LangGraph:add_conditional_edges详解
在 LangGraph 中,add_conditional_edges 是构建动态工作流的关键,用于创建基于条件判断的分支路径;它允许工作流根据当前状态动态决定下一步的执行路径,这种模式使 LangGraph 能够处理复杂的、状态驱动的对话流程,特别是在需要工具调用和多次交互的场景中。
示例
# State Management class State(TypedDict): messages: Annotated[List[AnyMessage], add_messages] # Nodes def chat_node(state: State) -> State: state["messages"] = chat_llm.invoke({"messages": state["messages"]}) return state # Building the graph graph_builder = StateGraph(State) graph_builder.add_node("chat_node", chat_node) graph_builder.add_node("tool_node", ToolNode(tools=tools)) graph_builder.add_edge(START, "chat_node") graph_builder.add_conditional_edges("chat_node", tools_condition, {"tools": "tool_node", "__end__": END}) graph_builder.add_edge("tool_node", "chat_node") graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=MemorySaver()) return graph
解读:
上述示例的执行流程如下:

细节描述
执行工具节点
class ToolNode: def __init__(self, tools): self.tools = tools def __call__(self, state: State) -> State: # 执行工具调用 tool_results = [] for tool_call in state["messages"][-1].tool_calls: tool = self.tools[tool_call["name"]] result = tool.invoke(tool_call["args"]) tool_results.append(result) return {"messages": tool_results}
状态更新:将工具执行结果作为新消息添加
工具节点执行后,通过 graph_builder.add_edge("tool_node", "chat_node") 返回聊天节点继续生成对工具结果的响应
重点关注
add_conditional_edges,这个方法包含三个核心参数

A、源节点:条件分支的起点
B、条件函数:决定分支路径的函数
C、分支映射:将条件函数返回值映射到目标节点的字典
条件函数
条件函数是一个自定义函数,它接收当前状态作为输入,返回一个字符串值,表示下一步应该执行的路径。
在上面示例中,tools_condition 函数可能类似这样:
def tools_condition(state: State) -> str: """判断是否需要调用工具""" # 获取最后一条消息 last_message = state["messages"][-1] # 检查是否是工具调用请求 if hasattr(last_message, "tool_calls") and last_message.tool_calls: return "tools" # 需要调用工具 else: return "__end__" # 结束对话
tools_condition(LangGraph源码)
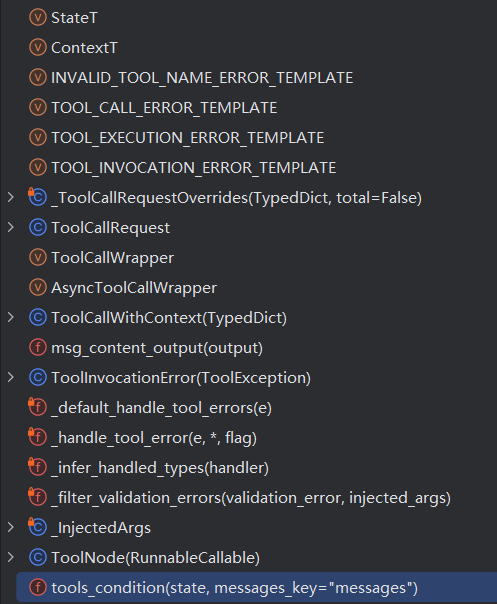
def tools_condition( state: list[AnyMessage] | dict[str, Any] | BaseModel, messages_key: str = "messages", ) -> Literal["tools", "__end__"]: """Conditional routing function for tool-calling workflows. This utility function implements the standard conditional logic for ReAct-style agents: if the last `AIMessage` contains tool calls, route to the tool execution node; otherwise, end the workflow. This pattern is fundamental to most tool-calling agent architectures. The function handles multiple state formats commonly used in LangGraph applications, making it flexible for different graph designs while maintaining consistent behavior. Args: state: The current graph state to examine for tool calls. Supported formats: - Dictionary containing a messages key (for `StateGraph`) - `BaseModel` instance with a messages attribute messages_key: The key or attribute name containing the message list in the state. This allows customization for graphs using different state schemas. Returns: Either `'tools'` if tool calls are present in the last `AIMessage`, or `'__end__'` to terminate the workflow. These are the standard routing destinations for tool-calling conditional edges. Raises: ValueError: If no messages can be found in the provided state format. Example: Basic usage in a ReAct agent: ```python from langgraph.graph import StateGraph from langchain.tools import ToolNode from langchain.tools.tool_node import tools_condition from typing_extensions import TypedDict class State(TypedDict): messages: list graph = StateGraph(State) graph.add_node("llm", call_model) graph.add_node("tools", ToolNode([my_tool])) graph.add_conditional_edges( "llm", tools_condition, # Routes to "tools" or "__end__" {"tools": "tools", "__end__": "__end__"}, ) ``` Custom messages key: ```python def custom_condition(state): return tools_condition(state, messages_key="chat_history") ``` !!! note This function is designed to work seamlessly with `ToolNode` and standard LangGraph patterns. It expects the last message to be an `AIMessage` when tool calls are present, which is the standard output format for tool-calling language models. """ if isinstance(state, list): ai_message = state[-1] elif (isinstance(state, dict) and (messages := state.get(messages_key, []))) or ( messages := getattr(state, messages_key, []) ): ai_message = messages[-1] else: msg = f"No messages found in input state to tool_edge: {state}" raise ValueError(msg) if hasattr(ai_message, "tool_calls") and len(ai_message.tool_calls) > 0: return "tools" return "__end__"
分支映射
分支映射是一个字典,将条件函数的返回值映射到具体的节点或特殊端点:
{ "tools": "tool_node", # 当条件返回 "tools" 时,跳转到 tool_node "__end__": END # 当条件返回 "__end__" 时,结束工作流 }
特殊端点:
START:工作流起点END:工作流终点
条件分支的高级应用
多分支条件
可以创建包含多个可能路径的条件分支
def advanced_condition(state: State) -> str: last_message = state["messages"][-1] if "help" in last_message.content: return "help_flow" elif "purchase" in last_message.content: return "checkout_flow" elif "cancel" in last_message.content: return "cancellation_flow" else: return "__end__" graph_builder.add_conditional_edges( "chat_node", advanced_condition, { "help_flow": "help_node", "checkout_flow": "checkout_node", "cancellation_flow": "cancellation_node", "__end__": END } )
嵌套条件分支
# 第一层条件分支 graph_builder.add_conditional_edges( "initial_node", determine_flow_type, {"support": "support_flow", "sales": "sales_flow"} ) # 支持流中的子分支 graph_builder.add_conditional_edges( "support_flow", support_condition, {"technical": "tech_support_node", "billing": "billing_support_node"} ) # 销售流中的子分支 graph_builder.add_conditional_edges( "sales_flow", sales_condition, {"new": "new_customer_node", "existing": "existing_customer_node"} )
最佳实践
保持条件函数纯净
只读取状态,不修改状态
避免副作用
明确的返回值
使用描述性的字符串作为返回值
确保返回值在分支映射中有对应项
错误处理
def safe_condition(state: State) -> str: try: # 业务逻辑 except Exception as e: # 记录错误 state["errors"].append(str(e)) return "error_handling"
状态设计
确保状态包含条件判断所需的所有信息
使用清晰的字段命名
扩展阅读


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号