代码随想录day16 | 104. 二叉树的最大深度 111. 二叉树的最小深度 222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
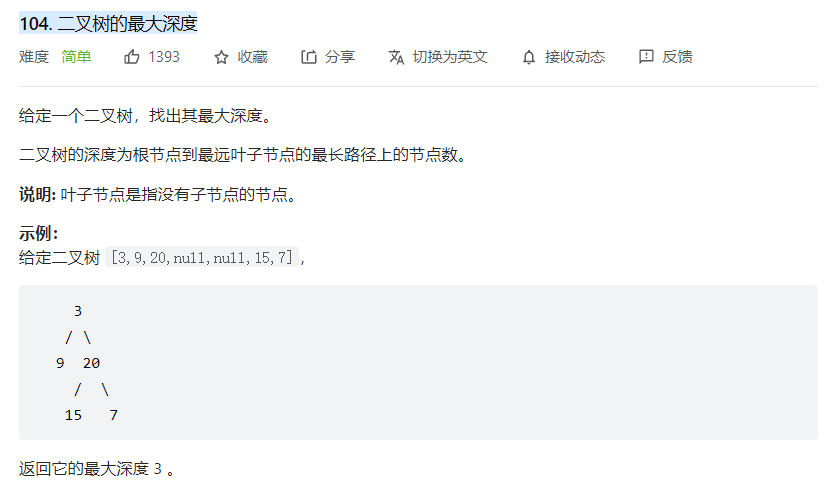
104. 二叉树的最大深度
1.前序遍历+递归(求深度)
思路
通过不断传递深度depth来实现回溯。
实现
点击查看代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
getDepth(root,1);
return result;
}
int result;
void getDepth(TreeNode* cur,int depth){
result = result > depth ? result :depth;
if(cur->left)getDepth(cur->left,depth+1);
if(cur->right)getDepth(cur->right,depth+1);
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(height)
2.后序遍历+递归(求高度)
思路
不断比较左右子节点的高度,求出最大高度。
实现
点击查看代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root,depth);
}
int depth = 1;
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur,int depth){
if(cur == nullptr)return 0;
int leftTree = getDepth(cur->left,depth);
int rightTree = getDepth(cur->right,depth);
depth = 1 + max(leftTree,rightTree);
return depth;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(height)
3.层序遍历
思路
遍历所有节点,求出最大深度
实现
点击查看代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int result = 0;
if(root == nullptr) return 0;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left)que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right)que.push(cur->right);
}
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
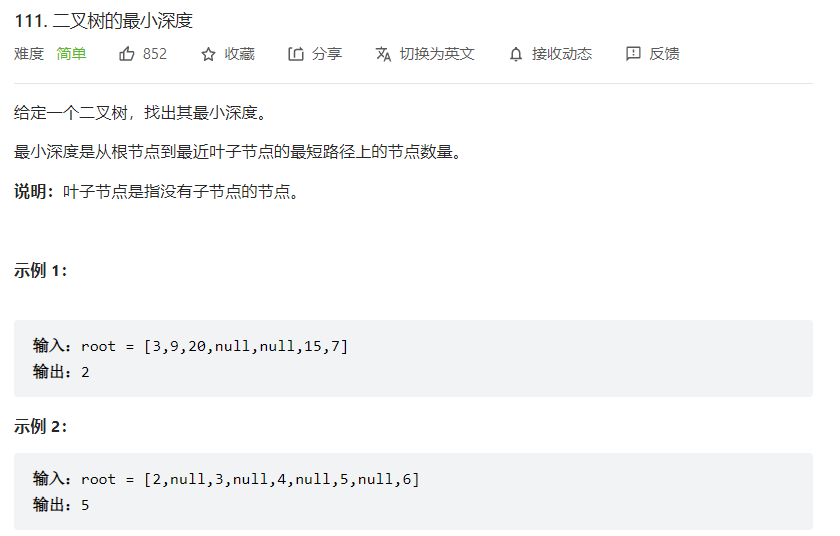
111. 二叉树的最小深度
1.前序遍历+递归
思路
主要对于只有一个子节点的节点的处理。
实现
点击查看代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
getDepth(root,1);
return result;
}
int result = INT32_MAX;
void getDepth(TreeNode* cur, int depth){
if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr){
result = result < depth ? result : depth;
}
if(cur->left)getDepth(cur->left,depth+1);
if(cur->right)getDepth(cur->right,depth+1);
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(H)
2.后序遍历+递归
思路
对于每一个非叶子节点,我们只需要分别计算其左右子树的最小叶子节点深度。这样就将一个大问题转化为了小问题,可以递归地解决该问题
实现
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
return getDepth(root,0);
}
int getDepth(TreeNode* cur,int depth){
if(cur == nullptr)return depth;
int left = getDepth(cur->left,depth);
int right = getDepth(cur->right,depth);
if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right != nullptr)depth = 1 + right;
else if(cur->left != nullptr && cur->right == nullptr)depth = 1 + left ;
else depth = 1+min(left,right);
return depth;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(H)
3.层序遍历
思路
当我们找到一个叶子节点时,直接返回这个叶子节点的深度。广度优先搜索的性质保证了最先搜索到的叶子节点的深度一定最小。
实现
点击查看代码
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
int result =0;
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
que.push(root);
while(!que.empty()){
int size = que.size();
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left == nullptr && cur->right == nullptr) return result+1;
if(cur->left)que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right)que.push(cur->right);
}
result++;
}
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
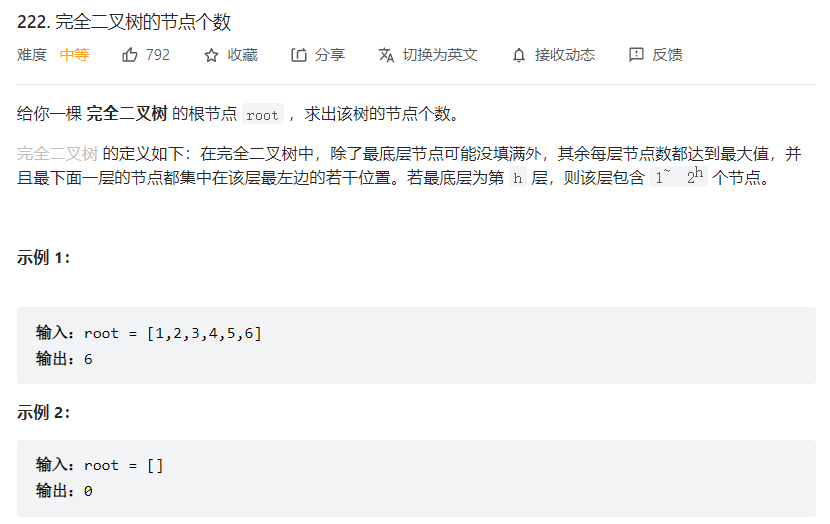
222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
1.完全二叉树特点解法
思路
1.本题的关键在于如果能判断一个子树是满二叉树,那么便可以直接判断出子树的节点个数,从而减少时间复杂度。
2.本题已知是完全二叉树,那么只需遍历判断每个节点是不是满二叉树即可。
实现
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
int countNodes(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr)return 0;
TreeNode* leftNode = root->left;
TreeNode* rightNode = root->right;
int left = 0, right = 0;
while(leftNode){
left++;
leftNode = leftNode->left;
}
while(rightNode){
right++;
rightNode = rightNode->right;
}
if(left == right){
return (2 << left) - 1;
}
left = countNodes(root->left);
right = countNodes(root->right);
return left+right+1;
}
};
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(logn*logn),二叉树的总层数为logn,每一层需要判断logn次。
- 空间复杂度:O(logn)




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号