Mybatis入门
什么是框架
生活中的框架


软件开发中的框架
- 框架是可被应用开发者定制的应用骨架
- 框架是一种规则,保证开发者遵循相同的方式开发程序
- 框架提倡“不重复造轮子”,对基础功能进行封装
框架的优点
- 极大提高了开发效率
- 统一的编码规则,利于团队管理
- 灵活配置应用,拥有更好的维护性

什么是MyBatis
MyBatis是优秀的持久化框架、它使用XML将SQL与程序解耦、学习简单,执行高效是JDBC的延伸。
MyBatis的开发流程
- 引入MyBatis
- 创建依赖配置文件
- 创建实体(Entity)类
- 创建Mapping映射文件
- 初始化SessionFactory
- 利用SqlSession对象操作数据
MyBatis的环境配置
mybatis-config.xml
MyBatis采用XML格式配置数据库环境信息,MyBatis环境配置标签<environment>、environment包含数据库驱动、URL、用户名与密码;
<!--设置默认指向的数据库-->
<environments default="dev">
<!--配置环境,不同的环境不同的id名字-->
<environment id="dev">
<!-- 采用JDBC方式对数据库事务进行commit/rollback -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!--采用连接池方式管理数据库连接-->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/babytun?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="****"/>
<property name="password" value="****"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
SqlSessionFactory
- SqlSessionFactory是Mybatis的核心对象
- 用于初始化MyBatis,创建SqlSession对象
- 保证SqlSessionFactory在应用全局唯一
SqlSession
- SqlSessionFactory是Mybatis操作数据库的核心对象
- SqlSession使用JDBC方式与数据库交互
- SqlSession对象提供了数据库表CRUD对应方法
MyBatis数据查询
查询步骤
- 创建实体类(Entity)
- 创建Mapper XML
- 编写<select>SQL标签
- 开启驼峰命名
- 新增<mapper>
- SqlSession执行select语句
举例select:
Goods.java
package com.imooc.mybatis.entity;
public class Goods {
private Integer goodsId;//商品编号
private String title;//标题
private String subTitle;//子标题
private Float originalCost;//原始价格
private Float currentPrice;//当前价格
private Float discount;//折扣率
private Integer isFreeDelivery;//是否包邮 ,1-包邮 0-不包邮
private Integer categoryId;//分类编号
public Integer getGoodsId() {
return goodsId;
}
public void setGoodsId(Integer goodsId) {
this.goodsId = goodsId;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public String getSubTitle() {
return subTitle;
}
public void setSubTitle(String subTitle) {
this.subTitle = subTitle;
}
public Float getOriginalCost() {
return originalCost;
}
public void setOriginalCost(Float originalCost) {
this.originalCost = originalCost;
}
public Float getCurrentPrice() {
return currentPrice;
}
public void setCurrentPrice(Float currentPrice) {
this.currentPrice = currentPrice;
}
public Float getDiscount() {
return discount;
}
public void setDiscount(Float discount) {
this.discount = discount;
}
public Integer getIsFreeDelivery() {
return isFreeDelivery;
}
public void setIsFreeDelivery(Integer isFreeDelivery) {
this.isFreeDelivery = isFreeDelivery;
}
public Integer getCategoryId() {
return categoryId;
}
}
goods.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="goods">
<select id = "selectAll" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods order by goods_id desc limit 10
</select>
</mapper>
mybatis-config.xml中增加
<mappers>
<mapper resource="mappers/goods.xml"/>
</mappers>
执行查询:
/**
* select查询语句执行
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectAll() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("goods.selectAll");
for(Goods g : list){
System.out.println(g.getTitle());
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
SQL传参
单参数传递
使用parameterType指定参数的数据类型即可,SQL中#{value}提取参数。
goods.xml中增加
<select id="selectById" parameterType="Integer" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
</select>
然后测试方法:
/**
* 传递单个SQL参数
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectById() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Goods goods = session.selectOne("goods.selectById" , 1603);
System.out.println(goods.getTitle());
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
传递多个参数
多参数传递时,使用parameterType指定Map接口,SQL中#{key}提取参数
goods.xml中添加
<select id="selectByPriceRange" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods
where
current_price between #{min} and #{max}
order by current_price
limit 0,#{limt}
</select>
测试方法:
/**
* 传递多个SQL参数
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectByPriceRange() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Map param = new HashMap();
param.put("min",100);
param.put("max" , 500);
param.put("limt" , 10);
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("goods.selectByPriceRange", param);
for(Goods g:list){
System.out.println(g.getTitle() + ":" + g.getCurrentPrice());
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
获取多表关联查询结果
goods.xml
<!-- 利用LinkedHashMap保存多表关联结果
MyBatis会将每一条记录包装为LinkedHashMap对象
key是字段名 value是字段对应的值 , 字段类型根据表结构进行自动判断
优点: 易于扩展,易于使用
缺点: 太过灵活,无法进行编译时检查
-->
<select id="selectGoodsMap" resultType="java.util.LinkedHashMap" flushCache="true">
select g.* , c.category_name,'1' as test from t_goods g , t_category c
where g.category_id = c.category_id
</select>
测试方法:
/**
* 利用Map接收关联查询结果
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectGoodsMap() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<Map> list = session.selectList("goods.selectGoodsMap");
for(Map map : list){
System.out.println(map);
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
ResultMap结果映射
- ResultMap可以将查询结果映射为复杂类型的Java对象、
- ResultMap适用于Java对象保存多表关联结果、
- ResultMap支持对象关联查询等高级特性
举例:
新增GoodsDTO.java
package com.imooc.mybatis.dto;
import com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods;
//Data Transfer Object--数据传输对象
public class GoodsDTO {
private Goods goods = new Goods();
private String categoryName;
private String test;
public Goods getGoods() {
return goods;
}
public void setGoods(Goods goods) {
this.goods = goods;
}
public String getTest() {
return test;
}
public void setTest(String test) {
this.test = test;
}
}
goods.xml增加
<!--结果映射-->
<resultMap id="rmGoods" type="com.imooc.mybatis.dto.GoodsDTO">
<!--设置主键字段与属性映射-->
<id property="goods.goodsId" column="goods_id"></id>
<!--设置非主键字段与属性映射-->
<result property="goods.title" column="title"></result>
<result property="goods.originalCost" column="original_cost"></result>
<result property="goods.currentPrice" column="current_price"></result>
<result property="goods.discount" column="discount"></result>
<result property="goods.isFreeDelivery" column="is_free_delivery"></result>
<result property="goods.categoryId" column="category_id"></result>
<result property="categoryName" column="category_name"></result>
<result property="test" column="test"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="selectGoodsDTO" resultMap="rmGoods">
select g.*, c.*, '1' as test
from t_goods g,
t_category c
where g.category_id = c.category_id
</select>
测试方法:
/**
* 利用ResultMap进行结果映射
*
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectGoodsDTO() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try {
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
List<GoodsDTO> list = session.selectList("goods.selectGoodsDTO");
for (GoodsDTO g : list) {
System.out.println(g.getGoods().getTitle());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
} finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
数据库事务
数据库事务是保证数据库数据操作完整性的基础
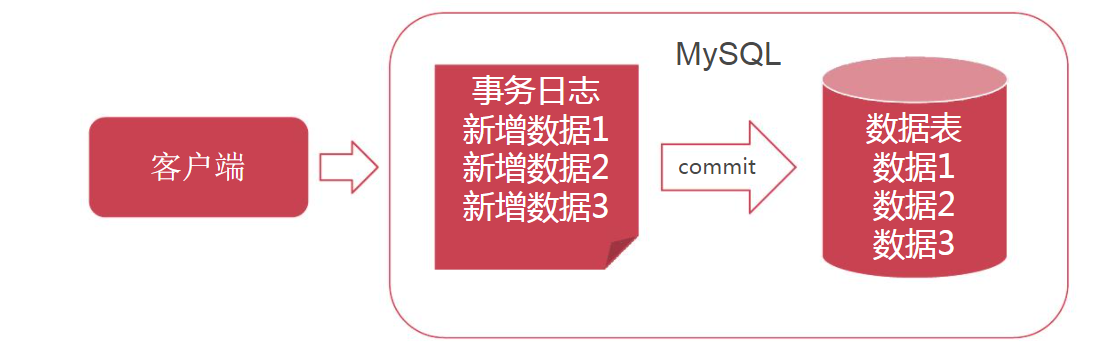
数据库的写操作包含三种:
- insert
- update
- delete
insert
flushCache="true"在sql执行后强制清空缓存
<insert id="insert" parameterType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods" flushCache="true">
INSERT INTO t_goods(title, sub_title, original_cost, current_price, discount, is_free_delivery, category_id)
VALUES (#{title} , #{subTitle} , #{originalCost}, #{currentPrice}, #{discount}, #{isFreeDelivery}, #{categoryId})
<!--<selectKey resultType="Integer" keyProperty="goodsId" order="AFTER">-->
<!--select last_insert_id()-->
<!--</selectKey>-->
</insert>
update
<update id="update" parameterType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
UPDATE t_goods
SET
title = #{title} ,
sub_title = #{subTitle} ,
original_cost = #{originalCost} ,
current_price = #{currentPrice} ,
discount = #{discount} ,
is_free_delivery = #{isFreeDelivery} ,
category_id = #{categoryId}
WHERE
goods_id = #{goodsId}
</update>
delete
<delete id="delete" parameterType="Integer">
delete from t_goods where goods_id = #{value}
</delete>
Mybatis预防SQL注入攻击
SQL注入攻击是指攻击者利用SQL漏洞,绕过系统约束,越权获取数据的攻击方式。

MyBatis的两种传值方式
${} 文本替换,未经任何处理对SQL文本替换
#{} 预编译传值,使用预编译传值可以预防SQL注入
SQL注入攻击举例:
<select id="selectByTitle" parameterType="java.util.Map" resultType="com.imooc.mybatis.entity.Goods">
select * from t_goods where title = ${title} 或者 #{title}
</select>
测试代码:
/**
* 预防SQL注入
* @throws Exception
*/
@Test
public void testSelectByTitle() throws Exception {
SqlSession session = null;
try{
session = MyBatisUtils.openSession();
Map param = new HashMap();
/*
${}原文传值
select * from t_goods
where title = '' or 1 =1 or title = '【德国】爱他美婴幼儿配方奶粉1段800g*2罐 铂金版'
*/
/*
#{}预编译
select * from t_goods
where title = "'' or 1 =1 or title = '【德国】爱他美婴幼儿配方奶粉1段800g*2罐 铂金版'"
*/
param.put("title","'' or 1=1 or title='【德国】爱他美婴幼儿配方奶粉1段800g*2罐 铂金版'");
List<Goods> list = session.selectList("goods.selectByTitle", param);
for(Goods g:list){
System.out.println(g.getTitle() + ":" + g.getCurrentPrice());
}
}catch (Exception e){
throw e;
}finally {
MyBatisUtils.closeSession(session);
}
}
当时用${ } 原文传值 时,执行命令为:
select * from t_goods where title = '' or 1 =1 or title = '【德国】爱他美婴幼儿配方奶粉1段800g*2罐 铂金版'
当时用#{ } 预编译 时,执行命令为:
select * from t_goods where title = "'' or 1 =1 or title = '【德国】爱他美婴幼儿配方奶粉1段800g*2罐 铂金版'"
使用原文传值会将所有数据输出,会造成数据泄露。
什么时候回用到原文传值呢?
比如,想要根据前端数据的条件来动态变化SQL查询方式。
举例:
param.put("order" , " order by title desc");
这时候必须配合 ${} 一起使用。(但是不建议使用)
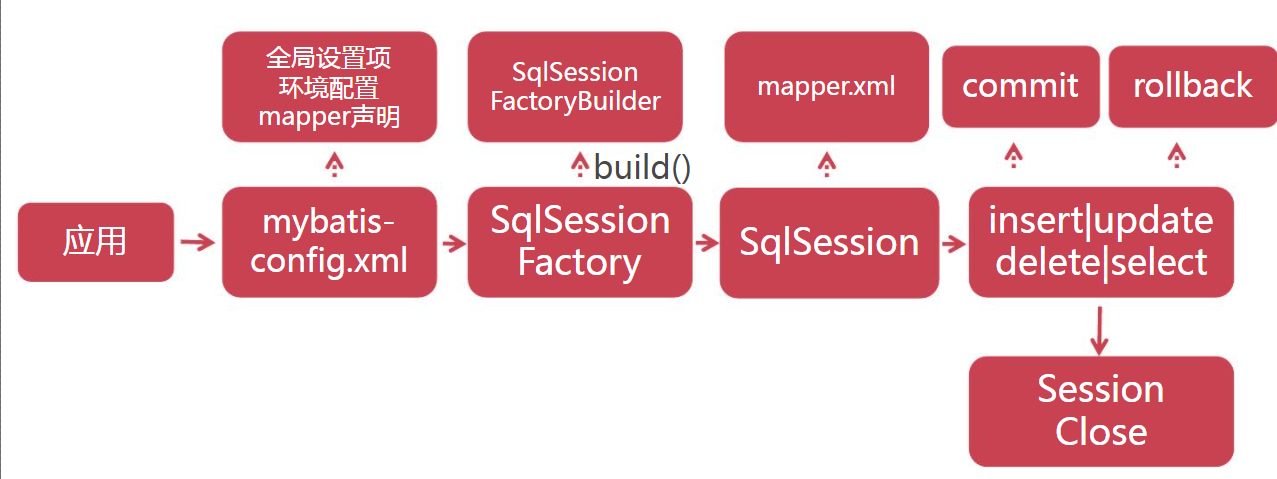
MyBatis的工作流程



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号