P1379题解报告
这是一个五年级蒟蒻的第 11 篇题解,望通过。
我将挑战用四种方法 AC 此题,先放一个题目传送门。
F1-BFS
这道题是一种经典的最短路径题,每次操作都会让步数加一,所以考虑 BFS。
写搜索题,最重要的就是状态和转移。显然,这道题的状态是目前的八数码和走过的步数。
但是问题显现,八数码如何存储呢?
- 我会 STL,我用
map。可以定义一个结构体 node,就是一个二维数组,加上比较函数(没有这个,map就不能运行),定义一个map<node, int>表示每个八数码走了多少步。 - 我会 hash,可以将每个八数码映射成一个数,同样用
map存储。 - 我会康托展开,将一个八数码看成一个 \(0 \sim 9\) 的全排列,然后套用康托展开的公式,用数组存储即可。
- 我啥都不会,但是我可以将一个八数码的 \(9\) 位拼在一起变成一个 \(9\) 位数,用
map即可。
所以有了状态,转移就很好想了,每次交换 \(0\) 与它旁边的位置,步数加一即可。
复杂度:时间和空间都是 \(9!\),可以通过。
code
这里采用第一种方法,结构体 \(+\) map。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
struct node{
int a[3][3];
bool operator < (node b) const{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(a[i][j] != b.a[i][j])
return a[i][j] < b.a[i][j];
}
}
return 0;
}
}s, t;
queue<node> q;
map<node, int> mp;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
t.a[0][0] = 1, t.a[0][1] = 2, t.a[0][2] = 3;
t.a[1][0] = 8, t.a[1][1] = 0, t.a[1][2] = 4;
t.a[2][0] = 7, t.a[2][1] = 6, t.a[2][2] = 5;
string str;
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
s.a[i][j] = str[i * 3 + j] - '0';
}
}
q.push(s);
mp[s] = 0;
while(q.size()){
node u = q.front();
q.pop();
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if(!u.a[i][j])
x = i, y = j;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
node v = u;
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3){
swap(v.a[x][y], v.a[xx][yy]);
if(!mp.count(v)){
mp[v] = mp[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
cout << mp[t];
return 0;
}
于是,你就愉快的 AC 了。走了走了不看后面了。
F2-双向 BFS
个人认为,双向 BFS 是一种较为冷门的算法,它通过空间换时间的方法降低了时间复杂度。
双向广搜,顾名思义,就是从起点和终点两个方向进行广搜,直到它们相遇。为什么复杂度会降低呢?这里放一张图片(画得有点丑,见谅):
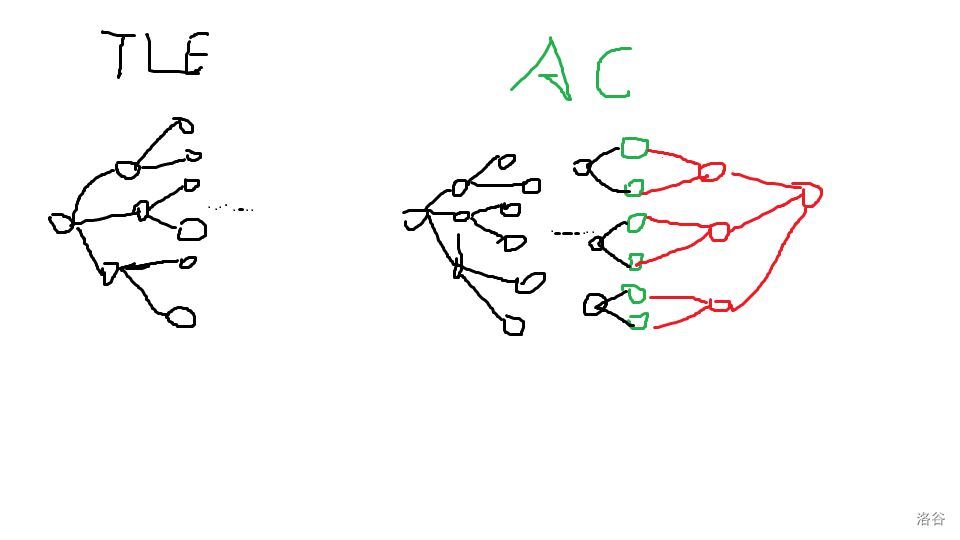
我们发现,两个点同时进行广搜,会比直接广搜复杂度低,因为省去了许多不必要的分支。
状态和转移和 F1 一样,我们讲一讲具体实现。
我们可以开两个队列,分别表示从起点扩张的情况和从终点扩张的情况。标记还是用两个 map,表示起点扩张和终点扩张。我们交替扩张,对于每次扩张,可以取出队头,进行扩张。如果扩出的状态已经在另一个 map 中被标记,那么在两个 map 中的答案之和就是最终的答案。如果还不懂的话,请移步代码。
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
struct node{
int a[3][3];
bool operator < (node b) const{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(a[i][j] != b.a[i][j])
return a[i][j] < b.a[i][j];
}
}
return 0;
}
}s, t;
queue<node> q1, q2;
map<node, int> mp1, mp2;
void r(queue<node> &q, map<node, int> &m1, map<node, int> &m2){
if(!q.size()) return;
node u = q.front();
q.pop();
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if(!u.a[i][j])
x = i, y = j;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
node v = u;
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3){
swap(v.a[x][y], v.a[xx][yy]);
if(m2.count(v)){
cout << m1[u] + m2[v] + 1;
exit(0);
}
if(!m1.count(v)){
m1[v] = m1[u] + 1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
t.a[0][0] = 1, t.a[0][1] = 2, t.a[0][2] = 3;
t.a[1][0] = 8, t.a[1][1] = 0, t.a[1][2] = 4;
t.a[2][0] = 7, t.a[2][1] = 6, t.a[2][2] = 5;
string str;
cin >> str;
if(str == "123804765") return cout << 0, 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
s.a[i][j] = str[i * 3 + j] - '0';
}
}
q1.push(s);
mp1[s] = 0;
q2.push(t);
mp2[t] = 0;
while(1){
r(q1, mp1, mp2);
r(q2, mp2, mp1);
}
return 0;
}
F3-A*
A* 搜索算法(A* search algorithm,A* 读作 A-star),简称 A* 算法,是一种在带权有向图上,找到给定起点与终点之间的最短路径的算法。它属于图遍历(graph traversal)和最佳优先搜索算法(best-first search),亦是 BFS 的改进。——摘自 OI-Wiki
在 A* 算法中,对于每一个状态 \(x\),我们设从起点经过它的估计总路程为 \(f(x)\),从起点走到此状态的答案为 \(g(x)\),\(h(x)\) 为当前状态到目标状态的一个估计,则
在 A* 算法中,我们将普通队列换成优先队列,每次取出 \(f(x)\) 最小的状态进行扩张,并利用真实的 \(g(x)\) 更新 \(f(x)\)。
在此题中,我们将 \(h(x)\) 定义为目前的八数码和目标状态之间的曼哈顿距离即可,不能加 0,会 WA!
我们定义两个结构体,一个判重用,一个优先队列里用,第一个结构体与前面一样,第二个结构体中为一个状态,一个 \(g(x)\),一个函数 \(h(x)\) 和比较器(用于优先队列)。A* 的实现就不多说了,理解上面的。
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, pos[9][2] = {{2, 2}, {0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}, {2, 1}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}};
struct node{
int a[3][3];
bool operator < (node b) const{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(a[i][j] != b.a[i][j])
return a[i][j] < b.a[i][j];
}
}
return 0;
}
}s, t;
struct Node{
int dis;
node x;
int h() const{
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(!x.a[i][j]) continue;
ans += abs(i - pos[x.a[i][j]][0]) + abs(j - pos[x.a[i][j]][1]);
}
}
return ans;
}
bool operator < (Node y) const{
return dis + h() > y.dis + y.h();
}
};
priority_queue<Node> q;
map<node, int> mp;
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
t.a[0][0] = 1, t.a[0][1] = 2, t.a[0][2] = 3;
t.a[1][0] = 8, t.a[1][1] = 0, t.a[1][2] = 4;
t.a[2][0] = 7, t.a[2][1] = 6, t.a[2][2] = 5;
string str;
cin >> str;
if(str == "123804765") return cout << 0, 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
s.a[i][j] = str[i * 3 + j] - '0';
}
}
mp[s] = 0;
q.push({0, s});
while(q.size()){
if(!q.top().h()){
cout << q.top().dis;
break;
}
node u = q.top().x;
q.pop();
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if(!u.a[i][j])
x = i, y = j;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
node v = u;
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3){
swap(v.a[x][y], v.a[xx][yy]);
if(!mp.count(v)){
mp[v] = mp[u] + 1;
q.push({mp[v], v});
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
F4-IDA*
IDA* 是 IDDFS 与 A* 的结合,我们只讲一下 IDDFS。
迭代加深搜索本质是深搜,但它限定了深度,一旦当前搜索深度大于或等于限定深度,就立刻回溯,如果当前限制的深度有答案就直接结束,如果没有就放宽限制。
有人就会问:在限定新深度时,浅深度的状态会被枚举很多次,会不会浪费时间导致 \(T\) 飞?
我的回答是:这个得具体情况具体分析,当一个状态能转移出的状态不多时,在枚举新限定深度时,需要记录上一层状态;但如果转移状态是指数级的增长时,就没必要,因为前几层的状态在后几层来说就是九牛一毛,记状态也快不了多少。
迭代加深弥补了广搜的空间开销太大,也弥补了深搜的无底洞,是一个好算法。——摘自我的第一篇题解
关于 IDDFS 的实现,可以参考我的第一篇题解的不过样例的实现。
IDA* 就是在 IDDFS 的基础上跑 A*,只是把层数上限改为 \(f(x)\) 的上限。这里使用 map 去重,记得 erase。
code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1}, dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0}, pos[9][2] = {{2, 2}, {0, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {1, 2}, {2, 2}, {2, 1}, {2, 0}, {1, 0}};
struct node{
int a[3][3];
bool operator < (node b) const{
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
if(a[i][j] != b.a[i][j])
return a[i][j] < b.a[i][j];
}
}
return 0;
}
}s, t;
int depth;
map<node, int> mp;
int h(node x){
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
int num = x.a[i][j];
if(!num) continue;
ans += abs(i - pos[num][0]) + abs(j - pos[num][1]);
}
}
return ans;
}
void dfs(int dep, node u){
int cnt = h(u);
if(!cnt){
cout << depth;
exit(0);
}
if(dep + cnt > depth) return;
mp[u] = 1;
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++)
if(!u.a[i][j])
x = i, y = j;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
node v = u;
int xx = x + dx[i], yy = y + dy[i];
if(0 <= xx && xx < 3 && 0 <= yy && yy < 3){
swap(v.a[x][y], v.a[xx][yy]);
if(!mp.count(v)) dfs(dep + 1, v);
}
}
mp.erase(u);
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
t.a[0][0] = 1, t.a[0][1] = 2, t.a[0][2] = 3;
t.a[1][0] = 8, t.a[1][1] = 0, t.a[1][2] = 4;
t.a[2][0] = 7, t.a[2][1] = 6, t.a[2][2] = 5;
string str;
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++){
s.a[i][j] = str[i * 3 + j] - '0';
}
}
for(; ; depth++){
mp.clear();
dfs(0, s);
}
return 0;
}


