实验3 类和对象
task1:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string> 5 6 class Button{ 7 public: 8 Button(const std::string &label_); 9 const std::string& get_label() const; 10 void click(); 11 12 private: 13 std::string label; 14 }; 15 16 Button::Button(const std::string &label_):label{label_}{} 17 18 inline const std::string& Button::get_label() const{ 19 return label; 20 } 21 22 inline void Button::click(){ 23 std::cout<<"Button "<<label<<" clicked\n"; 24 }
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<vector> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 #include"Button.hpp" 7 8 class Window{ 9 public: 10 Window(const std::string &title_); 11 void display() const; 12 void close(); 13 void add_button(const std::string &label); 14 void click_button(const std::string &label); 15 16 private: 17 bool has_button(const std::string &label) const; 18 19 private: 20 std::string title; 21 std::vector<Button> buttons; 22 }; 23 24 Window::Window(const std::string &title_):title{title_}{ 25 buttons.push_back(Button("close")); 26 } 27 28 inline void Window::display() const{ 29 std::string s(40,'*'); 30 std::cout<<s<<std::endl; 31 std::cout<<"window:"<<title<<std::endl; 32 int cnt=0; 33 for(const auto &button:buttons) 34 std::cout<<++cnt<<"."<<button.get_label()<<std::endl; 35 std::cout<<s<<std::endl; 36 } 37 38 inline void Window::close(){ 39 std::cout<<"close window '"<<title<<"'"<<std::endl; 40 click_button("close"); 41 } 42 43 44 inline bool Window::has_button(const std::string &label)const{ 45 for(const auto &button:buttons) 46 if(button.get_label()==label) 47 return true; 48 49 return false; 50 } 51 52 inline void Window::add_button(const std::string &label){ 53 if(has_button(label)) 54 std::cout<<"button"<<label<"already exists!\n"; 55 else 56 buttons.push_back(Button(label)); 57 } 58 59 inline void Window::click_button(const std::string &label){ 60 for(auto &button:buttons) 61 if(button.get_label()==label){ 62 button.click(); 63 return; 64 } 65 66 std::cout<<"no button:"<<label<<std::endl; 67 }
1 #include"Window.hpp"; 2 #include<iostream> 3 4 void test(){ 5 Window w("Demo"); 6 w.add_button("add"); 7 w.add_button("remove"); 8 w.add_button("modify"); 9 w.add_button("add"); 10 w.display() ; 11 w.close() ; 12 } 13 14 int main(){ 15 std::cout<<"用组合类模拟简单GUI:\n"; 16 test(); 17 }
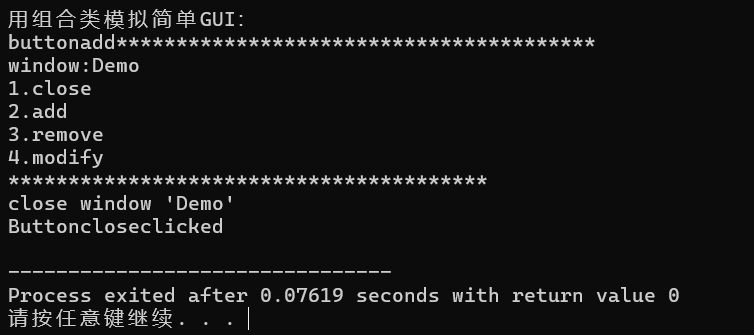
问题1:
是组合关系
问题2:
(1)has_button()函数的作用主要是判断某个label是否已经存在。若将其改为公有接口,可能会导致数据被篡改,类的安全性降低,从而影响整个类;设计为公有的优点是可以在类的外部实现交互,但是has_button()并没有交互的需求
(2)用户是否需要:需要和用户实现交互功能可以设计为public
是否仅为内部实现细节:如判断或是计算,在内部完成,只需输出结果的函数设计为private
是否易破坏对象状态:如果某个函数设计为public,在与用户交互的过程中会容易被破坏或篡改那么这个函数应该设计为private
问题3:
性能:两个接口没有差别
安全性:接口1使用const引用类型作为函数返回值,label本身为类成员且较为安全,所以使用const引用更加高效
接口使用const类型作为函数返回值,相当于将label拷贝了一个副本,相对来说也很安全但是没有那么高效
问题4:
正常运行
push_back()需要创建新对象或者该对象本身已经存在,然后加入到容器对象中
emplace_back()可以直接获取对象的参数,自行构造对象,然后加入到容器对象中
task2:
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<vector> 3 4 void test1(); 5 void test2(); 6 void output1(const std::vector<int>&v); 7 void output2(const std::vector<int>&v); 8 void output3(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>&v); 9 10 int main(){ 11 std::cout<<"深复制验证1:标准库vector<int>\n"; 12 test1(); 13 14 std::cout<<"\n深复制验证2:标准库vector<int>嵌套使用\n"; 15 test2(); 16 17 } 18 19 void test1(){ 20 std::vector<int>v1(5,42); 21 const std::vector<int>v2(v1); 22 23 std::cout<<"**********拷贝构造后**********\n"; 24 std::cout<<"v1:"; 25 output1(v1); 26 std::cout<<"v2:"; 27 output1(v2); 28 29 v1.at(0)=-1; 30 31 std::cout<<"**********修改v1[0]后**********\n"; 32 std::cout<<"v1:"; 33 output1(v1); 34 std::cout<<"v2:"; 35 output1(v2); 36 } 37 38 void test2(){ 39 std::vector<std::vector<int>> v1{{1,2,3},{4,5,6,7}}; 40 const std::vector<std::vector<int>> v2(v1); 41 42 std::cout<<"**********拷贝构造后**********\n"; 43 std::cout<<"v1:"; 44 output3(v1); 45 std::cout<<"v2:"; 46 output3(v2); 47 48 v1.at(0).push_back(-1); 49 50 std::cout<<"**********修改v1[0]后**********\n"; 51 std::cout<<"v1:\n"; 52 output3(v1); 53 std::cout<<"v2:\n"; 54 output3(v2); 55 56 } 57 //使用XX.at()+循环输出vector<int>数据项 58 void output1(const std::vector<int>&v){ 59 if(v.size()==0){ 60 std::cout<<"\n"; 61 return; 62 } 63 64 std::cout<<v.at(0); 65 for(auto i=1;i<v.size();++i) 66 std::cout<<","<<v.at(i); 67 std::cout<<'\n'; 68 } 69 70 //使用迭代器+循环输出vector<int>数据项 71 void output2(const std::vector<int>&v){ 72 if(v.size()==0){ 73 std::cout<<'\n'; 74 return; 75 } 76 77 auto it=v.begin(); 78 std::cout<<*it; 79 80 for(it=v.begin()+1;it!=v.end();++it) 81 std::cout<<","<<*it; 82 std::cout<<'\n'; 83 } 84 85 //使用auto for分行输出vector<int>数据项 86 void output3(const std::vector<std::vector<int>>&v){ 87 if(v.size()==0){ 88 std::cout<<'\n'; 89 return; 90 } 91 92 for(auto &i:v) 93 output2(i); 94 }
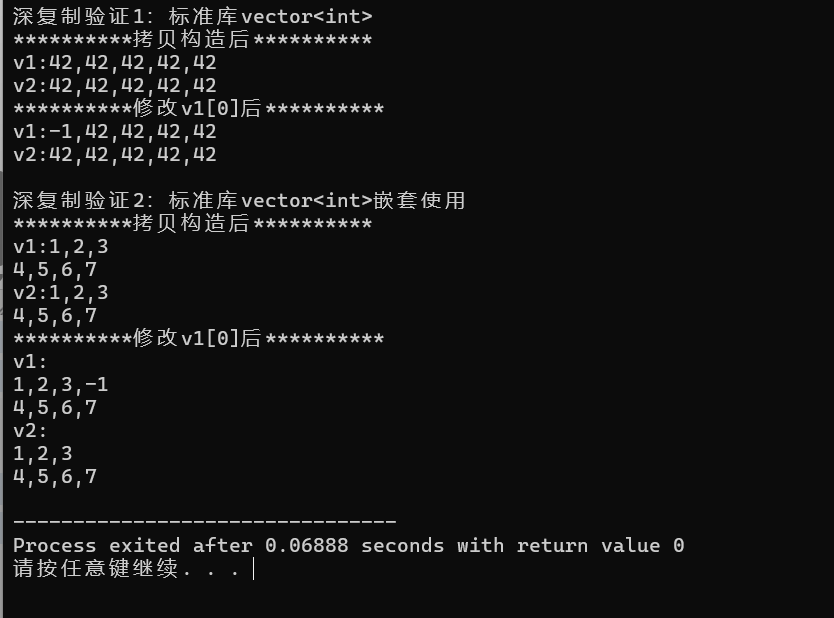
问题1:
第一行用的是普通构造,第二行用的是复制构造,v1和v2都包含5个值
问题2:
v1.size()为2,v2.size()为2,v1[0].size()为3
问题3:
可以实现同等效果
v1.at(0)=-1,会进行越界检查,例如当v1.size()小于0时,就会抛出错误
v1[0]=-1,则直接访问,不进行越界检查,安全性较低
问题4:
(1)可以输出-1,第一行代码就是将v1的第一个元素{1,2,3,-1}赋值给引用类型 r,第二行代码中r.size()-1的值为3,那么第二行代码访问的就是r[3],即为-1
(2)内存上的优势:const引用接受返回值不需要另外的内存来存储该返回值,与原来的v1的第一个元素共用内存空间
限制:const引用类型需要保证该返回值绝对安全,由于v1属于test2()函数内部的一个局部变量,所以相对来说并不绝对安全
问题5:
(1)是深复制
(2)vector<int>,返回值类型是int的引用类型;const vector<int>,返回值是const int的引用类型
不是必须提供
task3:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 5 //动态int数组类对象 6 class vectorint{ 7 public: 8 vectorint(); 9 vectorint(int n_); 10 vectorint(int n_,int value); 11 vectorint(const vectorint&vi); 12 ~vectorint(); 13 14 int size()const; 15 int& at(int index); 16 const int& at(int index)const; 17 vectorint& assign(const vectorint& vi); 18 19 int* begin(); 20 int* end(); 21 const int* begin()const; 22 const int* end()const; 23 24 25 private: 26 int n;//当前数据项个数 27 int* ptr;//数据区 28 29 }; 30 31 vectorint::vectorint():n{0},ptr{nullptr}{} 32 33 vectorint::vectorint(int n_):n{n_},ptr{new int[n]}{} 34 35 vectorint::vectorint(int n_,int value):n{n_},ptr{new int[n_]}{ 36 for(auto i=0;i<n;++i) 37 ptr[i]=value; 38 } 39 40 vectorint::vectorint(const vectorint& vi):n{vi.n},ptr{new int[n]}{ 41 for(auto i=0;i<n;++i) 42 ptr[i]=vi.ptr[i]; 43 } 44 45 vectorint::~vectorint(){ 46 delete [] ptr; 47 } 48 49 int vectorint::size()const{ 50 return n; 51 } 52 53 const int& vectorint::at(int index)const{ 54 if(index<0||index>=n){ 55 std::cerr<<"indexError:index out of range\n"; 56 std::exit(1); 57 } 58 59 return ptr[index]; 60 } 61 62 int& vectorint::at(int index){ 63 if(index<0||index>=n){ 64 std::cerr<<"indexError:index out of range\n"; 65 std::exit(1); 66 } 67 68 return ptr[index]; 69 } 70 71 vectorint& vectorint::assign(const vectorint& vi){ 72 if(this==&vi) 73 return *this; 74 75 int* ptr_tmp; 76 ptr_tmp=new int[vi.n]; 77 for(int i=0;i<vi.n;++i){ 78 ptr_tmp[i]=vi.ptr[i]; 79 } 80 81 delete [] ptr; 82 n=vi.n; 83 ptr=ptr_tmp; 84 return *this; 85 } 86 87 int* vectorint::begin(){ 88 return ptr; 89 } 90 91 int* vectorint::end(){ 92 return ptr+n; 93 } 94 95 const int* vectorint::begin()const{ 96 return ptr; 97 } 98 99 const int* vectorint::end()const{ 100 return ptr+n; 101 }
1 #include"vectorint.hpp" 2 #include<iostream> 3 4 void test1(); 5 void test2(); 6 void output1(const vectorint &vi); 7 void output2(const vectorint &vi); 8 9 int main(){ 10 std::cout<<"测试1:\n"; 11 test1(); 12 13 std::cout<<"\n测试2:\n"; 14 test2(); 15 } 16 17 void test1(){ 18 int n; 19 std::cout<<"Enter n:"; 20 std::cin>>n; 21 22 vectorint x1(n); 23 for(auto i=0;i<n;++i){ 24 x1.at(i)=(i+1)*10; 25 } 26 std::cout<<"x1:"; 27 output1(x1); 28 29 vectorint x2(n,42); 30 vectorint x3(x2); 31 x2.at(0)=-1; 32 std::cout<<"x2:"; 33 output1(x2); 34 std::cout<<"x3:"; 35 output1(x3); 36 } 37 38 void test2(){ 39 const vectorint x(5,42); 40 vectorint y; 41 42 y.assign(x); 43 44 std::cout<<"x:"; 45 output2(x); 46 std::cout<<"y:"; 47 output2(y); 48 } 49 50 //使用xx.at()+循环输出vectorint对象数据项 51 void output1(const vectorint &vi){ 52 if(vi.size()==0){ 53 std::cout<<'\n'; 54 return; 55 } 56 57 std::cout<<vi.at(0); 58 59 for(auto i=1;i<vi.size();++i){ 60 std::cout<<","<<vi.at(i); 61 } 62 std::cout<<'\n'; 63 } 64 65 //使用迭代器+循环输出vectorint对象数据项 66 void output2(const vectorint &vi){ 67 if(vi.size()==0){ 68 std::cout<<'\n'; 69 return; 70 } 71 72 auto it=vi.begin(); 73 std::cout<<*it; 74 75 for(it=vi.begin()+1;it!=vi.end();++it){ 76 std::cout<<","<<*it; 77 } 78 std::cout<<'\n'; 79 }
问题1:
两段代码的差异在于是否检查this指针是否指向当前传入的vectorint类型的对象vi
版本2的缺陷:没有检查this指针是否指向当前对象vi,直接释放了内存,如果就是指向当前对象vi,在后续赋值操作,访问的就是已经释放的内存
问题2:
(1)static_cast<const vectorint*>(this)的作用是将this指针改成const vectorint*类型的指针
转换前是vectorint*类型指针,转换后是const vectorint*类型指针
目的是为了调用const修饰的at()成员函数
(2)const_cast<int&>的作用是将const int&转变为int&类型
转换前为const int&,转换后为int&
目的是可以修改返回值,即修改容器中的元素值
问题3:
第4行调用begin()d的非const版本,第5行调用begin()的const版本
非const版本:调用的对象是非const对象,const版本:调用对象是const类型
问题4:
可以
fill_n()函数功能是从ptr指向的位置开始将后面n的对象赋值为value
copy_n()函数功能是从vi.ptr开始复制vi.n个元素,然后存入从 ptr指向的位置开始的区域
task4:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 5 class Martix{ 6 public: 7 Martix(int rows_,int cols_,double value=0);//构造rows_*cols_矩阵对象,初值为value 8 Martix(int rows_,double value=0);//构造rows_*rows_方阵对象,初值为value 9 Martix(const Martix &x);//深复制 10 ~Martix(); 11 12 void set(const double* pvalue,int size);//按行复制pvalue指向的数据,要求size=rows*cols。否则报错退出 13 void clear();//矩阵对象数据项置0 14 15 const double& at(int i,int j)const;//返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)对应的数据项const引用(越界则报错后退出) 16 double& at(int i,int j);// 返回矩阵对象索引(i,j)对应的数据项引用(越界则报错后退出) 17 18 int row()const;//返回矩阵对象行数 19 int col()const;//返回矩阵对象列数 20 21 void print()const;//按行打印数据 22 23 private: 24 int n_row; 25 int n_col; 26 double *ptr; 27 28 }; 29 30 Martix::Martix(int rows_,int cols_,double value):n_row{rows_},n_col{cols_},ptr{new double[n_row*n_col]}{ 31 for(auto i=0;i<n_row;++i){ 32 for(auto j=0;j<n_col;++j) 33 ptr[i*n_col+j]=value; 34 } 35 } 36 37 Martix::Martix(int rows_,double value):Martix(rows_,rows_,value){ 38 } 39 40 Martix::Martix(const Martix& x):n_row{x.n_row},n_col{x.n_col},ptr{new double[n_row*n_col]}{ 41 for(auto i=0;i<n_row*n_col;++i){ 42 ptr[i]=x.ptr[i]; 43 } 44 } 45 46 Martix::~Martix(){ 47 delete [] ptr; 48 } 49 50 void Martix::set(const double* pvalue,int size){ 51 if(size!=n_row*n_col){ 52 std::cout<<"Error\n"; 53 std::exit(1); 54 } 55 56 for(int i=0;i<n_row*n_col;++i) 57 ptr[i]=pvalue[i]; 58 59 std::cout<<"set"; 60 } 61 62 void Martix::clear(){ 63 for(auto i=0;i<n_row*n_col;++i){ 64 ptr[i]=0; 65 } 66 } 67 68 const double& Martix::at(int i,int j)const{ 69 if(i<0||i>n_row-1||j<0||j>n_col-1){ 70 std::cout<<"Error\n"; 71 std::exit(1); 72 } 73 74 return ptr[i*n_col+j]; 75 } 76 77 double& Martix::at(int i,int j){ 78 if(i<0||i>n_row-1||j<0||j>n_col-1){ 79 std::cout<<"Error\n"; 80 std::exit(1); 81 } 82 83 return ptr[i*n_col+j]; 84 } 85 86 int Martix::row()const{ 87 return n_row; 88 } 89 90 int Martix::col()const{ 91 return n_col; 92 } 93 94 void Martix::print()const{ 95 for(int i=0;i<n_row;++i){ 96 for(int j=0;j<n_col;++j){ 97 std::cout<<ptr[i*n_col+j]<<" "; 98 } 99 std::cout<<'\n'; 100 } 101 }
1 #include"martix.hpp" 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<cstdlib> 4 5 void test1(); 6 void test2(); 7 void output(const Martix &m,int row_index); 8 9 int main(){ 10 std::cout<<"测试1:\n"; 11 test1(); 12 13 std::cout<<"\n测试2:\n"; 14 test2(); 15 } 16 17 void test1(){ 18 double x[1000]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10}; 19 20 int n,m; 21 std::cout<<"Enter n and m:"; 22 std::cin>>n>>m; 23 24 Martix m1(n,m); 25 m1.set(x,n*m); 26 27 Martix m2(m,n); 28 m2.set(x,m*n); 29 30 Martix m3(n); 31 m3.set(x,n*n); 32 33 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m1:\n"; 34 m1.print(); 35 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m2:\n"; 36 m2.print(); 37 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m3:\n"; 38 m3.print(); 39 40 } 41 void test2(){ 42 Martix m1(2,3,-1); 43 const Martix m2(m1); 44 45 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m1:\n"; 46 m1.print(); 47 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m2:\n"; 48 m2.print(); 49 50 m1.clear(); 51 m1.at(0,0)=1; 52 53 std::cout<<"m1更新后:\n"; 54 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m1第0行:"; 55 output(m1,0); 56 std::cout<<"矩阵对象m2第0行:"; 57 output(m2,0); 58 } 59 60 61 void output(const Martix &m,int row_index){ 62 if(row_index<0||row_index>m.row()){ 63 std::cerr<<"indexError:row index out of range\n"; 64 std::exit(1); 65 } 66 67 std::cout<<m.at(row_index,0); 68 for(int j=1;j<m.col();++j) 69 std::cout<<","<<m.at(row_index,j); 70 std::cout<<'\n'; 71 }
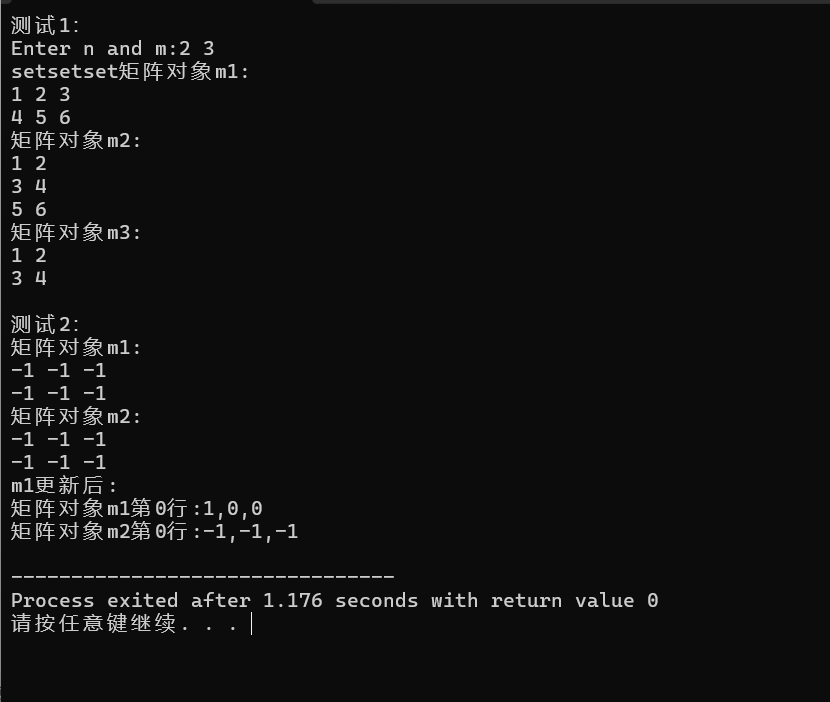
task5:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<string> 5 6 class contact{ 7 public: 8 contact(const std::string &name_,const std::string &phone_); 9 10 const std::string &get_name()const; 11 const std::string &get_phone()const; 12 void display()const; 13 14 private: 15 std::string name; 16 std::string phone; 17 18 }; 19 20 contact::contact(const std::string &name_,const std::string &phone_):name{name_},phone{phone_}{ 21 } 22 23 const std::string& contact::get_name() const{ 24 return name; 25 } 26 27 const std::string& contact::get_phone() const{ 28 return phone; 29 } 30 31 void contact::display()const{ 32 std::cout<<name<<","<<phone; 33 }
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include"contact.hpp" 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include<string> 6 #include<vector> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 9 //通讯录类 10 class contactbook{ 11 public: 12 void add(const std::string &name,const std::string &phone); 13 void remove(const std::string &name); 14 void find(const std::string &name)const; 15 void display()const; 16 size_t size()const; 17 18 private: 19 int index(const std::string &name)const;//返回联系人在contacts内索引,若不存在则返回-1 20 void sort();//按姓名字典升序排序 21 22 private: 23 std::vector<contact> contacts; 24 }; 25 26 void contactbook::add(const std::string &name,const std::string &phone){ 27 if(index(name)==-1){ 28 contacts.push_back(contact(name,phone)); 29 std::cout<<name<<" add successfully.\n"; 30 sort(); 31 return; 32 } 33 34 std::cout<<name <<" already exists.fail to add!\n"; 35 } 36 37 void contactbook::remove(const std::string &name){ 38 int i=index(name); 39 40 if(i==-1){ 41 std::cout<<name <<" not found, fail to remove!\n"; 42 return; 43 } 44 45 contacts.erase(contacts.begin()+i); 46 std::cout<<name <<" remove successfully.\n"; 47 } 48 49 void contactbook::find(const std::string &name)const{ 50 int i=index(name); 51 52 if(i==-1){ 53 std::cout<<name <<" not found!\n"; 54 return; 55 } 56 57 contacts[i].display(); 58 std::cout<<'\n'; 59 } 60 61 void contactbook::display()const{ 62 for(auto &c:contacts){ 63 c.display(); 64 std::cout<<'\n'; 65 } 66 } 67 68 size_t contactbook::size()const{ 69 return contacts.size(); 70 } 71 72 int contactbook::index(const std::string &name)const{ 73 for(int i=0;i<size();++i){ 74 if(name==contacts[i].get_name()) 75 return i; 76 } 77 return -1; 78 } 79 80 void contactbook::sort(){ 81 for(int i=0;i<size();++i){ 82 for(int j=0;j<size()-i-1;++j){ 83 if(contacts[j].get_name()>contacts[j+1].get_name()){ 84 std::swap(contacts[j],contacts[j+1]); 85 } 86 } 87 } 88 }
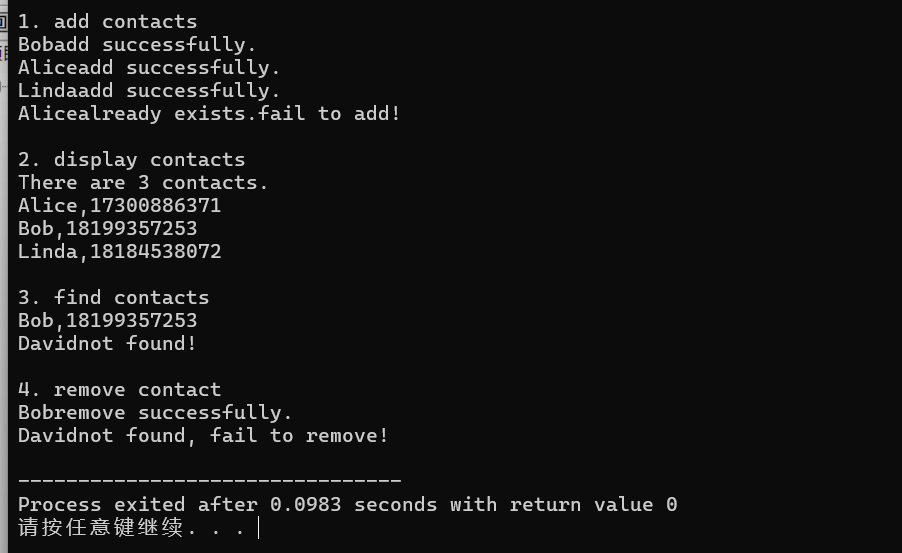
1 #include "contactBook.hpp" 2 3 void test() { 4 contactbook contactbook1; 5 6 std::cout << "1. add contacts\n"; 7 8 contactbook1.add("Bob", "18199357253"); 9 contactbook1.add("Alice", "17300886371"); 10 contactbook1.add("Linda", "18184538072"); 11 contactbook1.add("Alice", "17300886371"); 12 13 std::cout << "\n2. display contacts\n"; 14 std::cout << "There are " << contactbook1.size() << " contacts.\n"; 15 contactbook1.display(); 16 17 std::cout << "\n3. find contacts\n"; 18 contactbook1.find("Bob"); 19 contactbook1.find("David"); 20 21 std::cout << "\n4. remove contact\n"; 22 contactbook1.remove("Bob"); 23 contactbook1.remove("David"); 24 } 25 26 int main() { 27 test(); 28 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号