AtCoder Contest 188题解 (已补完)
A - Three-Point Shot
签
B - Orthogonality
签
C - ABC Tournament
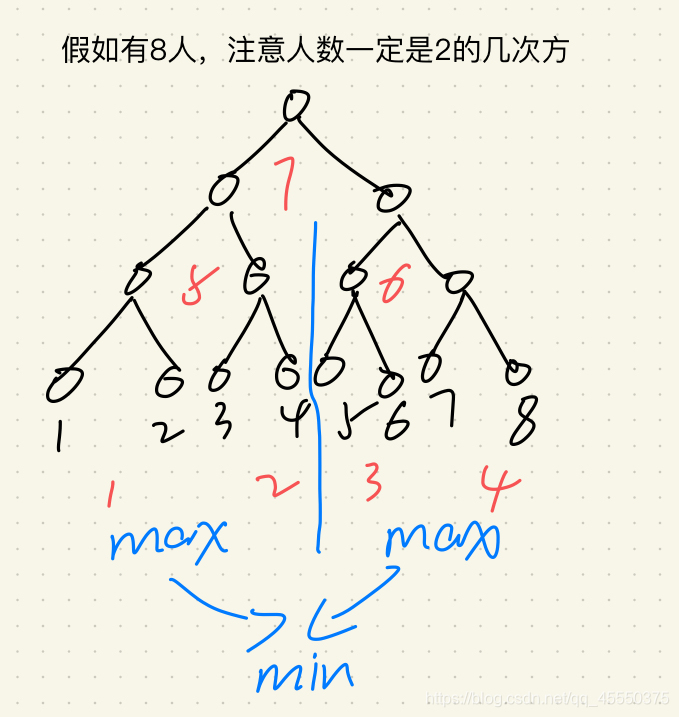
题意:
给你\(2^n\)个数,每轮相邻两位pk,分数高的获胜,进入下一轮,求最后进入决赛被淘汰的人的位置
思路:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
template<class T>inline void read(T &x){
x=0;register char c=getchar();register bool f=0;
while(!isdigit(c))f^=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar();
if(f)x=-x;
}
int main(){
int n,t;
cin>>n;
int min1=-INT_MAX,min2=-INT_MAX;
int ans1=0,ans2=0;
int l=pow(2,n)/2,r=pow(2,n);
for(int i=1;i<=l;i++){
read(t);
if(min1<t)
ans1=i,min1=t;
}
for(int i=l+1;i<=r;i++){
read(t);
if(min2<t)
ans2=i,min2=t;
}
if(min1>min2)cout<<ans2<<endl;
else cout<<ans1<<endl;
}
D - Snuke Prime
思路:
离散化 + 差分,判断一段区间的值如果比\(C\)大,那么这段区间价钱用\(C\)替代,反之不替代
复习stl:STL总结(14种)
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
#define mem(f, x) memset(f,x,sizeof(f))
#define Sca(x) scanf("%d", &x)
#define Sca2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y)
#define fo(i,a,n) for(int i=a;i<=n;++i)
using namespace std;
template<class T>inline void read(T &x){
x=0;register char c=getchar();register bool f=0;
while(!isdigit(c))f^=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar();
if(f)x=-x;
}
map<LL, LL> m;//离散化
int main(){
LL n,c;
cin>>n>>c;
LL t,t1,t2;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
read(t1);read(t2);read(t);
//构造离散差分数组
m[t1]+=t;
m[t2+1]-=t;
}
LL s=(*m.begin()).first,k=(*m.begin()).second;
LL p,q;
LL sum=0;
map<LL, LL>::iterator it=m.begin();
for(it++;it!=m.end();it++){
p=(*it).first,q=(*it).second;
if(k>c)sum+=c*(p-s);
else sum+=(k)*(p-s);
k+=q;//求差分
s=p;
}
cout<<sum;
return 0;
}
E - Peddler
题意:
n点m边的有向图,点权代表黄金价格,其中边\(<x,y>\)满足\(x_{i}\)一定小于\(y_{i}\)
现在他要选一个点买黄金,然后走到另外一个点卖黄金,求最大利润。
思路:
跑一个dfs,f[i]表示从第i个点走到最后黄金的最大价格,然后更新f[i] - a[i]最大值
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef pair<int,int> PII;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int f[N];//f[i]表示从第i个点走到最后黄金的最大价格
vector<int> g[N];//邻接表
bool st[N];
int n,m;
template<class T>inline void read(T &x){
x=0;register char c=getchar();register bool f=0;
while(!isdigit(c))f^=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar();
if(f)x=-x;
}
void dfs(int u){
st[u] = true;
for(auto t:g[u]){
if(!st[t]) dfs(t);
//f[i]表示从第i个点走到最后黄金的最大价格
f[u] = max(f[u],max(f[t],a[t]));//更新讨论各种情况
}
}
int main(){
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) read(a[i]);
while(m--){
int x,y;
read(x);read(y);
g[x].push_back(y);
}
memset(f,-0x3f,sizeof f);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
if(!st[i])dfs(i);
int ans = -INF;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
ans = max(f[i] - a[i],ans);//更新f[i]-a[i]的最大值
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
F - +1-1x2
思路:
记忆化dp裸题,类似滑雪
dp[y]和dfs(y)都表示将x变成y需要的步数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
template<class T>inline void read(T &x){
x=0;register char c=getchar();register bool f=0;
while(!isdigit(c))f^=c=='-',c=getchar();
while(isdigit(c))x=(x<<3)+(x<<1)+(c^48),c=getchar();
if(f)x=-x;
}
//记忆化dp裸题
map<ll, ll> dp;
ll x, y;
ll dfs(ll yy){
if(yy <= x) return x - yy;//x只能进行x-yy次 减操作到达yy
if(dp.count(y)) return dp[yy];//记忆化操作直接返回
ll res = yy - x;
if(yy % 2 == 0) res = min(res, dfs(yy / 2) + 1);//如果yy是偶数,那么就存在乘2的操作,使得x到达yy
else res = min(res, 1 + min(dfs(yy + 1), dfs(yy - 1))); //不然就看看加1减1操作使得x到达yy,取一个最小值
return dp[yy] = res;
}
int main(){
read(x);read(y);
cout << dfs(y);
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号