python学习笔记-并发和异步IO
一、并发请求实现
1、多线程实现并发

from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import requests import time def task(url): response=requests.get(url) print(url,response) pool=ThreadPoolExecutor(7) url_list=[ 'https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.zhihu.com', 'https://www.sina.com', 'https://www.autohome.com', 'https://www.bing.com', 'https://www.cnblogs.com', 'https://huaban.com/favorite/beauty' ] for url in url_list: pool.submit(task,url) pool.shutdown(wait=True)
**可以实现并发,但是请求发送出去和返回之前,线程是空闲的
2、多线程并发方式2

from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor import requests import time def task(url): response=requests.get(url) return response def done(future,*args,**kwargs): response=future.result() print(response.status_code,response.content) pool=ThreadPoolExecutor(7) url_list=[ 'https://www.baidu.com', 'https://www.zhihu.com', 'https://www.sina.com', 'https://www.autohome.com', 'https://www.bing.com', 'https://www.cnblogs.com', 'https://huaban.com/favorite/beauty' ] for url in url_list: v=pool.submit(task,url) v.add_done_callback(done) pool.shutdown(wait=True)
**把任务分成获取返回值和回调两步,耦合要低点
小结,两种编写方式:
1直接处理
2通过回调函数处理
3、多进程方式的并发
只需要修改这两行
from concurrent.futures import PocessPoolExecutor ... pool=ProcessPoolExecutor(7)
线程和进程的区别
多个线程共享进程的资源
io密集型用线程,计算密集型用进程
4、协程+异步IO实现并发请求
协程的理解:一个线程做很多事情,
协程+异步IO--》实现一个线程发送N个http请求

import asyncio @asyncio.coroutine def task(): print("before...task.....") yield from asyncio.sleep(5) print('end...task.....') tasks=[task(),task()] loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close()
*本段代码能执行,提示信息 "@coroutine" decorator is deprecated since Python 3.8, use "async def" instead
要实现并发http请求需改造,因为:
asyncio支持tcp,不支持http
https是基于tcp的,可以加以改造,自己封装http数据包

1 import asyncio 2 3 @asyncio.coroutine 4 def fetch_async(host,url='/'): 5 print("before...",host,url) 6 reader,writer=yield from asyncio.open_connection(host,80) 7 8 request_header_content="""GET %s HTTP /1.0\r\nHost:%s\r\n\r\n"""%(url,host) 9 request_header_content=bytes(request_header_content,encoding='utf-8') 10 11 writer.write(request_header_content) 12 yield from writer.drain() 13 text=yield from reader.read() 14 15 print('end...',host,url,text) 16 writer.close() 17 18 tasks=[fetch_async("www.sina.com.cn"), 19 fetch_async("m.weibo.cn","/detail/5255105515358240")] 20 21 loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() 22 results=loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) 23 loop.close()
*执行请求返回400的错误提示。
4.1、asyncio的用法
asyncio是Python3.4版本引入的标准库,直接内置了对异步IO的支持
asyncio的编程模型就是一个消息循环。asyncio模块内部实现了EventLoop,把需要执行的协程扔到EventLoop中执行,就实现了异步IO。
用asyncio提供的@asyncio.coroutine可以把一个generator标记为coroutine类型,然后在coroutine内部用yield from调用另一个coroutine实现异步操作。
为了简化并更好地标识异步IO,从Python 3.5开始引入了新的语法async和await,可以让coroutine的代码更简洁易读。
1 import asyncio 2 3 async def hello(): 4 print("Hello world!") 5 await asyncio.sleep(1) 6 print("Hello again!") 7 8 asyncio.run(hello())
async把一个函数变成coroutine类型,我们就把这个async函数仍到asyncio.run()中执行。结果如下,执行间隔1s
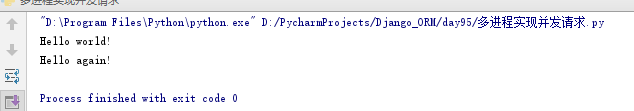
hello()会首先打印出Hello world!,然后,await语法可以让我们方便地调用另一个async函数。由于asyncio.sleep()也是一个async函数,所以线程不会等待asyncio.sleep(),而是直接中断并执行下一个消息循环。当asyncio.sleep()返回时,就接着执行下一行语句。
把asyncio.sleep(1)看成是一个耗时1秒的IO操作,在此期间,主线程并未等待,而是去执行EventLoop中其他可以执行的async函数了,因此可以实现并发执行
!!修改案例,让两个hello()同时并发执行
import asyncio import threading async def hello(name): print("Hello %s! (%s)!"%(name,threading.current_thread)) await asyncio.sleep(1) print("Hello %s again!(%s)!"%(name,threading.current_thread)) return name #用asyncio.gather()同时调度多个async函数 async def main(): L=await asyncio.gather(hello("Bob"),hello("Mark")) print(L) asyncio.run(main())
结果如下:

从结果可知,用asyncio.run()执行async函数,所有函数均由同一个线程执行。两个hello()是并发执行的,并且可以拿到async函数执行的结果(即return的返回值)
!!修改案例,实现异步发送网络请求

import asyncio async def wget(host): print(f"wget {host}...") # 连接80端口: reader, writer = await asyncio.open_connection(host, 80) # 发送HTTP请求: header = f"GET / HTTP/1.0\r\nHost: {host}\r\n\r\n" writer.write(header.encode("utf-8")) await writer.drain() # 读取HTTP响应: while True: line = await reader.readline() if line == b"\r\n": break print("%s header > %s" % (host, line.decode("utf-8").rstrip())) # Ignore the body, close the socket writer.close() await writer.wait_closed() print(f"Done {host}.") async def main(): await asyncio.gather(wget("www.sina.com.cn"), wget("www.sohu.com"), wget("www.163.com")) asyncio.run(main())
4.2、aiohttp的使用
aiohttp模块:封装了http数据包
安装:pip3 install aiohttp
使用asyncio+aiohttp实现并发请求

import asyncio,aiohttp @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(url): print(url) response=yield from aiohttp.ClientSession().get(url) #response=yield from aiohttp.request('GET',url) print(url,response) response.close() tasks=[fetch_async("http://www.sina.com.cn"), fetch_async("http://www.chouti.com")] event_loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() results=event_loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) event_loop.close()
*执行**不能自动关闭,有提示Unclosed client session
asyncio可以实现单线程并发IO操作。如果仅用在客户端,发挥的威力不大。如果把asyncio用在服务器端,例如Web服务器,由于HTTP连接就是IO操作,因此可以用单线程+async函数实现多用户的高并发支持
额外案例:编写http服务器。

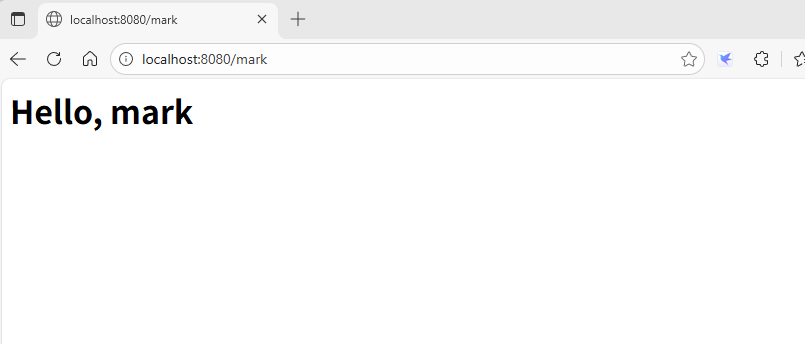
from aiohttp import web async def index(request): text = "<h1>Index Page</h1>" return web.Response(text=text, content_type="text/html") async def hello(request): name = request.match_info.get("name", "World") text = f"<h1>Hello, {name}</h1>" return web.Response(text=text, content_type="text/html") app = web.Application() # 添加路由: app.add_routes([web.get("/", index), web.get("/{name}", hello)]) if __name__ == "__main__": web.run_app(app)

执行后,从浏览器访问
4.3、使用asyncio+aiohttp实现并发请求

import asyncio,requests @asyncio.coroutine def fetch_async(func,*args): loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() future=loop.run_in_executor(None,func,*args) response=yield from future print(response.url,response.content) tasks=[fetch_async(requests.get,"http://www.sina.com.cn"), fetch_async(requests.get,"http://www.chouti.com")] loop=asyncio.get_event_loop() results=loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.gather(*tasks)) loop.close()
*执行后,访问chouti.com有超时提示
5、使用gevent的并发
内部会依赖greenlet,这是个协程的模块,微线程
内部实现了异步IO的功能
gevent帮我们做的类似socket级别的,也要用requests发送请求
安装:
pip install greenlet
pip install gevent
示例:

import requests,gevent from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() def task(method,url,req_kwargs): print(method,url,req_kwargs) response=requests.request(method=method,url=url,**req_kwargs) print(response.url,response.content) #发送请求## gevent.joinall([ gevent.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://www.python.org/',req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://www.yahoo.com/',req_kwargs={}), gevent.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://github.com/',req_kwargs={}), ]) #执行报错循环深度的问题:RecursionError: maximum recursion depth exceeded。(版本相关原因)

import requests,gevent from gevent import monkey monkey.patch_all() def task(method,url,req_kwargs): print(method,url,req_kwargs) response=requests.request(method=method,url=url,**req_kwargs) print(response.url,response.content) ##发送请求(协程池控制最大协程数量)### from gevent.pool import Pool pool=Pool(5) gevent.joinall([ pool.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://www.python.org/',req_kwargs={}), pool.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://www.yahoo.com/',req_kwargs={}), pool.spawn(task,method='get',url='https://github.com/',req_kwargs={}), ])
解释:
通过gevent.spawn()方法创建job
通过gevent.joinall将jobs加入到协程任务队列中等待其完成,可设置超时时间
补充:继承gevent的greenlet的用法

import gevent from gevent import monkey from gevent import Greenlet monkey.patch_all() class task(Greenlet): def __init__(self,name): Greenlet.__init__(self) self.name=name def _run(self): print("Task %s:some task..."%self.name) t1=task("task1") t2=task("task2") t1.start() t2.start() gevent.joinall([t1,t2])
执行结果:

5.1、grequests模块
封装实现了gevent+requests功能
安装:pip install grequests

import grequests request_list=[ grequests.get('https://www.python.org/',timeout=0.001), grequests.get('https://github.com/') ] #执行并获取响应列表 response_list=grequests.map(request_list)#map传size参数,为设置协程池数量,如size=5 print(response_list)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号