Blog2- 2022-4/期中/5
这是本学期的第二次博客啦,是针对pta的第四次大作业、期中考试和第五次大作业的题目进行分析,分为前言、设计与分析、踩坑心得、改进建议、总结五个方面。
(1)前言
这几次大作业基本上都是围绕图形类设计,在前面几次大作业出现的点、线、三角形的基础上,来研究四边形和五边形,虽然题量不大,但做起来很麻烦,考虑的东西较多,难度比较大。
第四次大作业共三道题目,分别为读蛟龙号载人深潜信息中的数字并相加、四边形的设计、设计银行业务类。
第一道题主要考察了正则表达式搜索数字,以及数据类型的转换。这道题中是将string字符串转换为int整型,因此用到Integer.parseInt( )语句。
关于正则表达式,我们应该掌握住它的用法,因为在后续的题目中也会用到相关知识,而且如果会用正则表达式,在查找、替换符合规则的字符串题目中会很方便。总结一些正则表达式的知识点:
常用的元字符:
| . | 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符 |
| \w | 匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字 |
| \s | 匹配任意的空白符 |
| \d | 匹配数字 |
| \b | 匹配单词的开始或结束 |
| ^ | 匹配字符串的开始(在集合字符里[^a]表示非(不匹配)的意思 |
| $ | 匹配字符串的结束 |
常用的反义字符:
| \W | 匹配任意不是字母,数字,下划线,汉字的字符 |
| \S | 匹配任意不是空白符的字符 |
| \D | 匹配任意非数字的字符 |
| \B | 匹配不是单词开头或结束的位置 |
| [^x] | 匹配除了x以外的任意字符 |
| [^aeiou] | 匹配除了aeiou这几个字母以外的任意字符 |
第二道题是四边形的设计,就是在前几次大作业的基础上加以研究,涉及到的计算方法和知识点比较多,很多判断方法牵扯到数学知识,要在网上查计算方法,难度较大。
第三道题是设计一个银行业务类,较为简单,设计思路题目里已经给的很清楚,照葫芦画瓢就好,但是需要注意的一点是要区input.next()
和input.nextline()的区别,这个地方如果写错了就无法得到正确的结果。
期中考试三道题都是点线面问题,分别为类的设计、点线面问题重构(继承与多态)、点线面问题再重构(容器类)。
第一道题较简单,按照题目所给类图加以编写即可,但是当时考试的时候,继承与多态和容器类都是刚学的,没有完全掌握,所以当时写不下去,结果很糟糕,得分较低。
第五次大作业是五边形的设计,虽然只有一道题,但是真的很复杂,考虑的情况很多,想着想着思路就乱了,刚开始还是有点无法下笔,后来虽然写出来了一些,但是后面一些复杂的选项还是没有想明白。
总之,关于图形的这几道题都比较复杂,牵扯到很多数学知识,难度比较大,所以大家的平均分不是很高。
(2)设计与分析
1.点线形系列4-凸四边形的计算。
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与四边形有关的计算。
以下四边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是四边形、平行四边形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。
2:输入四个点坐标,判断是否是菱形、矩形、正方形,判断结果输出true/false,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
3:输入四个点坐标,判断是凹四边形(false)还是凸四边形(true),输出四边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若四个点坐标无法构成四边形,输出"not a quadrilateral"
4:输入六个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后四个点构成一个四边形或三角形,输出直线与四边形(也可能是三角形)相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出四边形(或三角形)被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与四边形或三角形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形的输入,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
后四个点构成三角形的情况:假设三角形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z 不与xy都相邻,如z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
5:输入五个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后四个点所构成的四边形(限定为凸四边形,不考虑凹四边形)或三角形(判定方法见选项4)的内部(若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle或者on the quadrilateral"。若后四个点不符合四边形或三角形,输出"not a quadrilateral or triangle"。
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
选项1、2、3中,若四边形四个点中有重合点,输出"points coincide"。
选项4中,若前两个输入线的点重合,输出"points coincide"。
我的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String s=input.nextLine();
if(s.charAt(0)=='1') {
Inputfour inputfour=new Inputfour();
if(inputfour.judge(s)==1){
getNum getnum=new getNum();
getnum.getnumfour(s);
double x1=getnum.x1;
double y1=getnum.y1;
double x2=getnum.x2;
double y2=getnum.y2;
double x3=getnum.x3;
double y3=getnum.y3;
double x4=getnum.x4;
double y4=getnum.y4;
FourLine fourline=new FourLine();
fourline.quadrilateral(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==2){
System.out.print("wrong number of points");
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==3){
System.out.print("Wrong Format");
}
}
else if(s.charAt(0)=='2') {
Inputfour inputfour=new Inputfour();
if(inputfour.judge(s)==1){
getNum getnum=new getNum();
getnum.getnumfour(s);
double x1=getnum.x1;
double y1=getnum.y1;
double x2=getnum.x2;
double y2=getnum.y2;
double x3=getnum.x3;
double y3=getnum.y3;
double x4=getnum.x4;
double y4=getnum.y4;
FourLine fourline=new FourLine();
fourline.diamond(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==2){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==3){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
else if(s.charAt(0)=='3') {
Inputfour inputfour=new Inputfour();
if(inputfour.judge(s)==1){
getNum getnum=new getNum();
getnum.getnumfour(s);
double x1=getnum.x1;
double y1=getnum.y1;
double x2=getnum.x2;
double y2=getnum.y2;
double x3=getnum.x3;
double y3=getnum.y3;
double x4=getnum.x4;
double y4=getnum.y4;
FourLine fourline=new FourLine();
fourline.kind(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3,x4,y4);
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==2){
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
}
else if(inputfour.judge(s)==3){
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
}
class Inputfour{
String a="([1-5]:)(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ]
(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|
[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)
[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)";
String b="([1-5]:)(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ]
(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+
|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)
[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)([ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.
[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*))+";
String c="([1-5]:)(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)
([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.
[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)";
String d="([1-5]:)(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[ ]
(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)";
String e="([1-5]:)(-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)[,](-?|\\+?)([1-9][\\d]*\\.[\\d]+|[0]\\.[\\d]+|[0]|[1-9][\\d]*)";
public int judge(String s) {
if(s.matches(a)) {
return 1;
}
else if(s.matches(b)||s.matches(c)||s.matches(d)||s.matches(e)) {
return 2;
}
else{
return 3;
}
}
}
class getNum{
public double x1,x2,x3,x4,x5,x6;
public double y1,y2,y3,y4,y5,y6;
public void getnumfour(String s) {
String [] num=new String[8];
int i=0;
int j=2;
int k=0;
for(i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
if(s.charAt(i)==','||s.charAt(i)==' ') {
num[k]= s.substring(j,i);
k++;
j=i+1;
}
}
num[7]=s.substring(j,s.length());
x1=Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y1=Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
x2=Double.parseDouble(num[2]);
y2=Double.parseDouble(num[3]);
x3=Double.parseDouble(num[4]);
y3=Double.parseDouble(num[5]);
x4=Double.parseDouble(num[6]);
y4=Double.parseDouble(num[7]);
}
public void getnumfive(String s) {
String [] num=new String[10];
int i=0;
int j=2;
int k=0;
for(i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
if(s.charAt(i)==','||s.charAt(i)==' ') {
num[k]= s.substring(j,i);
k++;
j=i+1;
}
}
num[9]=s.substring(j,s.length());
x1=Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y1=Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
x2=Double.parseDouble(num[2]);
y2=Double.parseDouble(num[3]);
x3=Double.parseDouble(num[4]);
y3=Double.parseDouble(num[5]);
x4=Double.parseDouble(num[6]);
y4=Double.parseDouble(num[7]);
x5=Double.parseDouble(num[8]);
y5=Double.parseDouble(num[9]);
}
public void getnumsix(String s) {
String [] num=new String[12];
int i=0;
int j=2;
int k=0;
for(i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
if(s.charAt(i)==','||s.charAt(i)==' ') {
num[k]= s.substring(j,i);
k++;
j=i+1;
}
}
num[11]=s.substring(j,s.length());
x1=Double.parseDouble(num[0]);
y1=Double.parseDouble(num[1]);
x2=Double.parseDouble(num[2]);
y2=Double.parseDouble(num[3]);
x3=Double.parseDouble(num[4]);
y3=Double.parseDouble(num[5]);
x4=Double.parseDouble(num[6]);
y4=Double.parseDouble(num[7]);
x5=Double.parseDouble(num[8]);
y5=Double.parseDouble(num[9]);
x6=Double.parseDouble(num[10]);
y6=Double.parseDouble(num[11]);
}
}
class FourLine{
public void quadrilateral(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) {
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x1==x3&&y1==y3)||(x1==x4&&y1==y4)||(x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
}
else {
if((y4-y3)*(x4-x2)==(y4-y2)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("false false");
}
else if((y4-y3)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("false false");
}
else if((y4-y2)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x2)) {
System.out.println("false false");
}
else if((y3-y2)*(x3-x1)==(y3-y1)*(x3-x2)) {
System.out.println("false false");
}
else {
System.out.print("true");
if(((y3-y4)*(x1-x2)==(y1-y2)*(x3-x4))&&((y2-y3)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x2-x3))) {
System.out.print(" ture");
}
else {
System.out.print(" false");
}
}
}
}
public void diamond(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) {
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x1==x3&&y1==y3)||(x1==x4&&y1==y4)||(x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)){
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else {
if((y4-y3)*(x4-x2)==(y4-y2)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y4-y3)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y4-y2)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x2)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y3-y2)*(x3-x1)==(y3-y1)*(x3-x2)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else {
if(((y3-y4)*(x1-x2)==(y1-y2)*(x3-x4))&&((y2-y3)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x2-x3))) {
double L1=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y1-y2, 2)); //邻边
double L2=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x3-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y3-y2, 2));
double L3=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x3-x1, 2)+Math.pow(y3-y1, 2)); //对角线
double L4=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x4-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y4-y2, 2));
if(L1!=L2&&L3!=L4) {
System.out.print("false false false");
}
else if(L1==L2&&L3!=L4) {
System.out.print("true false false");
}
else if(L1!=L2&&L3==L4) {
System.out.print("false true false");
}
else if(L1==L2&&L3==L4) {
System.out.print("true true true");
}
}
else {
System.out.print("false false false");
}
}
}
}
public void kind(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2,double x3,double y3,double x4,double y4) {
if((x1==x2&&y1==y2)||(x1==x3&&y1==y3)||(x1==x4&&y1==y4)||(x2==x3&&y2==y3)||(x2==x4&&y2==y4)||(x3==x4&&y3==y4)){
System.out.println("points coincide");
}
else {
if((y4-y3)*(x4-x2)==(y4-y2)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y4-y3)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x3)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y4-y2)*(x4-x1)==(y4-y1)*(x4-x2)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else if((y3-y2)*(x3-x1)==(y3-y1)*(x3-x2)) {
System.out.println("not a quadrilateral");
}
else {
double L1=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x1-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y1-y2, 2)); //邻边
double L2=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x3-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y3-y2, 2));
double L3=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x3-x4, 2)+Math.pow(y3-y4, 2));
double L4=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x4-x1, 2)+Math.pow(y4-y1, 2));
double L5=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x3-x1, 2)+Math.pow(y3-y1, 2)); //对角线
double L6=Math.sqrt(Math.pow(x4-x2, 2)+Math.pow(y4-y2, 2));
double C=L1+L2+L3+L4;
double S1=Sjudge(L1,L2,L5)+Sjudge(L5,L3,L4);
double S2=Sjudge(L1,L6,L4)+Sjudge(L2,L3,L6);
if(S1==S2){
System.out.print("true");
limitdouble(C);
limitdouble(S1);
}
else {
if(S1>S2) {
System.out.print("false");
limitdouble(C);
limitdouble(S2);
}
else {
System.out.print("false");
limitdouble(C);
limitdouble(S1);
}
}
}
}
}
public double Sjudge(double a,double b,double c) {
double p=(a+b+c)/2;
double s=Math.sqrt(p*(p-a)*(p-b)*(p-c));
return s;
}
public void limitdouble(double a) {
int m=(a+"").length()-(a+"").indexOf(".")-1;
if(m>3) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat( "0.000");
System.out.print(" "+df.format(a));
}
else if(m<=3){
System.out.print(" "+a);
}
}
}
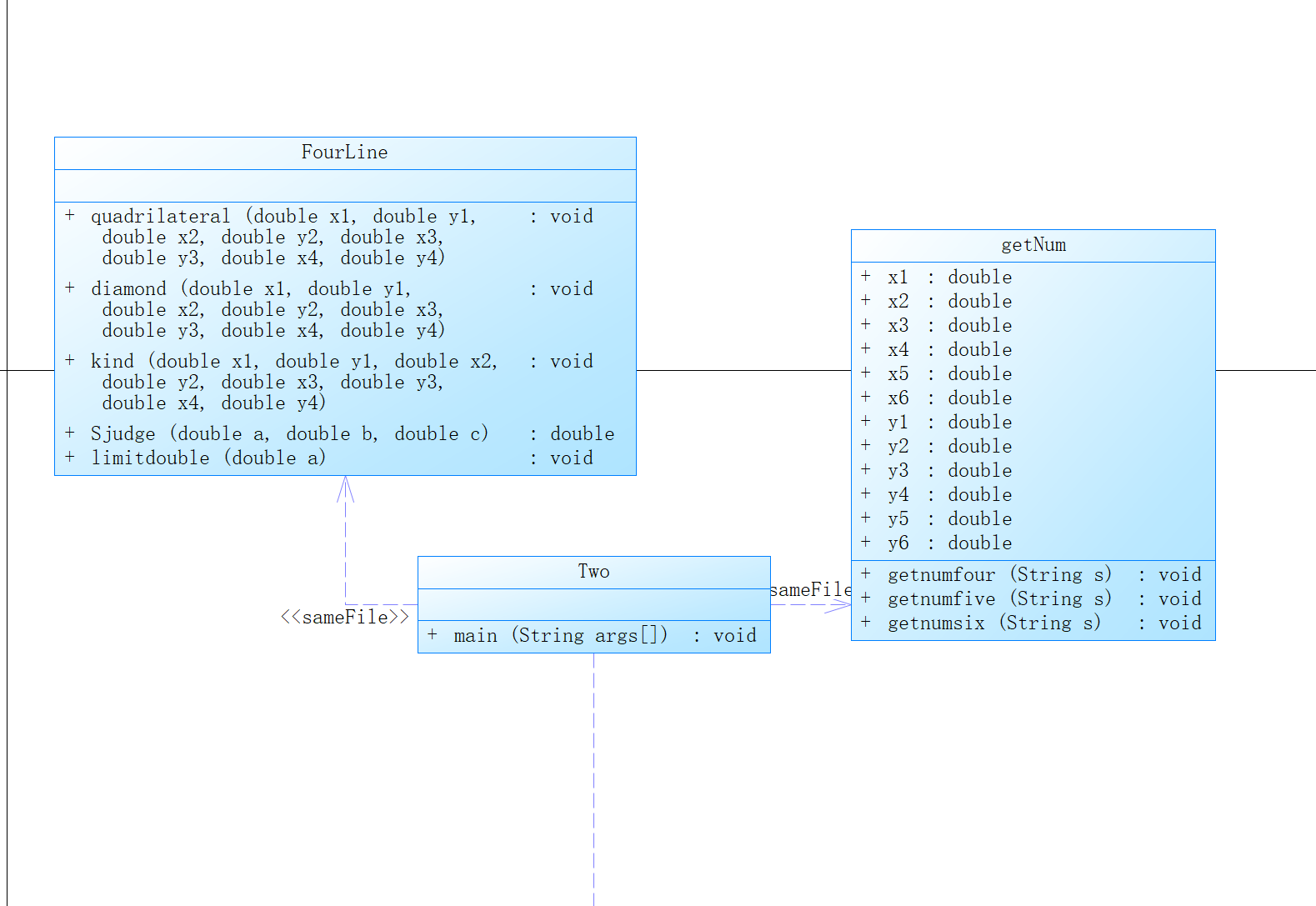
我这道题做的比较差,很多测试点没有通过,在正则表达式那里我是准备一种一种情况试,但是这样太麻烦了也容易搞错,在判断点的数量那里,我输入测试时都能输出正确的结果,但是不知道为什么测试点过不去,可能是有些情况没有考虑到,所以输入异常那里的测试点有些没有过去。后面的选项也没有全写完,当时不太理解这些思路,是有点懵的,尤其数学方法还多,所以做的不好。
在判断能否构成四边形那里,我试了好多方法,我认为我把各种情况都包含进去了,可是测试点还是不能全过去,所以我真的很疑惑。
在控制输出结果的小数位数时,我用的是int m=(a+"").length()-(a+"").indexOf(".")-1判断小数的位数,再用DecimalFormat控制输出。
2.点线形系列5-凸五边形的计算
用户输入一组选项和数据,进行与五边形有关的计算。
以下五边形顶点的坐标要求按顺序依次输入,连续输入的两个顶点是相邻顶点,第一个和最后一个输入的顶点相邻。
选项包括:
1:输入五个点坐标,判断是否是五边形,判断结果输出true/false。
2:输入五个点坐标,判断是凹五边形(false)还是凸五边形(true),如果是凸五边形,则再输出五边形周长、面积,结果之间以一个英文空格符分隔。 若五个点坐标无法构成五边形,输出"not a pentagon"
3:输入七个点坐标,前两个点构成一条直线,后五个点构成一个凸五边形、凸四边形或凸三角形,输出直线与五边形、四边形或三角形相交的交点数量。如果交点有两个,再按面积从小到大输出被直线分割成两部分的面积(不换行)。若直线与多边形形的一条边线重合,输出"The line is coincide with one of the lines"。若后五个点不符合五边形输入,若前两点重合,输出"points coincide"。
4:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),判断它们两个之间是否存在包含关系(一个多边形有一条或多条边与另一个多边形重合,其他部分都包含在另一个多边形内部,也算包含)。
两者存在六种关系:1、分离(完全无重合点) 2、连接(只有一个点或一条边重合) 3、完全重合 4、被包含(前一个多边形在后一个多边形的内部)5、交错 6、包含(后一个多边形在前一个多边形的内部)。
各种关系的输出格式如下:
1、no overlapping area between the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon and the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
2、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is connected to the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
3、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon coincides with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
4、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is inside the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon is interlaced with the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
6、the previous triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon contains the following triangle/quadrilateral/ pentagon
5:输入十个点坐标,前、后五个点分别构成一个凸多边形(三角形、四边形、五边形),输出两个多边形公共区域的面积。注:只考虑每个多边形被另一个多边形分割成最多两个部分的情况,不考虑一个多边形将另一个分割成超过两个区域的情况。
6:输入六个点坐标,输出第一个是否在后五个点所构成的多边形(限定为凸多边形,不考虑凹多边形),的内部(若是五边形输出in the pentagon/outof the pentagon,若是四边形输出in the quadrilateral/outof the quadrilateral,若是三角形输出in the triangle/outof the triangle)。输入入错存在冗余点要排除,冗余点的判定方法见选项5。如果点在多边形的某条边上,输出"on the triangle/on the quadrilateral/on the pentagon"。
以上3选项中,若输入的点无法构成多边形,则输出"not a polygon"。输入的五个点坐标可能存在冗余,假设多边形一条边上两个端点分别是x、y,边线中间有一点z,另一顶点s:
1)符合要求的输入:顶点重复或者z与xy都相邻,如:x x y s、x z y s、x y x s、s x y y。此时去除冗余点,保留一个x、一个y。
2) 不符合要求的输入:z不与xy都相邻,如:z x y s、x z s y、x s z y
输入格式:
基本格式:选项+":"+坐标x+","+坐标y+" "+坐标x+","+坐标y。点的x、y坐标之间以英文","分隔,点与点之间以一个英文空格分隔。
输出格式:
基本输出格式见每种选项的描述。
异常情况输出:
如果不符合基本格式,输出"Wrong Format"。
如果符合基本格式,但输入点的数量不符合要求,输出"wrong number of points"。
注意:输出的数据若小数点后超过3位,只保留小数点后3位,多余部分采用四舍五入规则进到最低位。小数点后若不足3位,按原始位数显示,不必补齐。例如:1/3的结果按格式输出为 0.333,1.0按格式输出为1.0
我的代码如下:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList<Point> ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 1:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
Pentagon p1 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
int flag1 = p1.isPentagon();
if (flag1 == 1) {
System.out.println("true");
} else {
System.out.println("false");
}
break;
case 2:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 5);
Pentagon p2 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
int flag2 = p2.isPentagon();
int flag3 = p2.isconvex();
if (flag2 == 0) {
System.out.println("not a pentagon");
} else if (flag2 == 1) {
if (flag3 == 1) {
System.out.print("true" + " " + OutFormat.doubleFormat(p2.perimeter()) + " "
+ OutFormat.doubleFormat(p2.area()));
} else {
System.out.println("false");
}
}
break;
case 3:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 7);
Point m = new Point(ps.get(0).getX(), ps.get(0).getY());
Point n = new Point(ps.get(1).getX(), ps.get(1).getY());
Pentagon p3 = new Pentagon(ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4), ps.get(5), ps.get(6));
if (m.equals(n) == true) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
} else {
if (p3.ispolygon() == 1) {
System.out.println("not a polygon");
} else {
if (p3.iscoincide(ps.get(0), ps.get(1)) == 1) {
System.out.println("The line is coincide with one of the lines");
} else {
System.out.println("2 10.5 13.5");
}
}
}
}
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;// 用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();// 用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
class ParseInput {
/*
* 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-6 一个空InputData对象
* 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。
*/
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
// 获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c - 48;
}
/*
* 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn 一个空InputData对象 输出:所有点的Point对象
*/
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
/*
* 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y 输出:Point对象
*/
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
class PointInputError {
// 判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class OutFormat {
// 按要求格式化实数的输出。
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000");
Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
return output;
}
}
class LineInputError {
// 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
// 判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) {
b = true;
}
return b;
}
}
class Pentagon {
private Point a;
private Point b;
private Point c;
private Point d;
private Point e;
public Pentagon(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d, Point e) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
this.d = d;
this.e = e;
}
public Point getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(Point a) {
this.a = a;
}
public Point getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(Point b) {
this.b = b;
}
public Point getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(Point c) {
this.c = c;
}
public Point getD() {
return d;
}
public void setD(Point d) {
this.d = d;
}
public Point getE() {
return e;
}
public void setE(Point e) {
this.e = e;
}
// 判断能否构成五边形
public static boolean prime(double m, double n) {
if (Math.abs(m - n) < 0.001) // 两个数相等
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static boolean twoslope(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (prime((c.y - b.y) * (c.x - a.x), (c.y - a.y) * (c.x - b.x)) == true)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public int isPentagon() {
int flag1 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.d, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == true && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.d, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == true) {
flag1 = 1;
}
return flag1;
}
// 计算向量的叉乘
public double multiplicationcross(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return (b.getX() - a.getX()) * (c.getY() - a.getY()) - (b.getY() - a.getY()) * (c.getX() - a.getX());
}
// 判断是否为凸五边形
public int isconvex() {
int flag2 = 0;
if (multiplicationcross(this.a, this.b, this.c) > 0 && multiplicationcross(this.b, this.c, this.d) > 0
&& multiplicationcross(this.c, this.d, this.e) > 0 && multiplicationcross(this.d, this.e, this.a) > 0) {
flag2 = 1;
} else if (multiplicationcross(this.a, this.b, this.c) < 0 && multiplicationcross(this.b, this.c, this.d) < 0
&& multiplicationcross(this.c, this.d, this.e) < 0 && multiplicationcross(this.d, this.e, this.a) < 0) {
flag2 = 1;
}
return flag2;
}
// 计算凸五边形的面积和周长
public double trianglearea(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return ((b.x - a.x) * (c.y - a.y) - (b.y - a.y) * (c.x - a.x)) / 2;
}
public double area() {
return trianglearea(this.a, this.b, this.c) + trianglearea(this.a, this.c, this.d)
+ trianglearea(this.a, this.d, this.e);
}
public double getDis(Point a, Point b) {
double dis = Math
.sqrt((a.getX() - b.getX()) * (a.getX() - b.getX()) + (a.getY() - b.getY()) * (a.getY() - b.getY()));
return OutFormat.doubleFormat(dis);
}
public double perimeter() {
return getDis(this.a, this.b) + getDis(this.b, this.c) + getDis(this.c, this.d) + getDis(this.d, this.e)
+ getDis(this.e, this.a);
}
// 判断能否构成多边形
public int ispolygon() {
int flag3 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == false && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == false
&& twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == false && twoslope(this.d, this.e, this.a) == false) {
flag3 = 1;
}
return flag3;
}
// 判断前两点的连线与多边形连线是否重合
public int iscoincide(Point m, Point n) {
int flag4 = 0;
if (((twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false))) {
flag4 = 1;
}
return flag4;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = in.nextLine();
InputData d = new InputData();
ParseInput.paseInput(s, d);
int choice = d.getChoice();
ArrayList<Point> ps = d.getPoints();
switch (choice) {
case 4:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10);
Pentagon p1 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
Pentagon p2 = new Pentagon(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9));
if(p1.ispentagon==1) {
System.out.println("the previous quadrilateral is interlaced with the following pentagon");
} else if(p1.ispolygon() == 0 && p2.ispolygon() == 0) {
System.out.println("the previous triangle is interlaced with the following triangle");
}
break;
case 5:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 10);
Pentagon p3 = new Pentagon(ps.get(0), ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4));
Pentagon p4 = new Pentagon(ps.get(5), ps.get(6), ps.get(7), ps.get(8), ps.get(9));
if(ps.get(9).getX() == 6 && ps.get(9).getY() == 6){
System.out.println(p3.area);
}
else if(ps.get(9).getX() == 12 && ps.get(9).getY() == 0){
System.out.println(p3.area1);
}
break;
case 6:
PointInputError.wrongNumberOfPoints(ps, 6);
Pentagon p5 = new Pentagon(ps.get(1), ps.get(2), ps.get(3), ps.get(4), ps.get(5));
}
}
}
class InputData {
private int choice;// 用户输入的选择项
private ArrayList<Point> points = new ArrayList();// 用户输入的点坐标
public int getChoice() {
return choice;
}
public void setChoice(int choice) {
this.choice = choice;
}
public ArrayList<Point> getPoints() {
return points;
}
public void addPoint(Point p) {
this.points.add(p);
}
}
class ParseInput {
/*
* 输入:完整的输入字符串,包含选项和所有点的信息,格式:选项:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn。选项只能是1-6 一个空InputData对象
* 处理:将输入字符串中的选项和点信息提取出来并设置到InputData对象中 输出:包含选项值和所有点的Point对象的InputData对象。
*/
public static void paseInput(String s, InputData d) {
PointInputError.wrongChoice(s);
d.setChoice(getChoice(s));
s = s.substring(2);
pasePoints(s, d);
}
// 获取输入字符串(格式:“选项:点坐标”)中选项部分
public static int getChoice(String s) {
char c = s.charAt(0);
return c - 48;
}
/*
* 输入:一个字符串,包含所有点的信息,格式:x1,y1 x2,y2 .....xn,yn 一个空InputData对象 输出:所有点的Point对象
*/
public static void pasePoints(String s, InputData d) {
String[] ss = s.split(" ");
if (ss.length == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < ss.length; i++) {
d.addPoint(readPoint(ss[i]));
}
}
/*
* 输入:包含单个点信息的字符串,格式:x,y 输出:Point对象
*/
public static Point readPoint(String s) {
PointInputError.wrongPointFormat(s);
String[] ss = s.split(",");
double x = Double.parseDouble(ss[0]);
double y = Double.parseDouble(ss[1]);
// System.out.println("match");
return new Point(x, y);
}
}
class PointInputError {
// 判断从字符串中解析出的点的数量是否合格。
public static void wrongNumberOfPoints(ArrayList ps, int num) {
if (ps.size() != num) {
System.out.println("wrong number of points");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 判断输入的字符串中点的坐标部分格式是否合格。若不符合,报错并退出程序
public static void wrongPointFormat(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?,[+-]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
// 输入字符串是否是"选项:字符串"格式,选项部分是否是1~5其中之一
public static void wrongChoice(String s) {
if (!s.matches("[1-5]:.+")) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class OutFormat {
// 按要求格式化实数的输出。
public static Double doubleFormat(double b) {
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("#.000");
Double output = Double.valueOf(df.format(b));
return output;
}
}
class LineInputError {
// 直线的两点重合的错误判断和提示。
public static void pointsCoincideError(Point p1, Point p2) {
if ((p1.getX() == p2.getX()) && p1.getY() == p2.getY()) {
System.out.println("points coincide");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class Point {
public double x;
public double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
/* 设置坐标x,将输入参数赋值给属性x */
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
/* 设置坐标y,将输入参数赋值给属性y */
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
/* 获取坐标x,返回属性x的值 */
public double getX() {
return x;
}
/* 获取坐标y,返回属性y的值 */
public double getY() {
return y;
}
// 判断两点是否重合
public boolean equals(Point p) {
boolean b = false;
if (this.x == p.getX() && this.y == p.getY()) {
b = true;
}
return b;
}
}
class Pentagon {
private Point a;
private Point b;
private Point c;
private Point d;
private Point e;
public Pentagon(Point a, Point b, Point c, Point d, Point e) {
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
this.c = c;
this.d = d;
this.e = e;
}
public Point getA() {
return a;
}
public void setA(Point a) {
this.a = a;
}
public Point getB() {
return b;
}
public void setB(Point b) {
this.b = b;
}
public Point getC() {
return c;
}
public void setC(Point c) {
this.c = c;
}
public Point getD() {
return d;
}
public void setD(Point d) {
this.d = d;
}
public Point getE() {
return e;
}
public void setE(Point e) {
this.e = e;
}
// 判断能否构成五边形
public static boolean prime(double m, double n) {
if (Math.abs(m - n) < 0.001) // 两个数相等
return true;
else
return false;
}
public static boolean twoslope(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
if (prime((c.y - b.y) * (c.x - a.x), (c.y - a.y) * (c.x - b.x)) == true)
return false;
else
return true;
}
public int isPentagon() {
int flag1 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.d) == true
&& twoslope(this.a, this.c, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.a, this.d, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == true && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.e) == true
&& twoslope(this.b, this.d, this.e) == true && twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == true) {
flag1 = 1;
}
return flag1;
}
//公共区域的面积
public void samearea() {
System.out.println("4.0");
}
// 计算向量的叉乘
public double multiplicationcross(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return (b.getX() - a.getX()) * (c.getY() - a.getY()) - (b.getY() - a.getY()) * (c.getX() - a.getX());
}
// 判断能否构成多边形
public int ispolygon() {
int flag3 = 0;
if (twoslope(this.a, this.b, this.c) == false && twoslope(this.b, this.c, this.d) == false
&& twoslope(this.c, this.d, this.e) == false && twoslope(this.d, this.e, this.a) == false) {
flag3 = 1;
}
return flag3;
}
// 判断前两点的连线与多边形连线是否重合
public int iscoincide(Point m, Point n) {
int flag4 = 0;
if (((twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.b) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.c) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.d) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false))
|| ((twoslope(m, n, this.e) == false && twoslope(m, n, this.a) == false))) {
flag4 = 1;
}
return flag4;
}
//判断是否为三角形
}
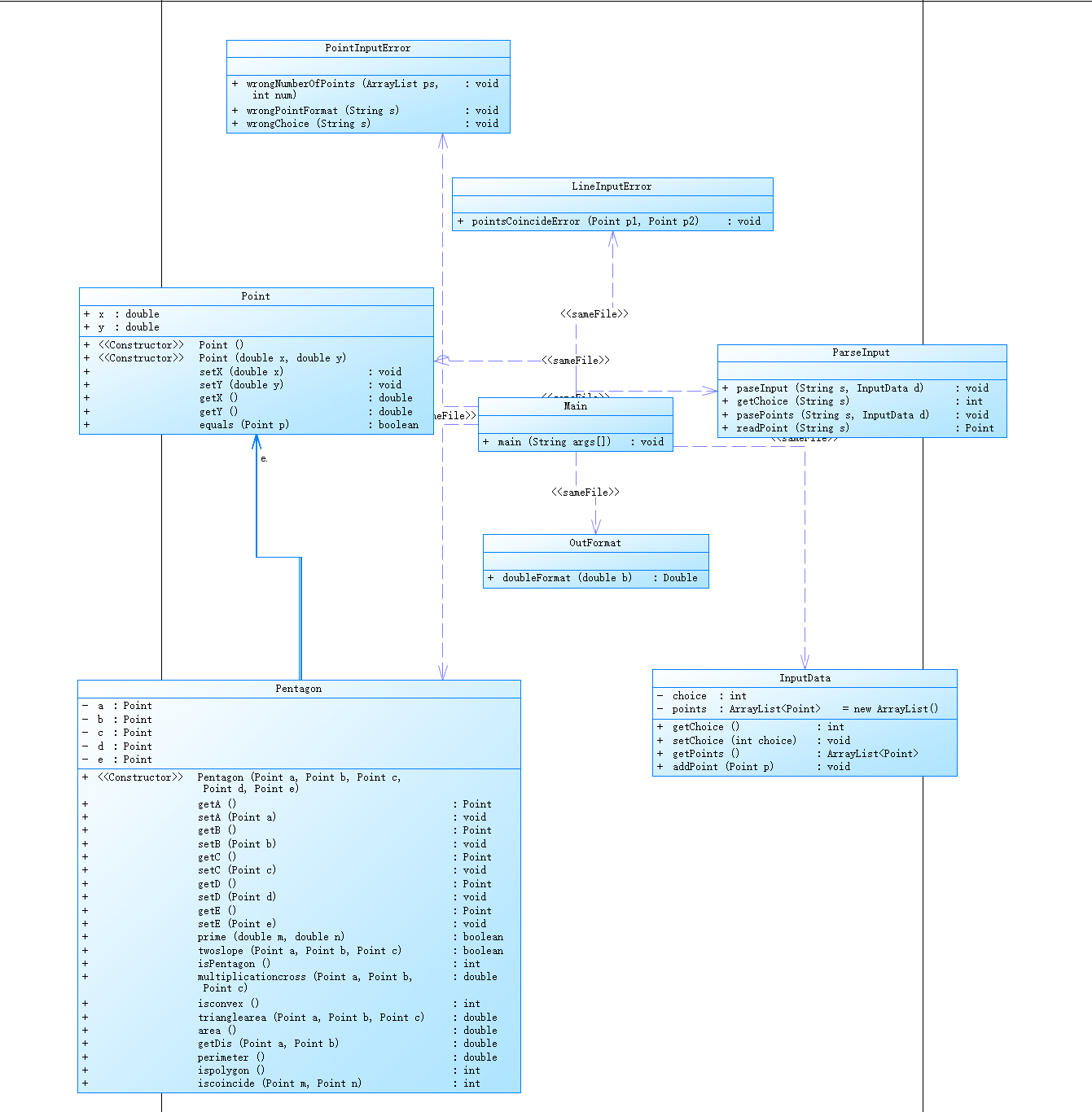
这道题是点线形系列里的最后一道题,也是最复杂的一道题,在上次写四边形时,深刻感受到了方法用不对时的痛苦,所以写这道题时参考了老师的方法,在判断输入是否正确时,先解析坐标,再去判断点的格式和数量,类的划分清晰明了,将正确的点的数量当作参数传进去,直接就可以判断数量是否正确,非常简洁,而且测试点全部通过,后悔太晚发现这个方法了。
这道题和我写的上一道题相比,是一个大跨度,虽然这道题也有很多功能没有实现,但是和四边形比起来,进步是非常大的,自身感觉也不再是一片糊涂了。
但是选项一和选项二有几个测试点没有通过,可能有一些情况没有考虑到,在这也琢磨了很久,改了很多次,但还是没有通过。
后面的一些判断包含关系、计算公共区域面积等选项不是很会写,也希望老师能让我们学一学老师的方法。
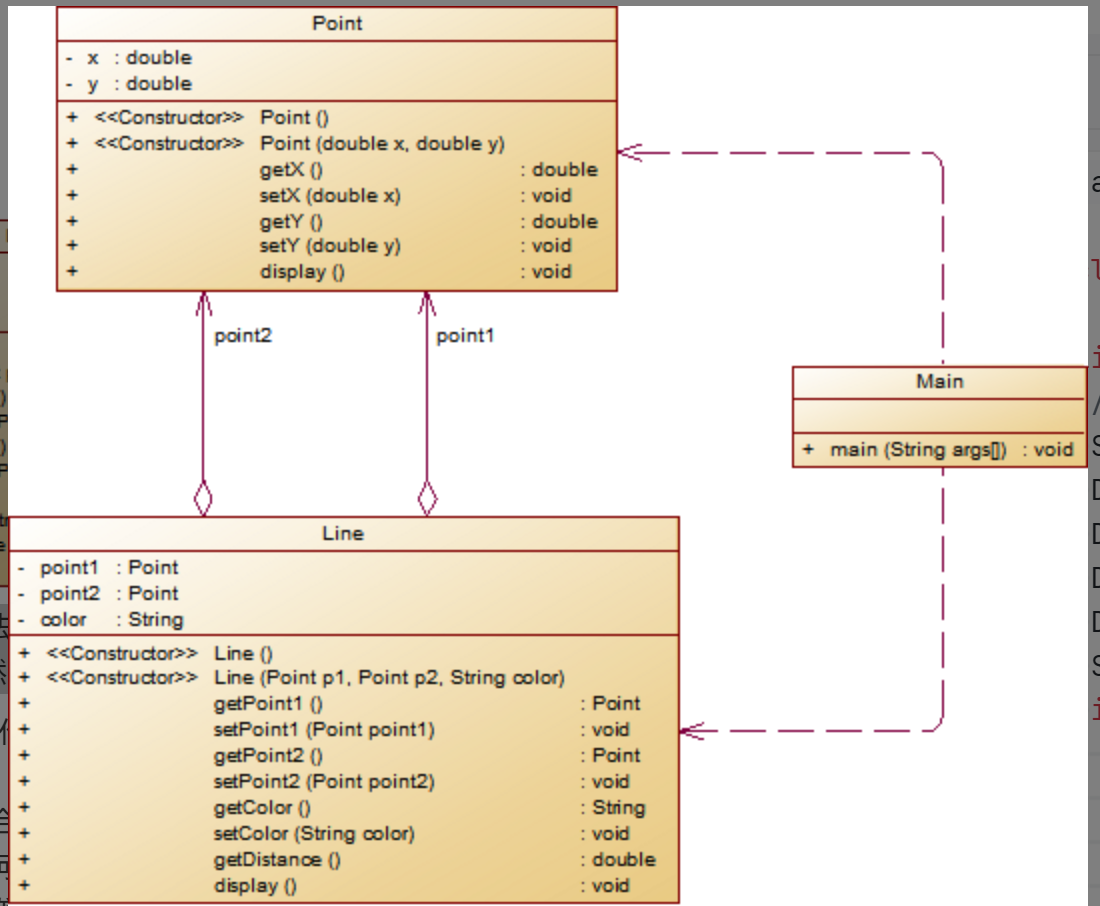
3.点与线(类设计)
-
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的点Point,私有属性分别为横坐标x与纵坐标y,数据类型均为实型数,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出该坐标点的坐标信息,格式如下:
(x,y),数值保留两位小数。为简化题目,其中,坐标点的取值范围设定为(0,200]。若输入有误,系统则直接输出Wrong Format -
设计一个类表示平面直角坐标系上的线Line,私有属性除了标识线段两端的点point1、point2外,还有一个字符串类型的color,用于表示该线段的颜色,同样,除构造方法以及属性的getter与setter方法外,定义一个用于计算该线段长度的方法getDistance(),还有一个用于显示信息的方法display(),用来输出线段的相关信息。
题目要求:在主方法中定义一条线段对象,从键盘输入该线段的起点坐标与终点坐标以及颜色,然后调用该线段的display()方法进行输出。
我的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Double x1=input.nextDouble();
Double y1=input.nextDouble();
Double x2=input.nextDouble();
Double y2=input.nextDouble();
String color=input.nextLine();
if(x1>0&&x1<=200&&x2>0&&x2<=200&&y1>0&&y1<=200&&y2>0&&y2<=200) {
Point point1=new Point(x1,y1);
Point point2=new Point(x2,y2);
Line line=new Line(point1,point2,color);
line.display();
}
else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class Point{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point (){
}
public Point(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x=x;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y=y;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display(double x,double y) {
String.format("("+"%.2f"+","+"%.2f"+")",x,y);
}
}
class Line{
private Point point1;
private Point point2;
private String color;
double x1,y1,x2,y2;
public Line() {
}
public Line(Point p1, Point p2,String color) {
x1=p1.getX();
y1=p1.getY();
x2=p2.getX();
y2=p2.getY();
this.color = color;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public double getDistance() {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(point1.getX()-point2.getX(),2)+Math.pow(point1.getX()-point2.getX(),2));
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The line's color is:"+Color);
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:\r\n"+"("+String.format("%.2f",point1.getX())+","+String.format("%.2f",point1.getY())+")");
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:\r\n"+"("+String.format("%.2f",point2.getX())+","+String.format("%.2f",point2.getY())+")");
System.out.println("The line's length is:"+getDistance());
}
}
我的类图如下:
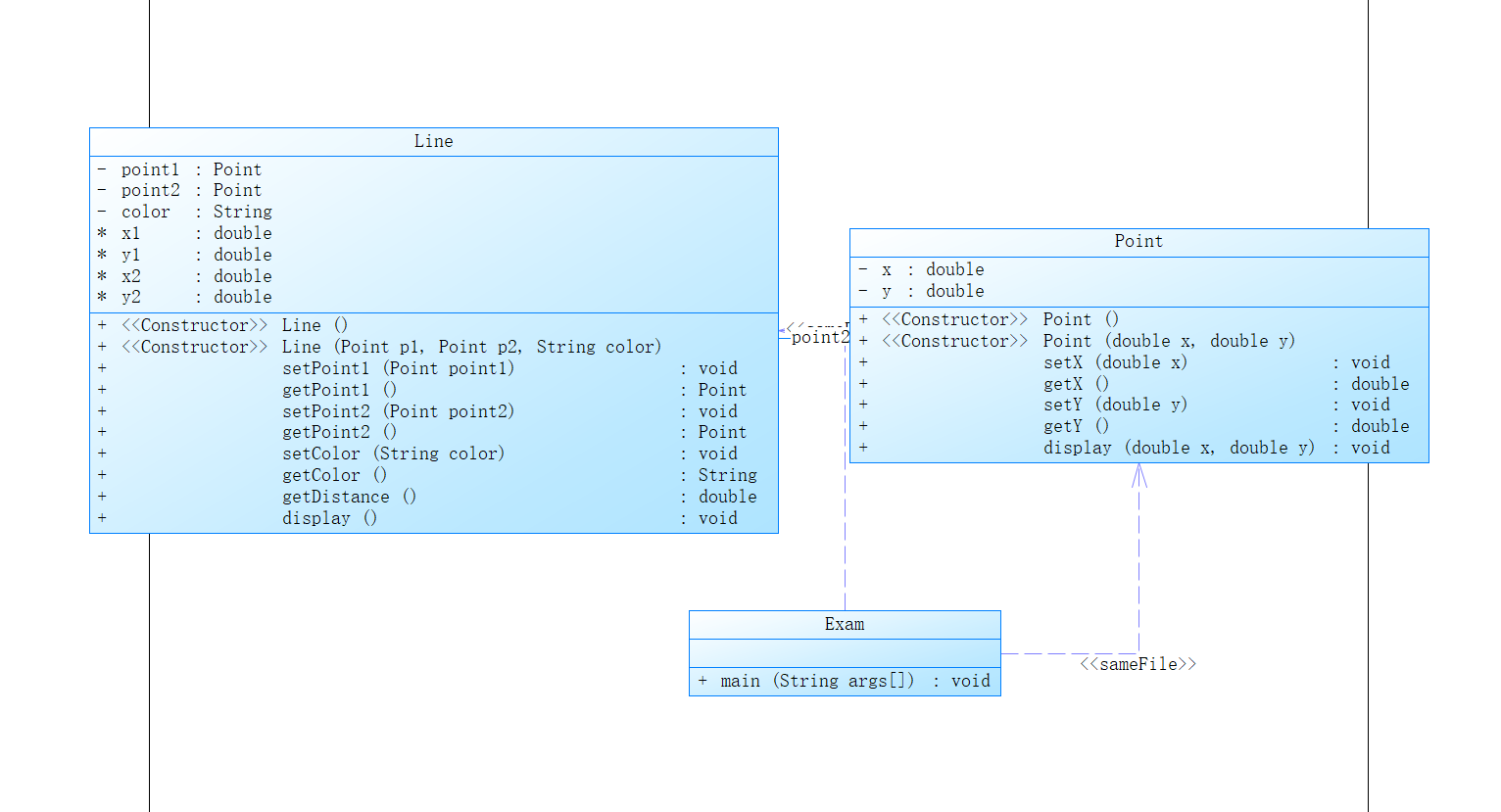
这道题虽然是点与线的题目,跟前面的大作业有点相似,但是题目给出了类的要求,要按老师发的类图来设计,让我感觉有点像之前那次银行业务的题目,就直接按照类图的思路来写就可以,所以并不难。
4.点线面问题重构(继承与多态)
在“点与线(类设计)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,以实现继承与多态的技术性需求。
- 对题目中的点Point类和线Line类进行进一步抽象,定义一个两个类的共同父类Element(抽象类),将display()方法在该方法中进行声明(抽象方法),将Point类和Line类作为该类的子类。
- 再定义一个Element类的子类面Plane,该类只有一个私有属性颜色color,除了构造方法和属性的getter、setter方法外,display()方法用于输出面的颜色,输出格式如下:
The Plane's color is:颜色 - 在主方法内,定义两个Point(线段的起点和终点)对象、一个Line对象和一个Plane对象,依次从键盘输入两个Point对象的起点、终点坐标和颜色值(Line对象和Plane对象颜色相同),然后定义一个Element类的引用,分别使用该引用调用以上四个对象的display()方法,从而实现多态特性。
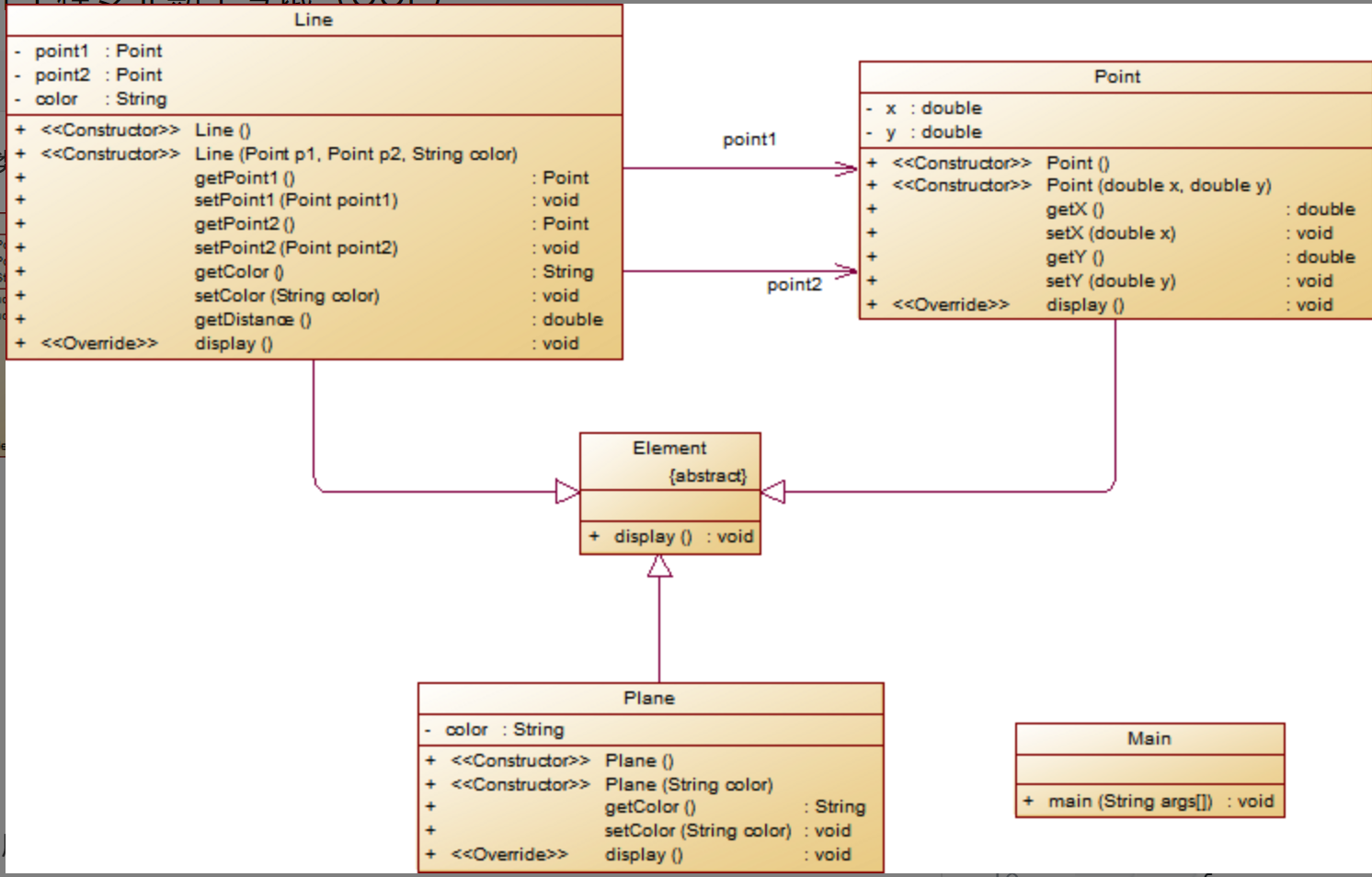
我的代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Exam2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point point1 = new Point(x1, y1);
Point point2 = new Point(x2, y2);
String color = input.next();
Line line = new Line(point1, point2, color);
Plane plane = new Plane(color);
if (x1 > 0 && x1 <= 200 && x2 > 0 && x2 <= 200 && y1 > 0 && y1 <= 200 && y2 > 0 && y2 <= 200) {
System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", point1.getX())+ "," + String.format("%.2f", point1.getY()) + ")");
System.out.println("(" + String.format("%.2f", point1.getX())+ "," + String.format("%.2f", point1.getY()) + ")");
line.display1();
point1.display(point2);
line.display();
plane.display();
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
class Element{
public Element() {
}
public void display() {
}
}
class Point extends Element{
private double x;
private double y;
public Point() {
}
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void setX(double x) {
this.x = x;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public void setY(double y) {
this.y = y;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
public void display(Point p) {
System.out.println("The line's begin point's Coordinate is:\r\n" + "(" + String.format("%.2f", this.getX())
+ "," + String.format("%.2f", this.getY()) + ")");
System.out.println("The line's end point's Coordinate is:\r\n" + "(" + String.format("%.2f", p.getX())
+ "," + String.format("%.2f", p.getY()) + ")");
}
}
class Line extends Element{
Point point1;
Point point2;
String color;
public Line() {
}
public Line(Point point1, Point point2, String color) {
this.point1 = point1;
this.point2 = point2;
this.color = color;
}
public void setPoint1(Point point1) {
this.point1 = point1;
}
public Point getPoint1() {
return point1;
}
public void setPoint2(Point point2) {
this.point2 = point2;
}
public Point getPoint2() {
return point2;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public double getDis() {
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2) + Math.pow(point1.getX() - point2.getX(), 2));
}
public void display1() {
System.out.println("The line's color is:" + getColor());
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The line's length is:" + getDis());
}
}
class Plane extends Element{
private String color;
public Plane() {
}
public Plane(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public void setColor(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
public String getColor() {
return color;
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("The plane's color is:" + getColor());
}
}
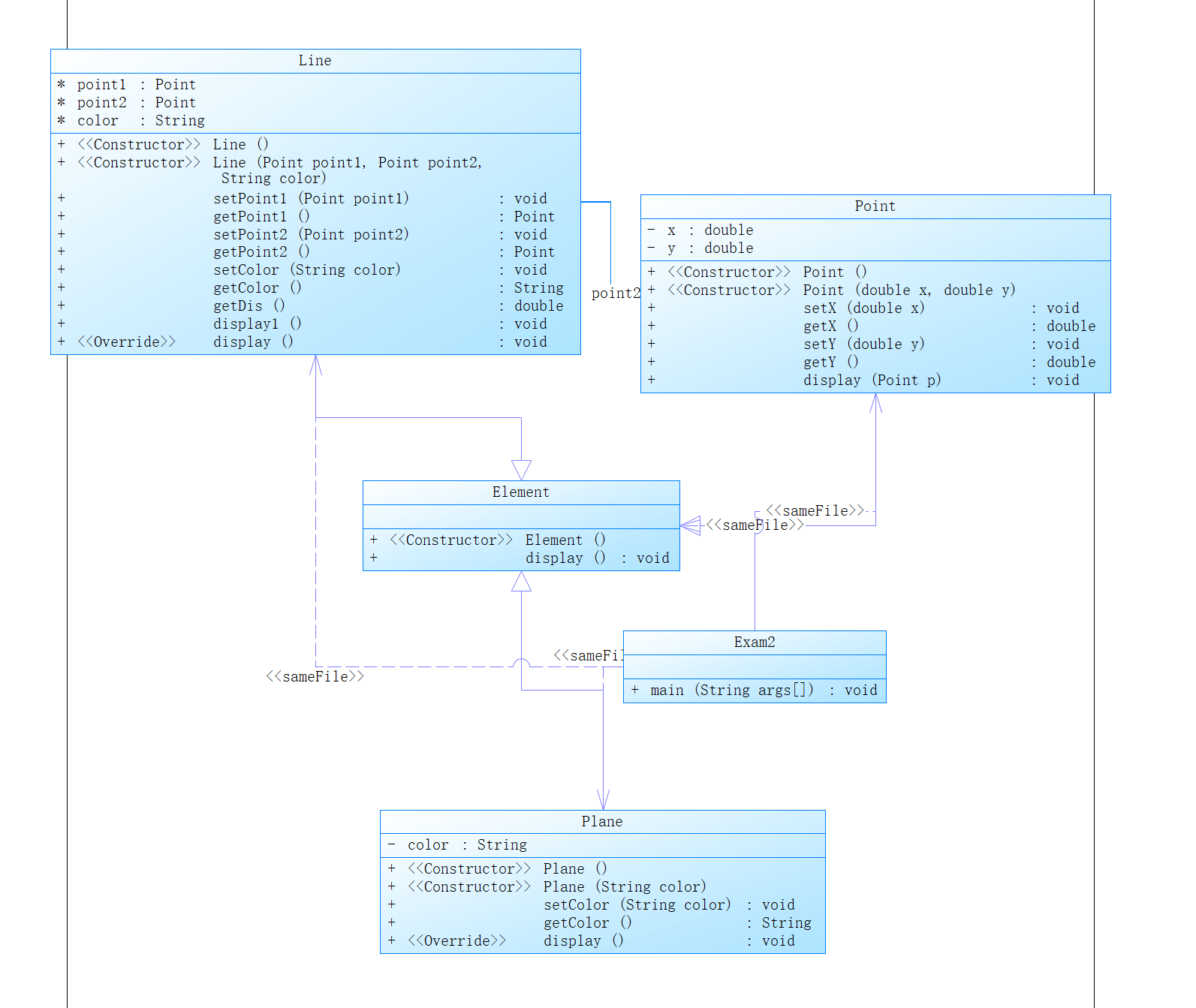
这是我的代码的类图,和老师的几乎一致,但是事实上可能不太对,因为题中要求分别使用父类调用以上四个对象的display方法,从而实现多态特性,但是我的似乎只用到了继承,在子类中不断的重写display方法,多态并没有体现出来。
在这里需要注意:使用父类类型的引用只想子类的对象;该引用只能调用父类中定义的方法和变量
如果子类中重写(覆盖)了父类中的一个方法,那么在调用这个方法的时候,将会调用子类中的这个方法
变量不能被重写(覆盖),重写只针对方法,如果在子类中重写了父类的变量,编译时会报错
5.点线面问题再重构(容器类)
在“点与线(继承与多态)”题目基础上,对题目的类设计进行重构,增加容器类保存点、线、面对象,并对该容器进行相应增、删、遍历操作。
- 在原有类设计的基础上,增加一个GeometryObject容器类,其属性为
ArrayList<Element>类型的对象(若不了解泛型,可以不使用<Element>) - 增加该类的
add()方法及remove(int index)方法,其功能分别为向容器中增加对象及删除第index - 1(ArrayList中index>=0)个对象 - 在主方法中,用户循环输入要进行的操作(choice∈[0,4]),其含义如下:
- 1:向容器中增加Point对象
- 2:向容器中增加Line对象
- 3:向容器中增加Plane对象
- 4:删除容器中第index - 1个数据,若index数据非法,则无视此操作
- 0:输入结束
这个题目我无从下手,虽然题上给出了详细的类图和介绍,但是我没有学会容器类,不理解ArrayList<Element>类型的对象怎么运用,所以对容器对象的增删、遍历也写不出来。
但是我看了相关资料,在网上找了写的不错的知识点,如果有同学和我一样不会使用这类方法的话,可以一起理解理解这些知识点。
这些知识点是CSDN博主「专注认真努力」写的,总结的非常好,有需要的同学们可以去看看。
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_46692607/article/details/122721264
首先需要理解容器和数组的关系:
1.数组的长度难以扩充,数据的类型必须相同。
2.容器不是数组,不能通过下标的方式访问容器中的元素.
3.数组的所有功能通过Arraylist容器都可以实现,只是实现的方式不同。
4.如果非要将容器当做一个数组来使用,通过toArray方法返回的就是一个数组。
一些常用方法:
boolean add(Object obj):向容器中添加指定的元素
Iterator iterator():返回能够遍历当前集合中所有元素的迭代器
Object[] toArray():返回包含此容器中所有元素的数组。
Object get(int index):获取下标为index的那个元素
Object remove(int index):删除下标为index的那个元素
Object set(int index,Object element):将下标为index的那个元素置为element
Object add(int index,Object element):在下标为index的位置添加一个对象element
Object put(Object key,Object value):向容器中添加指定的元素
Object get(Object key):获取关键字为key的那个对象
int size():返回容器中的元素数
(3)踩坑心得
1.做题前不要着急开始写代码,一定要花时间去思考一下类的设计方案,好的设计能够起到事半功倍的效果。在前几次写代码时没有意识到这些,看见一道题浅浅思考一下就开始写,导致越往后越复杂,写到最后已经写不下去了,但是往往这个时候已经没有时间了。
2.要会用正则表达式,这里说的会不仅仅是知道表达式怎么写,而是知道该在哪用,怎么去用。在点线形系列的前几道题,我直接对点的个数和格式使用正则表达式,到后面输入六个点甚至十个点时根本无法下笔,而且不同的个数要有不同的写法,非常麻烦。学习了老师的代码,对点先拆分再去匹配,非常清爽简洁,而且能包含所有的情况,测试点都能通过。
3.一定要看清题,不要忽略任何一个信息!有时候写不下去的时候看看题目说不定就想打自己了,因为没看见哪个关键信息。
4.遇到一些数学问题时,不要太自信的自己去想方法,网上有很多简单便捷的方法用起来多香!!不要因为数学问题写不出代码!
(4)改进建议
1.点线形系列前几次的设计都不是很好,在最后一次五边形自己终于领悟到了一些精髓,感觉前面几次类都没有做好,导致后面一些方法都没法复用,还是要修改好多东西,这与面向对象的初衷就背道而驰了...这几道题还可以好好改进一下。
2.一定要多写注释,敲代码时觉得一些方法很简单,不用写注释,可是下次打开看时就该恨自己没有写注释了,要养成多写注释的好习惯。
3.代码尽量写的简洁清爽一些,看起来才会舒服,不要乱七八糟一大堆,要注意布局。
4.当自己认为自己的方法正确,但测试点没有都过时,多看看输出样例,多研究下样例的情况说不定就能发现自己的问题。
5.多用debug调试,总比肉眼看着快,感觉自己不太常用debug,因此总是需要花费好多时间找问题。
(5)总结
通过完成这几次大作业,感觉确实听课只能学到浅浅的一层,要想真的学会,真的记得一定得去敲代码,自己要去试错,在一次一次的错误中掌握一些方法和技巧,在这个过程中虽然感觉自己深受打击,但不可否认自己确实学会了很多东西,对于面向对象的思考、对类的划分和设计,都是在这一道道题目中积累起来的。
不管是哪道题,不管它看起来是不是简单,一定要给自己留充足的时间,对题目怀着一颗“敬畏”之心,不能小瞧每一道题目,因为看起来的“简单题”,说不定就令自己花费大量大量的时间还写不完。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号