilter(StatFilter监控器中的Web模板)
web-stat-filter:
enabled: true # 开启 WebStatFilter,即开启监控功能中的 Web 监控功能
url-pattern: /* # 映射地址,即统计指定地址的web请求
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*' # 不统计的web请求,如下是不统计静态资源及druid监控页面本身的请求
session-stat-enable: true # 是否启用session统计
session-stat-max-count: 1 # session统计的最大个数,默认是1000。当统计超过这个数,只统计最新的
principal-session-name: userName # 所存用户信息的serssion参数名。Druid会依照此参数名读取相应session对应的用户名记录下来(在监控页面可看到)。如果指定参数不是基础数据类型,将会自动调用相应参数对象的toString方法来取值
principal-cookie-name: userName # 与上类似,但这是通过Cookie名取到用户信息
profile-enable: true # 监控单个url调用的sql列表(试了没生效,以后需要用再研究)
filter:
wall:
enabled: true # 开启SQL防火墙功能
config:
select-allow: true # 允许执行Select查询操作
delete-allow: false # 不允许执行delete操作
create-table-allow: false # 不允许创建表
# 更多用法,参考官方文档:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/%E9%85%8D%E7%BD%AE-wallfilter
9.整合mybatis
整体工程预览:
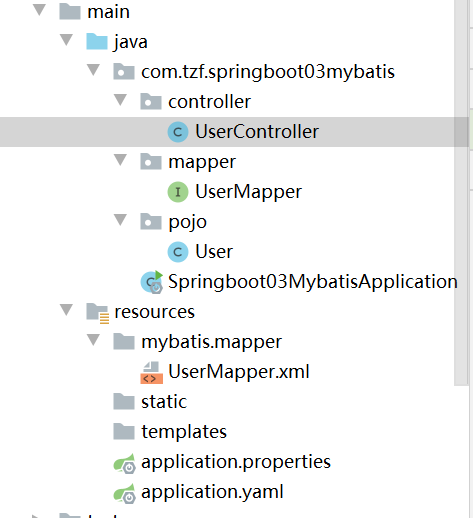
1.导包:
<!-- 此依赖不是springboot官方提供的-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String ped;
}
3.mapper
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> userList();
User queryUserById(int id);
int add(User user);
int update(User user);
int delete(int id);
}
4.resource下面配置xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.tzf.springboot03mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="userList" resultType="User">
select * from user1
</select>
<select id="queryUserById" resultType="User">
select * from user1 where id=#{id}
</select>
<update id="update" parameterType="User">
update user1 set name=#{name},pwd=#{pwd} where id=#{id}
</update>
<insert id="add" parameterType="User">
insert into user1(id,name,pwd) values(#{id},#{name},#{pwd})
</insert>
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from user1 where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
5.yaml配置mybatis
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#mybatis配置
mybatis:
#起别名
type-aliases-package: com/tzf/springboot03mybatis/pojo
#xml文件与mapper绑定
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
#com\tzf\springboot03mybatis\pojo
6.controller层
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired(required = false)
UserMapper userMapper;
// rest行为方法,get查询,post添加,put修改,delete删除
@GetMapping("/userList")
public List<User> userList(){
List<User> userlist = userMapper.userList();
for (User user:userlist) {
System.out.println(user);
}
return userlist;
}
}
rest行为方法get查询,post添加,put修改,delete删除
注意:
@PathVariablez(“xx”)注解,表示简单参数从路径中获取,xx是路径中的参数名字,与形参绑定
@RequestBody参数量比较大,如实体类参数,使用该注解用json格式传参
10.springSecurity
安全验证
官方文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.5.8/reference/html5
中文文档:
Introduction · Spring Boot 中文文档 (felord.cn)
(http://felord.cn/_doc/_springboot/2.1.5.RELEASE/_book/)
Spring Security 中文文档 :: Spring Security Reference (springdoc.cn)
1.导包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
11.工程打包与运行
windows环境
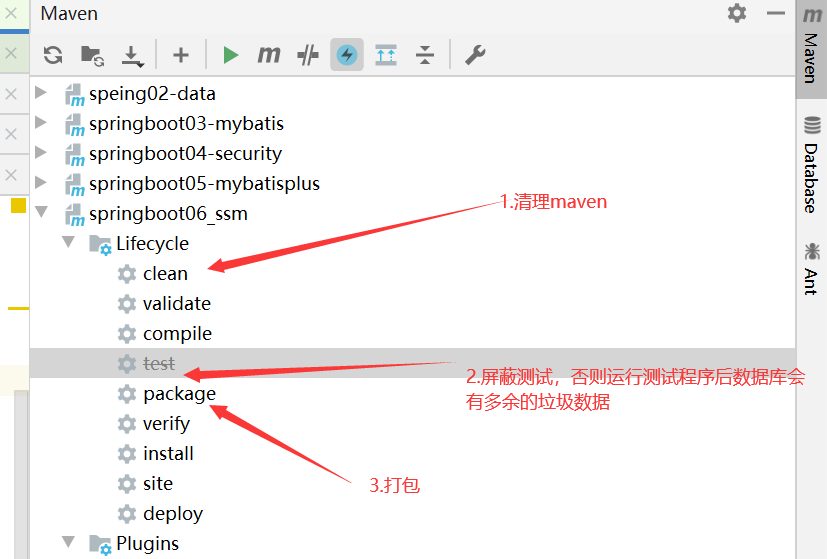
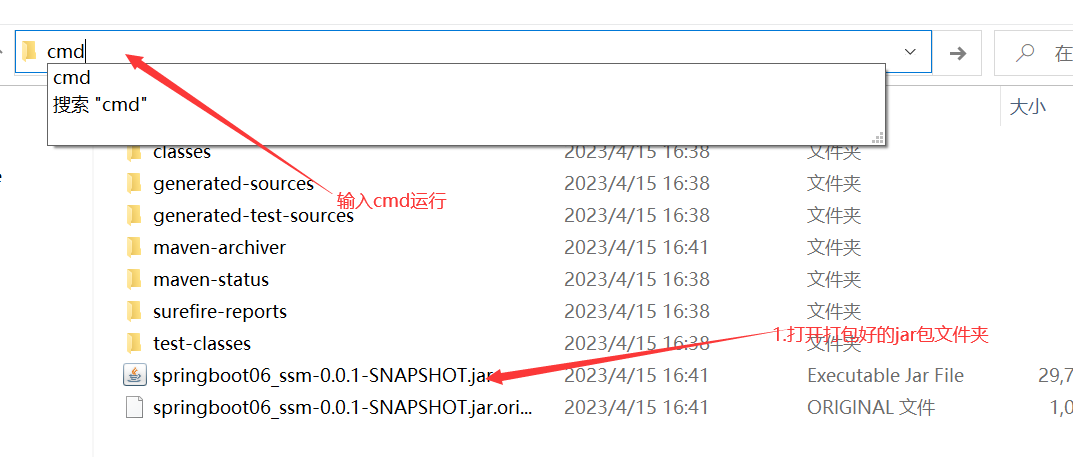
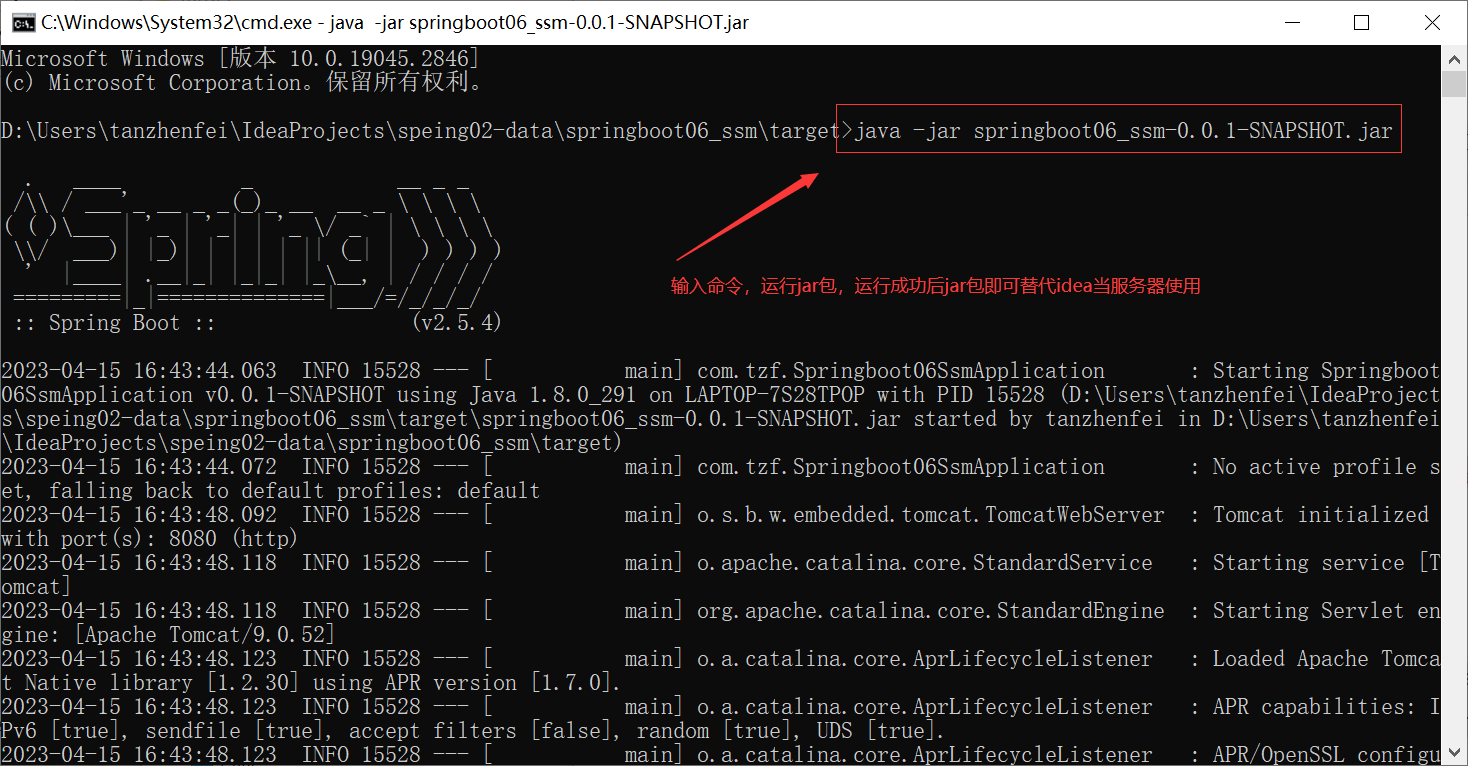
可能会遇到的问题:
1.“没有主清单属性”问题,可能是没有引入springboot-maven打包插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
springboot打的jar包包含maven打的jar包所有内容,以及程序运行所依赖的环境(比如需要的所有jar包)
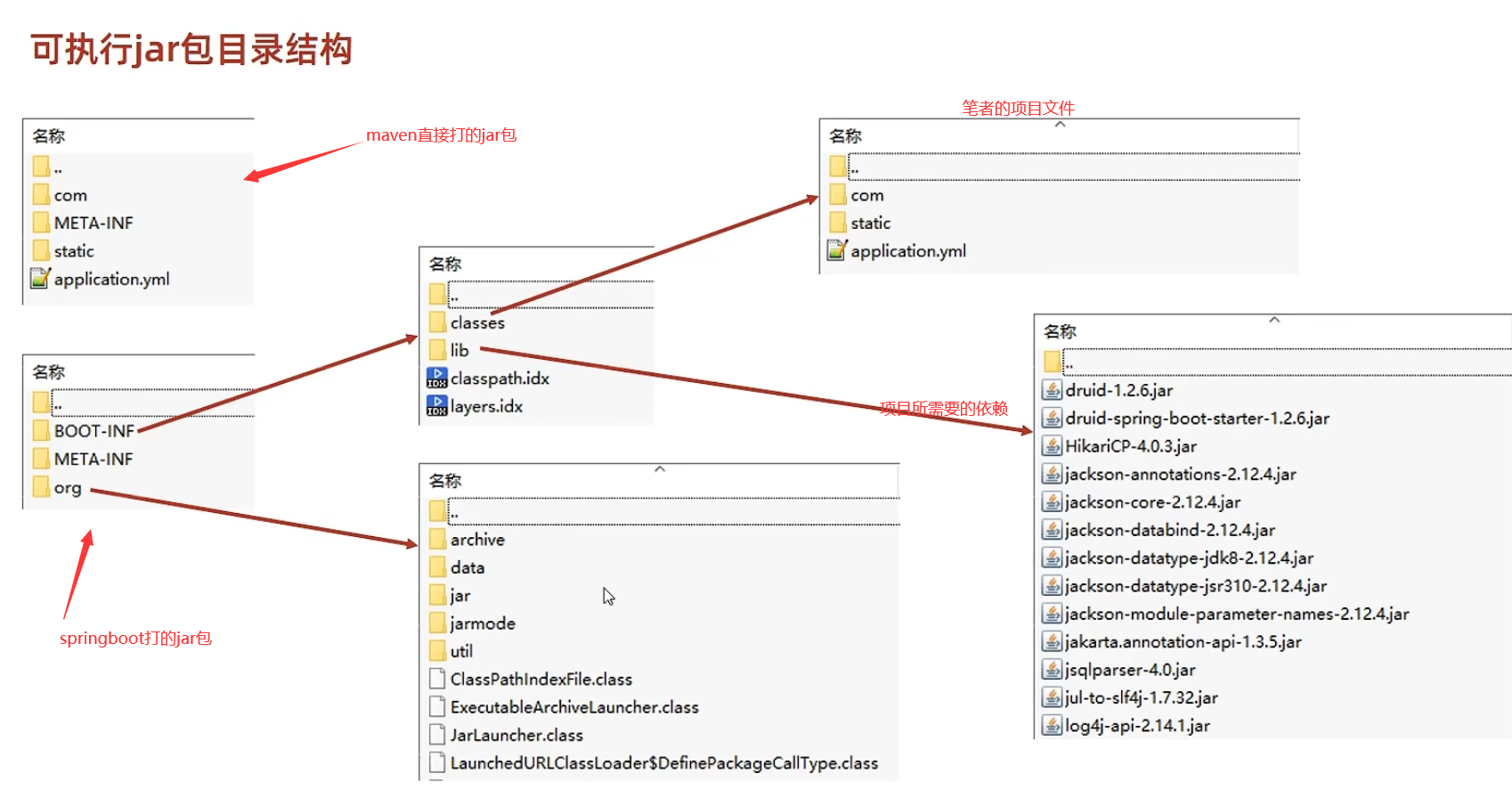
2.端口占用问题

linux环境
与windows环境基本一致,注意linux前提配置好jar包运行的换将,如SQL环境,jdk环境
12.临时属性
使用临时属性覆盖原有的属性,因此不同文件位置设置属性是有优先级的,优先级高的文件的属性值会会覆盖掉优先级低的属性值
在jar包运行环境下临时属性设置:
1.使用jar命令启动SpringBoot工程时可以使用临时属性替换配置件中的属性
java -jar springboot.jar --server.port=80
2.临时属性添加方式:java -jar工程名.jar --属性名=值
3.多个临时属性之间使用空格分隔
分
4.临时属性必须是当前boot工程支持的属性,否则设置无效
优先级详情:
参看https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/spring-boot-features.html#boot-features-external-config
在idea环境设置临时属性:
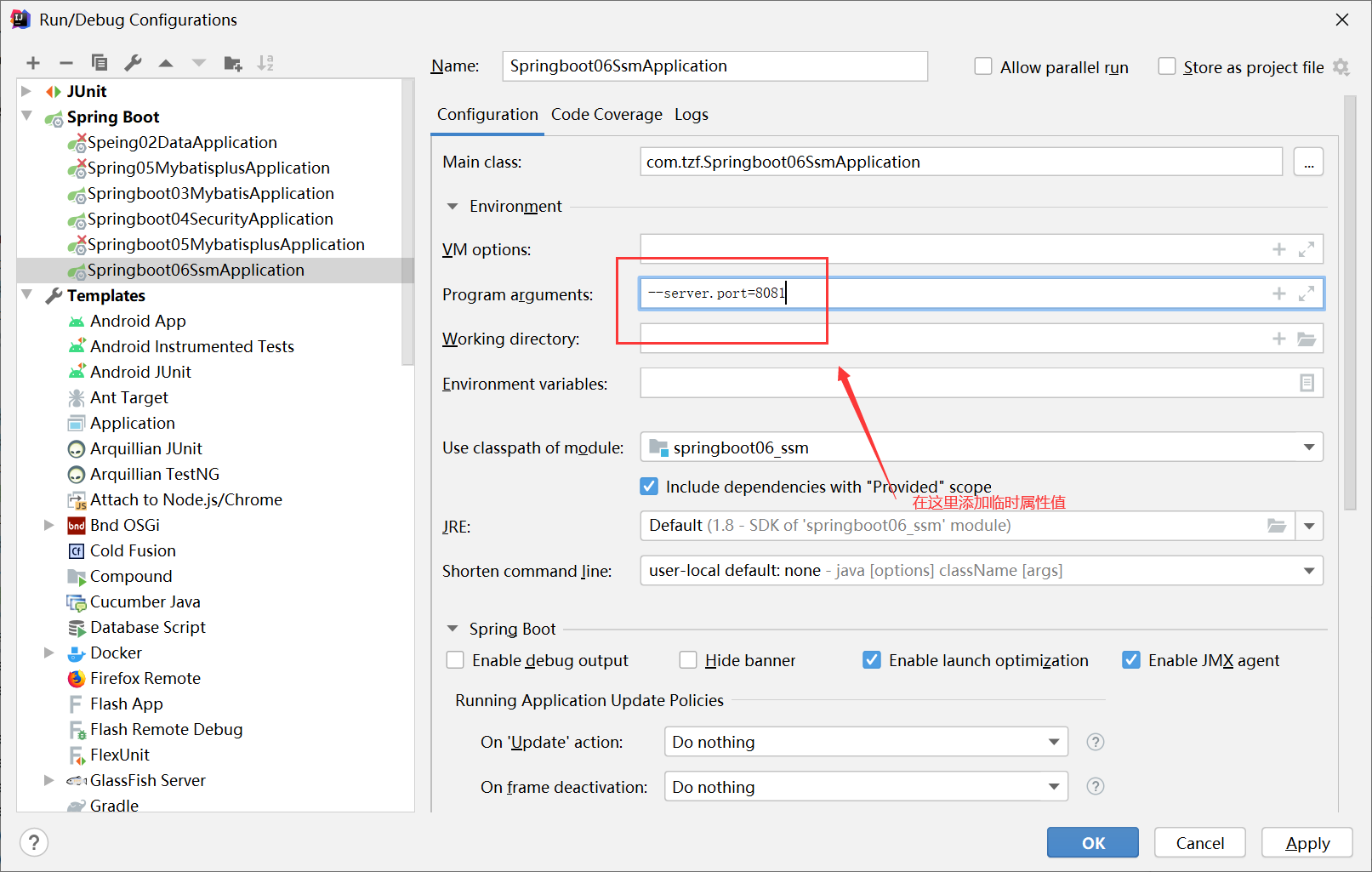
临时属性实则在启动类中作为args参数传入springboot:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot06SsmApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot06SsmApplication.class, args);
//args="server.port=8081"
}
}
如果将启动类中的args参数剔除,则不会有临时属性起作用,断开外部临时配置的入口。
如:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot06SsmApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot06SsmApplication.class);
}
}
同一种文件不同位置优先级:
项目工程/config/application.yml>项目工程/application.yml>resources/config/application.yml>resources/application.yml
不同文件同一位置优先级:
xx.properties>xx.ym>xx.yaml
SpringBoot中4级配置文件
1级: file : config/application.ym 【最高】
2级: file : application.yml
3级: classpath: config/application.yml
4级: classpath: application.yml【最低】
2.作用:
1级与2级留做系统打包后设置通用属性,1级常用于运维经理进行线上整体项目部署方案调控
3级与4级用于系统开发阶段设置通用属性,3级常用于项目经理进行整体项目属性调控
13.多环境开发
yaml版本
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
#生产环境
---
spring:
profiles: dev
server:
port: 8080
#开发环境
---
spring:
profiles: tt #格式过时
server:
port: 8082
#测试环境
---
spring:
config:
activate:
on-profile: zf #新格式
server:
port: 8083
properties版本:
与yaml相同,yaml现在也是使用冲突文件分开的形式,不再写在一个文件里了
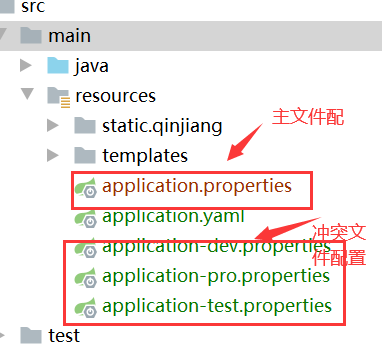
多环境分组管理:
spring:
profiles:
active: dev #启动的是dev组而不是单独的某个文件
# include: devDB,devMVC 之前运用的功能
group:
"dev":devDB,devMVC
"pro":proDB,proMVC
#启动配置是dev文件为主,也包括devDB,devMVC文件,有冲突了按照dev文件配置执行,如果dev没有配置则最后文件执行的属性会覆盖前面文件(不包括主文件)冲突的属性
14.整合Redis
是一款key-value存储结构的内存集NoSQL数据库
启动服务器:
redis-server.exe redis.windows.conf
启动服务器之后窗口不要关,新打开一个窗口启动redis
redis-cli.exe -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6379
将Redis启动之后我们来用idea使用,注意此时的Redis服务不要关
首先将Redis相关的配置依赖导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis-reactive</artifactId>
</dependency>
在yaml文件配置相关信息
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
测试Redis:
@SpringBootTest
class Sptingboot07RedisApplicationTests {
@Autowired(required = false)
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Test
void set(){
// 每一种数据都有不同的操作对象,现获取操作对象然后再对数据进行相关操作
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
valueOperations.set("gtt","mylover");
}
@Test
void get(){
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object gtt = valueOperations.get("gtt");
System.out.println(gtt);
}
@Test
void hset()
{
// opsForHash,对hash数据操作对象
HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
hashOperations.put("option","a1","aaa");
}
@Test
void hget(){
HashOperations hashOperations = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
Object o = hashOperations.get("option", "a1");
System.out.println(o);
}
}
注意:
// 以对象操作的基本单元
@Autowired(required = false)
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
// 以字符串操作的基本单元
@Autowired(required = false)
StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
@Test
void get(){
// ValueOperations<String, String> ops = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue();
// System.out.println(ops.get("gtt"));
ValueOperations valueOperations = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
Object gtt = valueOperations.get("gtt");
System.out.println(gtt);
Redis实现客户端切换(jedis):
导包:
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
配置:
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
client-type: jedis
jedis就是基于java语言的redis客户端,集成了redis的命令操作,提供了连接池管理。
lettcus与jedis区别:
springboot默认使用lettcus
- jedis连接Redis服务器是直连模式,当多线程模式下使用jedis会存在线程安全问题,解决方案可以通过配置连接池使每个连接专用,这样整体性能就大受影响。
- lettcus基于Netty框架进行与Redis服务器连接,底层设计中采用StatefulRedisConnection。StatefulRedisConnection自身是线程安全的,可以保障并发访问安全问题,所以一个连接可以被多线程复用。当然lettcus也支持多连接实例一起工作。
15.Mongodb
mysql不够快,redis速度快但是不能结构化,为了满足速度快且能够结构化特点,引入Mongodb存入经常修改的数据的变化
MongoDB是一个开源、高性能、无模式的文档型数据库。NoSQL数据库产品中的一种,是最像关系型数据库的非关系型数据库
iddea整合mongodb
1.导包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.在 yaml中配置mongo属性
spring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: mongodb://localhost/test
3.使用MongoTemplet操作MongoDB数据库中的数据
@Autowired
MongoTemplate mongoTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
Users users = new Users();
users.setAge(18);
users.setName("tzf");
users.setPwd("123456");
mongoTemplate.insert(users);
}
@Test
void FindTest(){
System.out.println(mongoTemplate.findAll(Users.class));
}
16.ES(分布式全文搜索引擎)
倒排索引:
通过提供的数据分词,分词后的关键字对应主键,再根据主键查找详细的信息。此操作大幅度加快了查找的速度
17.mybatisplus小结
mybatisplus的条件查询:
//方式一常规格式
Querywrapper<User> qw = new Querywrapper<User>();//查询年龄大于等于18岁,小于65岁的用户
qw.lt( "age" ,65);
qw.ge( "age",18);
List<User> userList = userDao.selectlist(qw);
system.out.print1n(userList);
//方式二: Lambda格式接条件合海
Querywrapper<User> qw= new Querywrapper<User>( );
qw.Lambda( ).lt(User : : getAge,10);
List<User> userList = userDao.seLectList(qw) ;
System.out.println(userList);
//方式三
LambdaQuerywrapper<User> lqw = new LambdeQueryiwrapper<User>();
//10.到30岁之间,lt小于,gt表示大于
lqw.Lt(user: : getAge,30 ).gt(User: :getAge,10);
//il小子1日岁或者人于30岁,.or()条件或者关系
lqw.lt(User : :getAge,val: 10).or().gt(User: : getAge,val: 30);
//应对参数为空
lqw.lt(null!=uq.getage,User : :getAge,val: 10);
List<User> userList = userDao.selectlist(lqw) ;
system.out.println(userList);



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号