![]()
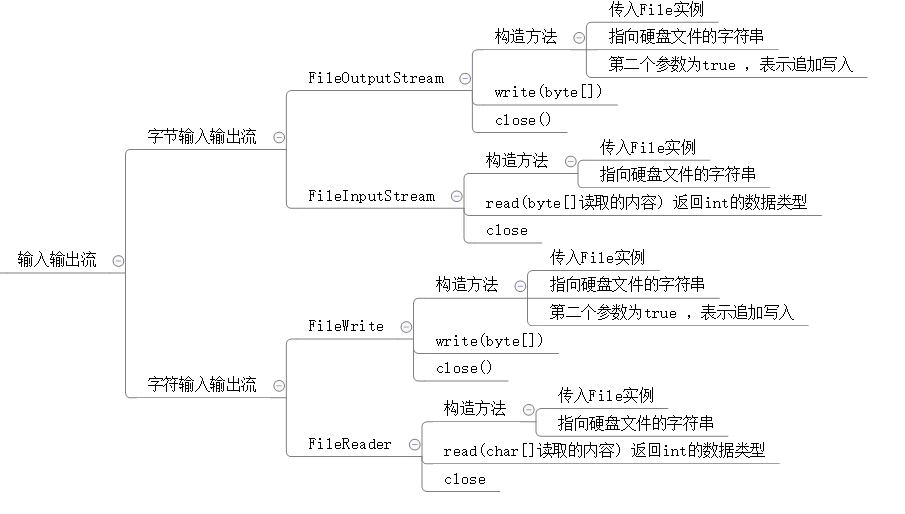
package 流;
//引用
import java.io.*;
public class lianxi {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 自动生成的方法存根
//利用file 创建文件
try {
File a=new File("d:\\呵呵哒.txt");
//确认存在
if(a.exists()){
System.out.println("文件存在");
}
else{
System.out.println("文件不存在,自动创建文件");
//创建文件
if(a.createNewFile()){
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
if(a.exists()){
System.out.println(a.getName()+"创建成功");
}
}
else{
System.out.println("文件创建失败");
}
}
//利用byte 写入
FileOutputStream a1=new FileOutputStream(a);
//把要输入的字符串转化成byte的数集
String b="其实我不是很懂...";
byte c[]=new byte[100000];
c=b.getBytes();
//写入 关闭
a1.write(c);
a1.close();
//读取
FileInputStream a2=new FileInputStream(a);
//创建数集准备接受
byte []c1=new byte[1000];
byte[]x=new byte[1000];
//这部必须有,代表执行 read方法 放入的集合是c1,读取到的长度是 i
int i=a2.read(c1);
String b1=new String(c1);
System.out.println("我的读取的内容是:"+b1);
//即使不写b1,但是由于没有执行read方法不会放入x中
String bd=new String(x);
System.out.println(bd+"呵呵");
a2.close();
//直接写入String,true 代表续写而不是覆盖
FileWriter a3=new FileWriter(a,true);
a3.write("\n是的,确实不是很明白");
a3.close();
FileReader a4=new FileReader(a);
char[] b3=new char[1000];
i=a4.read(b3);
String dd=new String(b3);
System.out.println("现在读取到的内容是:"+dd);
a4.close();
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO 自动生成的 catch 块
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号