实验四 继承
实验任务二
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
// definitation of Graph
class Graph
{
public:
void draw() { std::cout << "Graph::draw() : just as an interface\n"; }
};
// definition of Rectangle, derived from Graph
class Rectangle : public Graph
{
public:
void draw() { std::cout << "Rectangle::draw(): programs of draw a rectangle\n"; }
};
// definition of Circle, derived from Graph
class Circle : public Graph
{
public:
void draw() { std::cout << "Circle::draw(): programs of draw a circle\n"; }
};
// definitaion of fun(): as a call interface
void fun(Graph *ptr)
{
std::cout << "pointer type: " << typeid(ptr).name() << "\n";
std::cout << "RTTI type: " << typeid(*ptr).name() << "\n";
ptr -> draw();
}
// test
int main()
{
Graph g1;
Rectangle r1;
Circle c1;
// call by object name
g1.draw();
r1.draw();
c1.draw();
std::cout << "\n";
// call by object name, and using the scope resolution operator::
r1.Graph::draw();
c1.Graph::draw();
std::cout << "\n";
// call by pointer to Base class
fun(&g1);
fun(&r1);
fun(&c1);
}
测试结果如下:
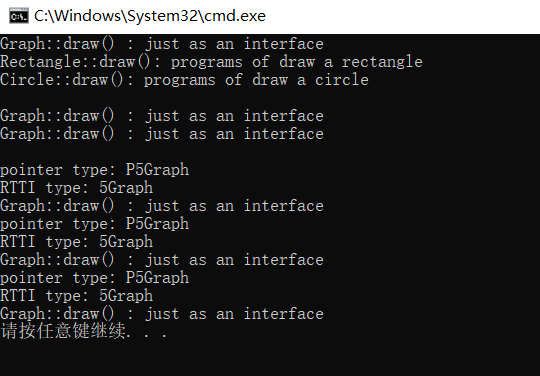
修改下列代码:
// definitation of Graph
class Graph
{
public:
// 声明时加了关键字virtual
virtual void draw() { std::cout << "Graph::draw() : just as an
interface\n"; }
};
测试结果如下:
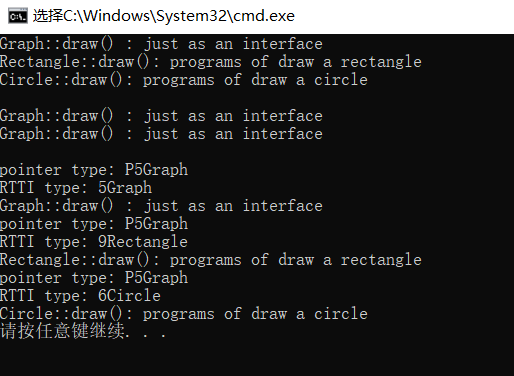
归纳总结:
1、同名覆盖原则:
派生类与基类中有相同成员时若未强行指名,则通过派生类对象使用的是派生类的同名成员。如果只需要访问父类的方法可以将子类对象用父类引用。
如果要通过派生类的对象访问基类被覆盖的同名成员,需要加 对象名.基类名::同名成员来限定。
2、兼容性原则
派生类成员可以当作基类来使用但是只能使用继承于基类的那一部分。
3、二元作用域分辨符
二元作用域分辨符的用法是:类名::成员
实验任务三
1、Battery类:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Battery
{
private:
int capacity;
public:
Battery(int capacity);
~Battery();
int get_capacity();
};
Battery::Battery(int capacity = 70)
{
this->capacity = capacity;
}
Battery::~Battery()
{
}
int Battery::get_capacity()
{
return this->capacity;
}
2、Car类
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Car
{
private:
string maker; //制造商
string model; //型号
int year; //生产年份
int odometers; //行车里程数
public:
Car(string maker, string model, int year);
~Car();
void info();
void update_odometers(int newOdometers);
};
Car::Car(string maker, string model, int year)
{
this->maker = maker;
this->model = model;
this->year = year;
this->odometers = 0;
}
Car::~Car()
{
}
void Car::info()
{
cout << "maker:\t\t" << this->maker << endl;
cout << "model:\t\t" << this->model << endl;
cout << "year:\t\t" << this->year << endl;
cout << "odometers:\t" << this->odometers << endl;
}
void Car::update_odometers(int newOdometers)
{
if (newOdometers < this->odometers)
cout << "更新里程数有误" << endl;
else
this->odometers = newOdometers;
}
3、ElectricCar类
#include <iostream>
#include "car.hpp"
#include "battery.hpp"
using namespace std;
class ElectricCar : public Car
{
private:
Battery battery;
public:
ElectricCar(string maker, string model, int year);
void info();
};
ElectricCar::ElectricCar(string maker, string model, int year) : Car(maker, model, year)
{
Battery battery(70);
this->battery = battery;
}
void ElectricCar::info()
{
Car::info();
cout << "capacity:\t" << this->battery.get_capacity() << "-kWh" << endl;
}
- 测试代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include "electricCar.hpp"
int main()
{
using namespace std;
// test class of Car
Car oldcar("Audi", "a4", 2016);
cout << "--------oldcar's info--------" << endl;
oldcar.update_odometers(25000);
oldcar.info();
cout << endl;
// test class of ElectricCar
ElectricCar newcar("Tesla", "model s", 2016);
newcar.update_odometers(2500);
cout << "\n--------newcar's info--------\n";
newcar.info();
}
- 测试结果:
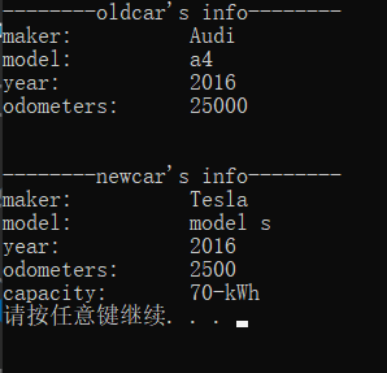
实验任务四
1、pets.hpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class MachinePets
{
private:
string nickname;
public:
MachinePets(const string nickname);
~MachinePets();
virtual string talk();
const string get_nickname();
};
MachinePets::MachinePets(const string nickname) : nickname(nickname) {}
MachinePets::~MachinePets() {}
string MachinePets::talk() { return ""; }
const string MachinePets::get_nickname()
{
return nickname;
}
class PetCats : public MachinePets
{
public:
PetCats(const string s);
~PetCats();
string talk();
};
PetCats::PetCats(const string s) : MachinePets(s) {}
PetCats::~PetCats() {}
string PetCats::talk()
{
return "miao wu~";
}
class PetDogs : public MachinePets
{
public:
PetDogs(const string s);
~PetDogs();
string talk();
};
PetDogs::PetDogs(const string s) : MachinePets(s) {}
PetDogs::~PetDogs() {}
string PetDogs::talk()
{
return "wang wang~";
}
- 测试代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include "pets.hpp"
void play(MachinePets *ptr)
{
std::cout << ptr->get_nickname() << " says " << ptr->talk() << std::endl;
}
int main()
{
PetCats cat("miku");
PetDogs dog("da huang");
play(&cat);
play(&dog);
}
- 测试结果:



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号