广搜和深搜(BFS和DFS)
邻接链表法,使用稀疏图 (为什么?个人理解:相比于邻接矩阵,这样可以减少存储占用的空间,遍历查询也更快)
小结:DFS遍历顺序:先平行着遍历,只到没有记录就遍历下一个元素,所以我们存放的时候每个链表存的是该节点直接相连接的节点就好
这里存在一个思维方式的升级:我们预知怎样遍历,需先选择好合适的存储结构
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40609809/article/details/96760864
https://www.cnblogs.com/yellowgg/p/7875459.html

#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <queue> using namespace std; //数据结构 //边节点结构, typedef struct EdgeNode { int adjvex; //用来存储邻节点的位置, struct EdgeNode* next; //下一个节点的位置 }EdgeNode; //顶点表节点结构 typedef struct VexList { string vexs;//用来存储顶点信息 EdgeNode* firstEdge; //用来存储当前顶点的下一个顶点信息 }VexList; //动态数组存放顶点表, typedef struct GraphList { vector<VexList> VexList; int vertex, edge; //一个图的顶点数和边数 }GraphList; //全局变量 bool VisitList[100]; //创建图 void CreateGraphSteem(GraphList* graph) { string v1, v2; EdgeNode* e, *p, *q; cout << "输入顶点数和边数:" << endl; cin >> graph->vertex >> graph->edge; cout << "输入顶点的信息:" << endl; for (int i = 0;i < graph->vertex;i++) { VexList tmp; cin >> tmp.vexs; tmp.firstEdge = nullptr; graph->VexList.push_back(tmp); } for (int j = 0;j < graph->edge;j++) { int m, n; cout << "输入边Vm,Vn:(顶点m,到顶点n有连线)" << endl; cin >> m >> n; if (graph->VexList[m].firstEdge == nullptr) { e = new EdgeNode; e->adjvex = n; e->next = nullptr; graph->VexList[m].firstEdge = e; } else { //当前m后面有顶点 EdgeNode* p = graph->VexList[m].firstEdge; while (p->next) { p = p->next; } //遍历到为空的时候跳出来 e = new EdgeNode; e->adjvex = n; e->next = nullptr; p->next = e; } //因为是无向图,所以Vm,n 和Vn,m都要连接起来 if (graph->VexList[n].firstEdge == nullptr) { e = new EdgeNode; e->adjvex = m; e->next = nullptr; graph->VexList[n].firstEdge = e; } else { //当前m后面有顶点 EdgeNode* p = graph->VexList[n].firstEdge; while (p->next) { p = p->next; } //遍历到为空的时候跳出来 e = new EdgeNode; e->adjvex = m; e->next = nullptr; p->next = e; } } } //打印链接链表 void PrintGraph(GraphList* graph) { cout << "所有建立的邻接链表如下:" << endl; for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertex;i++) { cout << graph->VexList[i].vexs; //先输出顶点信息 EdgeNode *e = graph->VexList[i].firstEdge; while (e) { cout << "-->" << e->adjvex; e = e->next; } cout << endl; } } void DestoryGraph(GraphList* praph) { EdgeNode *p = nullptr; for (int i = 0;i < praph->vertex;i++) { p = praph->VexList[i].firstEdge; while (p) { EdgeNode* tmp = p; p = p->next; delete tmp; } praph->VexList[i].firstEdge = nullptr; } } //BFS:边表的遍历,用遍历链表的方式 void BFSTravel(GraphList* graph) { cout << "广度优先搜索" << endl; EdgeNode* p; queue<int> Q; for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertex;i++) { VisitList[i] = false; } for (int i = 0; i < graph->vertex;i++) { if (!VisitList[i]) { VisitList[i] = true; cout << graph->VexList[i].vexs << " "; Q.push(i); while (!Q.empty()) { i = Q.front(); Q.pop(); p = graph->VexList[i].firstEdge; while (p) { if (!VisitList[p->adjvex]) { VisitList[p->adjvex] = true; cout << graph->VexList[p->adjvex].vexs << " "; Q.push(p->adjvex); } p = p->next; } } } } } //深度优先搜索 void DFS(GraphList* graph, int idex) { EdgeNode *p; VisitList[idex] = true; cout << graph->VexList[idex].vexs << " "; p = graph->VexList[idex].firstEdge; while (p) { if (!VisitList[idex]) { DFS(graph, p->adjvex); } p = p->next; } } void DFStravel(GraphList* graph) { cout << "深度优先遍历顺序:" << endl; for (int i = 0;i < graph->vertex;i++) { VisitList[i] = false; } for (int i = 0;i < graph->vertex;i++) { if (!VisitList[i]) { DFS(graph,i); } } cout << endl; } int main() { GraphList graph; CreateGraphSteem(&graph); PrintGraph(&graph); //BFSTravel(&graph); //邻接法BFS DFStravel(&graph); DestoryGraph(&graph); system("pause"); return 0; }
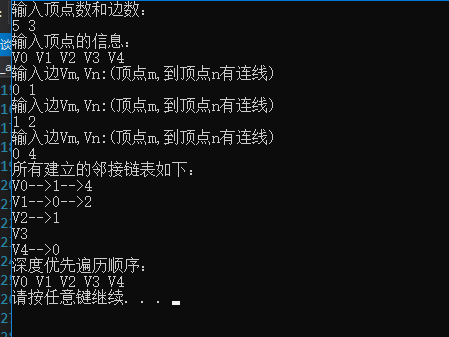
运行实例:如下图




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号