OOP第一次博客作业
关于Java与面向对象:
目录:
一、前言
前言:
这个学期才开始接触Java,对于第一次作业总结感触比较生疏,在很多语法中有些不适应,经常犯一些问题,对于面向对象上学期学习C语言的过程中是从来没有接触过的。
在这开学到现在的过程中,到现在为止一共进行了3周,虽然说时间非常短,但是在这每天的语法练习中,对于自己的水平都是有感觉到明显的进步的。从C语言到本学期Java的学习当中,老师不会再像之前一样的去一节课一节课教学我们的语法知识,而是在我们自己学习Java的基本使用语法的基础上教学如何面向对象去进行刨析项目的成分再到设计出逻辑关系(power designer),然而对于这一部分的自学还是要通过自己的实践能力去熟悉代码的写入,其次以便提升我的敲码速度。
知识点:
关于类:
1、类似C++中的struct,构造函数、内置方法(函数 )都比较相似
2、但是无法重载运算符,这是比较难受的一点。
3、尽量避免代码的重复,private和public的方法需要熟悉封装性。
4、为对象定义类,使用构造方法构造对象。
5、使用Java库中的类。
关于Java语法:
1、注意可变类的赋值是引用。
2、String类字符串的使用。
3、数组的基本用法。
关于作业题题量:
三次作业的题量相对还是比较多的。
关于作业难度:
三次作业的基本难度较简单易懂。
设计与分析:
第一次作业:总共有12道题目,分别为:
| 7-1 计算年利率 | 5 |
| 7-2 身体质量指数(BMI)测算 | 10 |
| 7-3 九九乘法表(双重循环) | 15 |
| 7-4 快递运费 | 10 |
| 7-5 去掉重复的字符 | 5 |
| 7-6 统计一个子串在整串中出现的次数
|
5 |
| 7-7 有重复的数据 | 5 |
| 7-8 从一个字符串中移除包含在另一个字符串中的字符 | 5 |
| 7-9 Prime Numbers | 5 |
| 7-10 GPS数据处理 | 10 |
| 7-11 求定积分 | 10 |
| 7-12 列出最简真分数序列* | 15 |
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String [] args){ 5 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 6 int b=input.nextInt(); 7 double c=0; 8 if(b>0){ 9 if(b<=1){ 10 c=0.077*0.5; 11 } 12 else if(b>1&&b<=3){ 13 c=0.077*0.7; 14 } 15 else if(b>3&&b<=5){ 16 c=0.077*1.0; 17 } 18 else{ 19 c=0.077*1.1; 20 } 21 System.out.print(String.format("实际利率=%.2f",c*100));//使用String.format() 22 System.out.print("%"); 23 } 24 else{ 25 System.out.println("error"); 26 } 27 } 28 }
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); 6 String s=scan.nextLine(); 7 String b=scan.nextLine(); 8 int index=0; 9 int count=0; 10 while(true) 11 { 12 index=s.indexOf(b); 13 if(index!=-1) 14 { 15 count++; 16 s=s.substring(index+b.length());/连接字符串 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 System.out.print(count); 24 } 25 }
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main{ 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 String s1=null,time = null; 6 while (in.hasNext()) 7 { 8 s1=in.nextLine(); 9 if(s1.equals("END")) 10 { 11 break; 12 } 13 int sum=0; 14 String []split=s1.split(","); 15 if(split[0].equals("$GPRMC")) 16 { 17 int end=s1.indexOf("*"); 18 for(int i=1;i<end;i++) 19 { 20 sum^=(int)s1.charAt(i); 21 } 22 sum%=65536; 23 Boolean flag=split[2].equals("A"); 24 Boolean S=sum==Integer.parseInt(s1.substring(end+1),16); 25 if(S==true&&flag==true) 26 { 27 time=split[1]; 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 if(time!=null) 32 { 33 int h=(Integer.parseInt(time.substring(0,2))+8)%24;//substring()返回字符串的子字符串 34 String m=time.substring(2,4); 35 String s=time.substring(4,6); 36 if(h<10) 37 System.out.print("0"); 38 System.out.print(h+":"+m+":"+s); 39 } 40 } 41 }
第二次作业:总共有9道题目,分别为:
| 7-1 长度质量计量单位换算 | 5 |
| 7-2 奇数求和 | 10 |
| 7-3 房产税费计算2022 | 12 |
| 7-4 游戏角色选择 | 14 |
| 7-5 学号识别 | 10 |
| 7-6 巴比伦法求平方根近似值 | 10 |
| 7-7 二进制数值提取 | 10 |
| 7-8 判断三角形类型 | 15 |
| 7-9 求下一天 | 14 |
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); 6 double a=scan.nextDouble(); 7 double b=scan.nextDouble(); 8 double c,d; 9 c=a/0.45359237; 10 d=b/0.0254; 11 System.out.print((float)c+" "+(float)d);//强制转化 12 } 13 }
其中7-8:这一道题在运用if与else的条件判断中要求比较高,其中印象最深的也就是本题的最难一个点,在多次测例中解决不了的是等腰直角三角形的判断。在最后交流与讨论中得知,两个整数的比值不可能必出无理数,于是将代码进行优化,类似于 Math.abs(ch1*ch1+ch2*ch2-ch3*ch3)<0.0000001 的办法进行判断。了解了浮点数类型的判断相等不能直接在if等语句的判定条件中去使用“==”进行判断,而是将其相减得出的值小于某个极小的数从而达到判断是否相等的目的。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); 6 double ch1=scan.nextDouble(); 7 double ch2=scan.nextDouble(); 8 double ch3=scan.nextDouble(); 9 if(ch1<1||ch1>200||ch2<1||ch2>200||ch3<1||ch3>200){ 10 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 11 }else if(ch1+ch2<=ch3||ch1+ch3<=ch2||ch2+ch3<=ch1){ 12 System.out.println("Not a triangle"); 13 }else if(ch1==ch2&&ch2==ch3&&ch1==ch3){ 14 System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); 15 }else if((ch1==ch2&&(Math.abs(ch1*ch1+ch2*ch2-ch3*ch3)<0.0000001) 16 ||(ch1==ch3&&(Math.abs(ch1*ch1+ch3*ch3-ch2*ch2)<0.0000001)) 17 ||(ch2==ch3&&(Math.abs(ch2*ch2+ch3*ch3-ch1*ch1)<0.0000001)))){//浮点数类型的判断 18 System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 19 }else if(ch1==ch2||ch1==ch3||ch2==ch3){ 20 System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); 21 }else if((ch1*ch1+ch2*ch2==ch3*ch3)||(ch1*ch1+ch3*ch3==ch2*ch2)||(ch3*ch3+ch2*ch2==ch1*ch1)){ 22 System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); 23 }else{ 24 System.out.println("General triangle"); 25 } 26 } 27 }
第三次作业:总共有4道题目,分别为:
| 7-1 创建圆形类 | 6 |
| 7-2 创建账户类Account | 16 |
| 7-3 定义日期类 | 34 |
| 7-4 日期类设计 | 44 |
对于第三次作业的训练,我深刻的感觉到题目的大大提升难度,从第一题开始学习如何为对象定义一个类型,构造里面的属性以及其种类,创建对象和定义类,使用无参或者有参的构造方法构造对象(使用new操作符调用构造方法创建对象,构造方法必须与所在类同名,构造方法没有返回类型,甚至连void也没有,构造方法是在创建一个对象时由new操作符调用的。构造方法的作用是初始化对象),然后是针对访问对象的数据和方法的学习,再包括对于date类的理解和其中如何进行的有进一步的理解。
其中7-3:这一题是继承第二次作业的7-9迭代过来的,要求输出下一天的日期,有第二题的引子下再重新优化这个源码,可以采用学习到的创建类的使用。有了类的帮助就非常轻松的完成了7-3的功能实现
这边是类图: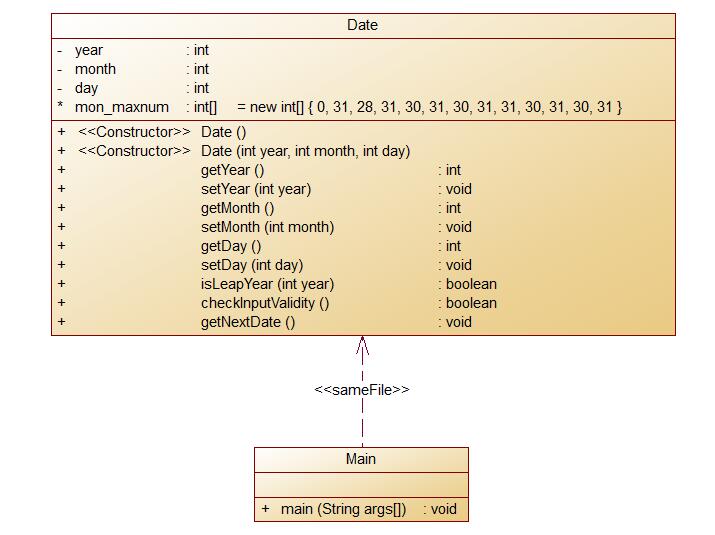
然后是源码展示:
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in); 6 Date date=new Date(); 7 int year=scan.nextInt(); 8 int month=scan.nextInt(); 9 int day=scan.nextInt(); 10 date.setYear(year); 11 date.setMonth(month); 12 date.setDay(day); 13 date.getNextDate(); 14 } 15 } 16 class Date{ 17 private int year; 18 private int month; 19 private int day; 20 int[] mon_maxnum=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 21 Date(){ 22 year=0; 23 month=0; 24 day=0; 25 } 26 Date(int year,int month,int day){ 27 this.year=year; 28 this.month=month; 29 this.day=day; 30 } 31 public int getYear(){ 32 return year; 33 } 34 public void setYear(int year){ 35 this.year=year; 36 } 37 public int getMonth(){ 38 return month; 39 } 40 public void setMonth(int month){ 41 this.month=month; 42 } 43 public int getDay(){ 44 return day; 45 } 46 public void setDay(int day){ 47 this.day=day; 48 } 49 public boolean isLeapYear(int year){//判断是否为闰年 50 if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0){ 51 return true; 52 }else{ 53 return false; 54 } 55 } 56 public boolean checkInputValidity(){//检查是否输入有误 57 if((year>=1900&&year<=2000)&& 58 (month>=1&&month<=12)&& 59 (day>=1&&day<=31)){ 60 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month==2&&(day>=1&&day<=29)){ 61 return true; 62 }else if(day>=1&&day<=mon_maxnum[month]){ 63 return true; 64 }else{ 65 return false; 66 } 67 }else{ 68 return false; 69 } 70 } 71 public void getNextDate(){//求下一天 72 if(checkInputValidity()==false){ 73 System.out.print("Date Format is Wrong"); 74 }else{ 75 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 76 mon_maxnum[2]=29; 77 } 78 if(day>=1&&day<mon_maxnum[month]){ 79 day++; 80 } 81 if(day==mon_maxnum[month]){ 82 day=1; 83 if(month!=12){ 84 month++; 85 }else{ 86 month=1; 87 year++; 88 } 89 } 90 System.out.println("Next day is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 91 } 92 } 93 }
不难发现,Java中的类的创建给代码的结构化提供了无可替代的作用,至于下一天的算法只需要注意闰年的二月份带来的变化考虑到特殊即可。
其中7-4:最为日期Date类的最后一个迭代题目,增加了前n天、后n天、两个日期之间相差多少天的功能。优化之后的类:
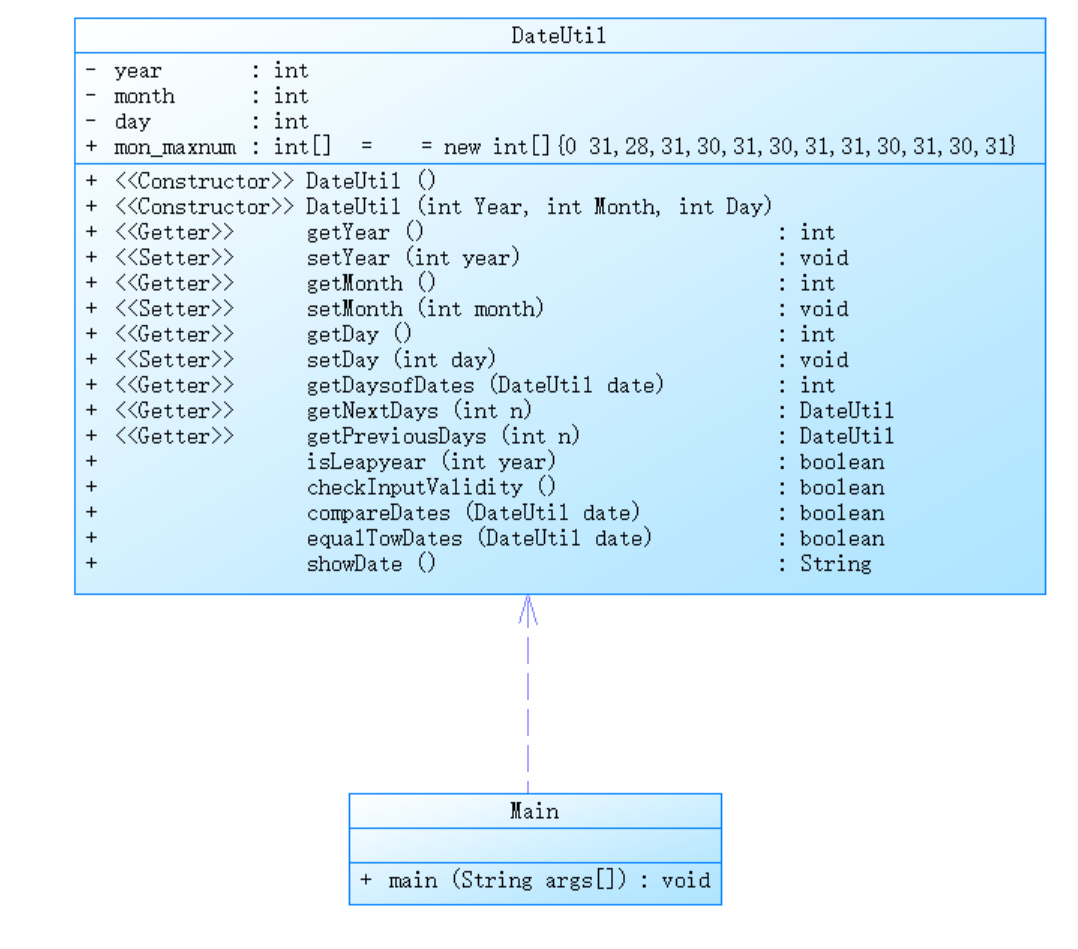
代码展示如下:
运用类的调用,使代码更加具有条理,看起来不会太烧脑
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); 4 int year = 0; 5 int month = 0; 6 int day = 0; 7 int choice = input.nextInt(); 8 if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method 9 int m = 0; 10 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 11 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 12 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 13 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 14 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 15 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 16 System.exit(0); 17 } 18 m = input.nextInt(); 19 if (m < 0) { 20 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 21 System.exit(0); 22 } 23 System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:"); 24 System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate()); 25 } else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method 26 int n = 0; 27 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 28 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 29 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 30 31 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 32 33 if (!date.checkInputValidity()) { 34 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 35 System.exit(0); 36 } 37 38 n = input.nextInt(); 39 40 if (n < 0) { 41 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 42 System.exit(0); 43 } 44 45 System.out.print( 46 date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:"); 47 System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate()); 48 } else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method 49 year = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 50 month = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 51 day = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 52 53 int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 54 int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 55 int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next()); 56 57 DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 58 DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay); 59 60 if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) { 61 System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() + 62 " and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:" 63 + fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate)); 64 } else { 65 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 66 System.exit(0); 67 } 68 } 69 else{ 70 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 71 System.exit(0); 72 } 73 } 74 }
1 class DateUtil{ 2 private int year; 3 private int month; 4 private int day; 5 int[] mon_maxnum=new int[]{0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31}; 6 public DateUtil(int year,int month,int day){ 7 this.year=year; 8 this.month=month; 9 this.day=day; 10 } 11 public int getYear(){ 12 return year; 13 } 14 public void setYear(int year){ 15 this.year=year; 16 } 17 public int getMonth(){ 18 return month; 19 } 20 public void setMonth(int month){ 21 this.month=month; 22 } 23 public int getDay(){ 24 return day; 25 } 26 public void setDay(int day){ 27 this.day=day; 28 } 29 public boolean isLeapYear(int year){ 30 if((year%4==0&&year%100!=0)||year%400==0){ 31 return true; 32 }else{ 33 return false; 34 } 35 } 36 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 37 if(year < 1820 || year > 2020) 38 return false; 39 if(month < 1 || month > 12) 40 return false; 41 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 42 if(month == 2){ 43 if(day < 1 || day > 29) 44 return false; 45 } 46 else 47 if(day < 1 || day > mon_maxnum[month]) 48 return false; 49 } 50 if(!isLeapYear(year)){ 51 if(day<1 || day > mon_maxnum[month]) 52 return false; 53 } 54 return true; 55 } 56 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n){ 57 while(n>365){ 58 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month<=2){ 59 if(day==29&&month==2){ 60 day=1; 61 month=3; 62 } 63 year++; 64 n-=366; 65 }else if(isLeapYear(year+1)&&month>2){ 66 year++; 67 n-=366; 68 }else{ 69 year++; 70 n-=365; 71 } 72 } 73 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 74 day++; 75 if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 2){ 76 if(day > 29){ 77 month++; 78 day = 1; 79 } 80 } 81 else if(day > mon_maxnum[month]){ 82 month++; 83 day = 1; 84 if(month > 12){ 85 month = 1; 86 year++; 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 91 return date; 92 } 93 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n){ 94 while(n>365){ 95 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month>2){ 96 year--; 97 n-=366; 98 }else if(isLeapYear(year-1)&&month<=2){ 99 year--; 100 n-=366; 101 }else{ 102 year--; 103 n-=365; 104 } 105 } 106 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 107 day--; 108 if(day < 1){ 109 month--; 110 if(month < 1){ 111 month = 12; 112 year--; 113 } 114 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month==2){ 115 day=29; 116 }else{ 117 day=mon_maxnum[month]; 118 } 119 } 120 } 121 DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day); 122 return date; 123 } 124 public String showDate(){ 125 return year+"-"+month+"-"+day; 126 } 127 }
对于求n天之后的代码,算法基本与7-3相似,在之前的基础上增加排除够量的日期,在做出这些算法的实现后,对照之后很容易知道前n天的算法如何推出来,两个十分相近。
踩坑心得:
1.作为一个刚入门的小白,对于最开始处理一些数据还是有很多地方做的非常差,例如在变量可取值范围很大的时候不能直接套上循环进行程序运行,有方法去调节循环次数,将其降低。从一开始的date中的天数加减一天天实现到降低循环次数分别从年月日去实现,部分修正后改成的算法,先判断年再到月,最后到日,可以是程序运行的更迅速。
加n天循环
1 while(n>365){//增加 2 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month<=2){ 3 if(day==29&&month==2){ 4 day=1; 5 month=3; 6 } 7 year++; 8 n-=366; 9 }else if(isLeapYear(year+1)&&month>2){ 10 year++; 11 n-=366; 12 }else{ 13 year++; 14 n-=365; 15 } 16 } 17 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 18 day++; 19 if(isLeapYear(year) && month == 2){ 20 if(day > 29){ 21 month++; 22 day = 1; 23 } 24 } 25 else if(day > mon_maxnum[month]){ 26 month++; 27 day = 1; 28 if(month > 12){ 29 month = 1; 30 year++; 31 } 32 } 33 }
减n天循环
1 while(n>365){ 2 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month>2){ 3 year--; 4 n-=366; 5 }else if(isLeapYear(year-1)&&month<=2){ 6 year--; 7 n-=366; 8 }else{ 9 year--; 10 n-=365; 11 } 12 } 13 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 14 day--; 15 if(day < 1){ 16 month--; 17 if(month < 1){ 18 month = 12; 19 year--; 20 } 21 if(isLeapYear(year)&&month==2){ 22 day=29; 23 }else{ 24 day=mon_maxnum[month]; 25 } 26 } 27 }
由此改变即可使代码更加有层次不会太繁琐去运行。
改进建议:
在以后的学习中,不断地练习写代码的能力,无非就是对之前的问题在不断地接受新的知识之后能够以更快的速度和更巧妙的办法去实现其功能,包括最基本的数组的建造可以去用ArrayList类去替换,其中包含的方法是非常好用的。不过对于这些的学习都是需要我们自己投入更多的时间去练习以及熟练掌握以后去实践。毕竟不管在学什么专业都应该去主动。随着入门的时间越来越长,接触的题目也会越来越难,一种类型的题目,如同此次的题目一样,都是不断完善不断迭代的。
总结:
本人第一次写博客,这在很多地方的运用还是非常懵懂,还需要多多学习,不管是对于eclipse得分使用还是对power designer的使用等等,都是需要不断去熟悉。对于这三次作业集,在结束了这刚开始Java代码书写,了解了Java的基本语法的实现。但是在类、方法什么的地方还是会有很多疑问,在日后的学习过程中,要不断的去学习更多种类的类的使用,并且让自己对基本的结构有更深的认识,积极参与讨论交流,代码的学习与未来的就业都不是一个人去实现,都需要团队合作共同进步。改进算法也是其中我想要说的一个点,在和他人交流后,可以得知别人的解题分析思维,让自己的思维更加活跃,当然在网络平台上也应该去多搜集他人推荐的学习方法、划重点的好用知识以及实用的学习办公的工具。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号