实验三
实验三代码如下:
1、Complex类实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
class Complex{
public:
Complex(){
}
Complex(double x,double y=0){
a = x;
b = y;
}
Complex(const Complex &t){
a = t.a;
b = t.b;
}
double get_real()const{
return a;
}
double get_imag()const{
return b;
}
void show()const{
if(b>0) std::cout<<a<<"+"<<b<<"i";
else if(b==0) std::cout<<a;
else std::cout<<a<<b<<"i";
}
void add(const Complex &t){
a = a + t.get_real();
b = b + t.get_imag();
}
friend Complex add(Complex &c1,const Complex &c2);
friend bool is_equal(Complex &c1,const Complex &c2);
friend double abs(Complex &c);
private:
double a;//实部
double b;//虚部
};
Complex add(Complex &c1,const Complex &c2){
return Complex(c1.a+c2.a , c1.b+c2.b);
}
bool is_equal(Complex &c1,const Complex &c2){
if(c1.a==c2.a && c1.b==c2.b )
return true;
else
return false;
}
double abs(Complex &c){
return sqrt(c.a*c.a+c.b*c.b);
}
2、测试代码如下:
#include "Complex.cpp"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
Complex c1(3, -4);
const Complex c2(4.5);
Complex c3(c1);
cout << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = ";
c2.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "c2.imag = " << c2.get_imag() << endl;
cout << "c3 = ";
c3.show();
cout << endl;
cout << "abs(c1) = ";
cout << abs(c1) << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c3 : " << is_equal(c1, c3) << endl;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
Complex c4;
c4 = add(c1, c2);
cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = ";
c4.show();
cout << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = ";
c1.show();
cout << endl;
}
3、实验结果如下:
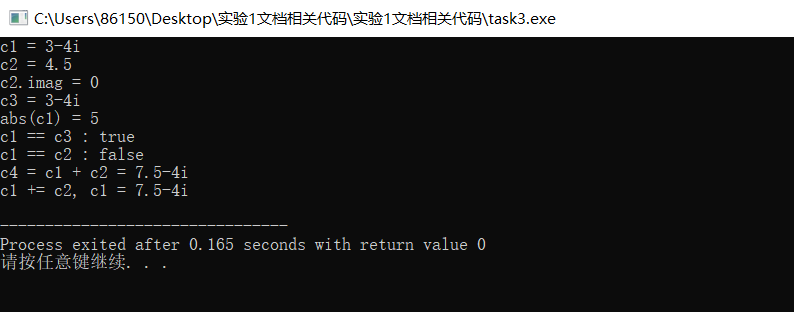
实验四
实验四代码如下:
1、User类实现:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
class User{
public:
User(char a[],char b[],char c[]){
strcpy(name,a);
strcpy(passwd,b);
strcpy(email,c);
n++;
}
User(char a[]){
strcpy(name,a);
strcpy(passwd,"111111");
strcpy(email,"");
n++;
}
void set_email(){
cout<<"Enter email address:";
cin>>email;
cout<<"email is set successfully...\n";
}
void change_passwd(){
int judge=1;
cout<<"Enter old password:";
char temp[50];
cin>>temp;
while(strcmp(passwd,temp)!=0){
cout<<"password input error. Please re-enter again:";
cin>>temp;
judge++;
if(judge==3) {
cout<<"password input error. Please try after a while.\n";
return;
}
}
cout<<"Enter new passwd:";
cin>>passwd;
cout<<"new passwd is set successfully...\n";
}
void print_info(){
cout<<"name: "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"passwd: ******"<<endl;
cout<<"email: "<<email<<endl;
}
void static print_n(){
cout<<"there are "<<n<<" users."<<endl;
}
private:
char name[50];
char passwd[50];
char email[50];
static int n;
};
int User::n = 0;
2、测试代码如下:
#include "User.cpp"
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "testing 1......" << endl;
User user1("Jonny", "92197", "xyz@hotmail.com");
user1.print_info();
cout << endl
<< "testing 2......" << endl
<< endl;
User user2("Leonard");
user2.change_passwd();
user2.set_email();
user2.print_info();
User::print_n();
}
3、实验结果如下:
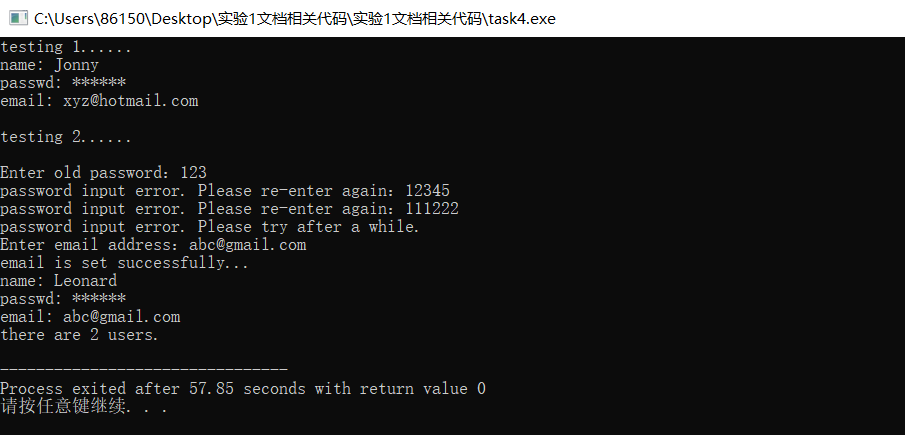
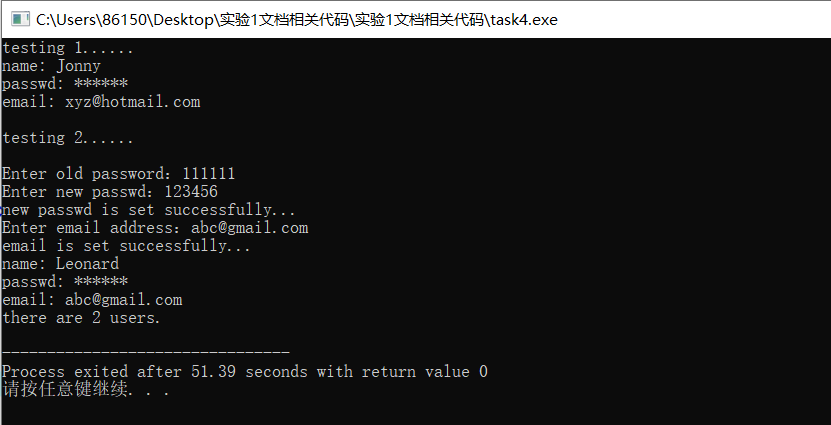
实验总结
1、头文件中只能声明函数,不能有函数实现;
2、当一个函数的参数为const类型时不能修改参数的值,const的使用遵循不可扩大限定范围但可以缩小范围的原则,非const可调用const的实现函数而const不可调用非const;
3、友元函数声明在哪个类内部,友元函数就可以直接访问该类的成员变量。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号