The Priority Ceiling Protocol
优先级上限协议(The Priority Ceiling Protocol)
原文:https://jcboseust.ac.in/it/images/studymaterial/Celing.pdf

关于我们如何锁定(wait,EnterMonitor)和解锁(Signal,LeaveMonitor)资源:
- 任务必须在两次调用之间释放所有资源
- 持有信号量s的任务的时间有限制,就是一个任务不能一直将一个资源锁死。
任务对资源拥有时间大致等于 临界区代码执行所花费的时间。 - 一个任务只能锁定一组固定的信号量。被称为priory
Restrictions on how we can lock (Wait, EnterMonitor) and unlock (Signal, LeaveMonitor) resources:
• a task must release all resources between invocations
• the computation time that a task i needs while holding semaphore s is bounded. csi,s = the time length of the
critical section for task i holding semaphore s
• a task may only lock semaphores from a fixed set of semaphores known a priory.
uses(i) = the set of semaphores that may be used by task i
协议内容:
- 信号量的上限:所有使用该信号量任务里面的最高优先级
the ceiling of a semaphore, ceil(s), is the priority of the
highest priority task that uses the semaphore - 注释: pri(i) 指的是task(i) 的优先级 pri(i) is the priority of task i
- 在运行时:
- 1.如果一个task(i)想锁定一个信号量,它必须满足下面情况:pri(i)严格高于当前被其他任务锁定的所有信号量的上限
if a task i wants to lock a semaphore s, it can only do
so if pri(i) is strictly higher than the ceilings of all
semaphores currently locked by other tasks - 2.否则 task(i)将会被阻塞
if not, task i will be blocked (task i is said to be blocked on the semaphore, S∗, with the highest priority ceiling
of all semaphores currently locked by other jobs and task i is said to be blocked by the task that holds S∗)
when task i is blocked on S∗, the task currently holding S∗ inherits the priority of task i
- 1.如果一个task(i)想锁定一个信号量,它必须满足下面情况:pri(i)严格高于当前被其他任务锁定的所有信号量的上限
优点:
- Deadlock free
列子1:
| Task name | T | Priority |
| :-----| ----: | :----: |
| A | 50 | 10 |
| B | 500 | 9 |
Task A Task B
lock(s1) lock(s2)
lock(s2) lock(s1)
... ...
unlock(s1) unlock(s1)
unlock(s2) unlock(s1)
(我们已经知道上述任务如果使用优先级继承不能解决死锁问题 )
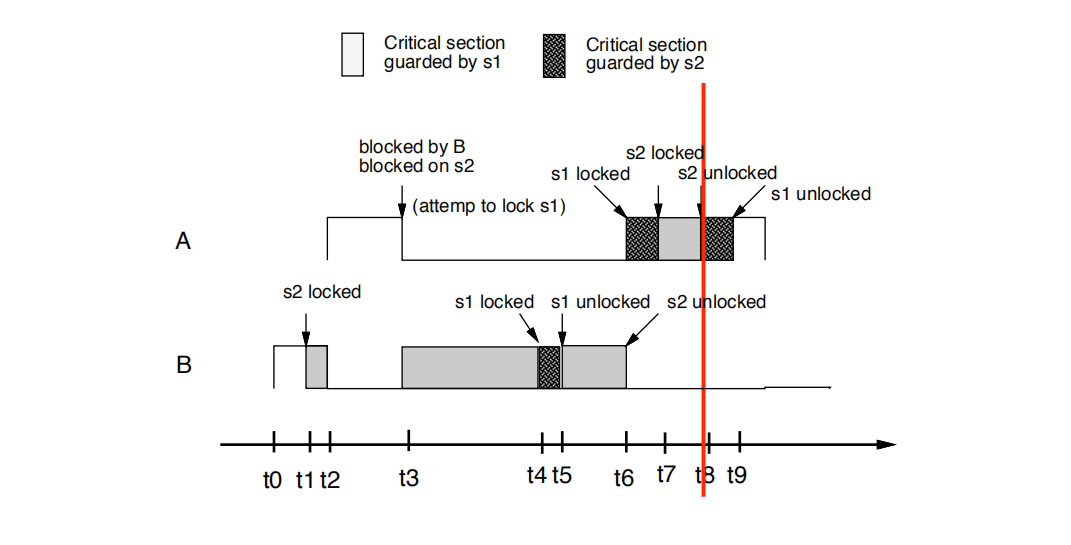
综上所述:ceil(s1)= 10, ceil(s2) =10
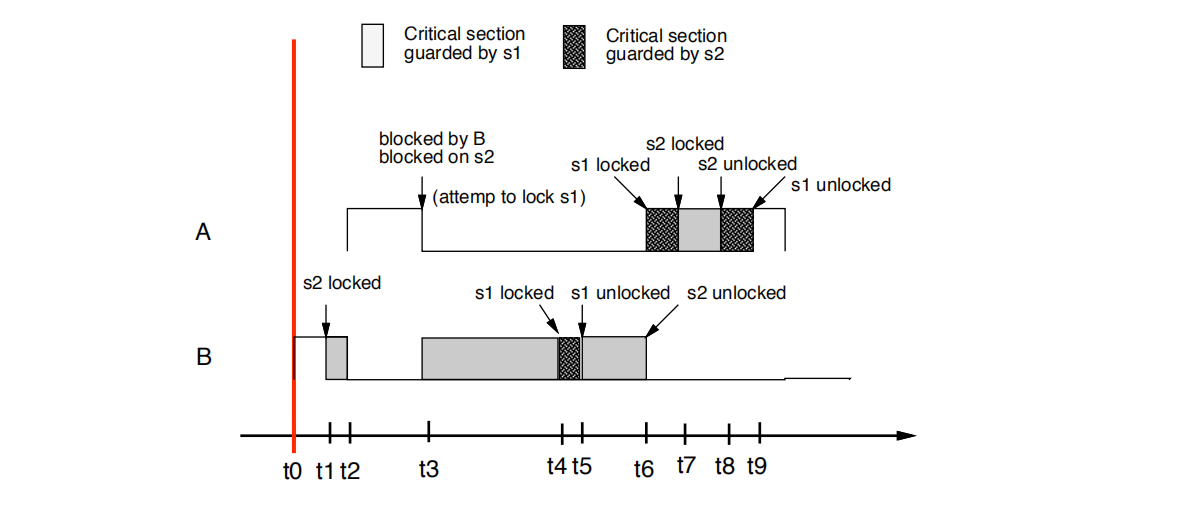
• t0时刻: B开始执行
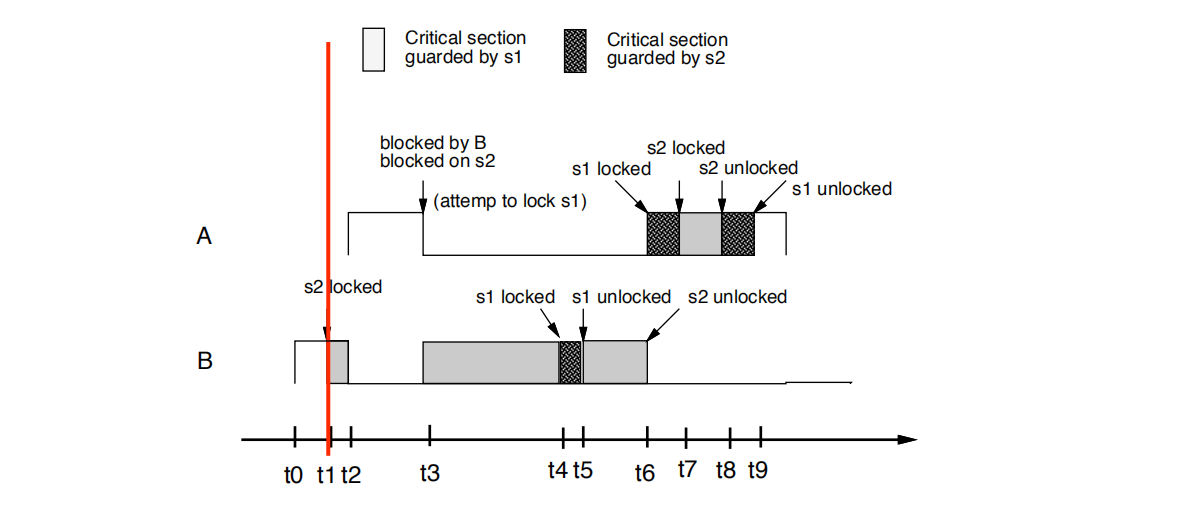
• t1时刻: B尝试锁住s2. 并且成功上锁s2。因为没有其他task需要s2
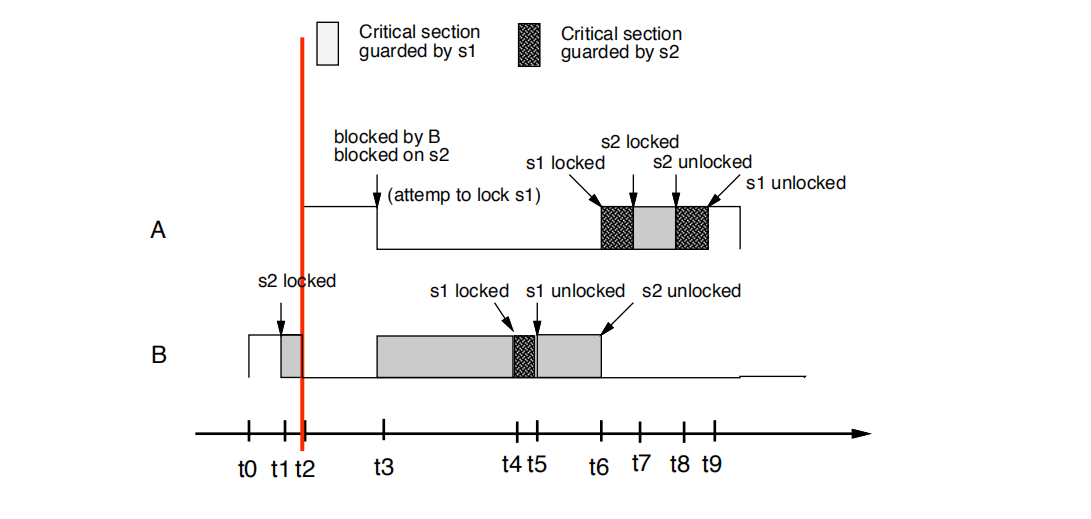
• t2时刻:因为pri(A) = 10 > pri(B) =9,所有A从B任务中把cpu的抢过来了
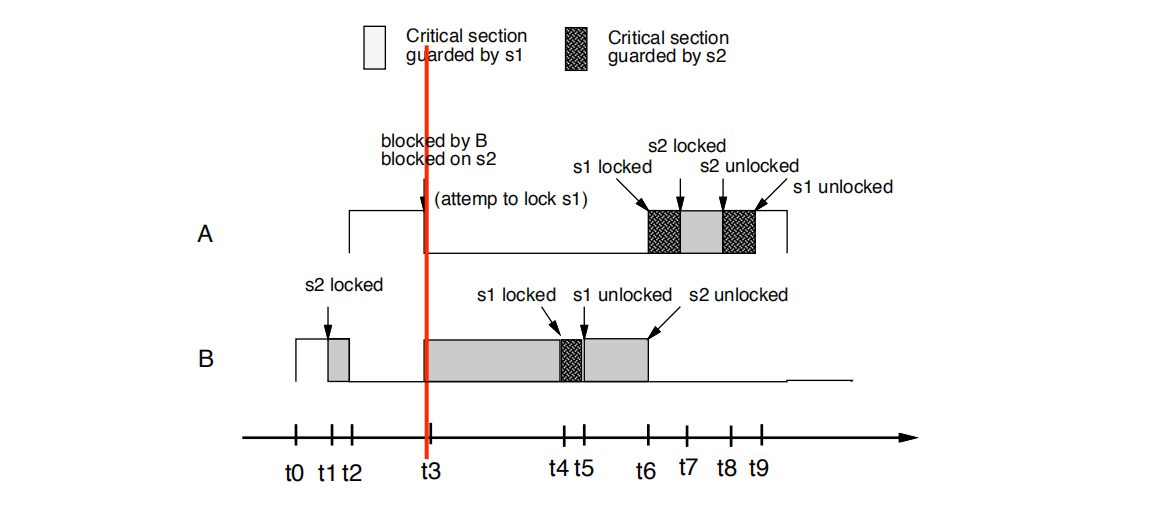
•t3时刻:
A尝试锁定s1。 A失败,因为pri(A)= 10 严格上不高于cell(s2)=10,s2 is held by B
A任务被B任务阻塞
A阻塞在s2上
pri(B)被提升为10 ,B继承了A的优先级
• t3: A tries to lock s1. A fails since A’s priority (10) is not
strictly higher than the ceiling of s2 (10) that is held by B
• A is blocked by B
• A is blocked on s2
• The priority of B is raised to 10.
the task B currently holding S2 inherits the priority of task A
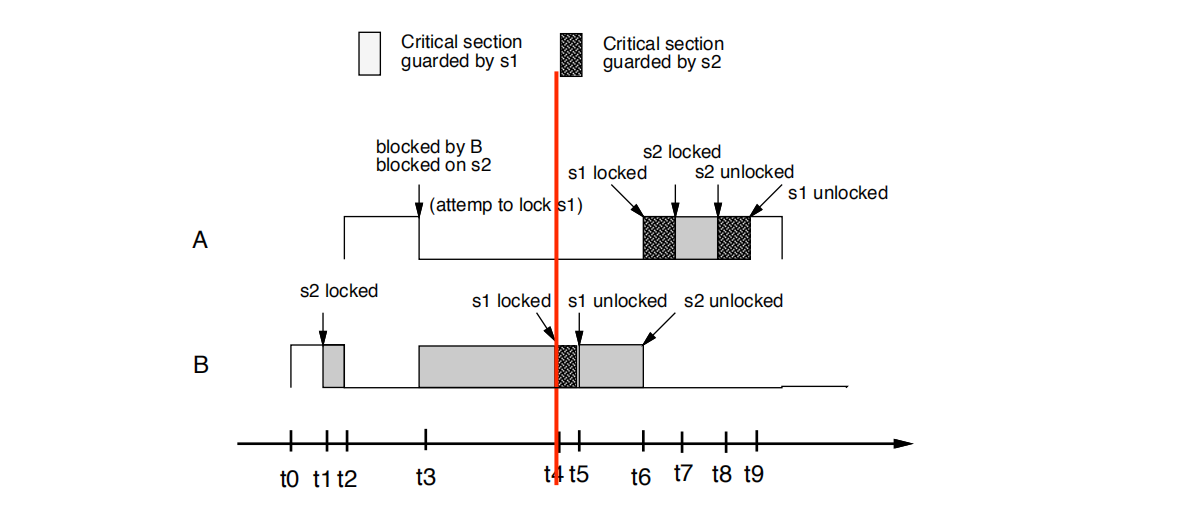
•t4时刻: B尝试锁定s1。 B成功,因为没有其他任何任务持有锁。
• t4: B attempts to lock s1. B succeeds since there are no
locks held by any other tasks.
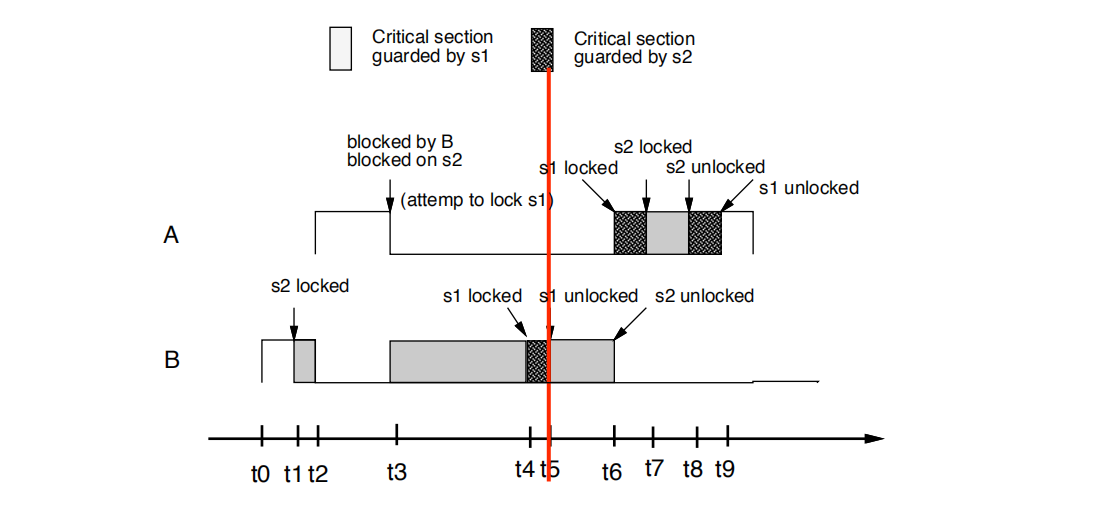
• t5时刻: B解锁s1
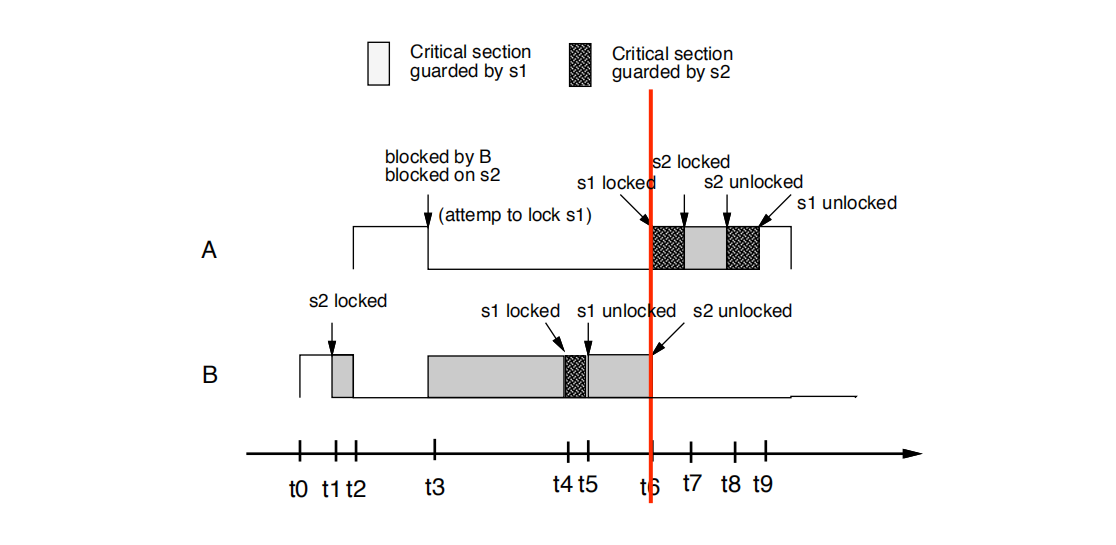
• t6时刻:
B解锁s2
B的优先级降低到为其分配的优先级。就是pri(B)=9
A抢占B(A把cpu从B那边抢过去了),尝试锁定s1并成功
• t6: B unlocks s2 • The priority of B is lowered to its assigned priority (9)
• A preempts B, attempts to lock s1 and succeeds
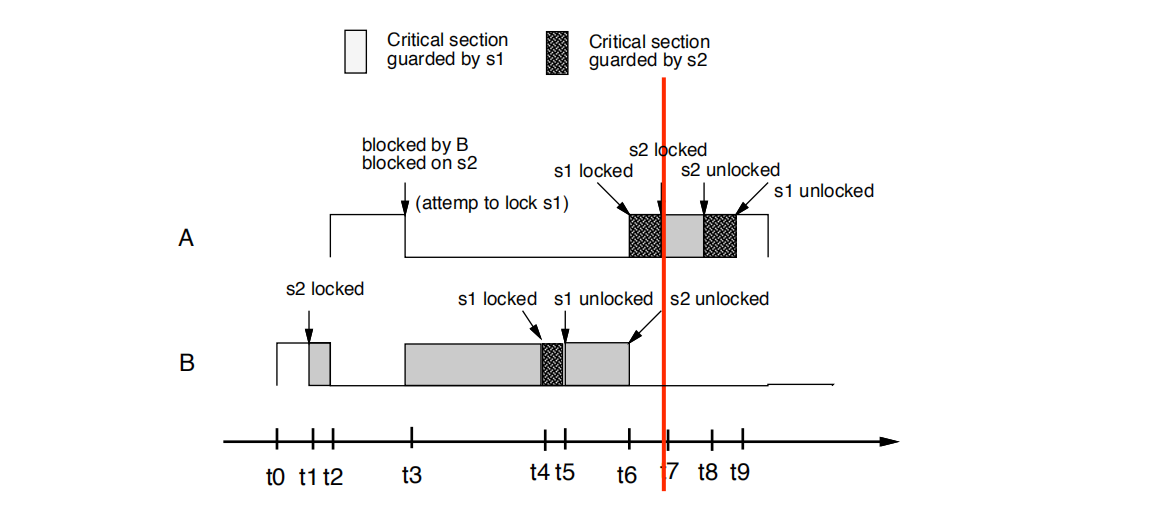
• t7时刻:A attempts to lock s2. Succeeds
• t8时刻:
A unlocks s2
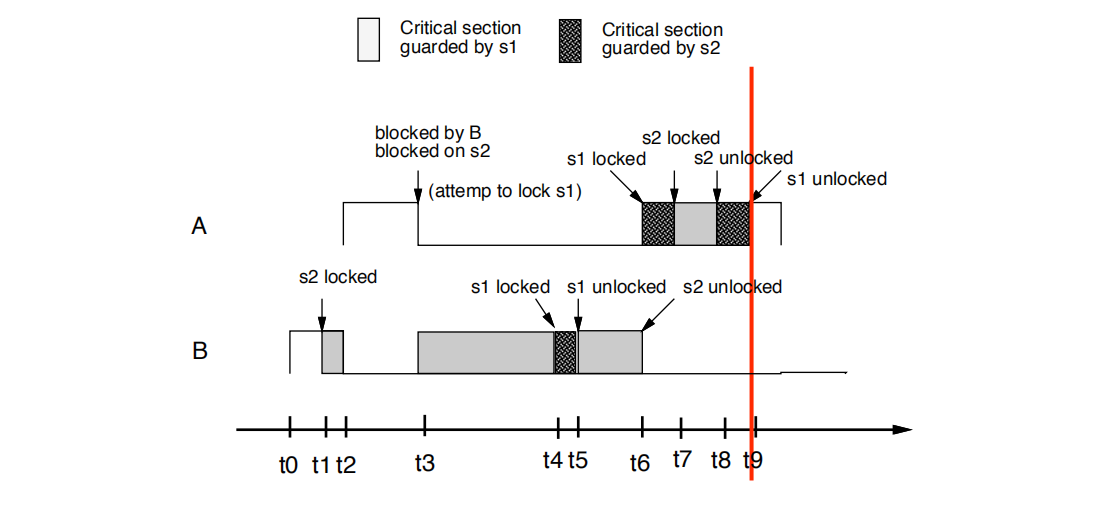
• t9时刻:
A unlocks s1
列子2:
| Task name | T | Priority |
| :-----| ----: | :----: |
| A | 50 | 10 |
| B | 500 | 9 |
| c | 3000 | 8 |
Task A TaskB Task C
lock(s1) lock(s2) lock(s3)
.. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
unlock(s1) lock(s3) lock(s2)
.. .. .. .. .. .. .. .. ..
unlock(s3) unlock(s2)
.. .. .. ..
unlock(s2) unlock(s3)
综上所述: ceil(s1) = 10, ceil(s2) = ceil(s3) = 9
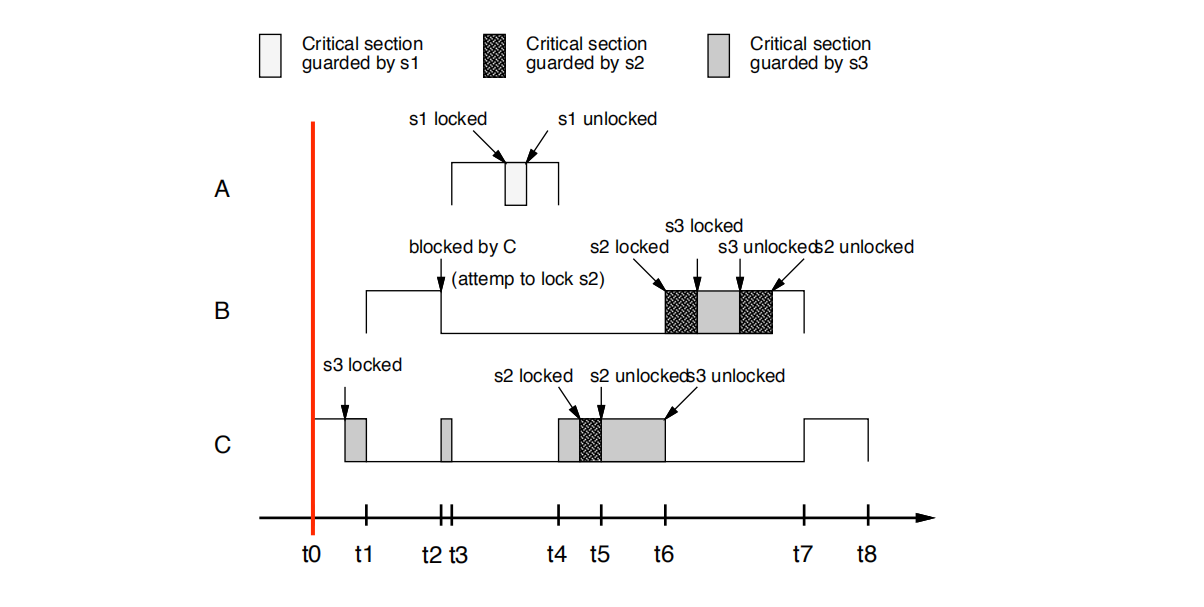
• t0时刻: C开始执行,然后锁定s3 C starts execution and then locks s3
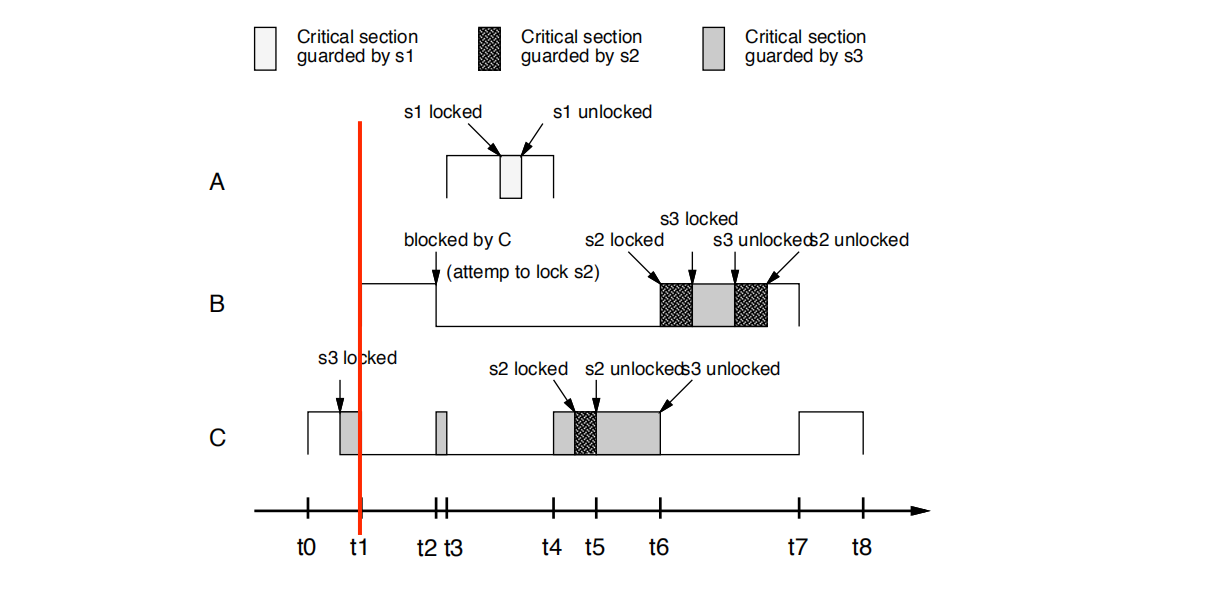
• t1时刻: B抢占C B preempts C
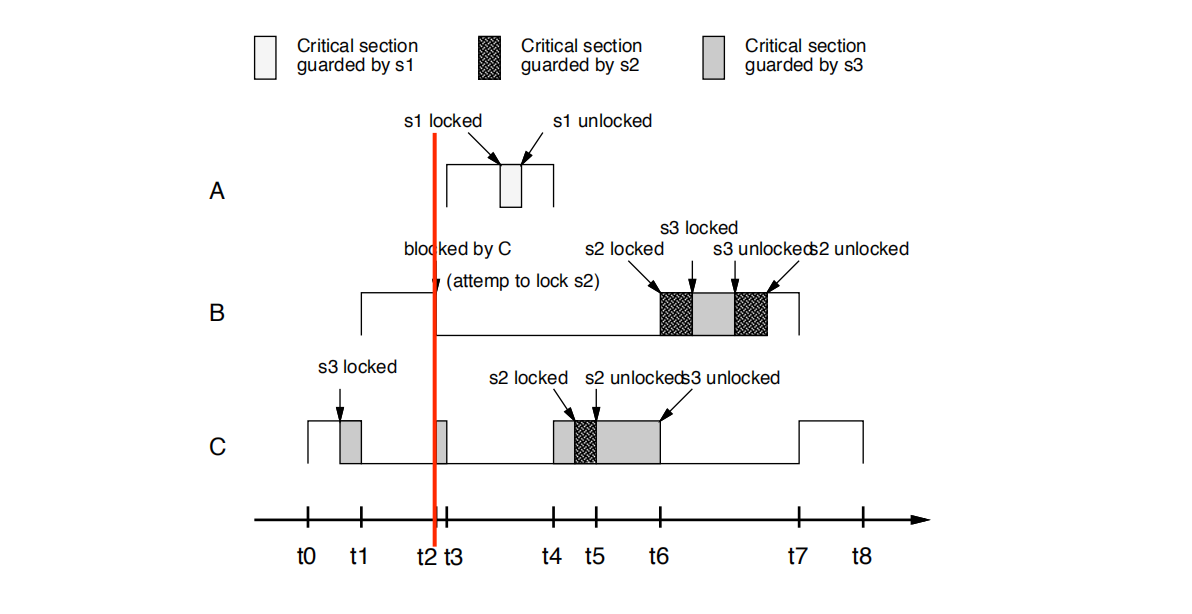
• t2时刻:
B尝试锁定s2。
B失败
B的优先级并不严格高于C所持有的s3的上限,即pri(B)=9 不大于cell(s3) =9 ,s3 is held by C
B阻塞在S3上
B被C阻塞
C继承了B的优先级。
t2: B tries to lock s2.
• B fails (the priority of B is not strictly
• higher than the ceiling of s3 that is held by C) and blocks
• on s3 (B is blocked by C).
• C inherits the priority of B
如果pri(B)不大于cell(s3)即 pri(B)=9 不大于cell(s3) =9,task B将会被阻塞在semaphore s3上。
if not,task B is said to be blocked on the semaphore s3 ,== with the highest priority ceiling == of all semaphores == which is currently locked by other jobs [因为只有S3被其他task,即task C锁住,所以优先级上限只能等于cell(s3)]
and task B is said to be blocked by the task C that holds S3 .
when task B is blocked on S3, the task C currently holding S3 inherits the priority of task B
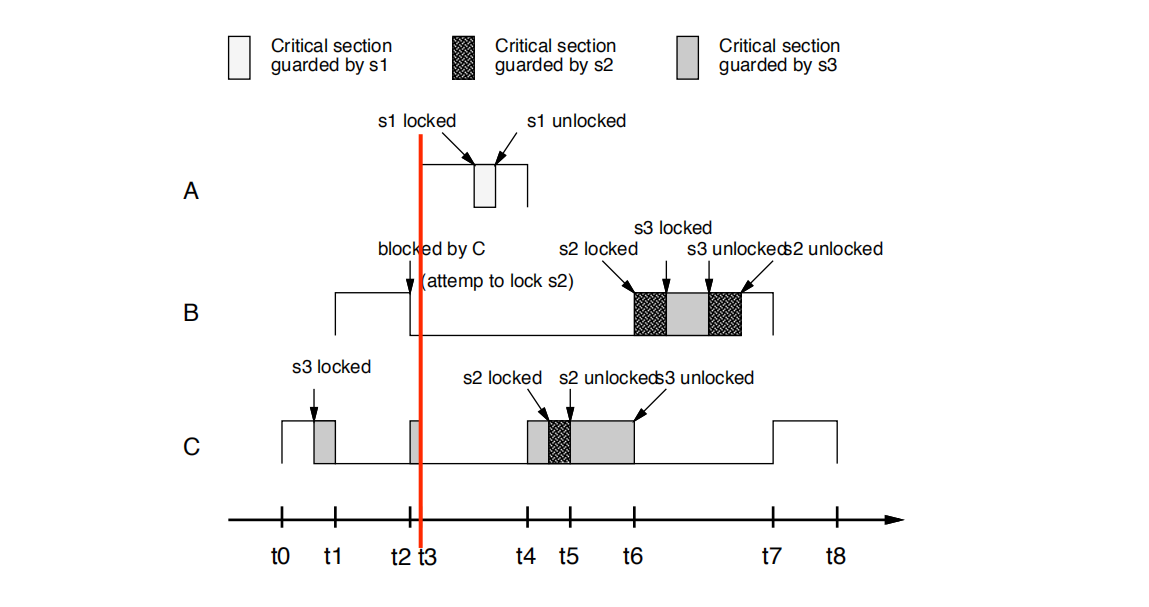
•t3时刻:
A抢占C。稍后尝试锁定s1并成功(因为pri(A) = 0 > cell(S3)= 9)
t3:A preempts C. Later is tries to lock s1 and succeeds
(the priority of A is higher than the ceiling of s3).
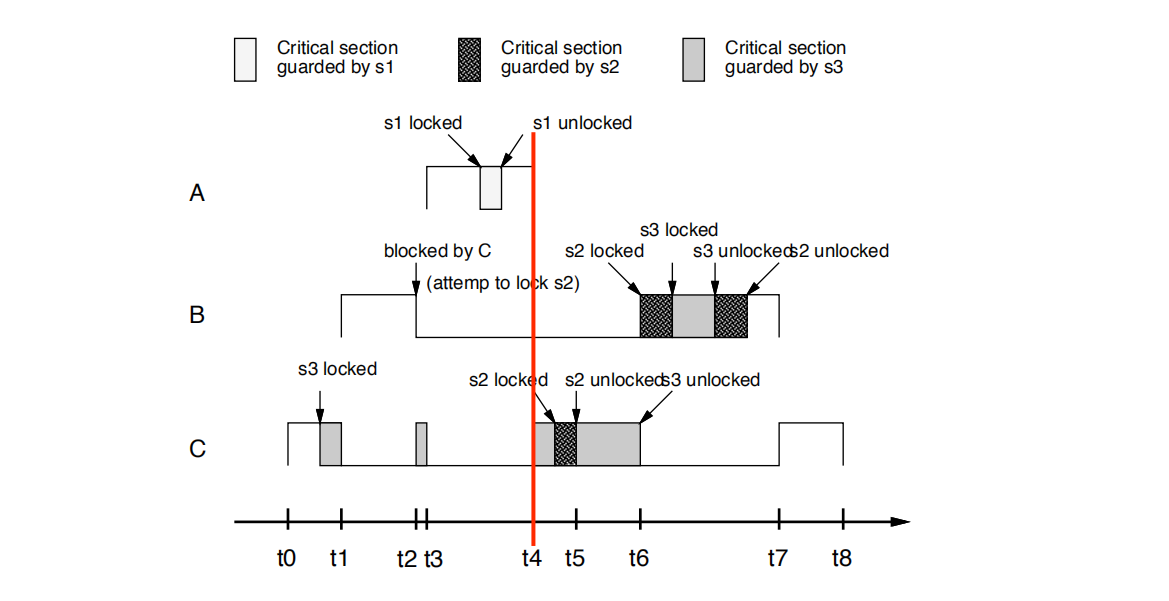
• t4时刻:
A 完成。C接着执行,稍后尝试锁定s2并且成功(持有s3的是C本身)。
A completes. C resumes and later tries to lock s2
and succeeds (it is C itself that holds s3)
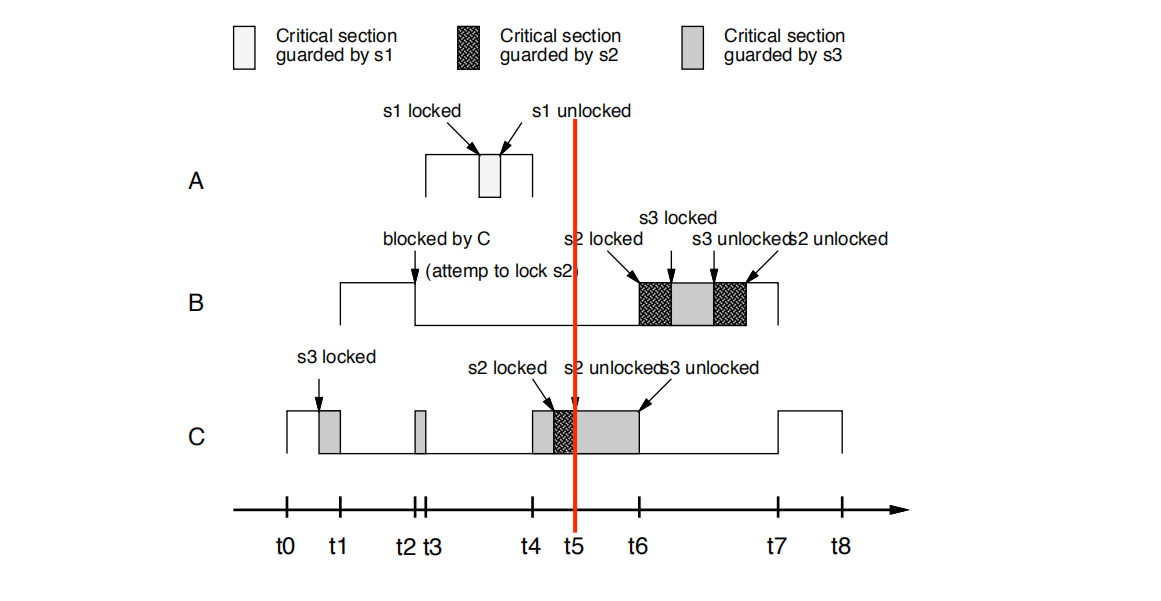
• t5时刻: C解锁s2
C unlocks s2
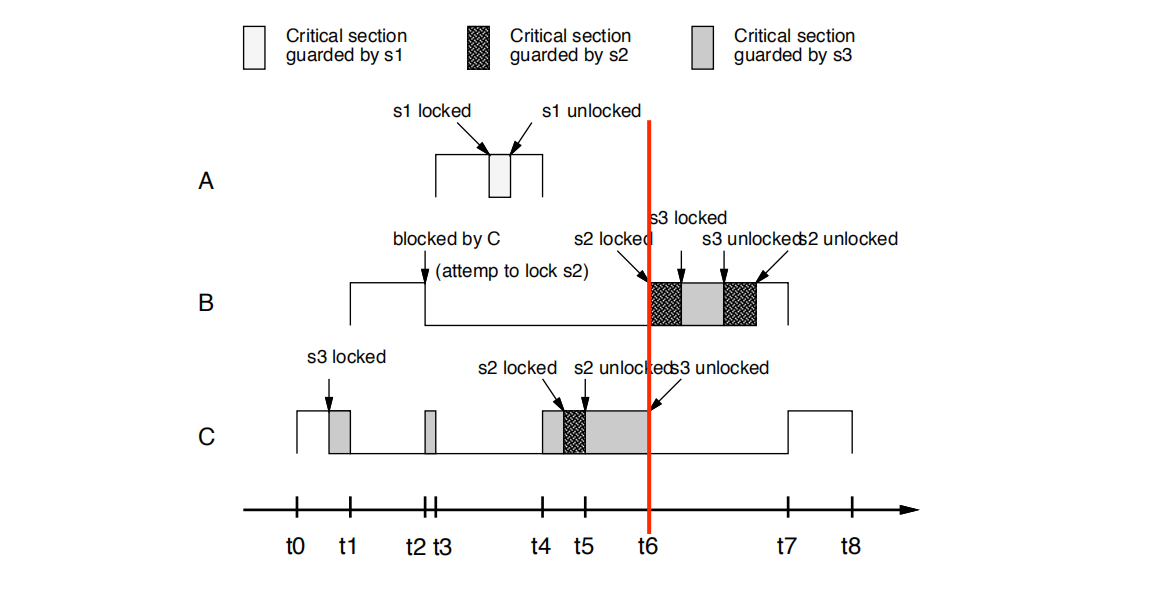
• t6时刻:
C解锁s3,并恢复其基本优先级。 B抢先C,尝试锁定s2并成功。 然后B锁定s3,解锁s3和解锁s2
• C unlocks s3, and gets back its basic priority.B preempts C,
tries to lock s2 and succeeds. Then B locks s3, unlocks s3 and unlocks s2
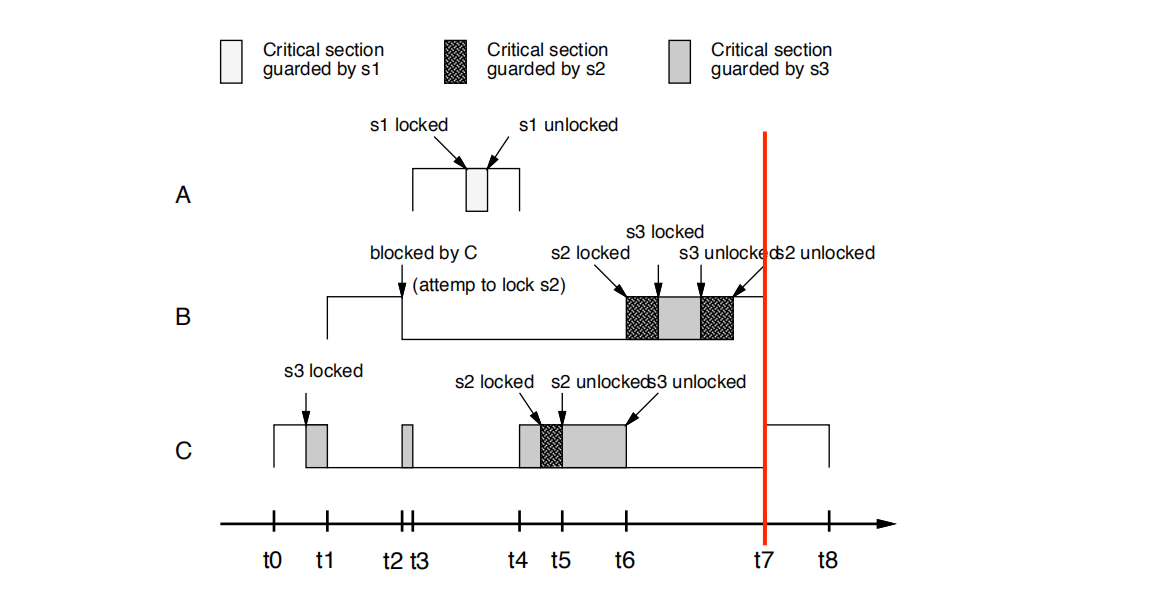
• t7时刻:
B完成,C接着执行.
B completes and C is resumed
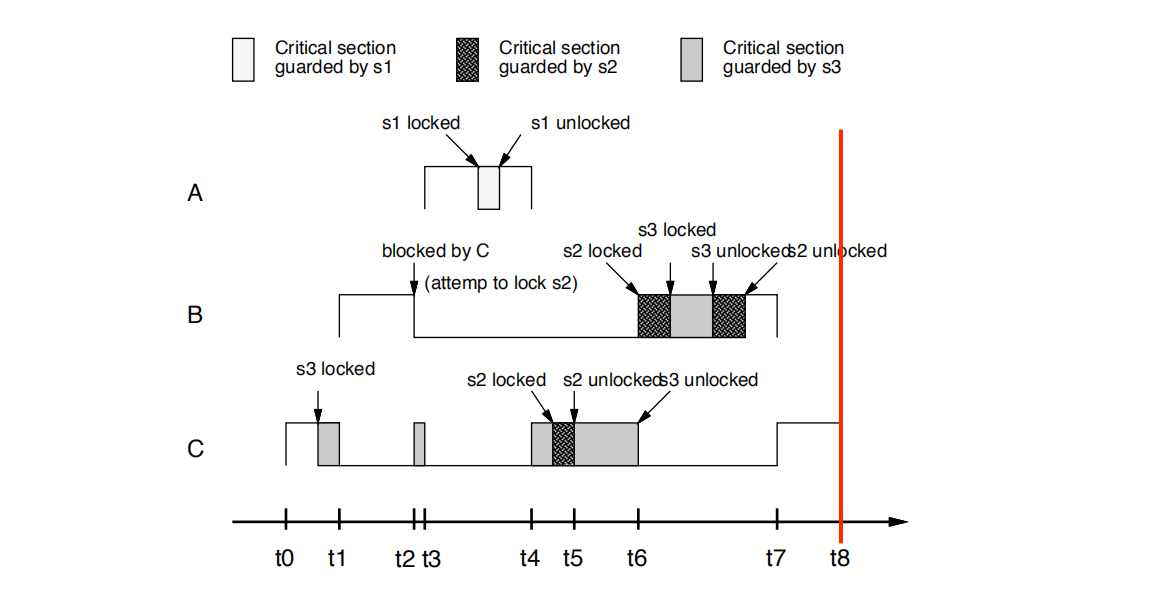
• t8时刻:
C completes
总结
A 从来未被阻塞 ,B在[t2,t3] and [t4,t6]时间段中被阻塞。
但是B被阻塞的时间不会超过task C进入临界区(S3)代码所执行的时间。即使实际阻塞发生在不相交的时间间隔内
• A is never blocked
• B is blocked by C during the intervals [t2,t3] and [t4,t6].
However, B is blocked for no more than the duration of one time critical section of the lower priority task C
even though the actual blocking occurs over disjoint time intervals
priority inheritance vs priority ceiling :
- with ordinary priority inheritance, a task i can be blocked for at most the duration of min(n, m) critical sections,
where n is the number of lower priority tasks that could block i
and m is the number of semaphores that can be used to block i - with the priority ceiling inheritance, a task i can be blocked for at most the duration of one longest critical section
- sometimes priority ceiling introduces unnecessary blocking
but the worst-case blocking delay is much less than for ordinary priority inheritance
有时优先级上限会引入不必要的阻止但最坏情况下的阻塞延迟远小于普通优先级继承


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号