[Swift]LeetCode987. 二叉树的垂序遍历 | Vertical Order Traversal of a Binary Tree
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
➤微信公众号:山青咏芝(shanqingyongzhi)
➤博客园地址:山青咏芝(https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/)
➤GitHub地址:https://github.com/strengthen/LeetCode
➤原文地址:https://www.cnblogs.com/strengthen/p/10351710.html
➤如果链接不是山青咏芝的博客园地址,则可能是爬取作者的文章。
➤原文已修改更新!强烈建议点击原文地址阅读!支持作者!支持原创!
★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★★
Given a binary tree, return the vertical order traversal of its nodes values.
For each node at position (X, Y), its left and right children respectively will be at positions (X-1, Y-1)and (X+1, Y-1).
Running a vertical line from X = -infinity to X = +infinity, whenever the vertical line touches some nodes, we report the values of the nodes in order from top to bottom (decreasing Y coordinates).
If two nodes have the same position, then the value of the node that is reported first is the value that is smaller.
Return an list of non-empty reports in order of X coordinate. Every report will have a list of values of nodes.
Example 1:
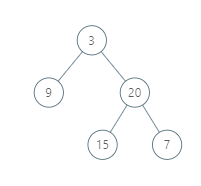
Input: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
Explanation:
Without loss of generality, we can assume the root node is at position (0, 0):
Then, the node with value 9 occurs at position (-1, -1);
The nodes with values 3 and 15 occur at positions (0, 0) and (0, -2);
The node with value 20 occurs at position (1, -1);
The node with value 7 occurs at position (2, -2).
Example 2:
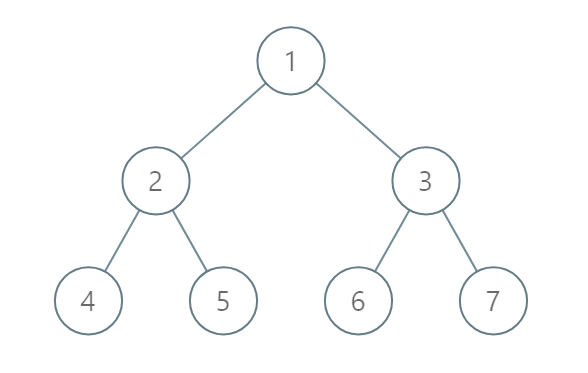
Input: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
Output: [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
Explanation:
The node with value 5 and the node with value 6 have the same position according to the given scheme.
However, in the report "[1,5,6]", the node value of 5 comes first since 5 is smaller than 6.
Note:
- The tree will have between 1 and
1000nodes. - Each node's value will be between
0and1000.
给定二叉树,按垂序遍历返回其结点值。
对位于 (X, Y) 的每个结点而言,其左右子结点分别位于 (X-1, Y-1) 和 (X+1, Y-1)。
把一条垂线从 X = -infinity 移动到 X = +infinity ,每当该垂线与结点接触时,我们按从上到下的顺序报告结点的值( Y 坐标递减)。
如果两个结点位置相同,则首先报告的结点值较小。
按 X 坐标顺序返回非空报告的列表。每个报告都有一个结点值列表。
示例 1:
输入:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7] 输出:[[9],[3,15],[20],[7]] 解释: 在不丧失其普遍性的情况下,我们可以假设根结点位于 (0, 0): 然后,值为 9 的结点出现在 (-1, -1); 值为 3 和 15 的两个结点分别出现在 (0, 0) 和 (0, -2); 值为 20 的结点出现在 (1, -1); 值为 7 的结点出现在 (2, -2)。
示例 2:
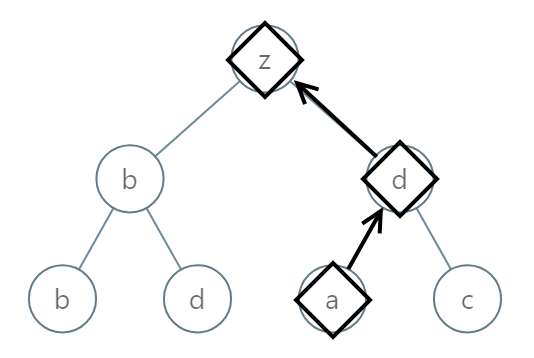
输入:[1,2,3,4,5,6,7] 输出:[[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]] 解释: 根据给定的方案,值为 5 和 6 的两个结点出现在同一位置。 然而,在报告 "[1,5,6]" 中,结点值 5 排在前面,因为 5 小于 6。
提示:
- 树的结点数介于
1和1000之间。 - 每个结点值介于
0和1000之间。
16ms
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * public var val: Int 5 * public var left: TreeNode? 6 * public var right: TreeNode? 7 * public init(_ val: Int) { 8 * self.val = val 9 * self.left = nil 10 * self.right = nil 11 * } 12 * } 13 */ 14 class Solution { 15 var map = [Int: [(Int, Int)]]() 16 func verticalTraversal(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] { 17 if root == nil { 18 return [] 19 } 20 map[0] = [(root!.val, 0)] 21 traversTree(root!.left, true, 0, -1) 22 traversTree(root!.right, false, 0, -1) 23 var ans = [[Int]]() 24 for k in map.keys.sorted() { 25 let sortedTuple = map[k]!.sorted {($0, $1) 26 if $0.1 > $1.1 { return true } 27 if $0.1 == $1.1 { return $0.0 < $1.0 } 28 return false 29 } 30 let arr = sortedTuple.map {$0.0} 31 ans.append(arr) 32 } 33 return ans 34 } 35 36 func traversTree(_ node: TreeNode?, _ left: Bool, _ v: Int, _ vv: Int) { 37 if node != nil { 38 let k = left ? v-1 : v+1 39 var arr = map[k] ?? [(Int, Int)]() 40 arr.append((node!.val, vv)) 41 map[k] = arr 42 traversTree(node!.left, true, k, vv-1) 43 traversTree(node!.right, false, k, vv-1) 44 } 45 } 46 }
Runtime: 20 ms
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * public class TreeNode { 4 * public var val: Int 5 * public var left: TreeNode? 6 * public var right: TreeNode? 7 * public init(_ val: Int) { 8 * self.val = val 9 * self.left = nil 10 * self.right = nil 11 * } 12 * } 13 */ 14 class Solution { 15 var hi:[[Int]] = [[Int]]() 16 func verticalTraversal(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] { 17 dfs(root, 0, 0) 18 hi.sort(by:sortArray) 19 var ret:[[Int]] = [[Int]]() 20 var i:Int = 0 21 while(i < hi.count) 22 { 23 var j:Int = i 24 while(j < hi.count && hi[j][1] == hi[i][1]) 25 { 26 j += 1 27 } 28 var item:[Int] = [Int]() 29 for k in i..<j 30 { 31 item.append(hi[k][0]) 32 } 33 ret.append(item) 34 i = j 35 } 36 return ret 37 } 38 39 func sortArray(_ a:[Int],_ b:[Int]) -> Bool 40 { 41 if a[1] != b[1] {return a[1] < b[1]} 42 if a[2] != b[2] {return a[2] > b[2]} 43 return a[0] < b[0] 44 } 45 46 func dfs(_ cur: TreeNode?,_ x:Int,_ y:Int) 47 { 48 if cur == nil {return} 49 hi.append([cur!.val,x,y]) 50 dfs(cur!.left, x-1, y-1) 51 dfs(cur!.right, x+1, y-1) 52 } 53 }
24ms
1 class Solution { 2 func verticalTraversal(_ root: TreeNode?) -> [[Int]] { 3 var res: [[Int]] = [] 4 5 var dict: [Int: [(Int, [Int])]] = [:] 6 7 func tra(_ node: TreeNode?, _ x: Int, y: Int) { 8 guard let node = node else { 9 return 10 } 11 12 if dict[x] == nil { 13 dict[x] = [(y, [node.val])] 14 } else { 15 var sameY = false 16 17 for (index, (yVal, nodeVal)) in dict[x]!.enumerated() { 18 if yVal == y { 19 sameY = true 20 21 var newVal = nodeVal 22 newVal.append(node.val) 23 24 dict[x]![index].1 = newVal.sorted() 25 } 26 } 27 28 if sameY == false { 29 dict[x]!.append((y, [node.val])) 30 } 31 } 32 33 tra(node.left, x - 1, y: y - 1) 34 tra(node.right, x + 1, y: y - 1) 35 } 36 37 tra(root, 0, y: 0) 38 39 let sortedDict = dict.sorted(by: {$0.key < $1.key}) 40 41 for dict in sortedDict { 42 var vals: [Int] = [] 43 44 for (_, val) in dict.value.sorted(by: { $0.0 > $1.0 }) { 45 vals += val 46 } 47 48 res.append(vals) 49 } 50 51 return res 52 } 53 }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号