来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/peida/archive/2012/10/23/2734829.html
因原文章格式不优美及内容有疏漏,特此修改
ls命令是linux下最常用的命令。ls命令就是list的缩写。缺省下ls用来打印出当前目录的清单,如果ls指定其他目录,那么就会显示指定目录里的文件及文件夹清单。 通过ls 命令不仅可以查看linux文件夹包含的文件,而且可以查看文件权限(包括目录、文件夹、文件权限)、查看目录信息等等。ls 命令在日常的linux操作中用的很多!
1. 命令格式:
ls [选项] [目录名]
2. 命令功能:
列出目标目录中所有的子目录和文件。
3. 常用参数:
| -a | --all |
do not ignore entries starting with . 显示隐藏的文件(文件名以点开头的文件) |
| -A | --almost-all |
do not list implied . and .. 不显示 . (当前目录) .. (上级目录) |
| --author |
with -l, print the author of each file 列出每个文件的编辑者 |
|
| -b | --escape |
print C-style escapes for nongraphic characters 【暂无现象】 |
| --block-size=SIZE |
scale sizes by SIZE before printing them; e.g., The SIZE argument is an integer and optional unit (example: 10K is 10*1024). 将大小以指定单位显示 |
|
| -B | --ignore-backups |
do not list implied entries ending with ~ 【暂无现象】 |
| -c |
with -lt: sort by, and show, ctime (time of last modification of file status information); with -l: show ctime and sort by name; otherwise: sort by ctime, newest first 和 -lt 一起使用:根据文件的最后一次修改时间排序,并显示修改时间 和 -l 一起使用:根据文件名排序,并显示修改时间 其它情况:根据修改时间排序,由新到旧排序 |
|
| -C |
list entries by columns 以列的形式列出项目 |
|
| --color[=WHEN] |
colorize the output; WHEN can be 'always' (default if omitted), 'auto', or 'never'; more info below 将输出进行着色,可选的条件有:always, auto, never |
|
| -d | --directory |
list directories themselves, not their contents 只显示目录自身,不显示其内的内容。配合 -l 效果好 |
| -D | --dired |
generate output designed for Emacs' dired mode 【暂无现象】 |
| -f |
do not sort, enable -aU, disable -ls --color 不排序,禁用颜色输出 |
|
| -F | --classify |
append indicator (one of */=>@|) to entries 在项目前加标志 |
| --file-type |
likewise, except do not append '*' 和前面类似,不过不加*号 |
|
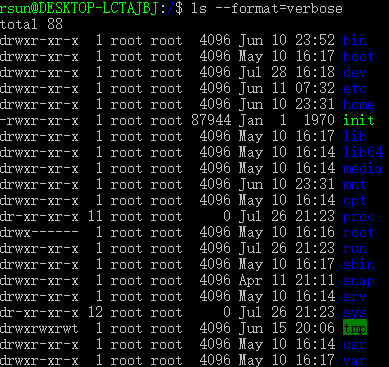
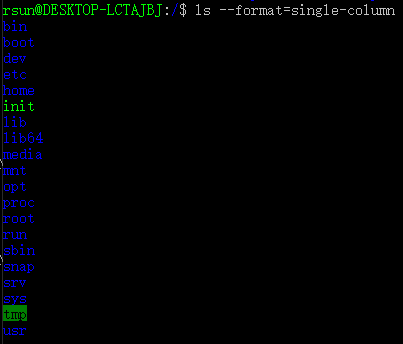
| --format=WORD |
across -x, commas -m, horizontal -x, long -l, single-column -1, verbose -l, vertical -C Valid arguments are: 可用的WORD选项: - ‘verbose’, ‘long’:长格式,显示详细
- ‘commas’:逗号分隔的项目列表
- ‘horizontal’, ‘across’:平铺,默认
- ‘vertical’:上下上下的方式,竖着来显示
- ‘single-column’:竖着显示,孤零零的一列
|
|
| --full-time |
like -l --time-style=full-iso |
|
| -g | like -l, but do not list owner | |
| --group-directories-first |
group directories before files; |
|
| -G | --no-group | in a long listing, don't print group names |
| -h | --human-readable |
with -l and/or -s, print human readable sizes |
| --si |
likewise, but use powers of 1000 not 1024 |
|
| -H | --dereference-command-line |
follow symbolic links listed on the command line |
| --dereference-command-line-symlink-to-dir |
follow each command line symbolic link |
|
| --hide=PATTERN |
do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN |
|
| --indicator-style=WORD |
append indicator with style WORD to entry names: |
|
| -i | --inode | print the index number of each file |
| -I | --ignore=PATTERN | do not list implied entries matching shell PATTERN |
| -k | --kibibytes | default to 1024-byte blocks for disk usage |
| -l | use a long listing format | |
| -L | --dereference |
when showing file information for a symbolic |
| -m |
fill width with a comma separated list of entries |
|
| -n | --numeric-uid-gid |
like -l, but list numeric user and group IDs |
| -N | --literal |
print raw entry names (don't treat e.g. control |
| -o |
like -l, but do not list group information |
|
| -p | --indicator-style=slash |
append / indicator to directories |
| -q | --hide-control-chars |
print ? instead of nongraphic characters |
| --show-control-chars |
show nongraphic characters as-is (the default, |
|
| -Q | --quote-name | enclose entry names in double quotes |
| --quoting-style=WORD |
use quoting style WORD for entry names: |
|
| -r | --reverse | reverse order while sorting |
| -R | --recursive | list subdirectories recursively |
| -s | --size | print the allocated size of each file, in blocks |
| -S | sort by file size, largest first | |
| --sort=WORD |
sort by WORD instead of name: none (-U), size (-S), |
|
| --time=WORD |
with -l, show time as WORD instead of default |
|
| --time-style=STYLE |
with -l, show times using style STYLE: |
|
| -t | sort by modification time, newest first | |
| -T | --tabsize=COLS | assume tab stops at each COLS instead of 8 |
| -u |
with -lt: sort by, and show, access time; |
|
| -U | do not sort; list entries in directory order | |
| -v | natural sort of (version) numbers within text | |
| -w | --width=COLS | set output width to COLS. 0 means no limit |
| -x | list entries by lines instead of by columns | |
| -X | sort alphabetically by entry extension | |
| -Z | --context | print any security context of each file |
| -1 | list one file per line. Avoid '\n' with -q or -b |
4. 常用范例:
例一:列出/home/peidachang文件夹下的所有文件和目录的详细资料
命令:ls -l -R /home/peidachang
在使用 ls 命令时要注意命令的格式:在命令提示符后,首先是命令的关键字,接下来是命令参数,在命令参数之前要有一短横线“-”,所有的命令参数都有特定的作用,自己可以根据需要选用一个或者多个参数,在命令参数的后面是命令的操作对象。在以上这条命令“ ls -l -R /home/peidachang”中,“ls” 是命令关键字,“-l -R”是参数,“ /home/peidachang”是命令的操作对象。在这条命令中,使用到了两个参数,分别为“l”和“R”,当然,你也可以把他们放在一起使用,如下所示:
命令:ls -lR /home/peidachang
这种形式和上面的命令形式执行的结果是完全一样的。另外,如果命令的操作对象位于当前目录中,可以直接对操作对象进行操作;如果不在当前目录则需要给出操作对象的完整路径,例如上面的例子中,我的当前文件夹是peidachang文件夹,我想对home文件夹下的peidachang文件进行操作,我可以直接输入 ls -lR peidachang,也可以用 ls -lR /home/peidachang。
例二:列出当前目录中所有以“t”开头的目录的详细内容,可以使用如下命令:
命令:ls -l t*
可以查看当前目录下文件名以“t”开头的所有文件的信息。其实,在命令格式中,方括号内的内容都是可以省略的,对于命令ls而言,如果省略命令参数和操作对象,直接输入“ ls ”,则将会列出当前工作目录的内容清单。
例三:只列出文件下的子目录
命令:ls -F /opt/soft |grep /$
列出 /opt/soft 文件下面的子目录
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# ls -F /opt/soft |grep /$
jdk1.6.0_16/
subversion-1.6.1/
tomcat6.0.32/
命令:ls -l /opt/soft | grep "^d"
列出 /opt/soft 文件下面的子目录详细情况
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# ls -l /opt/soft | grep "^d"
drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4096 09-17 18:17 jdk1.6.0_16
drwxr-xr-x 16 1016 1016 4096 10-11 03:25 subversion-1.6.1
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 4096 2011-11-01 tomcat6.0.32
例四:列出目前工作目录下所有名称是s 开头的档案,愈新的排愈后面,可以使用如下命令:
命令:ls -ltr s*
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# ls -ltr s*
src:
总计 0
script:
总计 0
soft:
总计 350644
drwxr-xr-x 9 root root 4096 2011-11-01 tomcat6.0.32
-rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 81871260 09-17 18:15 jdk-6u16-linux-x64.bin
drwxr-xr-x 10 root root 4096 09-17 18:17 jdk1.6.0_16
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 205831281 09-17 18:33 apache-tomcat-6.0.32.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 5457684 09-21 00:23 tomcat6.0.32.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 4726179 10-10 11:08 subversion-deps-1.6.1.tar.gz
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 7501026 10-10 11:08 subversion-1.6.1.tar.gz
drwxr-xr-x 16 1016 1016 4096 10-11 03:25 subversion-1.6.1
例五:列出目前工作目录下所有档案及目录;目录于名称后加"/", 可执行档于名称后加"*"
命令:ls -AF
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# ls -AF
log/ script/ soft/ src/ svndata/ web/
例六:计算当前目录下的文件数和目录数
命令:
ls -l * |grep "^-"|wc -l ---文件个数
ls -l * |grep "^d"|wc -l ---目录个数
例七: 在ls中列出文件的绝对路径
命令:ls | sed "s:^:`pwd`/:"
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# ls | sed "s:^:`pwd`/:"
/opt/log
/opt/script
/opt/soft
/opt/src
/opt/svndata
/opt/web
例九:列出当前目录下的所有文件(包括隐藏文件)的绝对路径, 对目录不做递归
命令:find $PWD -maxdepth 1 | xargs ls -ld
输出:
[root@localhost opt]# find $PWD -maxdepth 1 | xargs ls -ld
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 10-11 03:43 /opt
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2012-03-08 /opt/log
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2012-03-08 /opt/script
drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 10-11 03:21 /opt/soft
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2012-03-08 /opt/src
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 10-11 05:22 /opt/svndata
drwxr-xr-x 4 root root 4096 10-09 00:45 /opt/web
例十:递归列出当前目录下的所有文件(包括隐藏文件)的绝对路径
命令: find $PWD | xargs ls -ld
例十一:指定文件时间输出格式
命令:
ls -tl --time-style=full-iso
输出:
[root@localhost soft]# ls -tl --time-style=full-iso
总计 350644
drwxr-xr-x 16 1016 1016 4096 2012-10-11 03:25:58.000000000 +0800 subversion-1.6.1
ls -ctl --time-style=long-iso
输出:
[root@localhost soft]# ls -ctl --time-style=long-iso
总计 350644
drwxr-xr-x 16 1016 1016 4096 2012-10-11 03:25 subversion-1.6.1
扩展:
1. 显示彩色目录列表
打开/etc/bashrc, 加入如下一行:
alias ls="ls --color"
下次启动bash时就可以像在Slackware里那样显示彩色的目录列表了, 其中颜色的含义如下:
1. 蓝色-->目录
2. 绿色-->可执行文件
3. 红色-->压缩文件
4. 浅蓝色-->链接文件
5. 灰色-->其他文件






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号